Earth Science: Earth's Shape; Earth's Interior Layers; Layers of the Atmosphere
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/61
Last updated 2:21 AM on 10/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
Earth is .... a perfect ....
almost, sphere
2
New cards
Earth is actually a(n)...
oblate spheroid
3
New cards
Ship masts appear first on the horizon and seem as if its falling off the edge of the world because..
Earth is curved

4
New cards
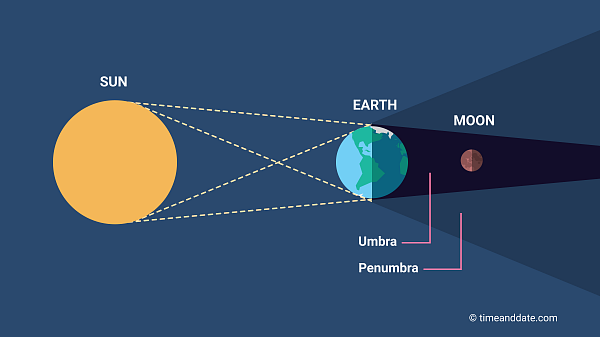
Earth's shadow is curved during a(n)...
lunar eclipse

5
New cards
Lunar Eclipse Definition
occurs when the Earth comes between the sun and moon
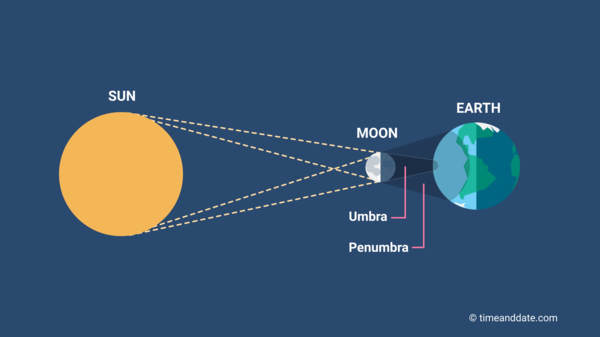
6
New cards
Solar Eclipse
occurs when the moon passes between the Earth and the Sun
7
New cards
North Star is also called
Polaris
8
New cards
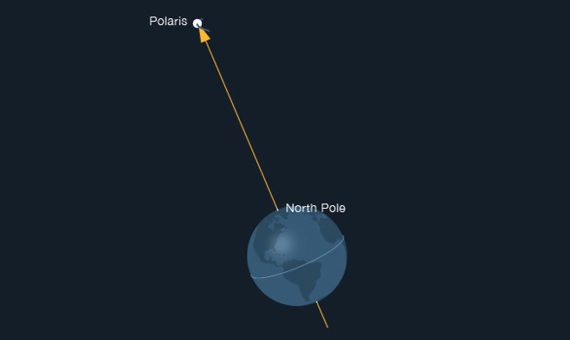
Polaris/North Star Definition
a star positioned above the North pole
9
New cards
Polaris is always on the horizon at the...
Equator
10
New cards
Polaris is always directly overhead at the...
North Pole
11
New cards
Polaris (can/cannot) be seen in the Southern Hemisphere/ Below the Equator
cannot
12
New cards
Best evidence of Earth's shape is..
pictures of Earth from space

13
New cards
Measurements of Earth from space indicate that it is a(n)..
oblate spheroid
14
New cards
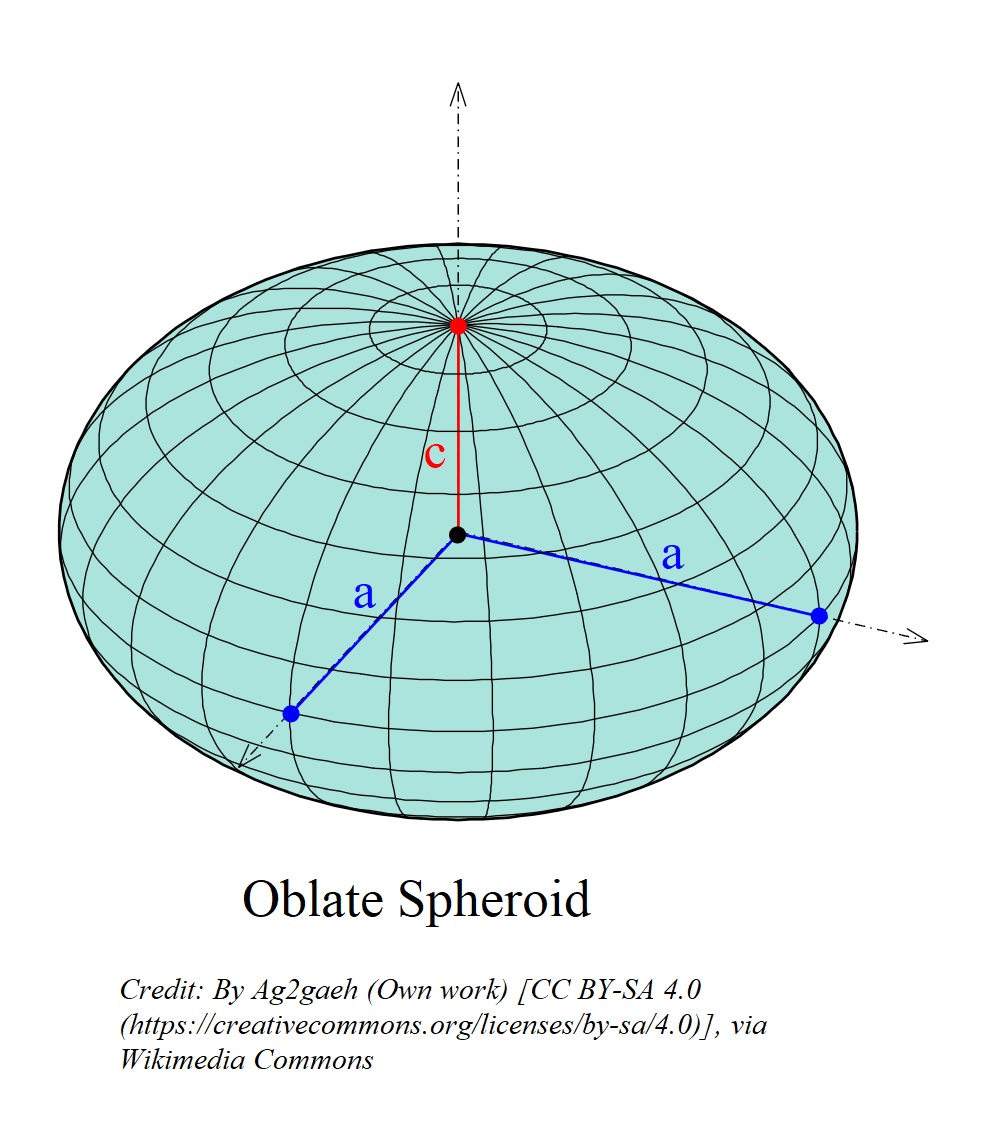
Oblate Spheroid Definition
A flattened sphere
15
New cards
Why is the Earth slightly flattened at the poles and slightly bulging at the Equator?
