IVC Biology Units 7-12
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Prokaryotic
-lack a nucleus
-single celled or colonial
-have no membranous organelles
-motile or non motile
-typical cell diameter is 1-10 microns
-Can be either autotroph or heterotroph
-cell wall is made out of peptidoglycan (combo of protein and carbohydrates)
-smaller ribosomes
-DNA tends to be circular and single
eukaryotic
-5% of all living things
-have four kingdoms within them
-have a nucleus
-have membranous organelles
-typical cell diameter: 10-100 microns
-larger ribosomes
-DNA tends to be multiple and linear
viruses
-nonliving
They Attach, penetrate, uncoat (contents are released) , release (new viral particles are made and released into the extracellular fluid), assemble (new phage particles are assembled), biosynthesis (viral RNA enters the cell)
-non-cellular
-protein capsule, no cell wall
-typical diameter >.1 microns
-DNA/RNA strand, possibly enzymes or other materials, with the protein capsule
bacteria
-replicate very quickly
-about 95% of all living things are bacteria
-asexual reproduction
-unicellular (or referred to as colonial)
-use binary fission, getting enough energy and materials to replicate, but splitting up
-some form chains, can make their own glucose and nitrogen, similar to multicellular but still considered unicellular
archaea
-found in rough, extreme environments (which is why its thought to be the first organisms to develop, but that's false) and normal ones
-are usually together
-further raises the ability that living things can be on other planets
plants
-have chloroplasts
-dominate environments
-adaptive
-non-motile
-autotrophs, some will be mixotrophs/heterotrophs
-multicellular
-cell walls of cellulose
-have chlorophyll
-Organic matter is their energy source
animals
-motile
-diverse
-multicellular
-heterotrophs (Ingestive)
-no cell walls
protists
-typically motile or non motile
-mostly unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes
-can be either autotrophs or heterotrophs or mixotrophs
-ex: algae, seaweed
-no cell walls, if there are cell walls its of cellulose or silica
-cellulose is used as a shield
-act as important food sources and medicines
fungis
-heterotrophs (absorptive
-eukaryotic
-multicellular
-non-motile
-cell walls of chitin
-can be parasites or neutralists
Centrioles:
involved in dna replication, guide the chromosomes to the proper places
nucleus
a double-membraned organelle that holds the major portion of the cell's DNA in the form of chromatin
nuclear pore
-hormones go into the nucleus through here to active multiple genes
-allows specific molecules to go through
-area where RNA passes through to get to ribosomes via Translation
chromatin
-most of our cells don't have any chromosomes, but chromatins
-when replicated, it winds down into a structure called a chromosome
-genes are exposed and read in chromatin form, but moved in chromosome form.
nucleolus
-much of the DNA isn’t readable, but codes for the ribosomes
-thought to be the oldest
-inbetween concentration of chromatin and chromosome
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
-functions like a double membrane structure, but is singular
-creates protein
-the ribosomes go to the golgi body
-stores peptides
a membranous organelle that produces transport vesicles & phospholipids; may also hold ribosomes in place
lysosome
a membranous organelle that merges with food vacuoles; may be important in embryological development, metamorphosis, and death
-have a wide variety of enzymes that break down a variety of things
-the organic matter left after is reused by the cell
-has a lipid bilayer
-hydrolytic enzyme mixture
-glycosylated membrane transport protein
-mitochondria makes ATP to give to the lysosomes so they don't eat their way out the cell
The chemical formula for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H20 -----light --------> C6H12O6 + 602
The light-independent reaction (Calvin Cycle) takes place in the ________ and uses ________ .
stroma; both carbon dioxide and water
Calvin cycle (independent light reactions)
sugar molecules are formed from carbon dioxide and water molecules. Occur in the stroma, the NADPH and ATP are used to energize the process.
The chemical formula for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H20 -----light --------> C6H12O6 + 602
A flagellum is -
a series of relatively long proteins that act to move the cell forward
A Golgi Body is a --
a series of enzyme-filled membranes that remanufacture polypeptides
-similar to a post office by modifying and packaging lipids and proteins
chloroplast
double membrane (inner is folded and outer is smooth)
-grana: whole stacks
-thylakoids: individual
-stroma: the liquid surrounding the grana
-chlorophyll: reflects and doesn't want to absorb green nor yellow light because they are not common and they want to much light energy because it’ll destroy pigaments due to too much heat
Pigment
molecule which functions to absorb light
Cell wall:
holds water and creates water pressure within, making the cells stackable, made out of cellulose, Middle lamella, and Intracellular space
Cytoskeleton:
made up of microtubule, flagellum, plasma membrane, and microfilaments
-holds organelles in place
-dynein arms have phosphate added which will push the microtubules together
Central vacuole:
Is a storage, has a different pressure than the surround area, making the plant cell more rigid
Structure of the plasma membrane gives it at least 3 important qualities:
Barrier capability:
a. larger molecules (3 carbons) are blocked by the tight packing of the phospholipids
b. Charged molecules are repelled by the hydrophobic core and are interfered with the electromagnetic charges on the phospholipid heads
Permeability based on the phospholipids:
a. smaller, non charged molecules can easily pass through the tight packing of the phospholipids
b. Some larger, non polar molecules can pass through due to their chemical similarity to the hydrophobic core
Permeability based on the integral proteins: Specific molecules can pass through the integral proteins, which act as channels, gates, or pumps
a. many are hollow with a tube like structure within.
