neuro muscle tone
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what is hypertonia ?
excessive resistance to active or passive stretch
what are the 2 types of spasticity ?
clasp-knife and clonus
what is spasticity?
velocity dependent resistance to movement due to neuromuscular over activity with resistance to movement increasing as the speed and amplitude increases
what is clasp-knife?
initial catch followed by release
what is clonus ?
cyclical spasmodic alteration of muscle contraction & relaxation with sustained passive stretch
what is rigidity?
severe hypertonia, both agonist & antagonist are hyperactive
NOT speed dependent
what are the two types of rigidity?
lead pipe and cogwheel
what is lead pipe rigidity?
constant resistance to motion throughout the entire ROM
what is cogwheel rigidity?
resistance that stops and starts as the limb is moved through its ROM (jerky, ratchet)
what is hypotonia ?
decreased resistance to active and passive stretch, LMN is not functioning
can also be due to disuse of muscle over time
paralysis
impaired ability to generate muscle tone, problem within the muscle/motor neuron leading to muscle or SCI
can have increased tone after initial shock
what is flaccidity?
absence of muscle tone, also problem with muscle/motor neuron leading to muscle or SCI
more severe than paralysis
what is a sustained clonus?
clonus greater than 10 beats
MAS 0
no increase in muscle tone
MAS 1
slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch & release or by minimal resistance at the end of the ROM when the affected part(s) is moved in flexion or extension
MAS 1+
slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance throughout the remainder (less than half) of the ROM
MAS 2
more marked increase in muscle tone throughout most of the ROM, but affected part(s) easily moved
MAS 3
considerable increase in muscle tone, passive movement is difficult
MAS 4
affected part(s) rigid in flexion or extension
what is the Brunnstrom Approach?
associated with stroke recovery, loss of top down control resulted in emergence of movement patterns (synergies) which are encouraged
Brunnstorm stage 1
no volitional movement (flaccidity)
Brunnstorm stage 2
appearance of basic limb synergies, movement in associated reactions (spasticity appears)
Brunnstorm stage 3
voluntary movement begin in synergies (increased spasticity)
Brunnstorm stage 4
movement patterns are not dictated solely by limb synergies, voluntary movement outside of synergies (spasticity decreases)
Brunnstorm stage 5
independence from limb synergy patterns, more complex movement (spasticity further decreases)
Brunnstorm stage 6
isolated joint movements are performed with coordination (spasticity disappears)
Brunnstorm stage 7
normal motor function is restored
what are limb synergies in regards to Brunnstorm?
group of muscles that produce a predictable pattern movement in flexion or extension patterns
what are associated reactions in regards to Brunnstorm?
involuntary and automatic movement of a body part as a result of an intentional active or resistive movement in another body part
what is homolateral synkinesis in regards to Brunnstorm?
flexion pattern of the involved UE facilitates flexion of the involved LE
what is Raimiste’s phenomenon in regards to Brunnstorm?
involved LE will abduct/adduct with applied resistance to the uninvolved LE in the same direction
what is Souque’s phenomenon in regards to Brunnstorm?
raising the involved UE above 100 degrees with elbow extension will result in extension/abduction of the fingers
what is the goal of neuro-development treatment (NDT) ?
patient learns to control movement through activities that promote normal movement patterns that integrate function
what is therapeutic handling?
primary intervention strategy, used to facilitate/inhibit movement interfering with normal movement patterns using key points of control
what are the different ways to manage hypertonicity?
