Chapter 21 - Species and Speciation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
speciation
the process that produces new and distinct forms of life
biological species concept (BSC)
Species are groups of actually or potentially interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups
morphospecies concept
members of the same species usually look alike
hybridization
closely related species can reproduce
wallace effect
there should be selection against hybridization
ring species
populations that can interbreed with neighboring populations but not with populations separated by larger geographical distances
limitations of the BSC and morphospecies concepts
Difficult to apply in real world
Cannot be applied to asexual or extinct organisms
Does not account for genetic exchange in ring species
Does not account for hybridization in plants
Ecological species concept (ESC)
The concept that there is a one-to-one correspondence between a species and its niche
- same niche, same species
Phylogenetic species concept (PSC)
the idea that members of a species all share a common ancestry and a common fate
- useful when thinking about asexual species
reproductive isolation
Separation of species or populations so that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring
prezygotic reproductive isolation
separation of species due to factors that prevent the formation of a zygote
- behavioral
- physical
- temporal
- ecological
postzygotic reproductive isolation
Genetic incompatibility usually leading to failure of the zygote to develop
- Sterile offspring (genetic dead end)
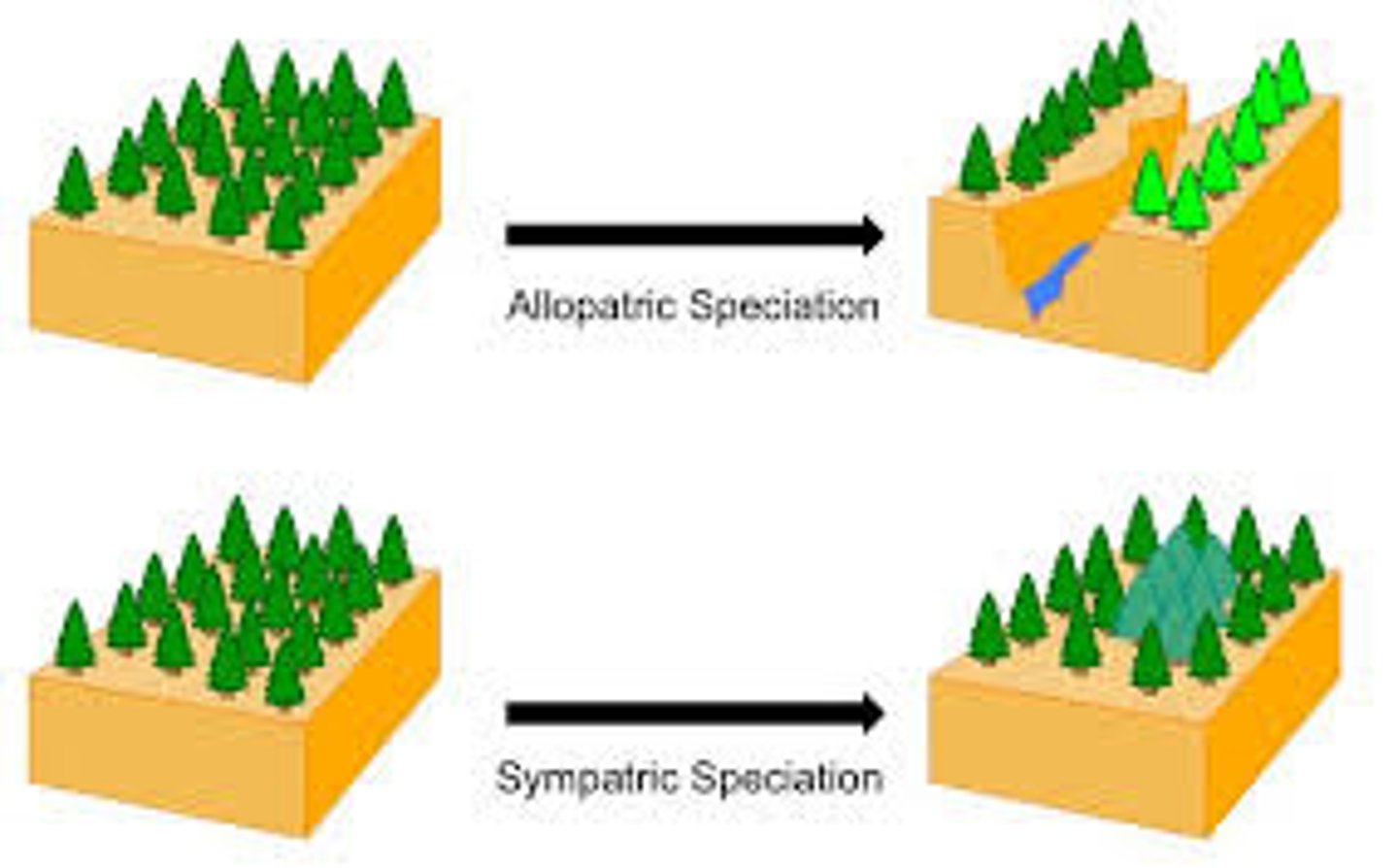
allopatric
geographically separate
vicariance-derived speciation
Geographic separation of a population (typically a physical barrier) causes allopathy
peripatric speciation
A specific kind of allopatric speciation in which a few individuals from a mainland population disperse to a new location remote from the original population and evolve separately.
