Neurons and Synapses
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to neurons and synapses, aimed at aiding in the understanding of the nervous system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Neuron
A cell that transmits electrical impulses.
Dendrite
short, branched nerve fibers. Many are located in the brain, for example.
Thin processes from the cell body that receive stimuli.
Cell body or soma
contains the organelles to keep the neuron alive and functioning
Axon
A long extension of the neuron that transmits nerve impulses to other neurons or effectors over long distances.
Motor axons
may be very long and, in the peripheral nervous system, many are myelinated
Axon branches of motor neurons
have synaptic knobs at each end, which release neurotransmitters that are chemicals that transmit the impulse between neurons or between a neuron and a muscle cell
Myelin Sheath
A fatty layer that insulates the axon and increases the speed of impulse transmission.
Synapse
The junction between two neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell.
Synapses exist between:
•Neurons
•Neurons and receptor cells
•Involved in sensory reception
•Neurons and effector cells
•Respond to a stimulus: muscle cells, gland cells, etc.
Neurotransmitter
Chemicals that transmit impulses across the synapse.
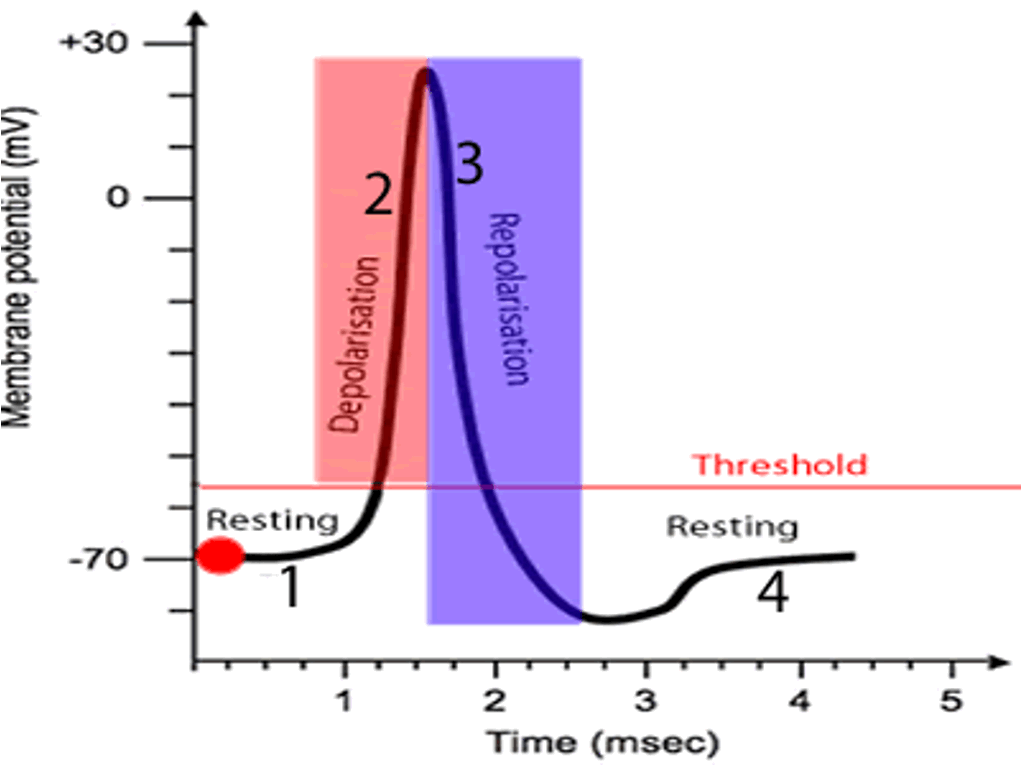
