Innate Immunity Overview and Key Concepts
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Innate Immunity
First line of defense against pathogens, non-specific.
Physical Defenses
Barriers preventing pathogen entry into tissues.
Chemical Defenses
Mediators inhibiting microbial growth in the body.
Cellular Defenses
Cells involved in recognizing and eliminating pathogens.
Pathogen Recognition
Identifying foreign substances by the immune system.
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing and digesting pathogens.
Inflammation
Response to injury or infection causing swelling and redness.
Fever
Increased body temperature to enhance immune response.
Physical Barriers
Structures preventing pathogens from reaching target tissues.
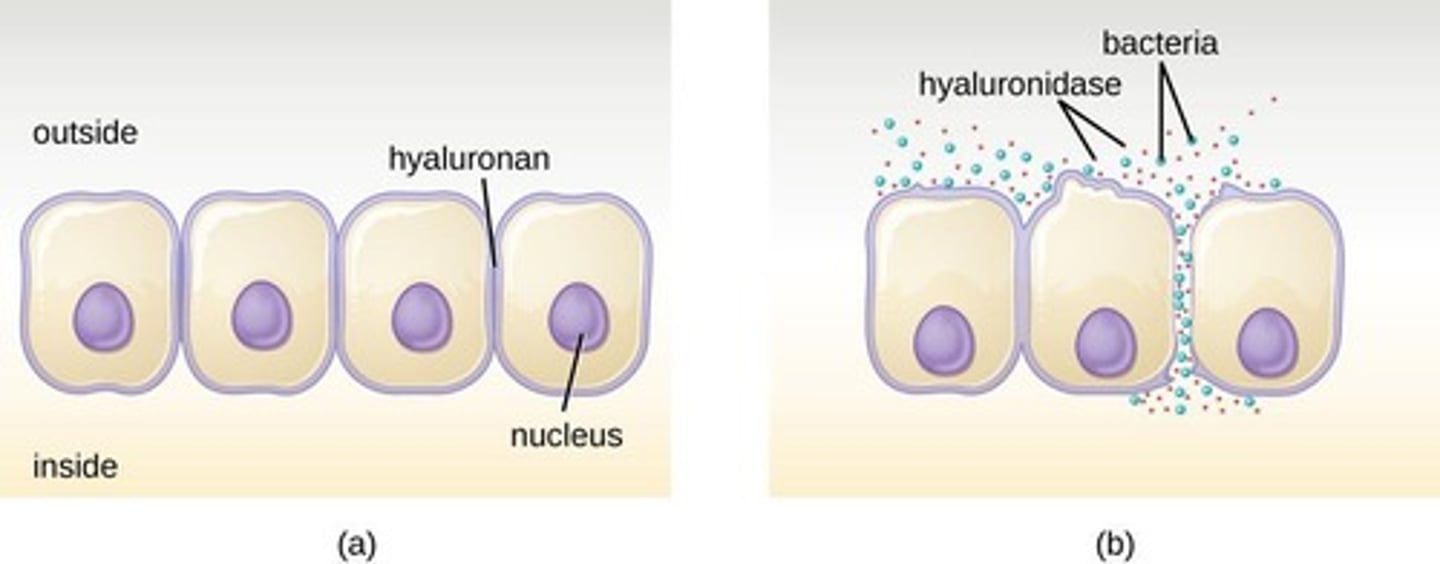
Tight Junctions
Cellular connections preventing pathogen passage between cells.
Desmosomes
Cell structures providing adhesion between adjacent cells.
Gap Junctions
Channels allowing communication between adjacent cells.
Hyaluronidase
Enzyme used by pathogens to break cellular junctions.
Skin
Primary physical barrier against environmental pathogens.
