The Kidneys
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
location, structure, macro + microstructure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Location of the kidneys
o retroperitoneal from T12 – L4
o Posterior-superior surface: deep to ribs 11 & 12
o Posterior-inferior surface: related to psoas major muscle and quadratus lumborum muscle
* R kidney lower than left
Why is the artery to the right kidney longer then the left?
the abdominal aorta being slightly left to midline + crosses the vena cava posteriorly
When do the ureters become pelvic rather then abdominal?
Once it passes the bifurcation at the common iliac artery
What is found at the transpyloric plane?
superior pole of R kidney and hilum of L kidney
Describe what surrounds the kidneys from deep to superficial
Renal capsule
Perirenal fat
Renal fascia (Gerota’s)
Pararenal fascia
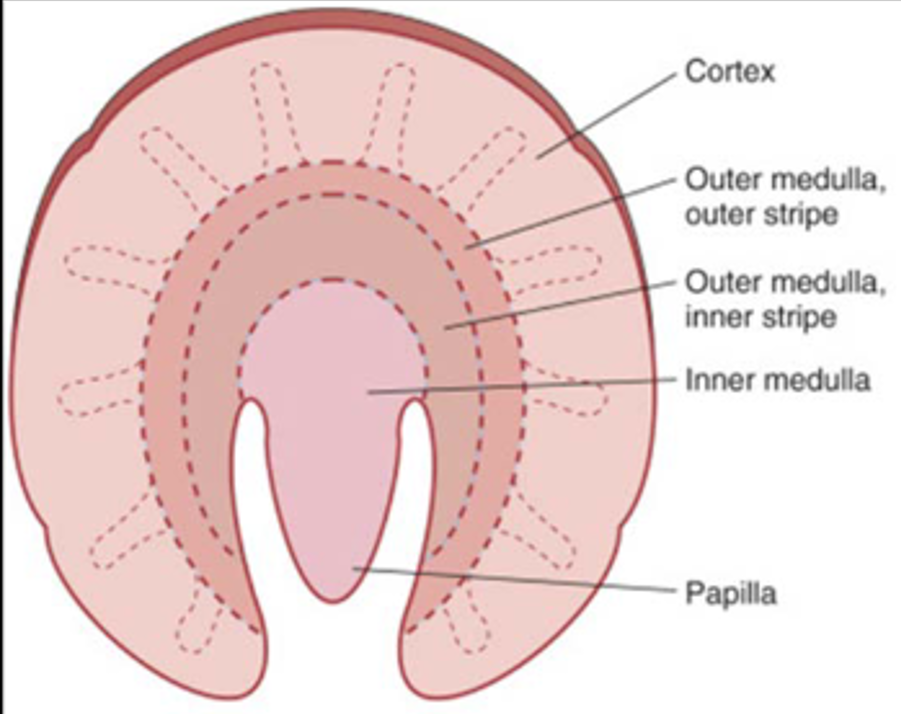
What is in the medial portion of the kidney?
Vertical cleft
renal hilum
renal sinus (space within the kidney occupied by renal pelvis, calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat)
At what level is the superior mesenteric artery
L1
Name the arteries that supply the kidneys
Anterior branch of renal artery:
o superior (apical) segmental artery
o anterosuperior segmental artery
o antero-inferior segmental artery
o inferior segmental artery
Posterior branch of renal artery:
o posterior segmental artery
What type of arteries are segmental arteries (arteries in the kidneys)?
end arteries
What imaginary line shows the segments of the kidney supplied by the anterior and posterior divisions?
Line of Brodel
What are the veins of the kidney called and where are they located?
right renal vein: anterior to the renal arteries
left renal vein: posterior to superior mesenteric artery
** both drain into the IVC
Which vein is longer and why?
left renal vein
the vena cava lies slightly to the right
What else drains into the left renal vein?
the left suprarenal vein and left gonadal vein
What is the Renal corpuscle made up of?