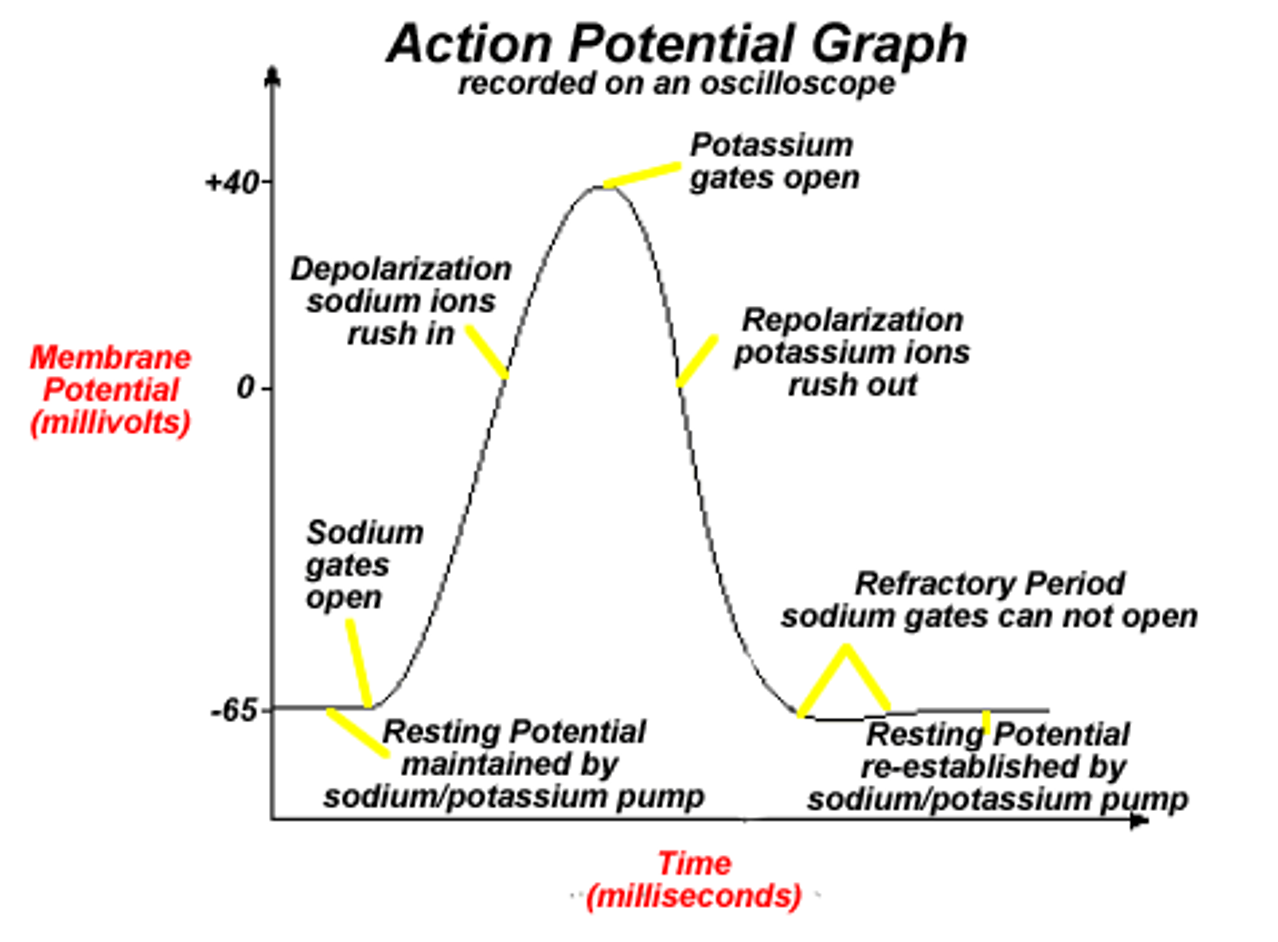
Action Potential
A rapid change in membrane potential that occurs when a neuron generates an impulse.
two phases:
•Depolarization: change form negative to positive
•Repolarization: Change back from positive to negative
Resting Potential
The state of a neuron when it is not transmitting an impulse, typically around -70 mV.
•Inside of axon is negatively charged, with respect to the outside
Saltatory Conduction
The process by which nerve impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next along a myelinated axon.
•Impulses travel in one direction-never backwards
Node of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath where action potentials are generated.
Calcium Influx
The influx of calcium ions that triggers the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles.
Potassium Ion (K+)
An ion that flows out of the neuron during repolarization.
Sodium Ion (Na+)
An ion that flows into the neuron during depolarization.
Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
Channels that open or close in response to changes in membrane potential, allowing ions to enter or exit the neuron.
CNS
Central Nervous System, consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System, consisting of all neural elements outside the CNS.
Myelination
The process of forming a myelin sheath around a nerve fiber.