prolonged icing, prolonged stretch, inhibitory pressure, neutral warmth, rhythmic rotation, weight bearing, modalities, serial casting
prolonged icing
reduced neurotransmission & spasticity, muscle spindles cooled to decrease excessive stretch reflex
effects can last 1-2 hrs
prolonged stretching
inhibition of hyperactive muscle responders, active/passive stretching for prolonged time
can also be done with splinting/casting
inhibitory pressure
firm/mod inhibitory pressure on tendons
manually and/or through devices such as splints or positioning (WB)
neural warmth
stimulates thermoreceptors and activates parasympathetic response
10-20 mins
rhythmic rotation
slow, repeated rotation of a limb at a point where limitation is noticed
gently moved into range and repeated
modalities
electrical stimulation such as NMES or TENS
used on antagonist muscle for reciprocal inhibition
serial casting
when others fail, maintained pressure, low load prolonged stretch
recast every 5-7 days as ROM progresses
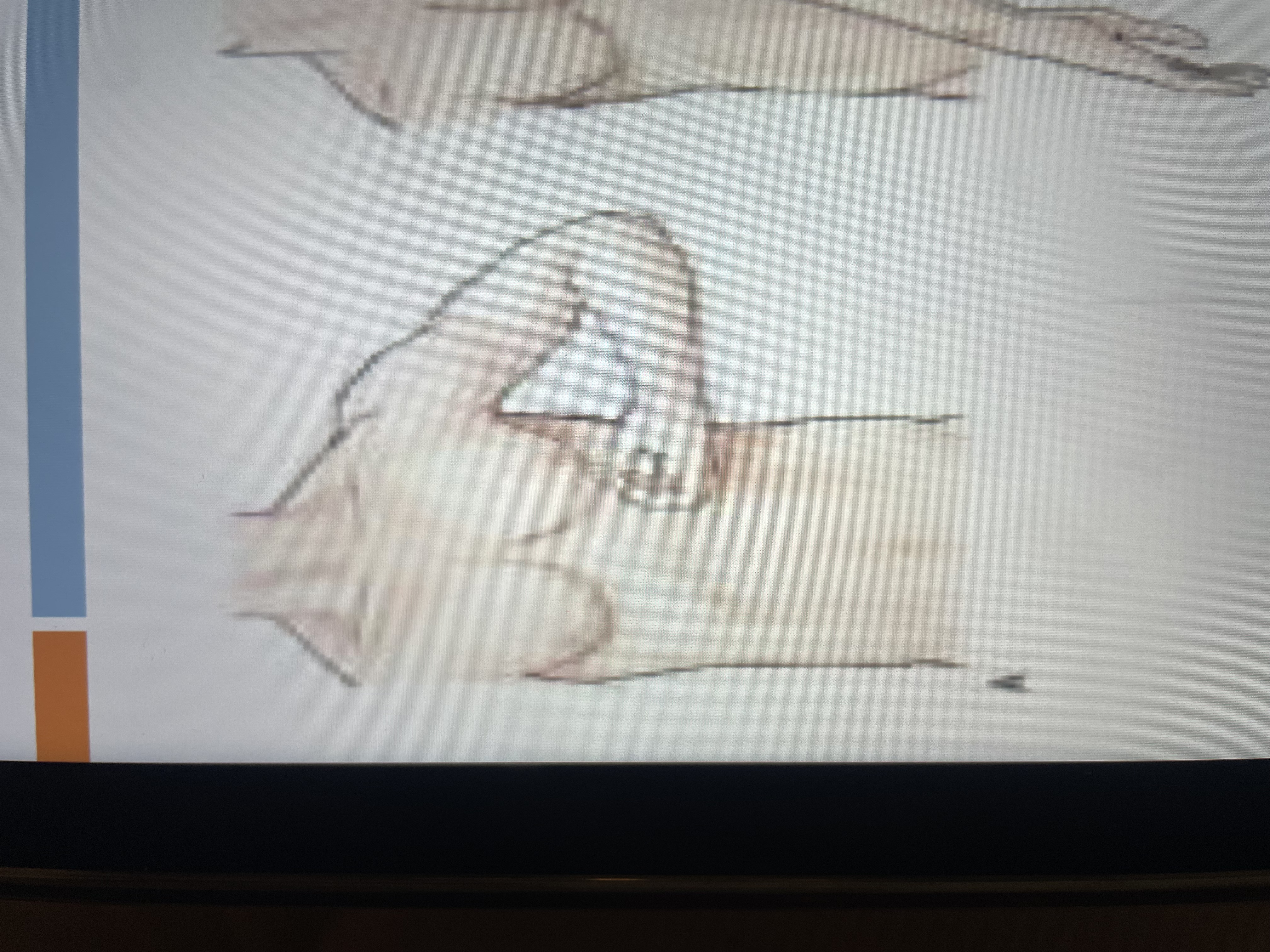
upper flexion synergy
scapular retraction, elevation
shoulder flexion, abduction, ER
elbow flexion
forearm supination
wrist & finger flexion
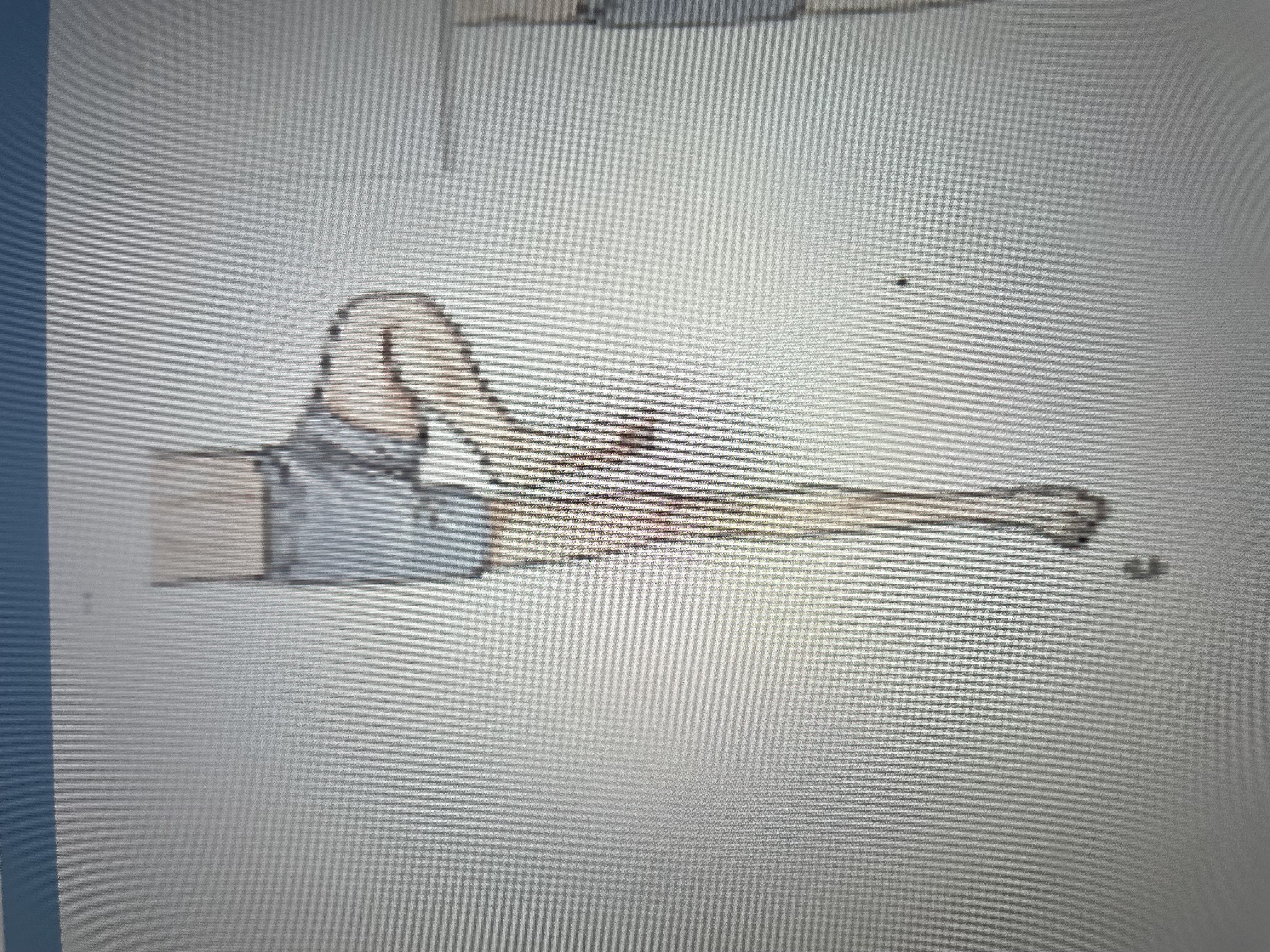
lower flexion synergy
