ESC 102- Time
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Geological time scale
boundaries are between eons, eras, period
determined by events like new fossils, disappearances of fossils, major events
dating or methods to know the age of a rock
absolute age ex: 4.6 Ma
relative dating ex: older than, younger than
absolute dating- radioactive decay
regular rate for each radioactive element
measured in half lives- SET
how we get accurate dates
absolute dating- uranium/lead dating of zircons
forms in igneous rocks
extract uranium signal
very hard and resistant to weathering
decay of uranium to lead
Relative dating
fossils, cross cutting relationships
relative dating- fossil succession
occur in regular non-repeating and predictable manner
reflects sequence of bio evolution
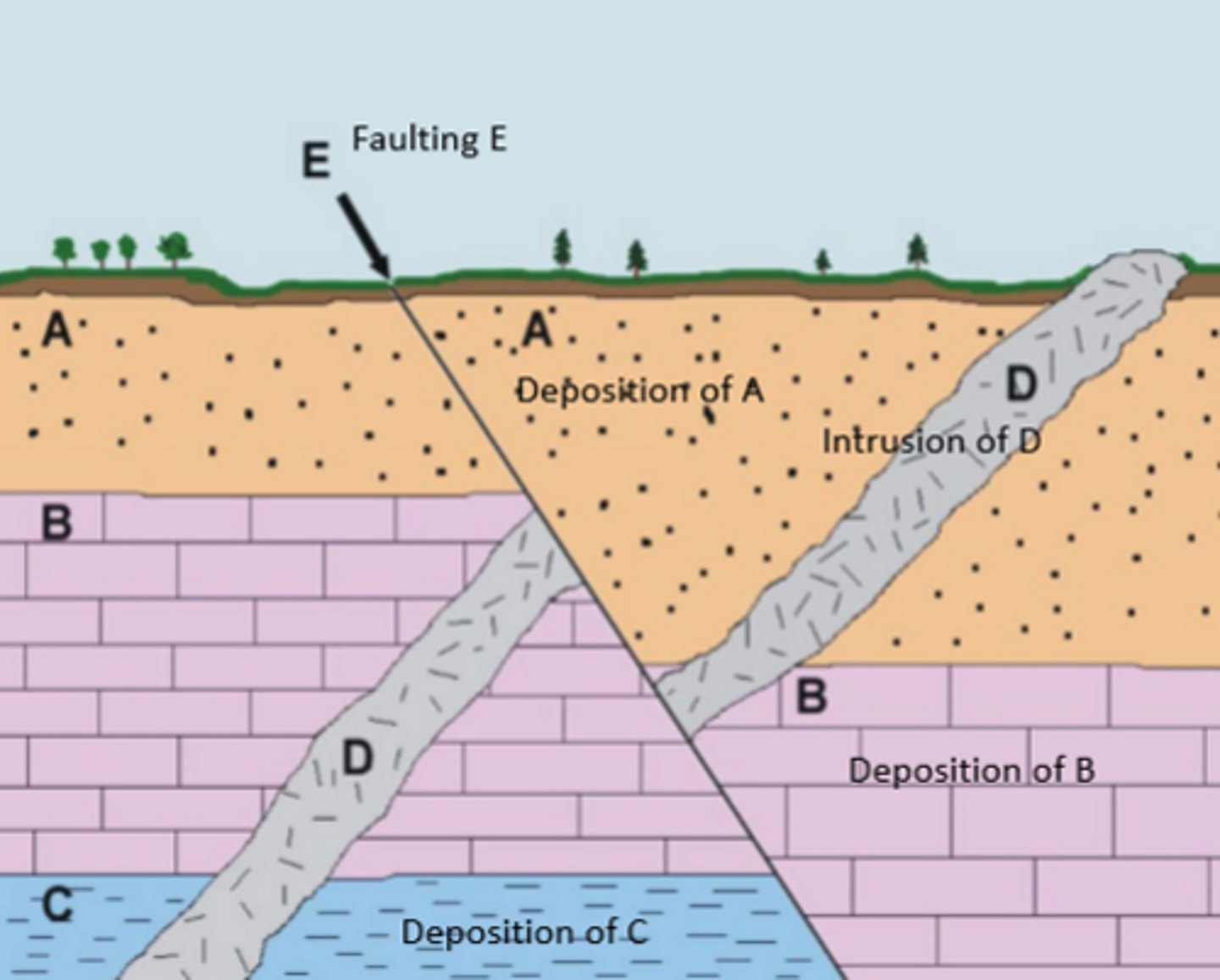
cross cutting relaitonships
"what is cutting what"
1. C 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. E
Eons
hadean, archean, proterozoic, phanerozoic
eras
palaeozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic
periods (old to young)
cambrian ordovician silurian devonian carboniferous permian triassic jurassic cretaceous tertiary quaternary
mnemonic to remember periods
cold oysters seldom develop coloured pearls. their juices congeal too quickly
paleozoic era
explosion of life (invertebrates)
fish evolve
glaciation, low sea level
mass extinction at the end of ordovician and devonian
reefs develop
end with extinction
3 extinctions in paleozoic
ordovician, devonian, permian
Mesozoic Era
life recovered
dinosoars rule
marine and flying reptiles
no ice in the poles
first flowering plants
rocky mountains form
ends with metor extinction
cenozoic era
giant beavers, bears, mastodons, giant sloths
last wooly mammoths
first hominids
human evolution