b. Another structure has moving arms that have a slight negative charge that can help ions to pass through. With atp added to the arm, it’ll flex and drop the ion to the next charge repeatedly until it goes down
Be able to differentiate or describe, using complete sentences, the four differences in the organelles, and organelle functioning, between plant cells and animal cells (and lysosomes aint one of them).
Animal cells are heterotrophic where as plant cells aren't
Animal cells have Microtubules , plant cells don't
Animal cells don't have cell walls, plants do
Plant cells have chloroplasts in order to utilize photosynthesis, animal cells don't create energy in this way
Plant cells don't have centrioles, animal cells do
big central Vacuole on plants, small ones on animal
Be able to differentiate between animal, fungal, plant and protistan cells, based on cell wall content; heterotrophy, autotrophy, multi/single celled structure, etc.
Animal - Heterotrophic, multi-cellular, no cell walls
Fungal - Heterotrophic, multi-cellular, walls of chitin
Plant - Autotrophs, single celled, made of cellulose
Protistan - Autotrophic/Heterotrophic, single celled, walls of silica /cellulose
Endomembrane System
the set of membranes that form a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport / nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, endosomes and the cell membrane
Cilia
small hairs like flagella but really small
Mitochondria
breaks down molecules, push to center and pull off electrons, then makes ATP
-small
-double membrane, smooth outer, folded inner membrane
-cristae: on the folds
-matrix: space within the inner membrane
Secretory Vesicles
- form from the trans Golgi network, and they release their contents to the cell exterior by exocytosis in response to extracellular signals.
Transport Vesicles
carry proteins within Golgi Body
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
acts as a phospholipid reservoir, has enzymes that break down toxic materials
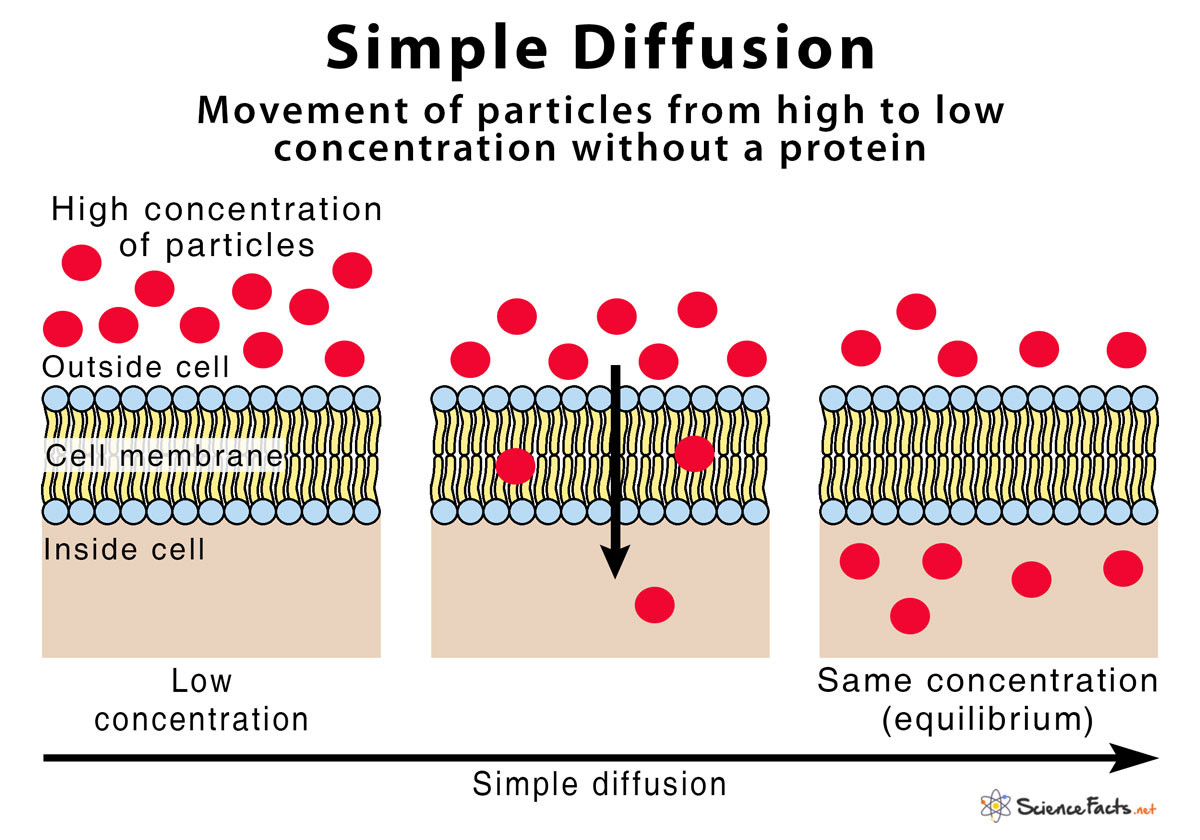
Simple Diffusion:
The net random movement of solutes from an area of their higher concentration to an area of their lower concentration
Go from low to high, will even out eventually, but aren't gonna stop moving
Concentration: amount per volume
When there is a higher concentration, where there should a lower one, diffusion comes in handy
Passive
Facilitated diffusion:
net random movement of solutes from an area of their higher concentration to an area of their lower concentration through an integral protein
Movement along a concentration gradient:
Passive
Active transport:
Movement of solutes from an area of their lower concentration to an area of their higher concentration through an integral protein using ATP
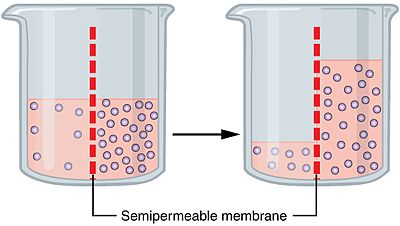
Osmosis
Net random movement of solvent from an area of its higher concentration to an area of its lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
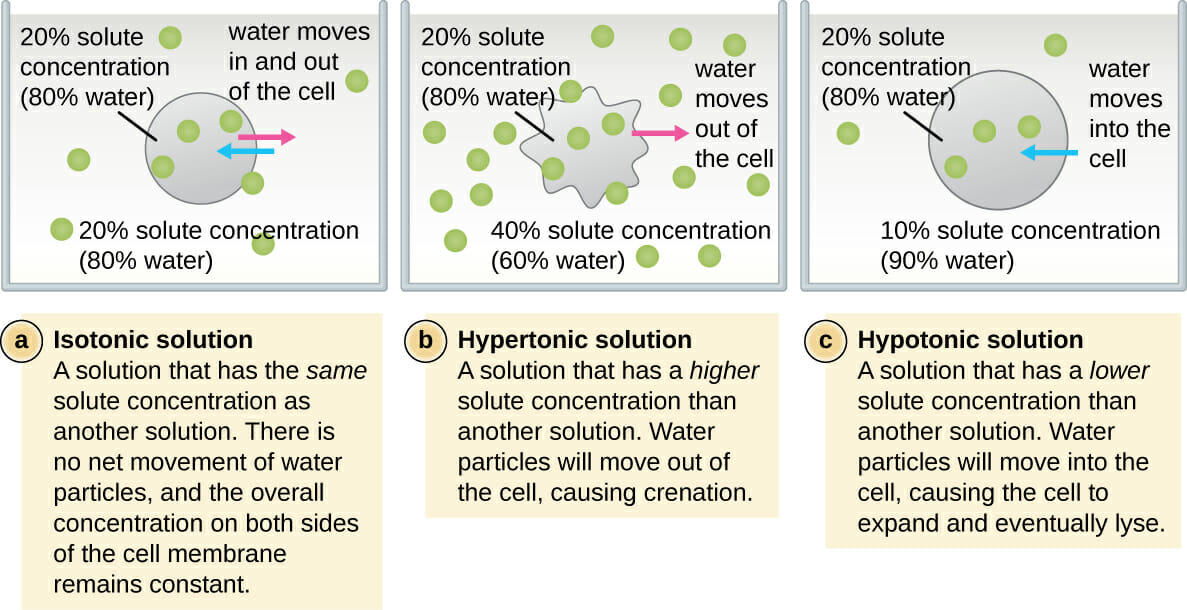