glomerulus
Bowmans capsule
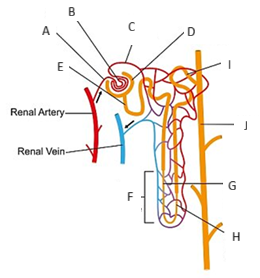
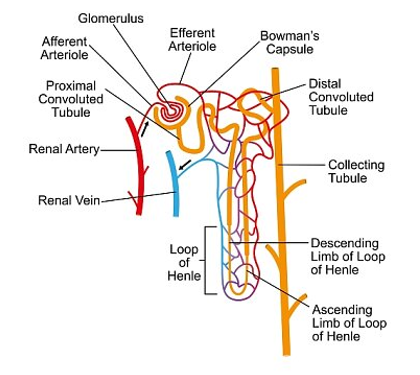
Name the vascular components of the nephron
o Afferent arteriole
o Glomerulus
o Efferent arteriole
Peritubular capillaries
Name the tubular components of the nephron
o Bowman’s capsule
o Proximal tubule
o Loop of Henle
o Distal tubule
Collecting duct
What part of the nephron is mixed tubular and vascular?
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
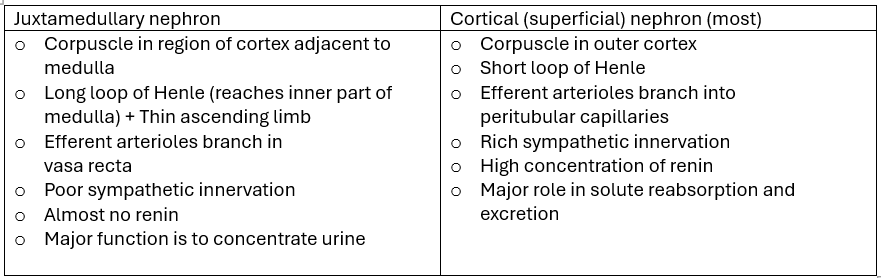
Difference between a Juxtamedullary nephron and a Cortical (superficial) nephron
What type of capillaries are in the renal capsule?
fenestrated
Name the layers of the glomerulus and how they ensure correct molecules are filtered
Fenestrated endothelium → permeable to water and low molecular weight solutes + negative charged
Glomerular Basement membrane → strongly negative charge
Visceral epithelial cells (made of podocytes → with spaces in between called slit diaphragm)
→ highly negatively charged matrix
→ filtration slit diaphragm: size selective filter (large molecules cannot enter)
Describe the arterial supply of the renal parenchyma
Renal segmental artery → interlobar artery (pass between 2 lobes) → arcurate artery (arch on top of the pyramid) → smaller interlobular artery → afferent arterioles