Because Earth spins on its axis
16
New cards
Is gravity the same everywhere on Earth? Why?
No, there is more gravity on the poles than at the Equator. This is due to Earth NOT being a perfect spheroid.
17
New cards
A Gravimeter...
shows that gravity is slightly less at the Equator than at the poles
18
New cards
an object will be (closer/farther) to the Earth's center at the poles than an object at the Equator
closer
19
New cards
As altitude increases, gravity...
decreases
20
New cards
You weigh (more/less) at the poles and (more/less) at the Equator
more, less
21
New cards
Earth's Average Diameter
12,735 km
22
New cards
Earth (is/isn't) very round and smooth
is

23
New cards
Relief Definition
variations in elevation of an area of the Earth's Surface
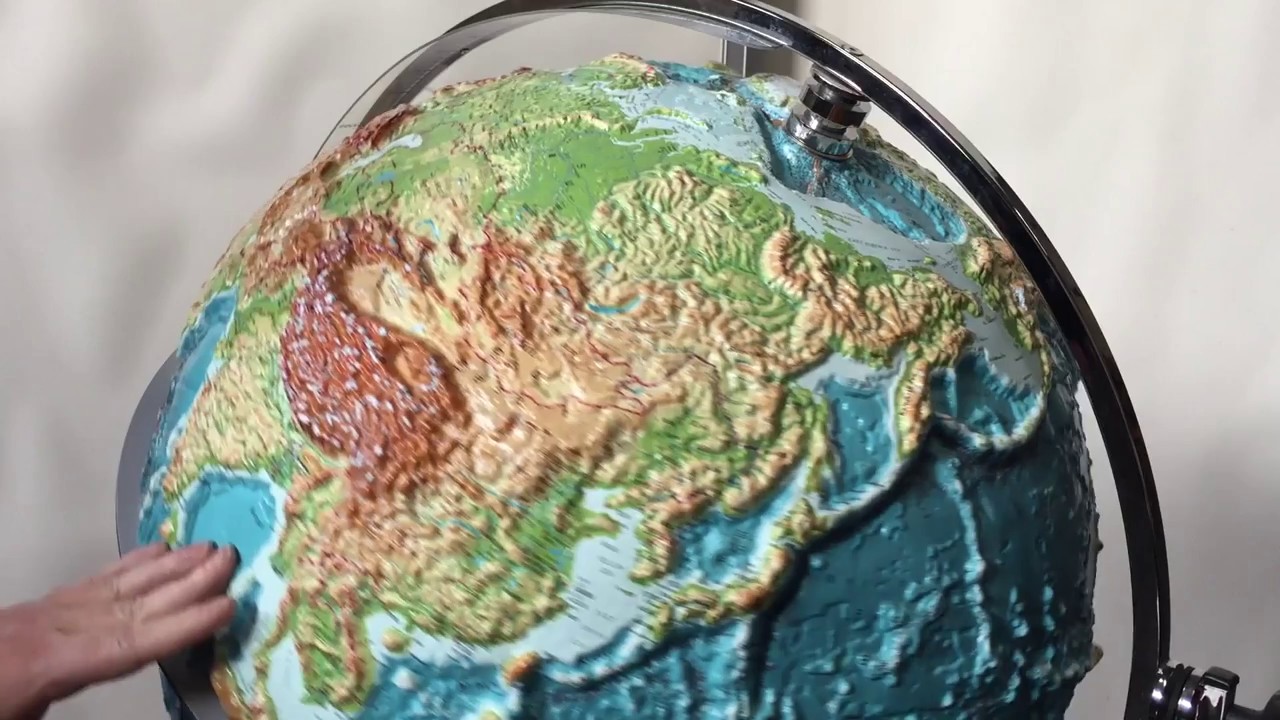

24
New cards
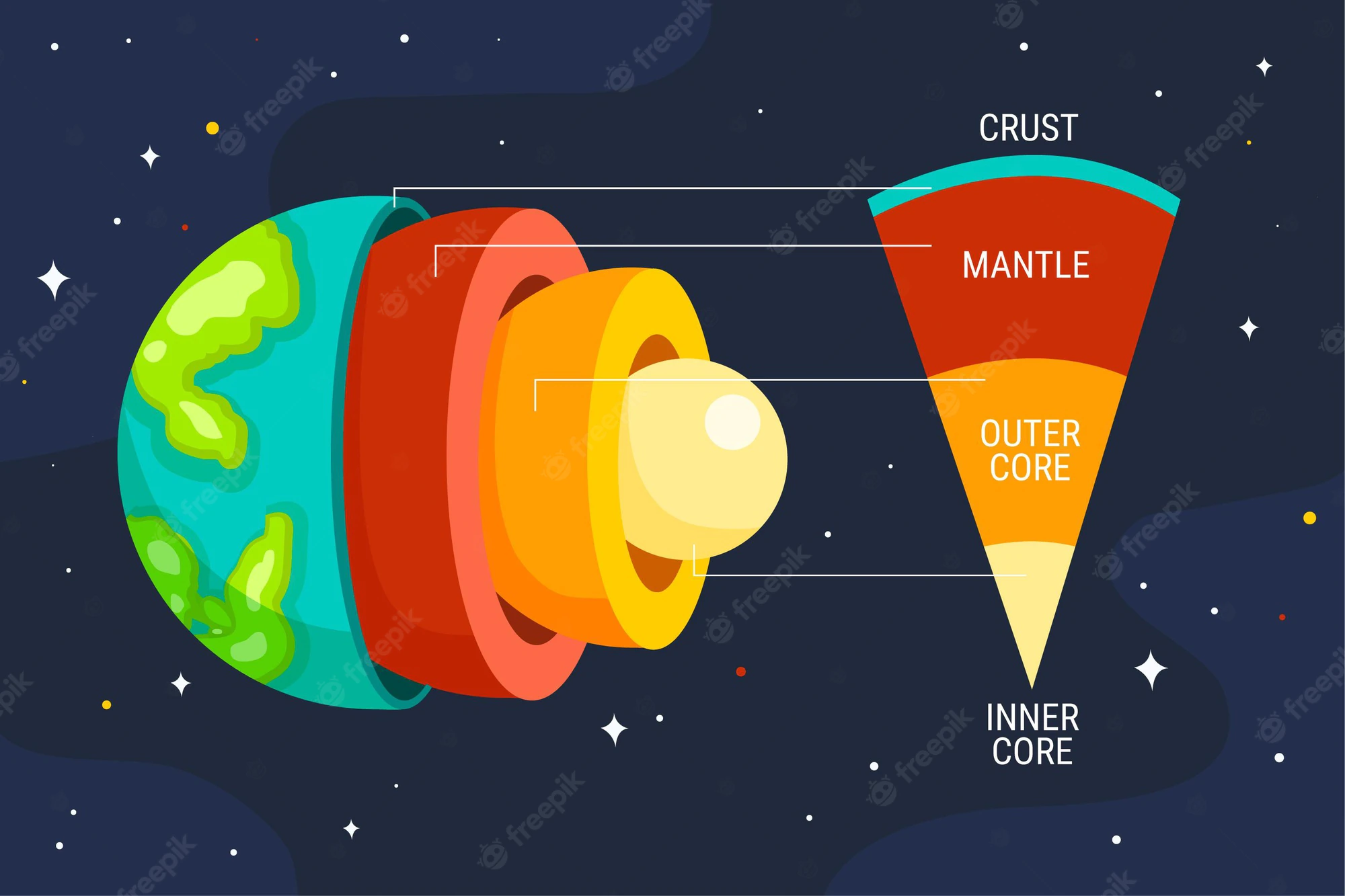
3 Major zones of Earth's interiors
Crust, Mantle, Core
25
New cards
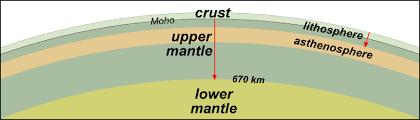
Lithosphere
the layer of solid rock that forms a shell around the Earth

26
New cards
The Lithosphere is made up of the ... and ... ...