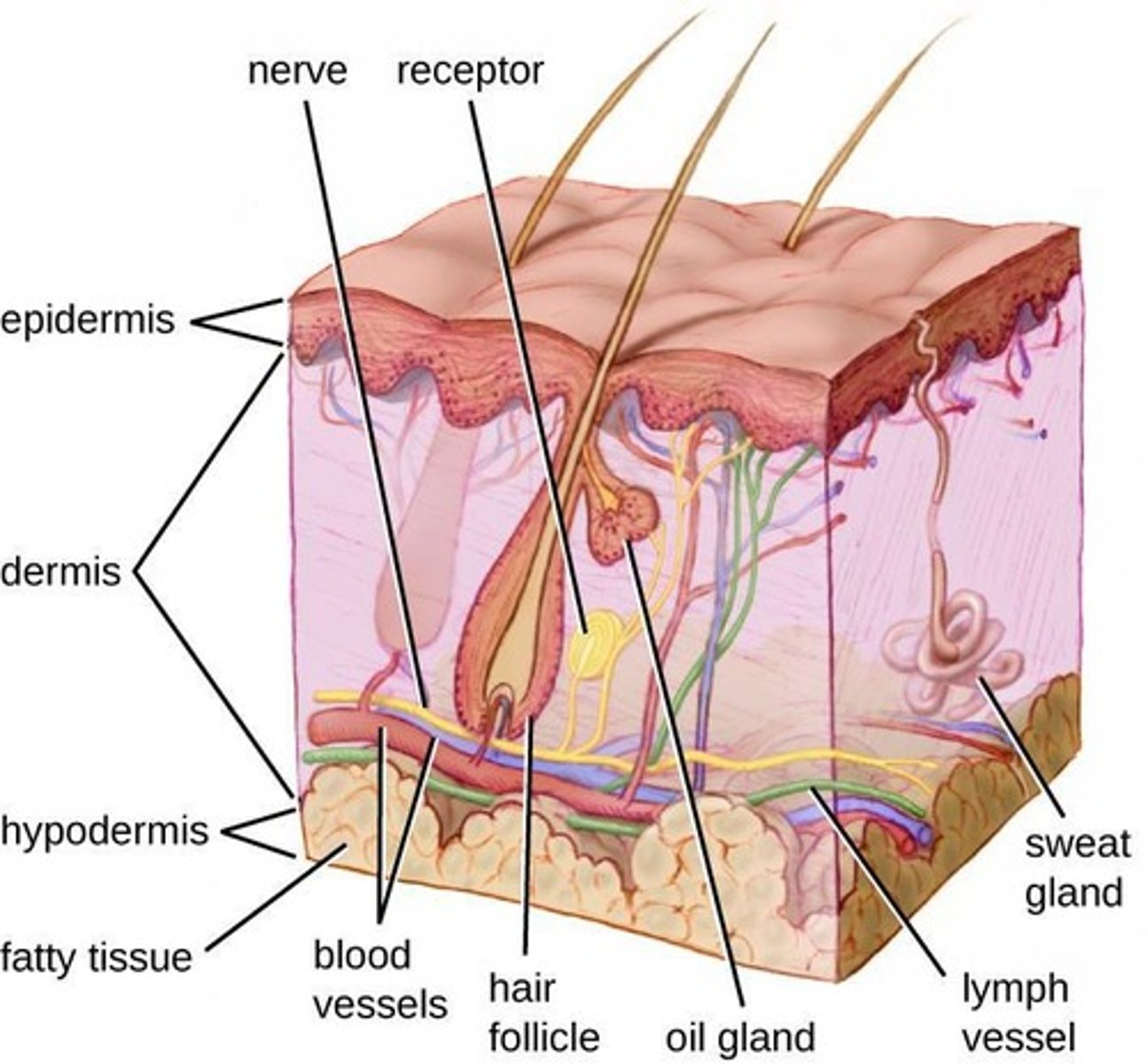
Epidermis Shedding
Process of skin cell loss aiding in microbe removal.
Keratin
Protein in skin providing resistance to microbial enzymes.
Salt
Chemical that inhibits microbial growth on skin.
Mucous Membranes
Protective linings in respiratory and digestive tracts.
