test 2 review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
squamous cells are for
diffusion and filtration
cuboidal cells are for
secretion and absorption
columnar cells are for
absorbtion and transportation
cuboidal cells are found in
the kidneys and the ovaries
columnar cells are found in
the digestive tract and the uterus
pseudo stratified ciliated cells are found in
the respiratory tract
merocrine glands produce
watery substances (hint: mermaid)
apocrine glands produce
waxy substances (hint: armpit)
holocrine glands produce
oily substances
The intercellular substance of Connective Tissue provides
shock absorption and protection to the body
Fibroblasts
cells in tissue that deal with healing and wound repair
The dermis contains
blood vessels, glands, hair follicles and sensory receptors
keratinization
the process of living skin cells dying by infusing with keratin. creates the epidermis.
Langerhan cells
immune cells
Merkel cells
touch (sensory) receptive cells
Papillary dermis
thin, outermost layer of dermis. houses sensory receptors for touch, pain and temperature.
Reticular dermis
thick, bottom layer of dermis. houses hair follicles, glands, and nerves.
dermal papillae
small finger like projections of the papillary dermis that increase surface area, signal hair growth and create finger prints
osteocyte
a mature bone cell (osteoblast) that resides in a lacuna
osteoclast
a bone cell that destroys bone. increases calcium in the body (resorption)
osteon
the functional unit of bone
osteoid
non-living bone matrix
appositional bone growth increases growth within the
concentric lamella
intramembranous ossification
the making of bone directly from mesenchymal cells.
the human body has ____ bones
206
the human body has ____ vertebrae
33
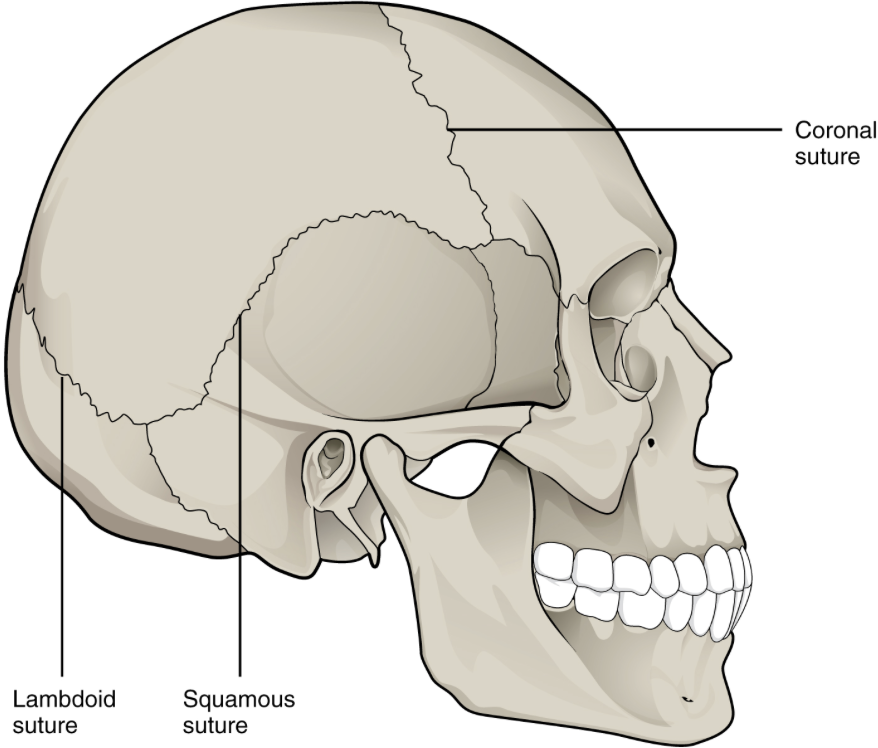
sutures, teeth (gomphosis) and syndesmosis are classified as _____ joints
fibrous
fibrous joints have
no movement
teeth are held in place by a
gomphosis (fibrous) joint
sycondrosis
temporary joints made with hyaline cartilage (ex; epiphyseal growth plates)
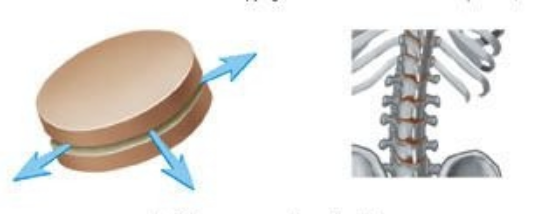
symphysis
a permanent joint held by fibrocartilage (ex; pubic symphysis, vertebral disks)