crust, upper mantle

27
New cards
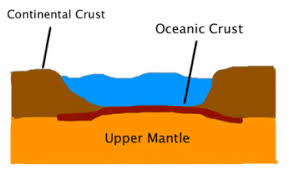
Crust Definition
the outermost layer of the Earth and makes up all the continents and ocean basins
thinnest layer
thinnest layer

28
New cards
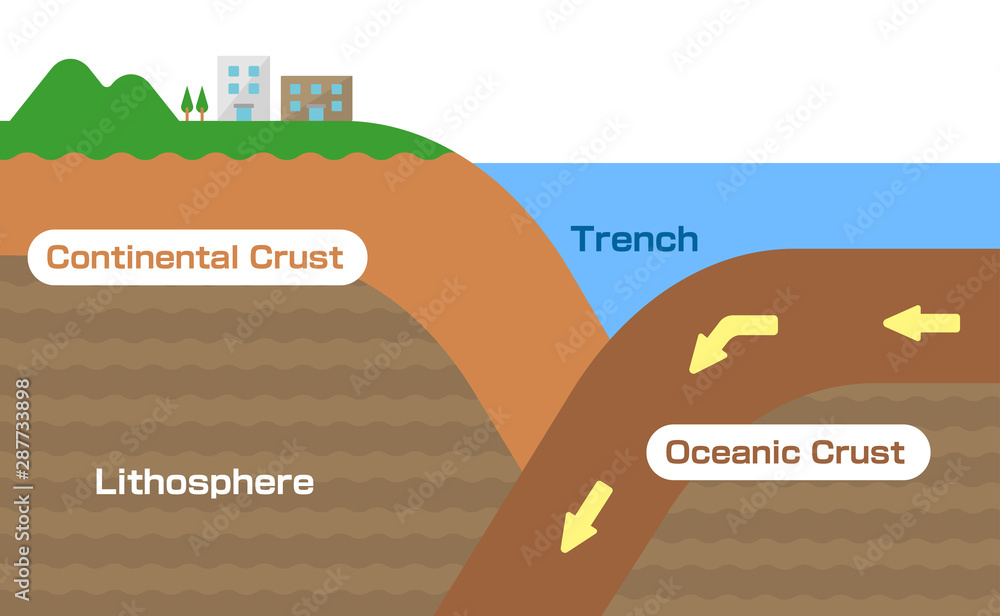
Oceanic crust Definition
crust that is under the ocean
29
New cards
Continental Crust Definition
crust that is not under the ocean
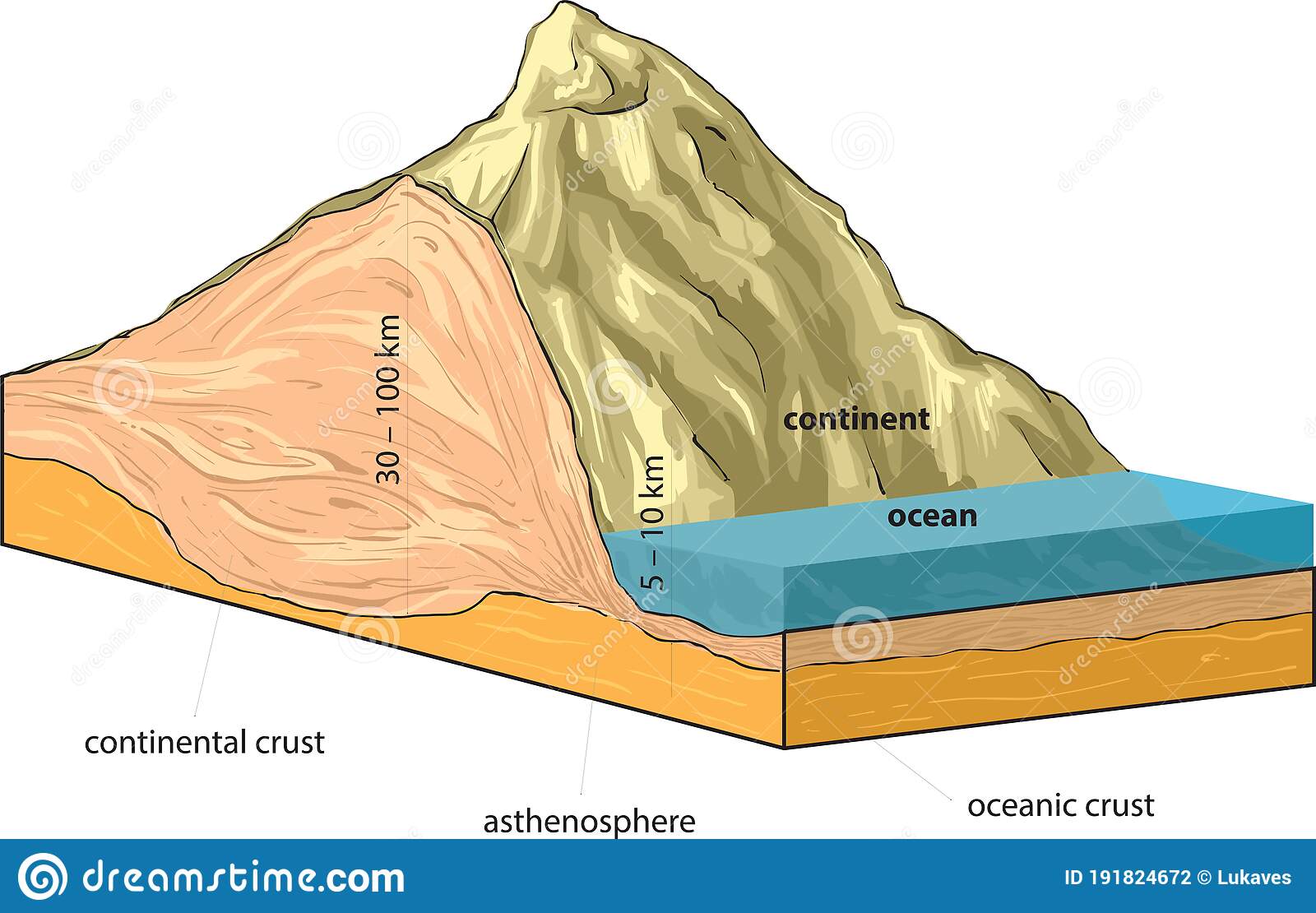
30
New cards
Continental Crust is (bigger/smaller) than Oceanic Crust
bigger
31
New cards
Continental Crust is (more/less) dense than Oceanic Crust
less
32
New cards
Uppermost Rigid/ Upper/ Rigid Mantle Definition
solid and upper part of the mantle
above the Asthenosphere