Myelination allows for
Saltatory conduction
Impulse Direction
The direction in which an electrical signal travels along a neuron.
post-synaptic cell
may be another neuron or an effector cells such as glands, muscles, etc.
nerve impulses are carried by-
temporary shifts in electrical charge
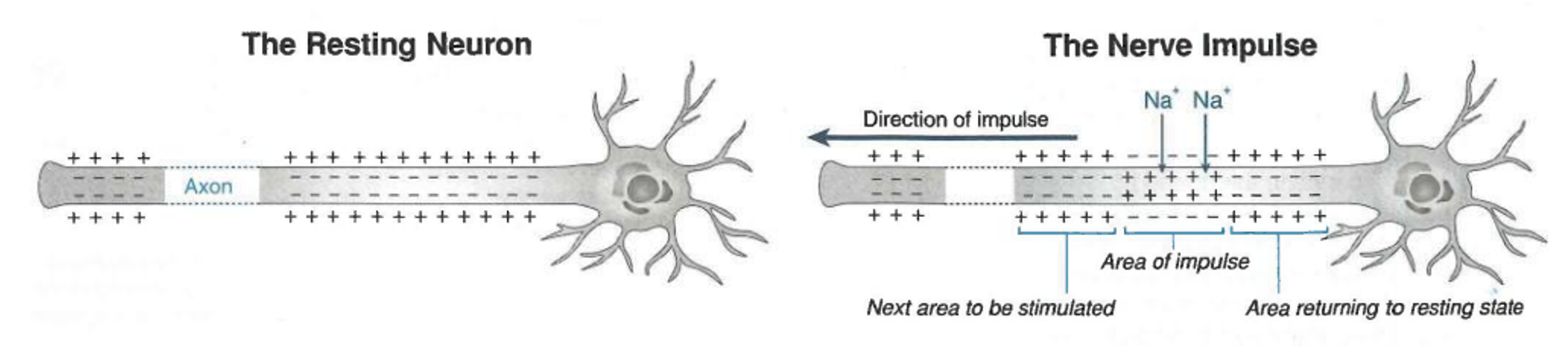
The charge is changed by moving ___ in and ___ out of the axon
SODIUM ions in
And
POTASSIUM ions out
Depolarization
Sodium ions (Na+) flow into the axon
Repolarization
Potassium ions (K+) flow out of the axon
Nerve fibers are
myelinated
Myelin
the membrane of Schwann cells, wrapped around a nerve fiber many times
Myelination insulates-
the axon, thereby increasing the speed of the impulse
Na+/K+ pumps
generate resting potential
*Reminder: 3 Na+ Out and 2 K+ in. This maintains the concentration gradient for both ions
Oscilloscope traces
Nerve impulses work on an “all or none” principal.
The impulse isonly initiatedif the threshold potential is reached.
The impulse is carried from node to node due to
action potentials being propagated along the axon
local currents
when ions migrate laterally
provide the threshold potential to open sodium and potassium voltage-gates
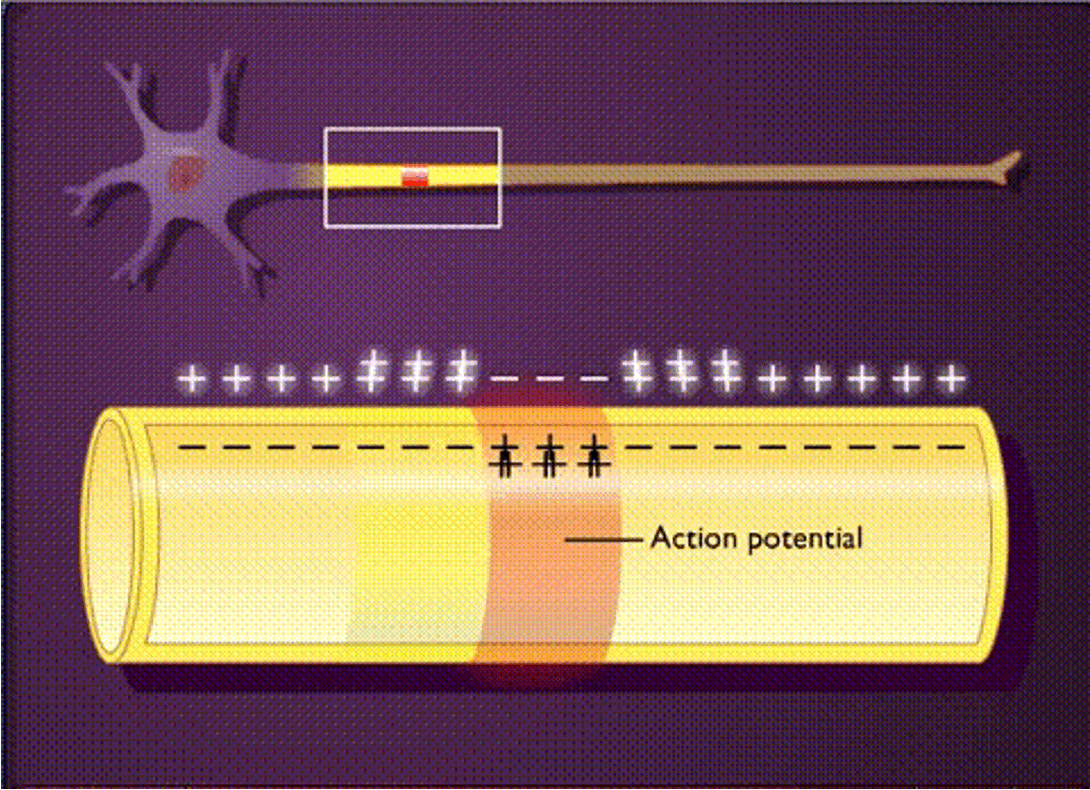
sodium and potassium channels are
voltage-gated
•Nerve impulses work on an “all or none” principal.