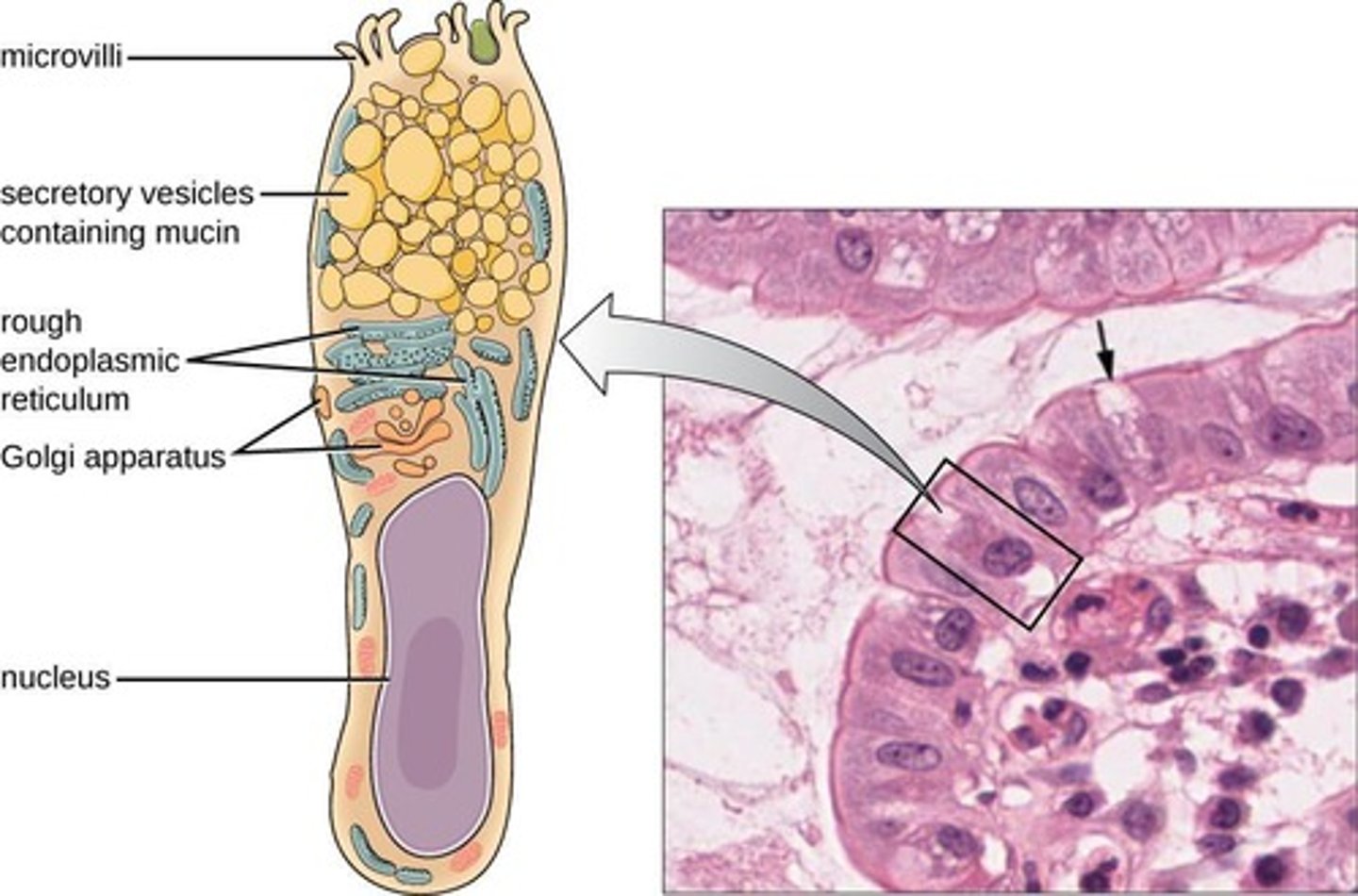
Goblet Cells
Intestinal cells producing mucus with antimicrobial properties.
Mucociliary Escalator
Mechanism moving mucus out of lungs via cilia.
Endothelia
Tightly packed cells lining blood and lymphatic vessels.
Blood-Brain Barrier
Endothelial barrier protecting the central nervous system.
Microbiome Defense
Beneficial microbes competing against potential pathogens.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins regulating immune responses.