above the Asthenosphere
33
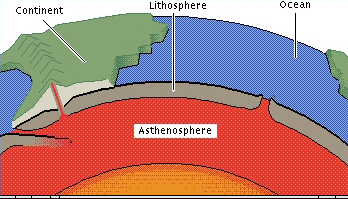
New cards
Asthenosphere/ Plastic Layer
a semi-liquid layer below the lithosphere
convection currents happen here
part of the Mantle
below the Uppermost Rigid Layer
convection currents happen here
part of the Mantle
below the Uppermost Rigid Layer
34
New cards
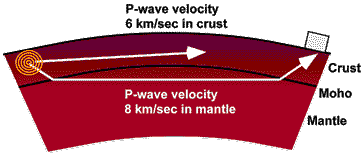
Moho/mohorovicic discontinuity
boundary/interface between crust and mantle
35
New cards
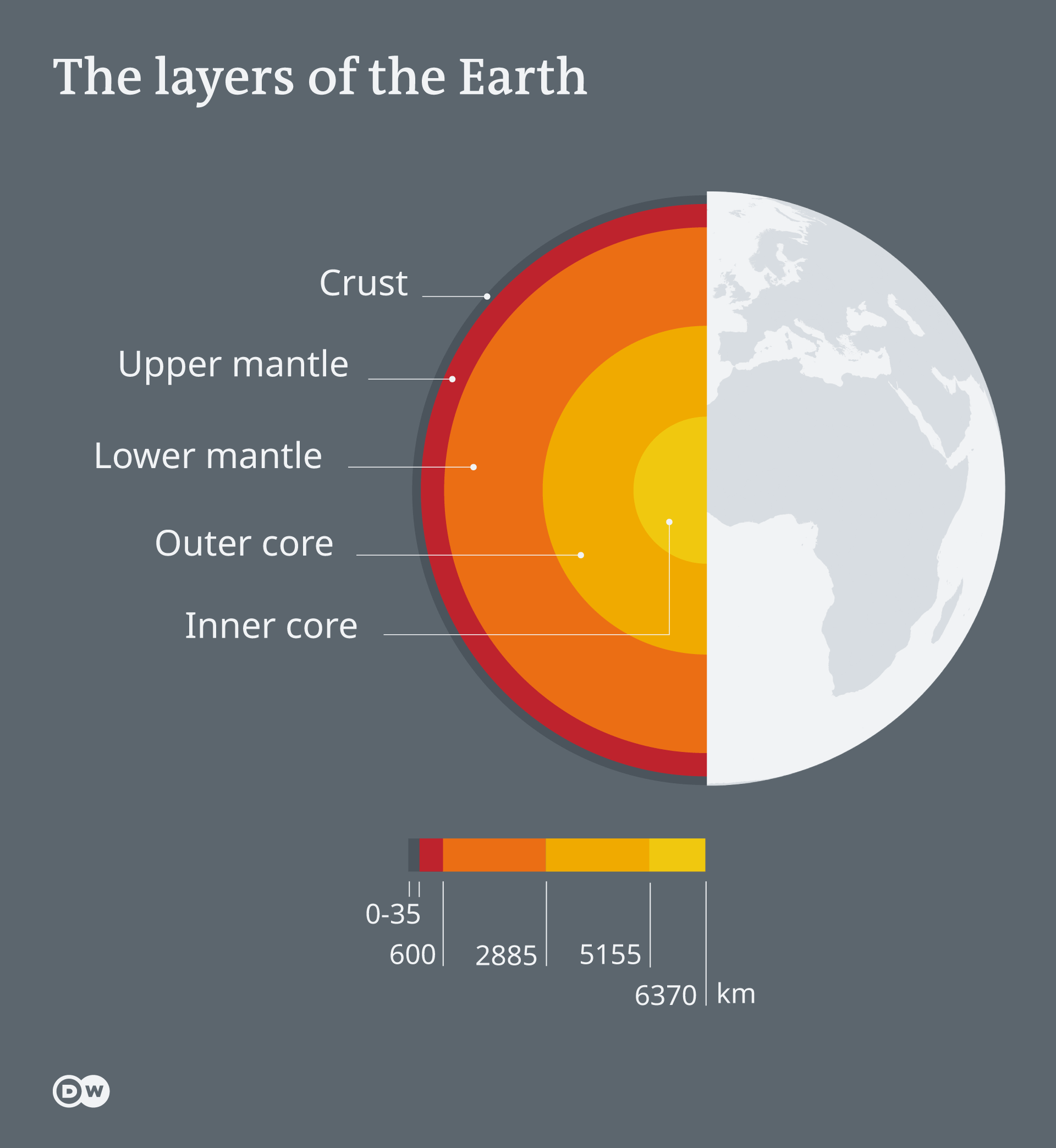
lower/stiffer mantle
a layer under the upper mantle, it is more rigid
36
New cards
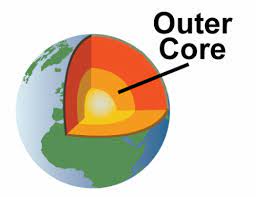
outer core
liquid layer
mostly made of iron
under the lower mantle