Tonicity
relative solute concentration of a solution
hypertonic
solution that is relatively higher in solute concentration
hypotonic
solution relatively lower in solute concentration
differences between isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic
Reactant
present at the beginning of the chemical reaction
Product
present at the end of the chemical reaction
Metabolism
totality of all chemical reactions occurring within a biological unit
Biological chemical reactions:
typically follow predictable pathways in which the products of one reaction become the reactants in another
-typically enzyme mediated: take place with the intervention of enzymes
Catalyst
something that participates in a reaction but isn’t consumed in the reaction
Enzymes: three-dimensional protein catalysts
determine which bonds will break
Determine which products will form
Speed up reaction rates
Lower activation energy
Bring reactants to their transition state without adding additional activation energy
Reusable
Can shut themselves off or on
Susceptible to catastrophic failure
Substrate
molecule in an enzyme-mediated reaction that bonds to the enzyme and is subsequently altered
Active site:
specific region on a enzyme where substrates bind to the enzyme and therefore enter a transition state
Transition state
molecular structures maximum point of instability as it begins to undergo a chemical reaction
Activation energy:
energy needed to push a given molecule to its transition state (energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur)
Heat for example
Enzyme mediated chemical reaction
already has activation energy
Induced fit:
changes to the structure of the enzyme and its substrate as they bond to each other. Takes place in the enzymes active site
When achieved, the substrate reaches a transition state, and the needed activation is far less than an ordinary reaction would require
Product inhibition
enzymes often have built in mechanisms by which they can be shut off
Once a enough product has been form the product can interfere with the functioning of the enzyme
Competitive product inhibition
Product molecule of the enzyme-driven reaction bonds into the active site, blocking substrates
Non competitive product inhibition
Product molecule of the enzyme driven reaction bonds away from the active site, altering the enzymes shape and eliminating the active site
Co-factors:
non protein particles that bind to enzymes, allowing the enzymes to achieve their functional shape
Coenzymes
organic, non protein cofactors
Protein denaturing:
changes to protein shape that inhibit or destroy protein function
Enzymes owe their functioning to their complex shapes, but that complexity comes with increased probability of catastrophic failure
Extreme environments disrupt protein shape and function
Heavy metal denature enzymes
pH
measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
Characterizes the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in the same solution