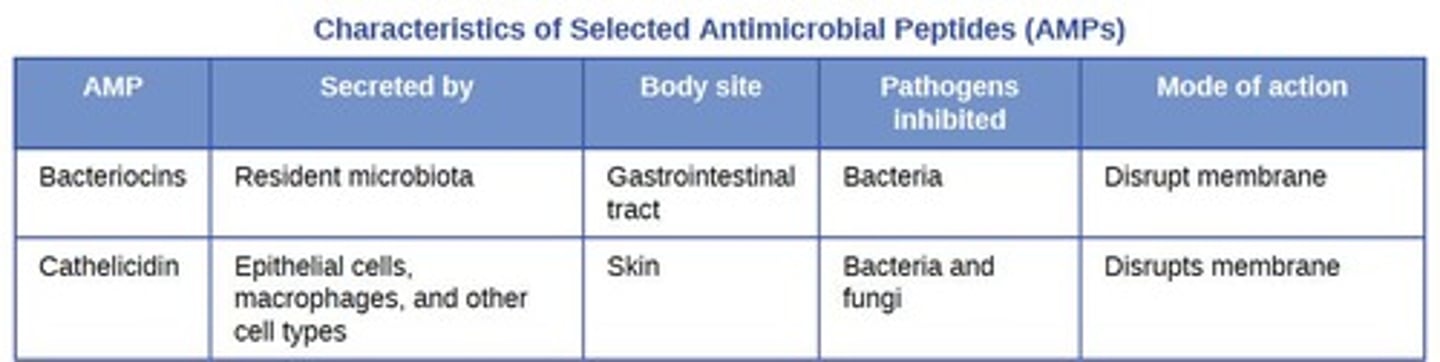
Antimicrobial Peptides
Small proteins disrupting microbial cell membranes.
Plasma Protein Mediators
Proteins in blood aiding in immune response.
Sebum
Oil from sebaceous glands sealing pores.
Propionibacterium acnes
Bacteria digesting sebum, lowering skin pH.
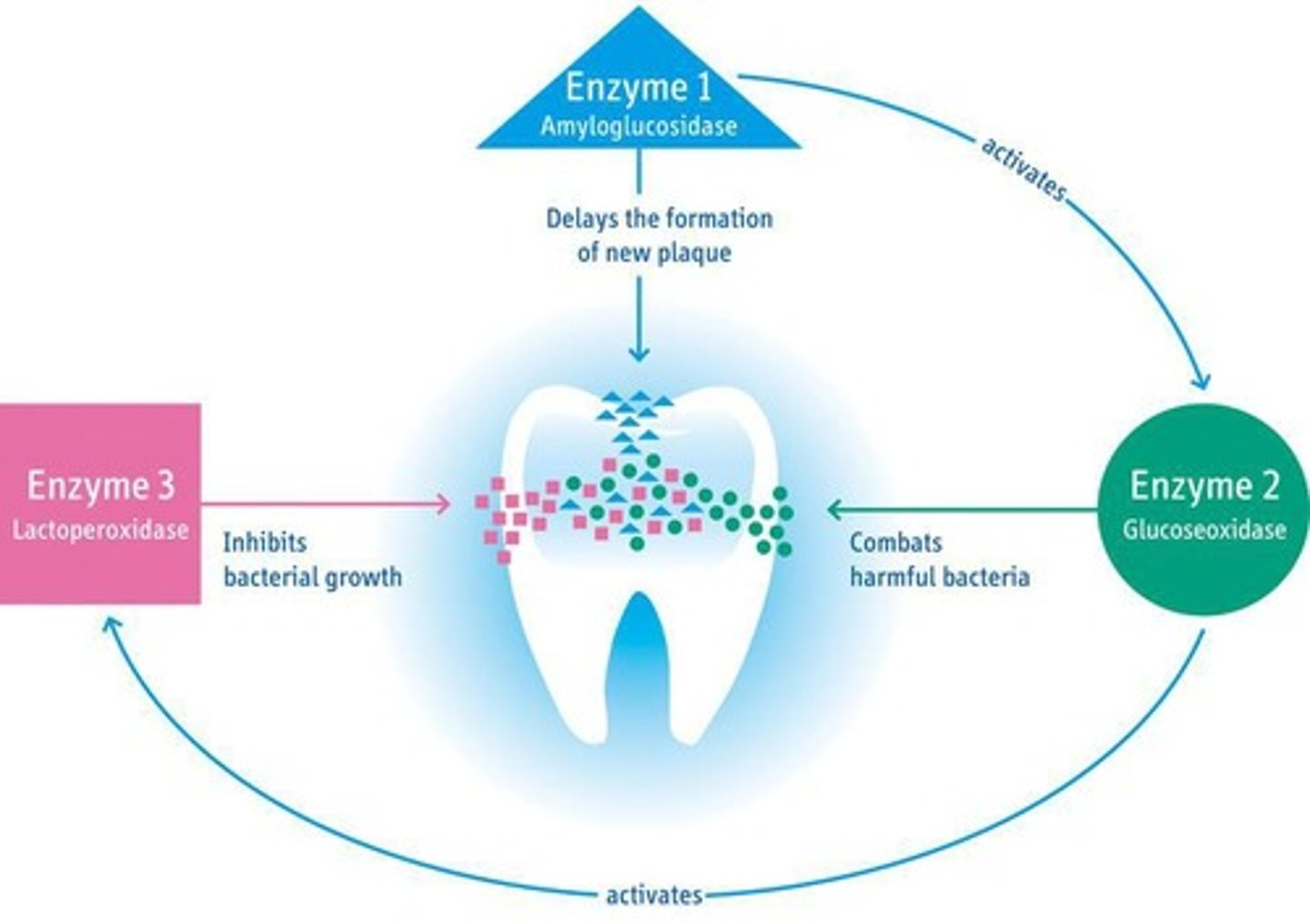
Saliva