causes Earth's magnetic field
mostly made of iron
under the lower mantle
causes Earth's magnetic field
37
New cards
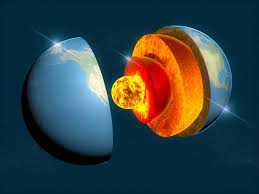
Inner Core
solid layer
under outer core
under outer core
38
New cards
Hydrosphere
the thin film of water that rests on the lithosphere and covers about 70% of the Earth's surface

39
New cards
Atmosphere
A gaseous layer surrounding Earth
layered into distinct zones
layered into distinct zones

40
New cards
Mantle
thickest layer of Earth
Includes: Upper/Rigid Mantle, Asthenosphere, Lower/Stiffer Mantle
Includes: Upper/Rigid Mantle, Asthenosphere, Lower/Stiffer Mantle
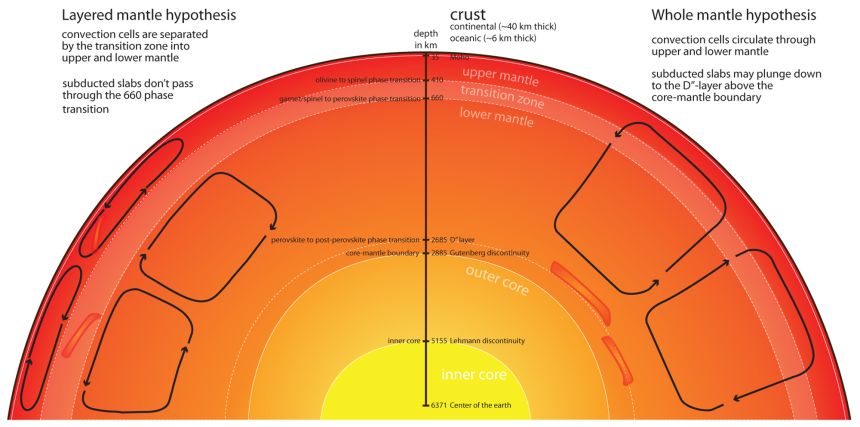
41
New cards
layers of the earth
...