•The impulse isonly initiated if-
the threshold potential is reached
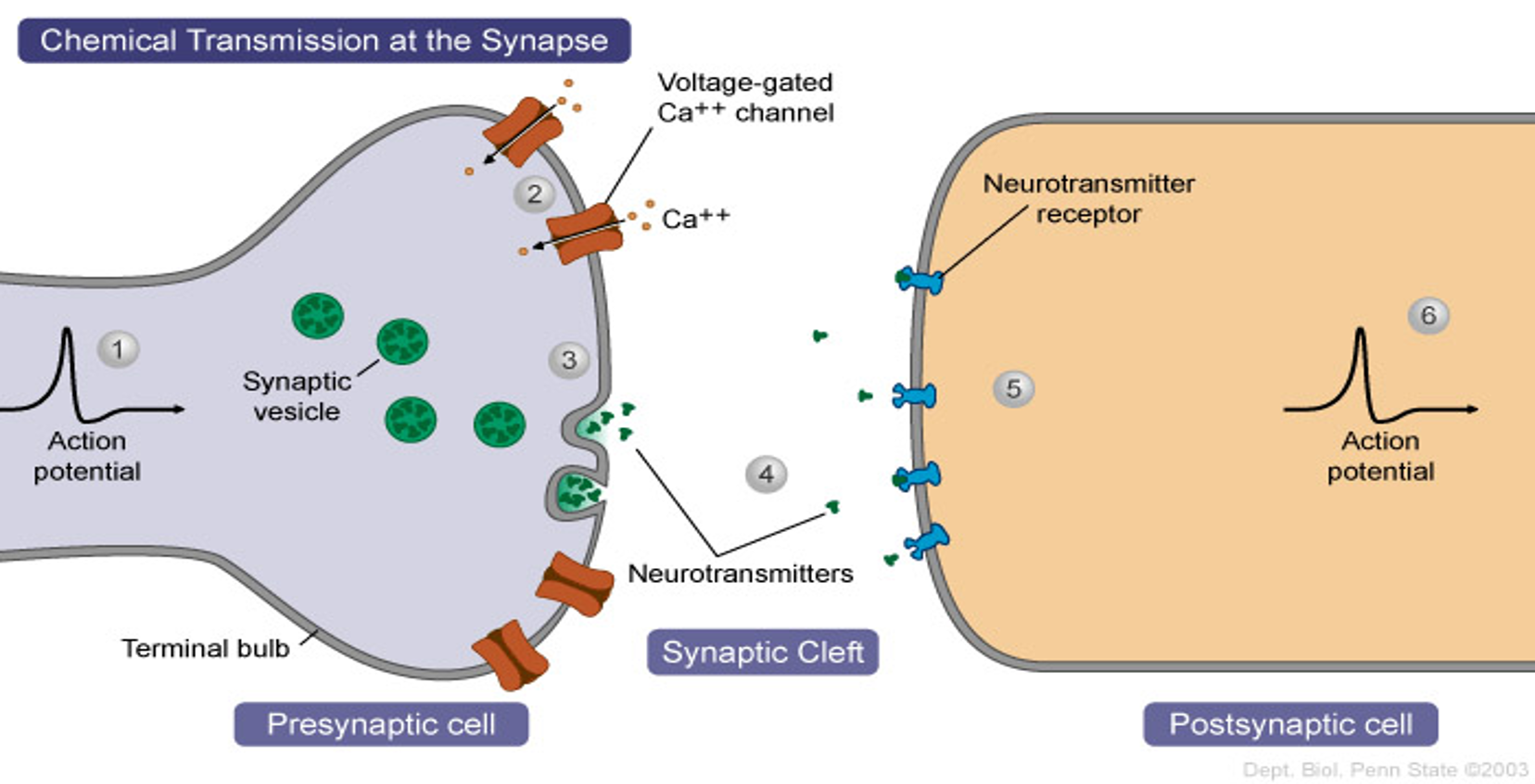
pre-synaptic neurons
depolarized, they release a neurotransmitter into the synapse
Depolarization opens
voltage gated calcium channels
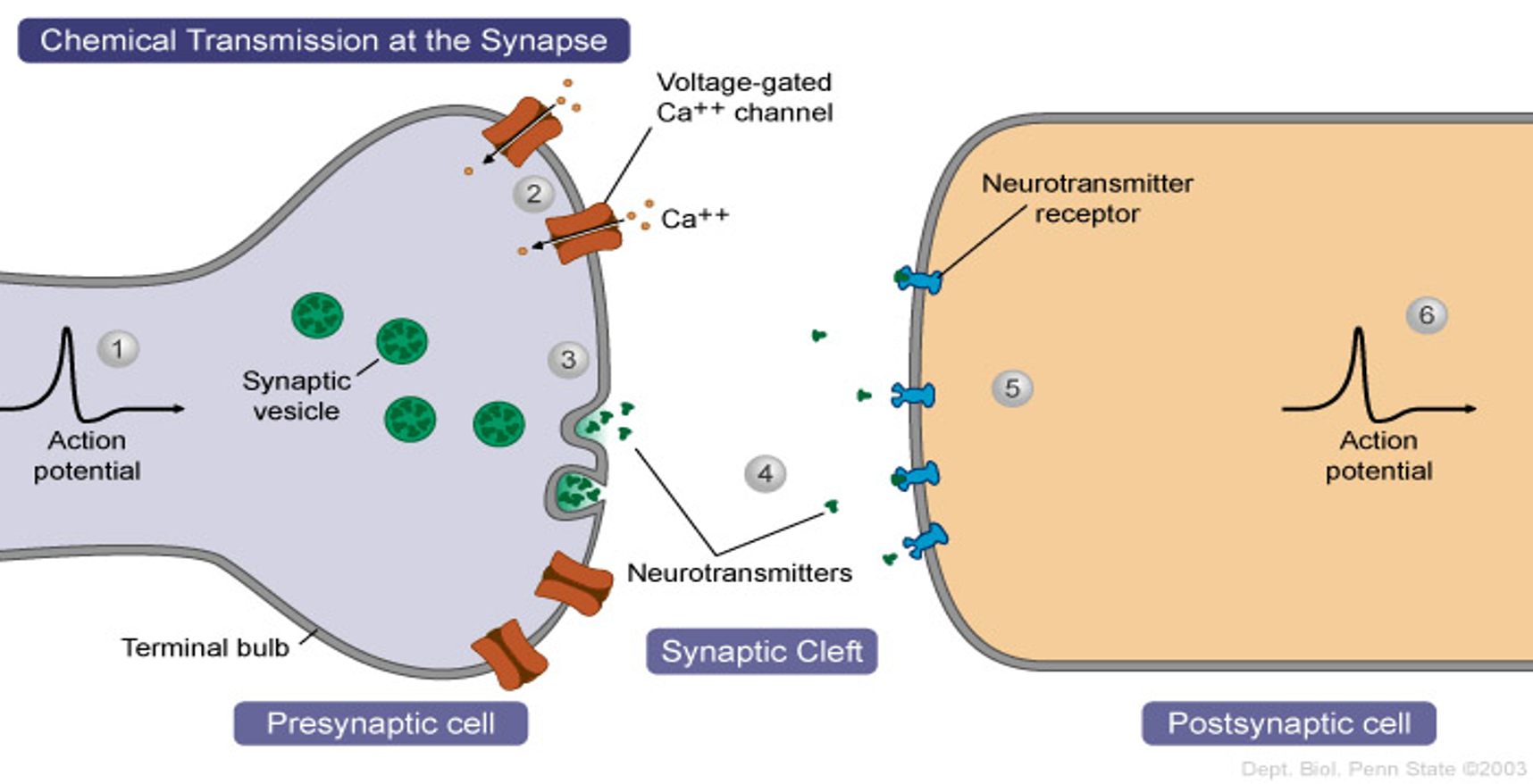