Fluid containing lactoperoxidase for pathogen defense.
Lactoperoxidase system
Catalyzes hydrogen peroxide activity in saliva.
Stomach acid
Digestive fluid eliminating most pathogens.
Paneth cells
Cells producing antimicrobial substances in intestines.
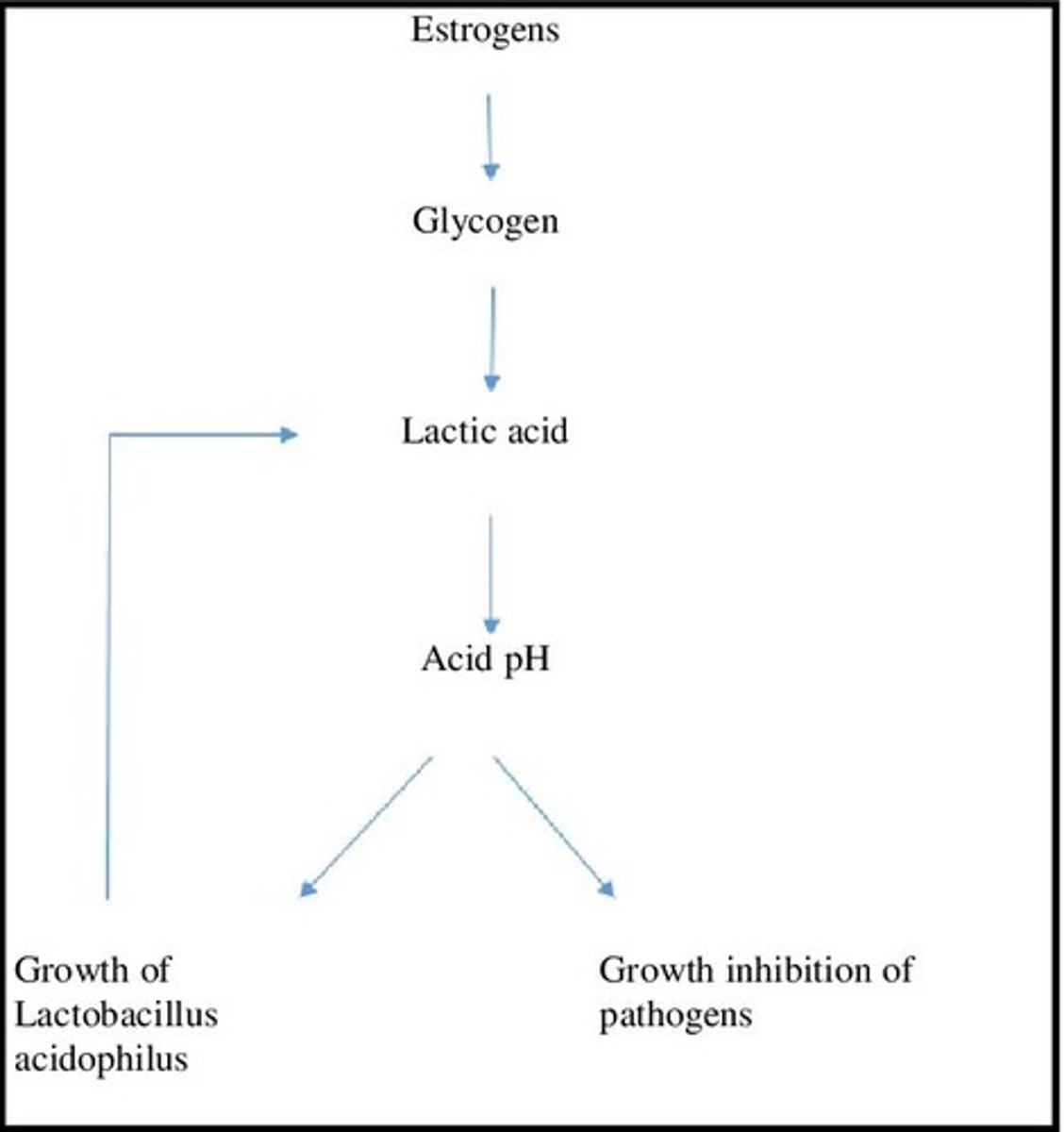
Lactobacilli
Bacteria fermenting glycogen to lower vaginal pH.
Tears