hip flexion, abduction, ER
knee flexion
ankle DF, inversion
toe DF
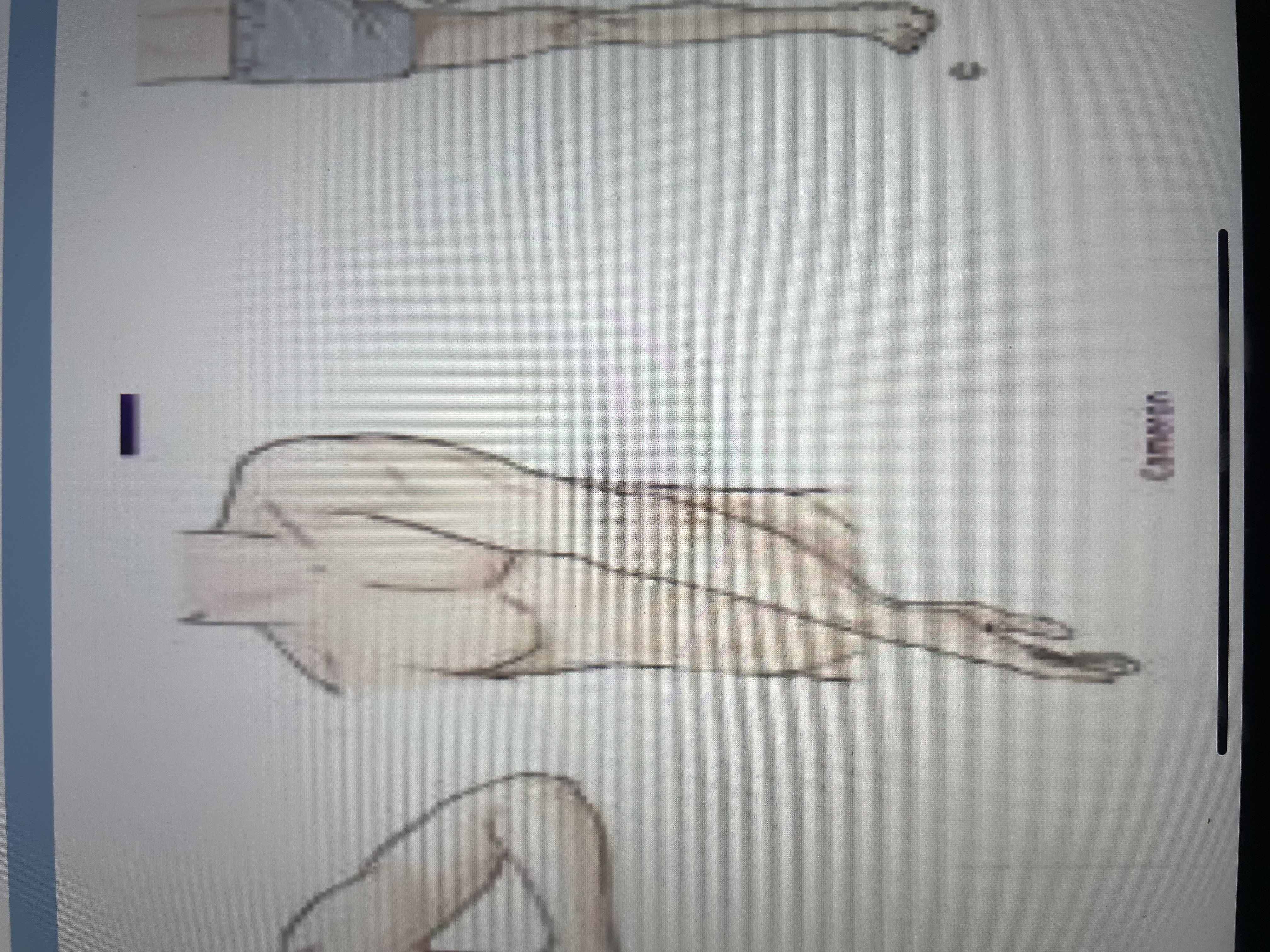
upper extension synergy
scapular protraction
shoulder extension, adduction, IR
elbow extension
forearm pronation
wrist and finger flexion
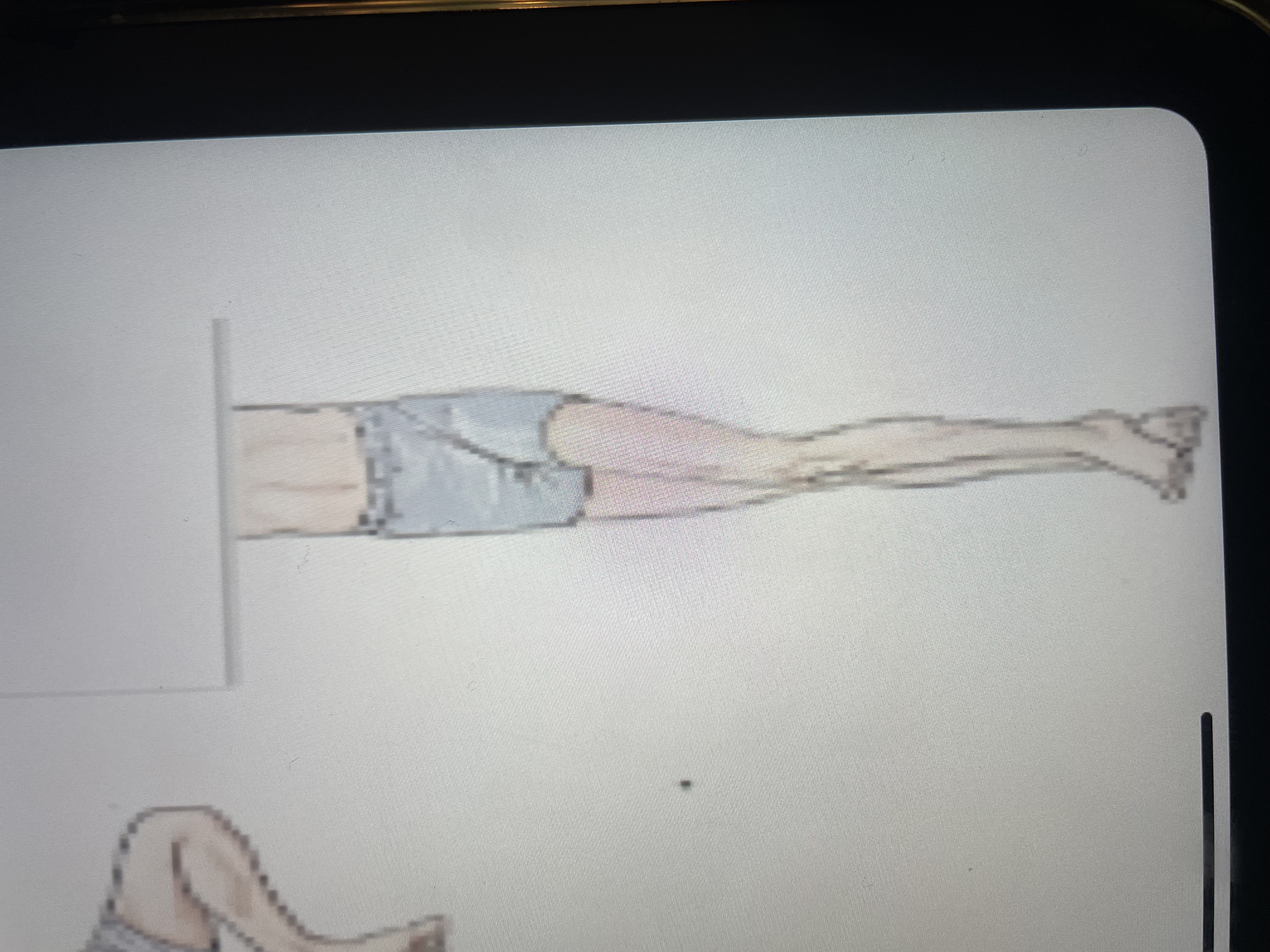
lower extension synergy
hip extension, adduction, IR
knee extension
ankle PF, inversion
toe PF
decorticate
elbows, wrist, and fingers flexed, legs extended & IR
decerebrate
elbows extended, legs extended, and IR
more indicative of severe damage
critical elements of managing synergies
movement opposite to pattern, reciprocal inhibition, begin distal to proximal for tone inhibition, static hold on intermediate joints opposite to pattern
things to manage hypotonicty
quick stretch
tapping
resistance w/o overload
approximation
weight bearing
positioning
strengthening w/o overload
quick stretch for hypotonicity
stimulation of muscle spindle which results in reflex facilitation of the muscle to prevent overstretching as a protective mechanism
approximation/weight bearing
facilitates postural extensors needed to stabilize the body
improved proprioception/joint awareness
tapping for hypotonicity
light tapping over a tendon or muscle belly to facilitate a voluntary contraction