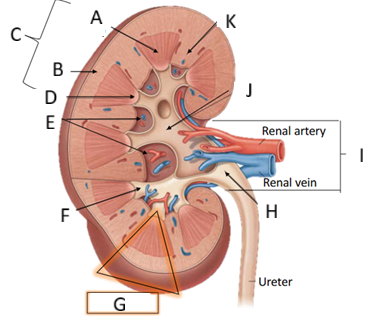
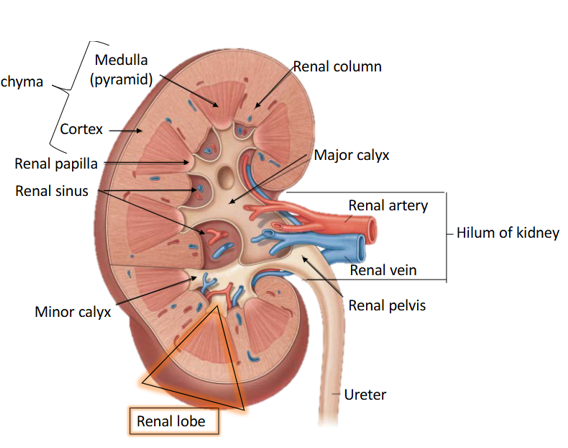
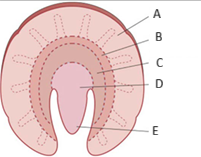
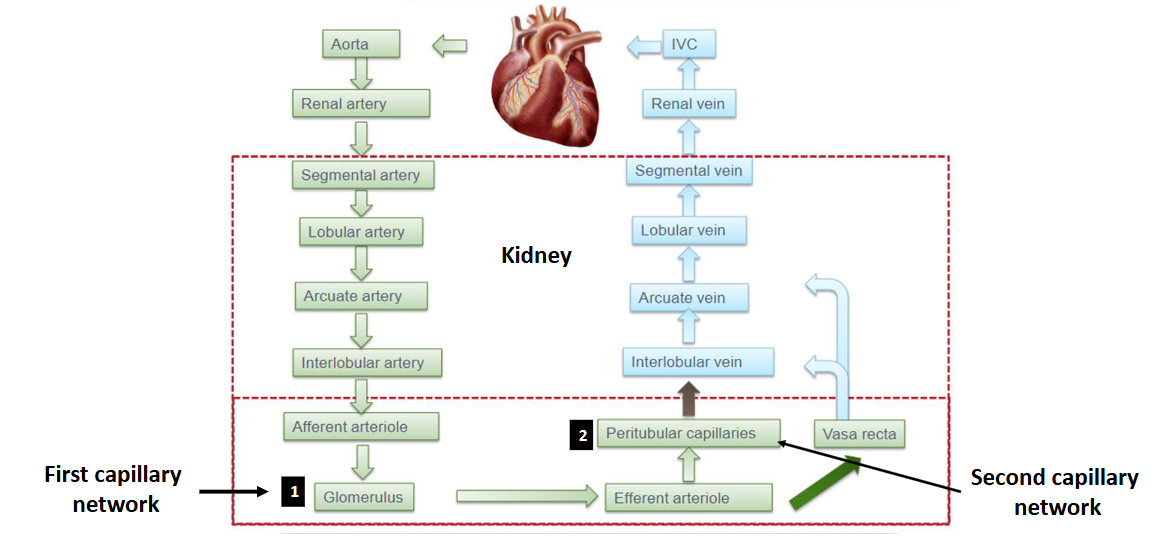
Describe the venous drainage of the kidneys
Peritubular capillaries → interlobular vein → acruate vein → ascending vasa recta
Lymphatic drainage of the kidneys
lateral aortic (or para-aortic) lymph nodes (located at the origin of the renal arteries)
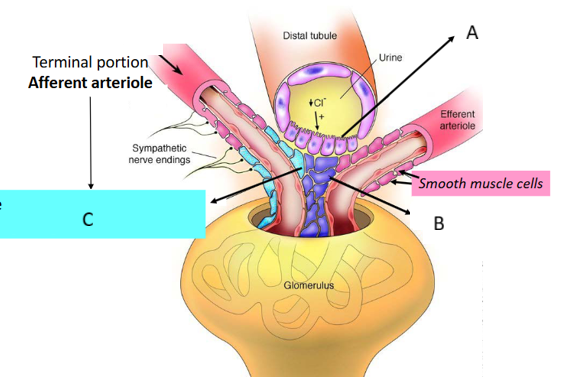
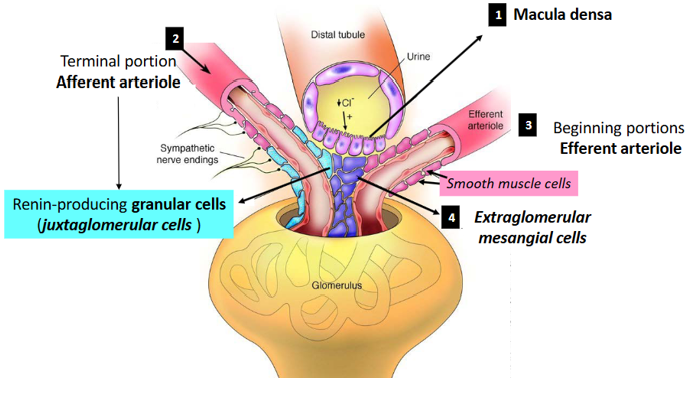
What is the function of the Juxtaglomerular apparatus?
regulate systemic blood pressure and glomerular arteriolar resistance (blood flow) and filtration rate
What are the components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
o macula densa
o juxtaglomerular granular cells (modified SMC in a/efferent arterioles)
o extraglomerular mesangial (Lacis) cells
Function of the macula densa
monitor the concentration of salt (NaCl) in the distal tubule
Describe the 2 poles of the renal corpuscle
vascular pole: where blood vessels enter and exit → afferent in and efferent out
tubular pole (also called the urinary pole): where the Bowman's capsule opens into the proximal convoluted tubule → glomerular filtrate exit
The proximal tubule is split into 2 parts, name them
pars convuluta (bendy bit)
pars recta (straight bit)