Fluid containing lysozyme and lactoferrin for protection.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)
Cell-derived mediators with broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties.
Cytokines
Proteins stimulating immune cells for chemical defenses.
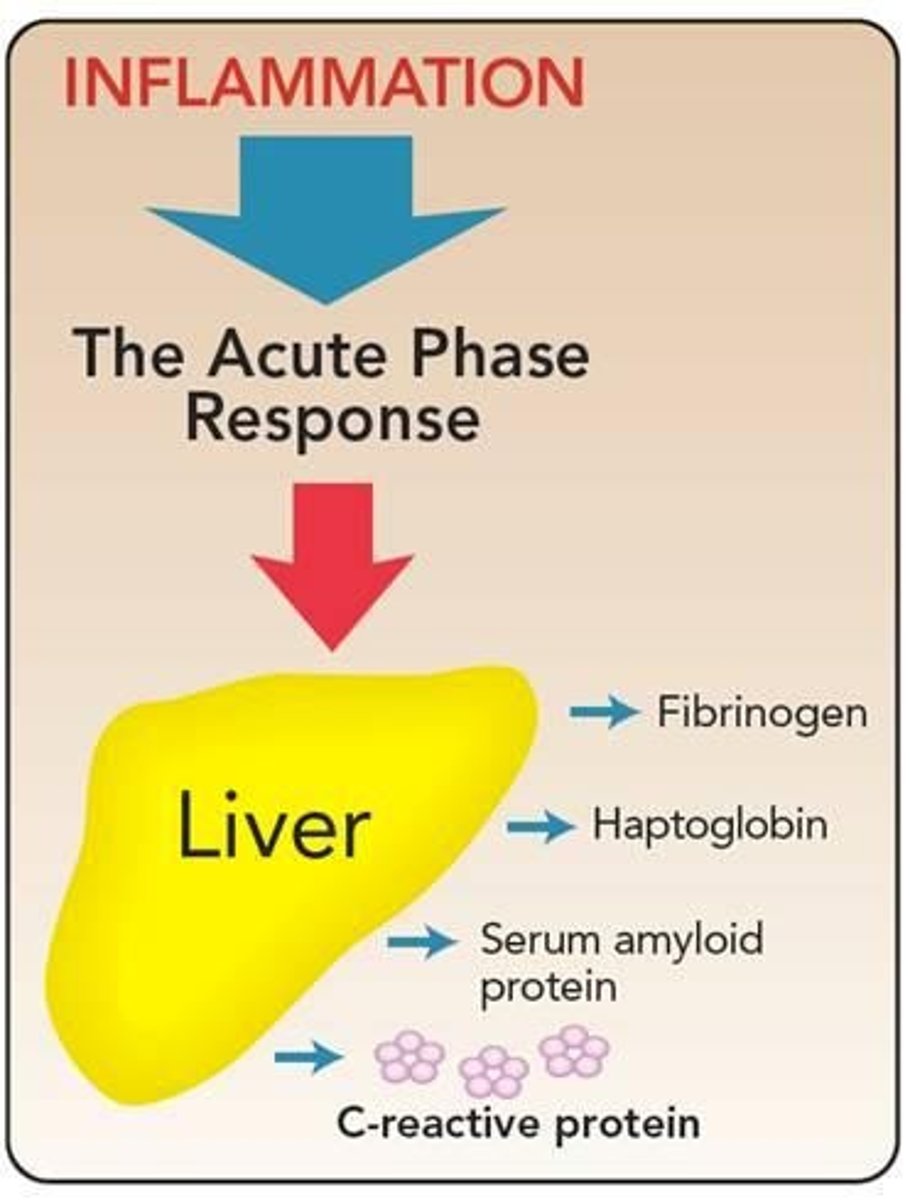
Acute phase proteins
Liver-produced proteins secreted into blood during inflammation.