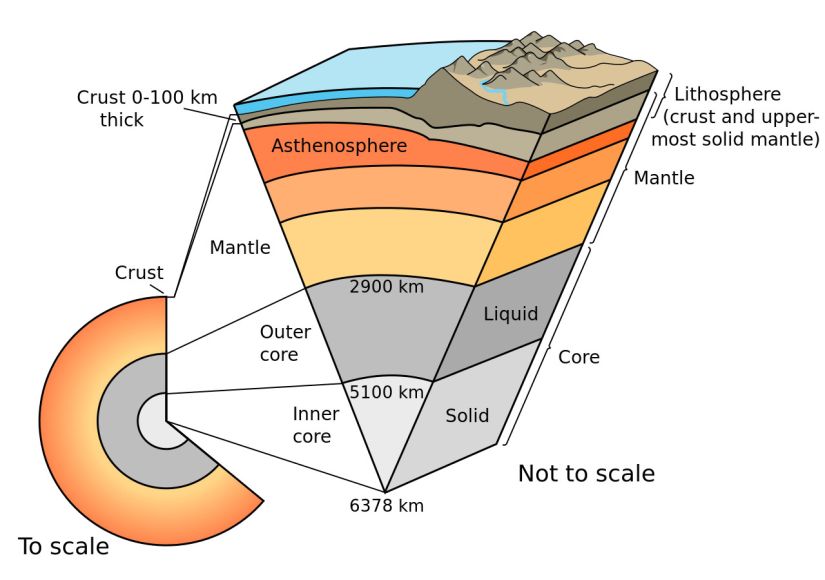
42
New cards
farthest layer humans have ever gone? why not farther?
12 km/ 8-9 miles into the crust, our technology isn't advanced enough and it's too hard
43
New cards
how do humans know what Earth's interior is like?
Seismic (Earthquake; P & S waves) waves/ Seismic Data
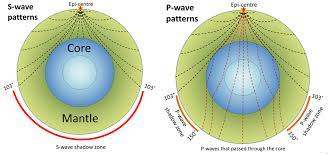
44
New cards
the 4 main layers of the atmosphere are classified by...
temperature
45
New cards
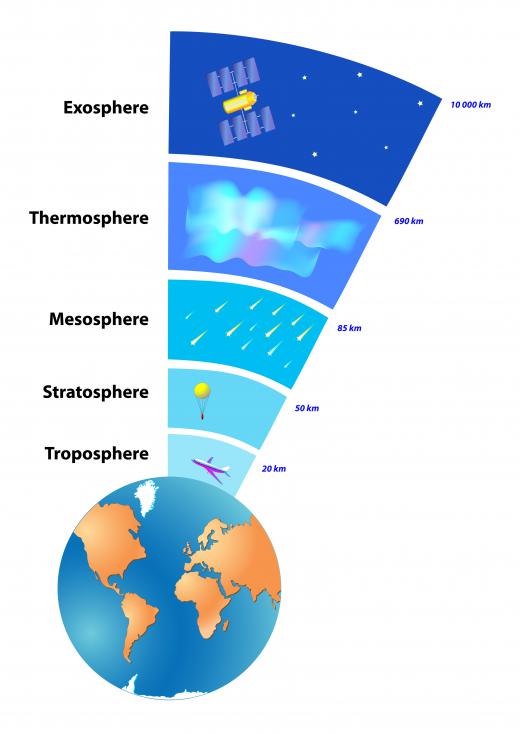
Troposphere
first layer of the atmosphere
0-12 km
increases in altitude, decreases in temperature
Earth's surface (bottom of Troposphere) absorbs the Sun's rays/heat and then emits some of the heat into the atmosphere
*think of an campfire, the closer you are to the fire the warmer you get*
contains nearly all of the mass of the atmosphere
weather occurs here
0-12 km
increases in altitude, decreases in temperature
Earth's surface (bottom of Troposphere) absorbs the Sun's rays/heat and then emits some of the heat into the atmosphere
*think of an campfire, the closer you are to the fire the warmer you get*
contains nearly all of the mass of the atmosphere
weather occurs here
46
New cards
tropopause
the boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere
temperature doesn't rise or cool down
temperature doesn't rise or cool down
47
New cards
stratosphere
found on top of tropopause (strato= spreading out) (2nd layer)
12-50 km
conatins ozone (03)
converts Sun's energy using ozone into heat, warming up the air
increases in altitude, increases with temperature
12-50 km
conatins ozone (03)
converts Sun's energy using ozone into heat, warming up the air
increases in altitude, increases with temperature
48
New cards
altitude of polaris=
latitude
49
New cards
Ozone
(03) *the three is written like an exponent but on the bottom*
absorbs Ultraviolet rays from the sun
converts the harnessed energy from the Sun's ray into heat
reason why temperature increases in the Stratosphere
absorbs Ultraviolet rays from the sun
converts the harnessed energy from the Sun's ray into heat
reason why temperature increases in the Stratosphere
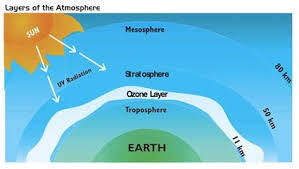
50
New cards
Mesosphere
found on top of stratosphere (meso=middle) (3rd layer)
50-80 km
most meteors burn up in here *known as shooting stars*
increases in altitude, decreases in temperature
doesn't absorb the Sun's rays
50-80 km
most meteors burn up in here *known as shooting stars*