adaptive radiation
speciation occurs quickly and a variety of ecologically distinct forms are generated as the organisms adapt to local conditions successfully
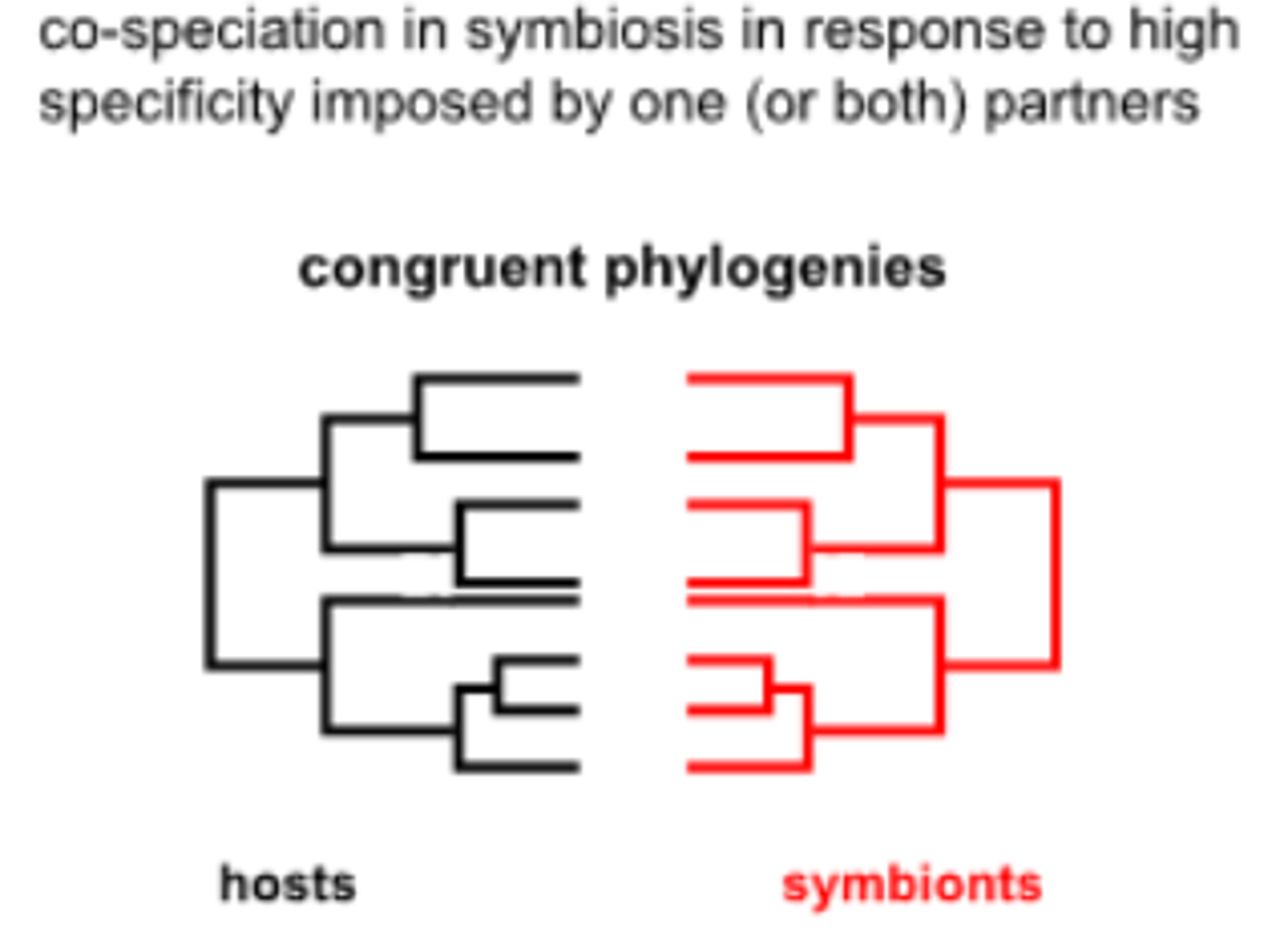
co-speciation
when organisms speciate in response to each other
sympatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area
instantaneous speciation
Speciation that occurs in a single generation.
polyploidy
produces offspring who cannot reproduce with the parent generation
- in plants, result of extra set of chromosomes during cell division