sycondrosis and symphysis are ____ joints
cartilaginous
plane joint
hinge joint
ball and socket joint
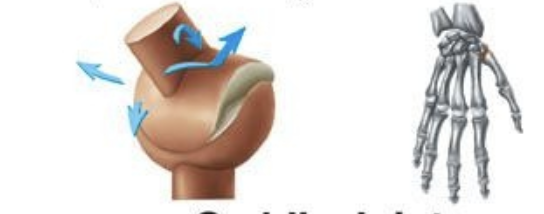
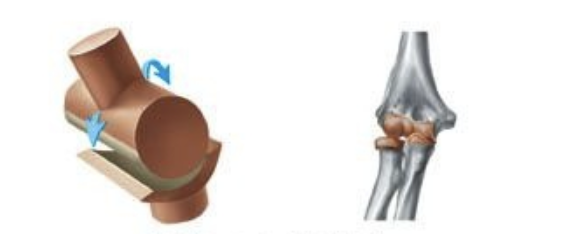
hinge joint

pivot joint
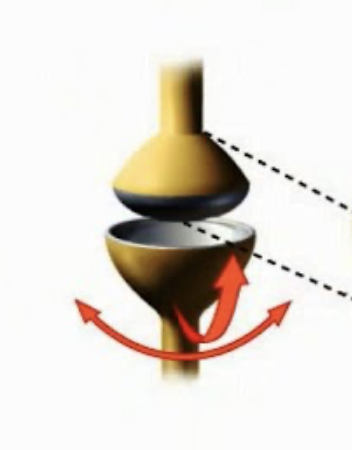
condyloid joint
pivot joint can be found
in our head (c1 c2 vertebrae) giving us the ability to move our head around
hinge joint can be found
in our elbow
saddle joint can be found
connecting our carpals to our metacarpals
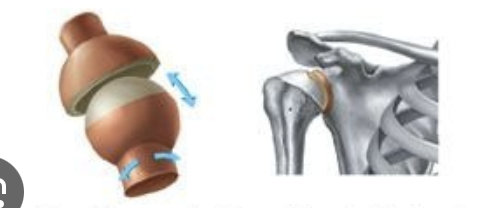
ball and socket joint can be found
in our hip
condyloid joint can be found
between the radius and carpals
plane joint can be found
between tarsal bones
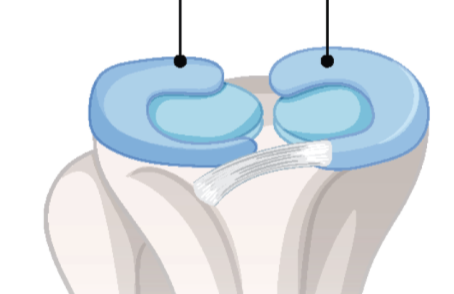
meniscus. a fibrocartilage pad found in the knee joint. reduces shock and stabilizes joint. AVASCULAR
bursae
small, fluid-filled sacs lined by synovial membrane. reduces friction
vitamin d is also known as
Calcitriol
synovial fluid
fluid produced within synovial joints.
synovial membrane
Inner lining of the joint capsule that encloses the joint cavity. rich in blood vessels
ligaments
connect bone to bone
tendons
connect muscle to bone
arthritis
the inflammation and degeneration of joints.
The MCL resides
medially to the body. Inner ligament of knee. connects the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial epicondyle of the tibia.
The LCL resides
laterally to the body. outer ligament of the knee. connects the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the lateral epicondyle of the tibia
ACL
originates in the anterior intercondylar fossa of the tibia and connects at the femoral notch. keeps tibia from sliding forward.
PCL
originates in the posterior intercondylar fossa of the tibia and connects at the medial femoral condyle. keeps tibia from sliding back.
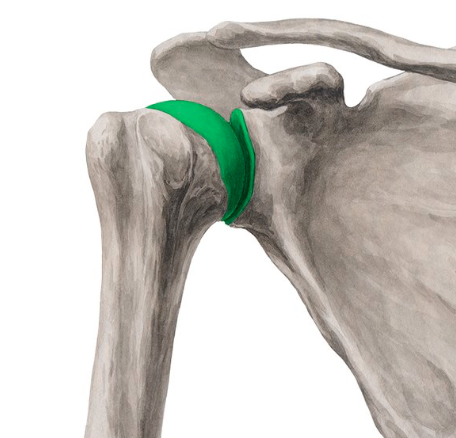
Glenohumeral joint
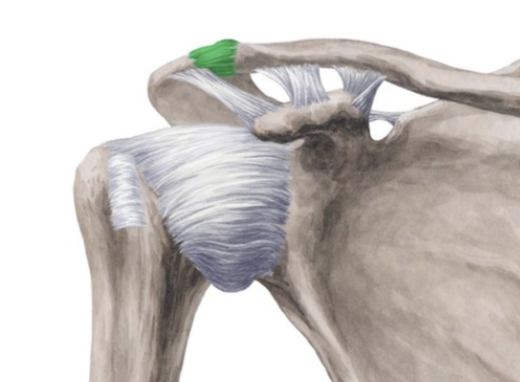
acromioclavicular joint
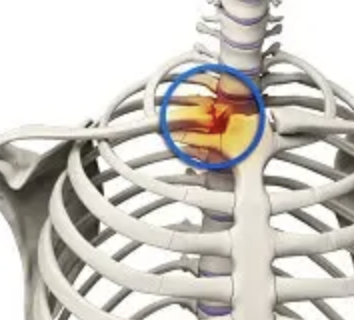
sternoclavicular joint
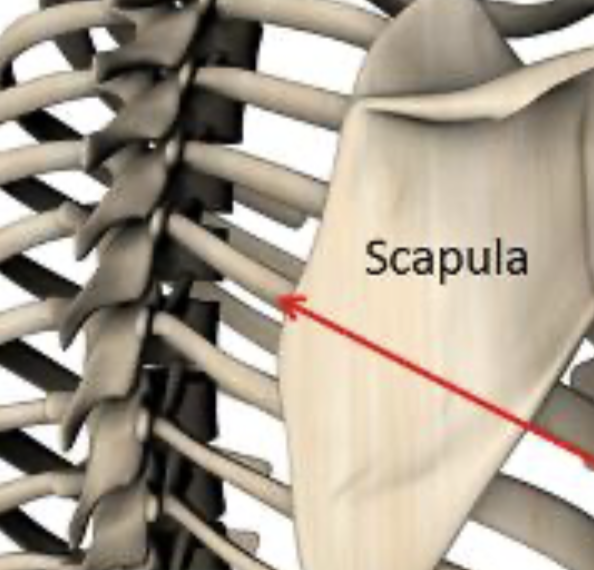
scapulothoracic joint
supraspinatus RC
initiates abduction (move away from body)
intraspinatus RC
initiates lateral rotation
teres minor RC
external rotation, assists in abduction
subscapularis RC
medial rotation