C-reactive proteins
Acute phase protein indicating inflammation in blood.
Ferritin
Protein storing iron, involved in immune response.
Transferrin
Protein transporting iron in the bloodstream.
Fibrinogen
Protein involved in blood clotting and inflammation.
Complement system
Blood proteins connecting innate and adaptive immunity.
Alternative pathway
Complement activation initiated by spontaneous C3 activation.
Classical pathway
Complement activation via antibody binding to pathogens.
Lectin pathway
Complement activation triggered by mannose-binding lectin.
Opsonization
Coating pathogens for easier phagocytosis.
Membrane attack complex (MAC)
Complex forming pores in Gram-negative bacteria.
Interleukins
Cytokines recruiting immune cells to infection sites.
Chemokines
Cytokines recruiting specific leukocytes to inflammation.
Interferons
Proteins released during viral infections to recruit immune cells.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins that induce inflammatory mediator production.
Histamine
Chemical causing bronchoconstriction during inflammation.
Leukotrienes
Mediators inducing coughing, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Prostaglandins
Compounds that induce fever during inflammatory responses.
Bradykinin
Peptide increasing capillary permeability, contributing to edema.
Hematopoiesis
Process of blood cell differentiation from stem cells.
Granulocytes
Type of white blood cells involved in innate immunity.
Neutrophils
White blood cells that destroy extracellular bacteria.
Eosinophils
White blood cells with 2-3 lobes, combating parasites.
Basophils
White blood cells with large granules, involved in allergies.
Natural Killer Cells
Agranulocytes targeting virus-infected and tumor cells.
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
Mesh of chromatin trapping pathogens during immune response.
Pus Formation
Accumulation of leukocytes, debris, and bacteria at infection site.
Eosinophils
Protect against protozoa and helminths.
Basophils
Involved in allergic reactions and inflammation.
Mast Cells
Reside near blood vessels and nerves.
Agranulocytes
Lack visible granules in cytoplasm.
Natural Killer Cells
Target tumors and virus-infected cells.
Monocytes
Largest type of white blood cells.
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing pathogens by cells.
Diapedesis
Leukocytes passing through capillary walls.
Transendothelial Migration
Leukocytes flatten and squeeze through junctions.
Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
Molecules recognized by phagocytes for pathogen detection.
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
Detect PAMPs on phagocytic cells.
Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
Bind PAMPs to activate phagocyte response.
Phagosome
Vesicle formed around engulfed pathogen.
Phagolysosome
Fusion of phagosome and lysosome for degradation.
Inflammation
Response to recruit immune cells and repair.
Acute Inflammation
Immediate response causing redness, swelling, heat.
Chronic Inflammation
Prolonged response with potential granuloma formation.
Fever
Systemic response raising body temperature.
Pyrogens
Substances that induce fever by altering hypothalamus.
Exogenous Pyrogens
Produced by pathogens, like LPS.
Endogenous Pyrogens
Produced by leukocytes, such as interleukins.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins involved in immune responses.
Granules
Contain histamine and enzymes in immune cells.