increases in altitude, decreases in temperature
doesn't absorb the Sun's rays
51
New cards
Stratopause
boundary between stratosphere and mesosphere
the temperature stays consistent
the temperature stays consistent
52
New cards
mesopause
boundary between mesopause and thermosphere
temperature stays consistent
temperature stays consistent
53
New cards
thermosphere
outermost layer (thermo=heat) (4th layer)
80km- has no limit
altitude increases, temperature increases
can get very hot
absorbs most of the Sun's heat
has 2 sublayers (ionosphere, exosphere)
Aurora Borealis & Satellites & International Space Stations are in here
80km- has no limit
altitude increases, temperature increases
can get very hot
absorbs most of the Sun's heat
has 2 sublayers (ionosphere, exosphere)
Aurora Borealis & Satellites & International Space Stations are in here
54
New cards
ionosphere
lower level of Thermosphere (ion= electrical charge)
80-550 km
electrically charged particles called ions cause radio waves to bounce off the ionosphere and bounce back into Earth's surface
Aurora Borealis (northen lights) occur here
80-550 km
electrically charged particles called ions cause radio waves to bounce off the ionosphere and bounce back into Earth's surface
Aurora Borealis (northen lights) occur here

55
New cards
exosphere
the outer layer of the Thermosphere (exo= outer)
satellites & the International Space Station orbit the Earth in the exosphere
satellites & the International Space Station orbit the Earth in the exosphere

56
New cards
Pressure
the force of pushing on an area or surface
57
New cards
air pressure
the weight (or force) of the atmosphere at any particular point
***as altitude increases, pressure decreases
***as altitude increases, pressure decreases
58
New cards
there (is/isn't) a thermopause
isn't
59
New cards
label pauses where they (begin/end)
begin
60
New cards
in which layer does the weather system have the greatest effect on living things? why?
troposphere
because all living things live in the troposphere and weather only occurs in the troposphere
Because all living things depend on water, the water cycles occurs in the troposphere
because all living things live in the troposphere and weather only occurs in the troposphere
Because all living things depend on water, the water cycles occurs in the troposphere
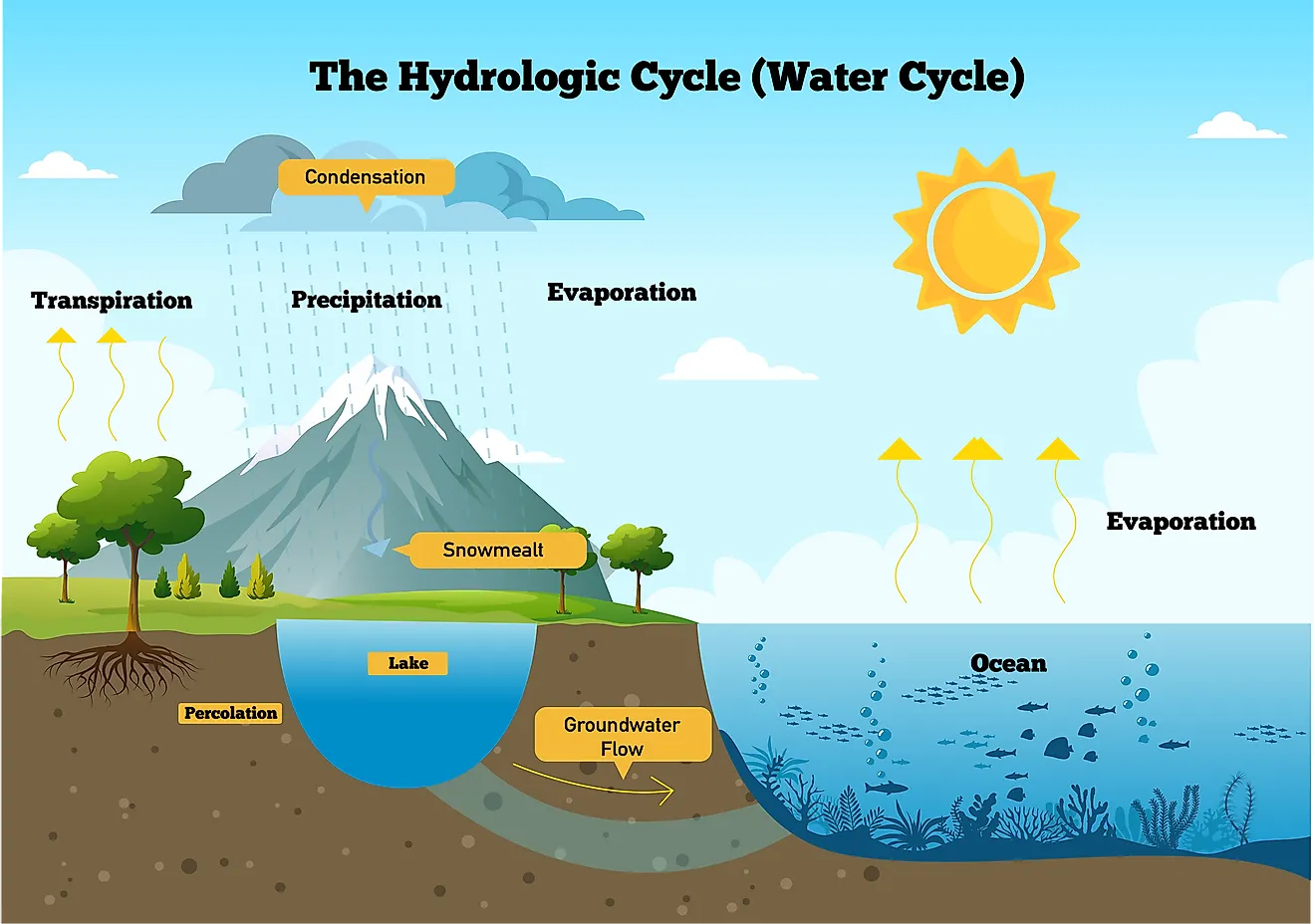
61
New cards
layers of the atmosphere
...
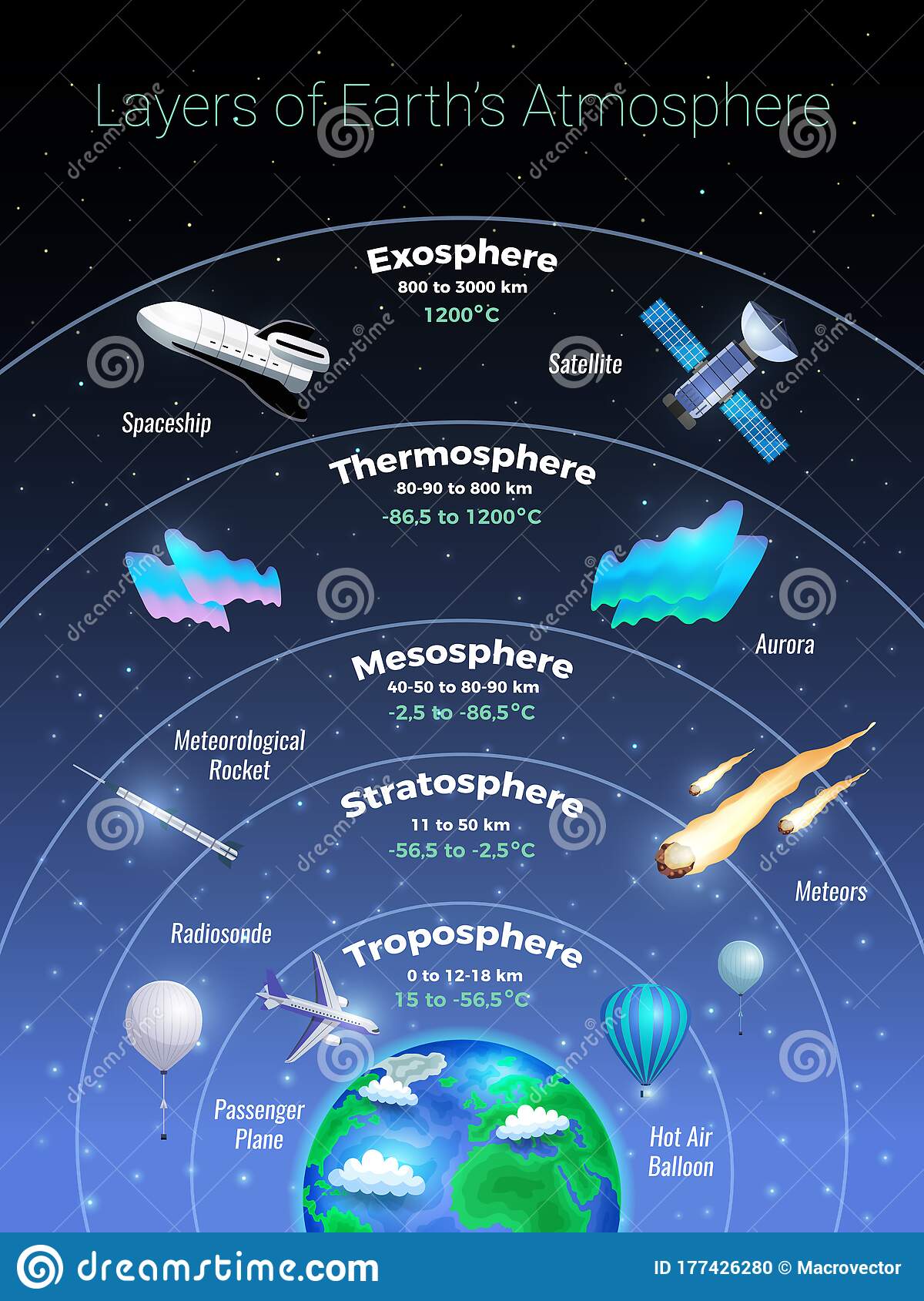
62
New cards
layers of the atmosphere
...