Aqueous (water-based) solutions are particularly susceptible to changes in hydrogen and hydroxide ion concentration depending upon their solute composition
Solutes that tend to increase H+ ion concentration in water are called acids
Solutes that decrease H+ ion concentration in water are called alkalis or bases (increase OH-)
When H+ and OH- concentration are balanced, the solution is neutral
Aerobic (Cellular Respiration)
conversion of organic matter energy to ATP, using oxygen and an electron transport system
Glycolysis
| Yields energy products: 2 ATP ; 2 NADH ; 2 pyruvates |
Citric Acid Cycle
(Krebs cycle)
| Yields energy products: 2 ATP ; 8 NADH ; 2 FADH2 |
Electron transport chain
| Yields 32 ATP |
Fermentation
conversion of organic matter energy to ATP, without oxygen or an electron transport system
Creation of atp from glycolysis in the cytoplasm under anaerobic conditions (no oxygen, mitochondria)
Yields 2 ATP
Converts glucose to pyruvate and then to one of the several possible waste products:
Ethanol, lactic acid, carbon dioxide, acetone
Aerobe
organism that uses oxygen
Anaerobe
organism that doesn’t use oxygen
Facultative anaerobe
organism that produces ATP using either fermentation or aerobic respiration
Transcription
development of the pre- mRNA chain according to the DNA nucleotide sequence
Steps:
Transcription factor bonds to the promoter site
mRNA polymerase unwinds the gene
Gene surface is read
mRNA strand is manufactured
Transcription is complete
Gene
sequence of DNA nucleotides that encodes for a specific polypeptide or mRNA sequence
RNA polymerase
Produces the RNA polymer, produces the RNA strand based on the DNA strand
Promoter
start sign, sequence of DNA nucleotides that accepts a transcription factor and guides the RNA polymerase enzyme to the gene
Transcription factor
Protein that binds to a promoter site to regulate mRNA production. Switches on and off certain promoters so that only certain genes are transcribed.
Gene surface
on a template/sense strand (partial) bonds to a Non-gene=nonsense strand (partial)
nonsense strand
is important because in the scenario an amino acid is destroyed, it will replace it by looking at the nonsense strand. Repairs gene surface
Ribosomes
Non-membranous particles made up of ribosomal RNA and various proteins
rRNAs and the proteins are organized into the two subunits
Large subunit
Small subunit
tRNA
have sections that will bond to the amino acids and sections that bond to the mRNA.
-Brings over correct amino acids to the ribosome. Since it is made up of RNA nucleotides, it uses anticodon: Opposite of mRNA codon, its the complementary nucleotides to what's on the mRNA
Translation
development of the growing polypeptide chain according to the mRNA codon sequence
Steps:
Initial codon arrives at synthesis site
An initial tRNA arrives at the ribosome
Ribosomes forms completely
Another anti codon arrives at the ribosome
An initial peptide bond forms
More peptide bonds form
Translation is complete