Calcium influx signals
synaptic vesicles to fuse with pre-synaptic membrane, releasing neurotransmitter (Acetylcholine in this case) by exocytosis
Acetylcholine (ACh) diffuses across
synaptic cleft and binds to receptor proteins on postsynaptic membrane
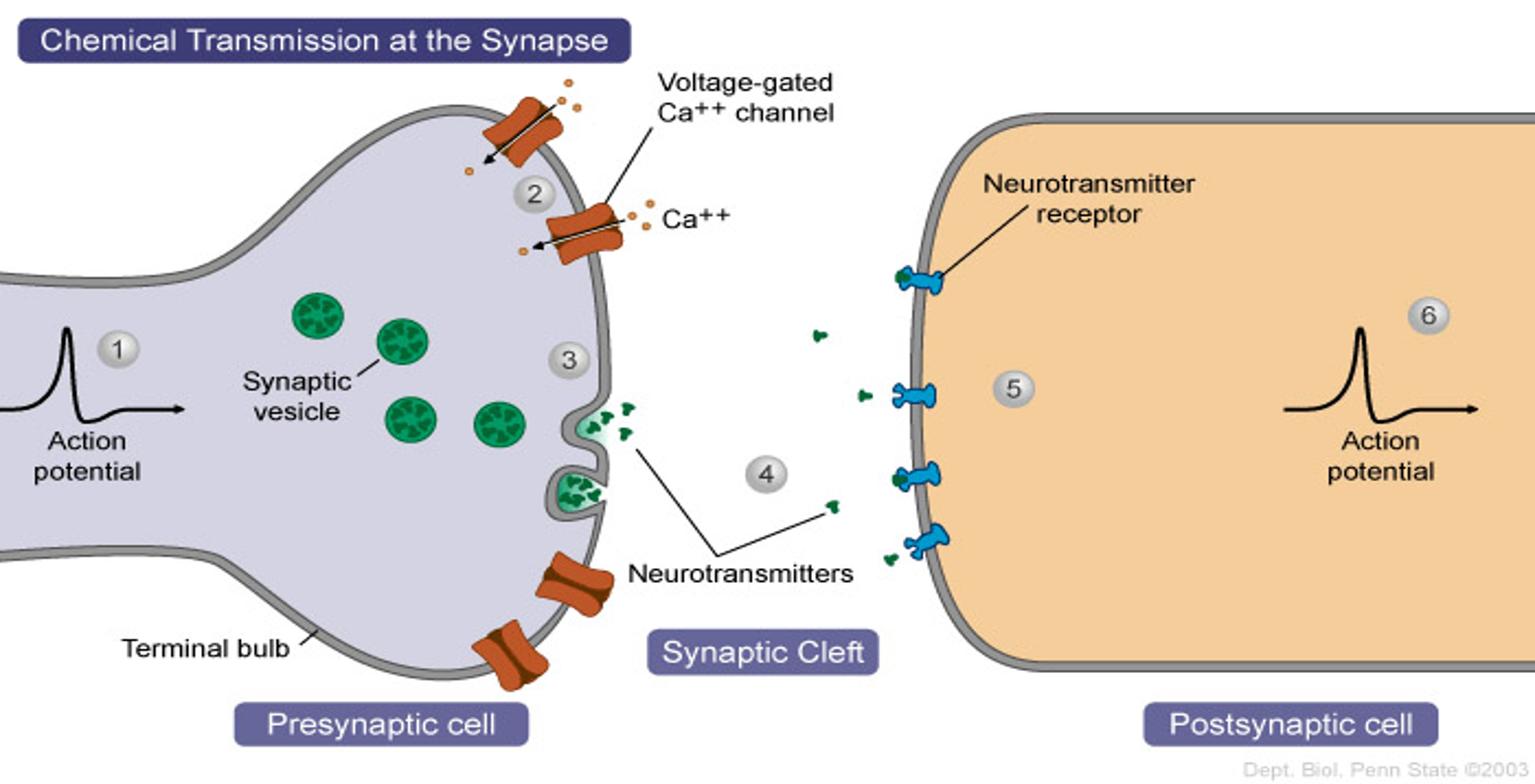
This binding of ACh opens
sodium ion channels and an action potential is initiated in the postsynaptic neuron
After ACh binds to receptor
it is rapidly broken down and reabsorbed by presynaptic neuron
This is called a cholinergic synapse
since acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter