hybridisation etc
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What do sp3 orbitals look like?

Explain sp3 hybridisation
Carbon forms 4 single bonds
Each valence electron has ¼ s-orbital character and ¾ p-orbital
Each orbital is sp3 hybridised
sp3 MO diagram
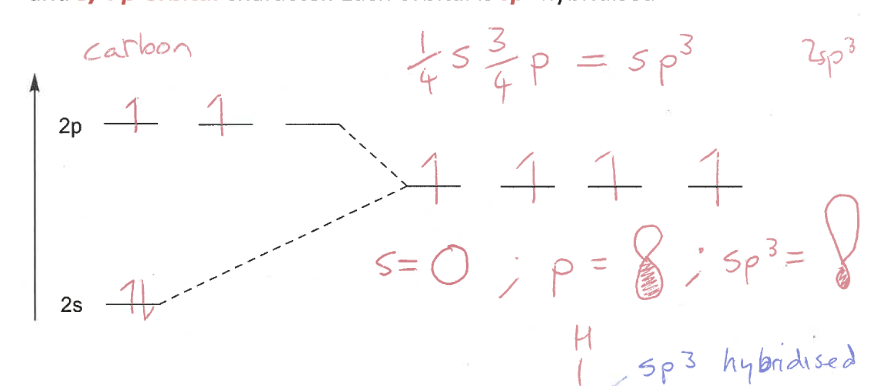
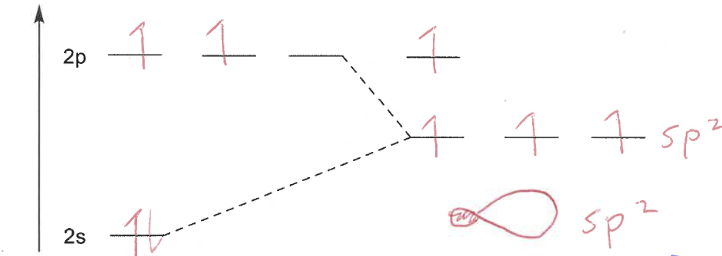
Explain sp2 hybridisation
Carbon is bonded to 3 atoms (double bond)
Three orbitals are hybridised to have 1/3 s-orbital character and 2/3 p-orbital
Each orbital is sp2 hybridised
What happens to the remaining p-orbital in sp2 hybridisation?
It forms a π-bond with a p-orbital from another atom
sp2 MO diagram
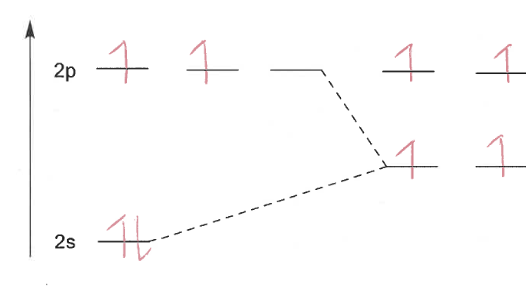
Explain sp hybridisation
C is bonded to 2 atoms (triple bond)
Two orbitals are hybridised; ½ s-orbital and ½ p-orbital character
sp hybridisation diagram
What does HOMO and LUMO stand for?
HOMO = highest occupied molecular orbital
LUMO = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital
What are inductive effects (±I)
Electron withdrawing (-I) effects and electron donating (+I) effects
electronegativity creating polar bonds
How to increase stability of carbocation intermediates? (inductive)
More +I (electron donating) groups increases stability
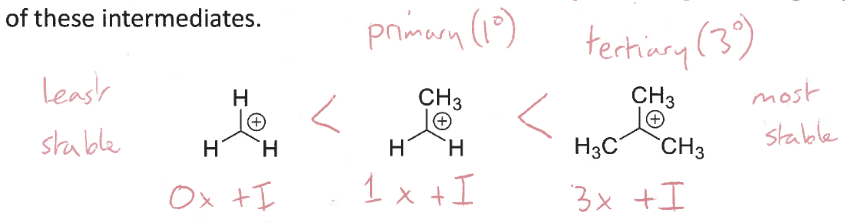
How to increase stability of carbocation intermediates? (alkyl groups)
They have an empty p-orbital
Having more alkyl groups through hyperconjugation
stabilise the charge
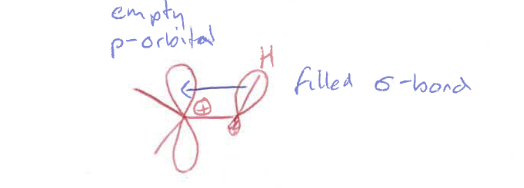
What is conjugation?
π-electrons on adjacent bonds can delocalise their electrons across the π-system
Why are conjugated systems flat?
Orbital overlap is most effective when the p-orbitals are parallel.
What happens as you increase the number of double bonds?
The HOMO-LUMO gap gets smaller
absorb light in the visible region
What are mesomeric (±M) effects?
The movement of electron density within the π system of the molecule by resonance conjugation
-M is electron withdrawing
+M is electron donating
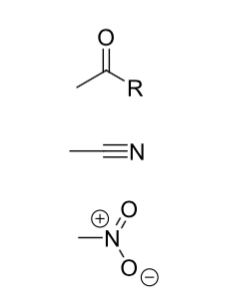
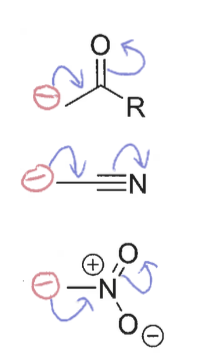
Diagrams of -M (electron withdrawing) effects
Where are electrons moving to/from?
From p-orbital to empty π* orbital
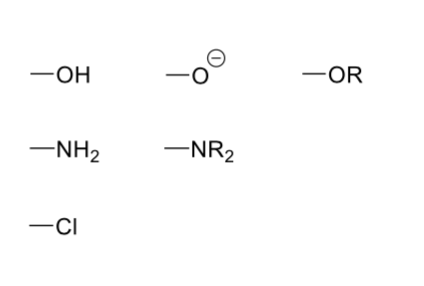
Diagrams of +M (electron donating) effects
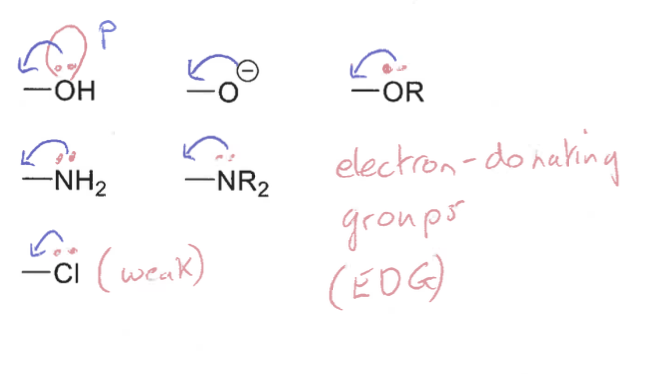
How do the orbitals overlap in -M (electron withdrawing) C=O with heteroatoms?
The π* orbital overlaps with lone pairs in p-orbitals of heteroatoms
What is pKa in terms of pH?
The pH at which the acid is half-dissociated
What does a high/low pKa mean?
basic/acidic?
high pKa is strong base
low (negative) pKa is weak base
How does equilibrium shift when two molecules are together in solution?
Equilibrium shifts towards the most stable conjugate base (lowest pKa)

Which way would equilibrium be favoured?
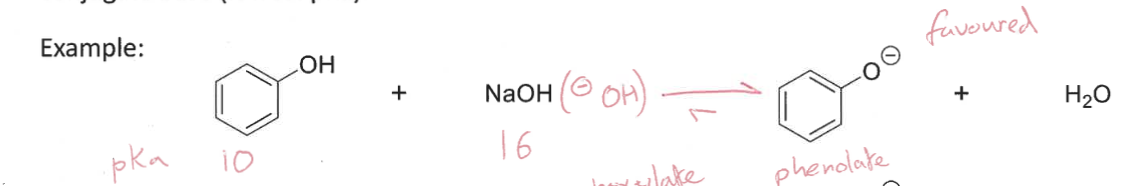
What pKa value do you need when deprotonating a molecule?
Use a base with a higher pKa value
How do orbitals overlap when forming a bond?
HOMO of one molecule overlaps with LUMO of another