Honors Chemistry LAP 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
atom
the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction
nucleus
the tiny central core of an atom that is composed of protons and neutrons
electrons
subatomic particle with negligible mass, making up most of the volume of an atom
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
atomic mass
the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element
isotopes
atoms with the same number of protons and but different numbers of neutrons
over 2,000 years ago, Democritus believed that atoms were _________________
a. made or protons and neutrons
b. indivisible and indestructible
c. created in laboratories
d. the size of a grain of salt
b. indivisible and indestructible
which is NOT part of Dalton’s atomic theory
a. all elements are composed of atoms
b. atoms of the same element are alike
c. during a chemical reaction, atoms of one element change into atoms of another element
d. atoms that combine do so in simple whole-number ratios
c. during a chemical reaction, atoms of one element change into atoms of another element
J.J. Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases and determined the resulting glowing beam consisted of _______________ which were attracted to a positively charged plate
a. protons
b. neutrons
c. alpha particles
d. electrons
d. electrons
In Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, why did some of the positively charged alpha particles bounce back towards the source at such large angles? They repelled by _______________
a. the electrons scattered throughout the atom like raisins in plum pudding
b. the edges of the gold foil
c. the protons in the nucleus of the gold foil atoms
d. the neutrons scattered throughout the atom like raisins in plum pudding
c. the protons in the nucleus of the gold foil atoms
which statement is consistent with the results of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment?
a. atoms are always positively charged
b. atoms are mostly empty space
c. the nucleus of an atom contains protons and electrons
d. mass is spread uniformly throughout an atom
b. atoms are mostly empty space
Which subatomic particles have a charge?
a. electrons only
b. protons and neutrons
c. protons and electrons
d. neutrons and electrons
c. protons and electrons
If we sucked out all the “empty space” from every atom in the human body, it would shrink down to a size smaller that a(n)_____________
a. grain of salt
b. hand
c. apple
d. football
a. grain of salt
How does the mass of an electron compare to the mass of a proton or a neutron?
a. electrons are 1840 times larger than protons and neutrons
b. electrons are 1840 times smaller than protons and neutrons
c. electrons, protons and neutrons all have equal masses
d. electrons have a mass equal to neutrons, but 1840 times less than protons
b. electrons are 1840 times smaller than protons and neutrons
If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be the size of a __________
a. small cat
b. human being
c. marble
d. planet
c. marble
Elements are defined by their _____________, which also is how they are arranged on the periodic table
a. mass number
b. atomic mass
c. electron number
d. atomic number
d. atomic number
Which of the following hydrogen atoms has the greatest mass
a. 1/1 H
b. 2/1 H
c. 3/1 H
d. They all have a mass of 1amu
c. 3/1 H
Nitrogen has an atomic number of 7. AN atom of nitrogen has __________ protons in the nucleus. In a neutral nitrogen atom, there are ______ electrons.
a. 7,0
b. 0,7
c. 7,7
d. 14,7
c. 7,7

What is the atomic number of Uranium, given the isotope symbol
a. 235
b. 92
c. 235-92=143
d. 235+92=327
b. 92
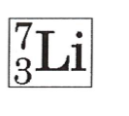
How many neutrons does the Lithium-7 isotope have?
a. 7
b. 3
c. 10
d. 4
d. 4
The number 197 in the name gold-197 represents the_____________
a. atomic number
b. element number
c. mass number
d. number of protons
c. mass number
Atoms of the same element can have different masses because they can have different numbers of _________
a. protons
b. electrons
c. neutrons
d. all of these
c. neutrons
Fluorine-19 has an atomic number of 9. How would this isotope of fluorine be represented in symbolic notation?
a. 19/9 F
b. 9/19 F
c. 28/9 F
d. 28/19 F
a. 19/9 F
If E is the symbol for an element, which two of the following symbols represent different isotopes of the same element?
a. 24/12 E & 24/12 E
b. 24/12 E & 12/6 C
c. 24/12 E & 25/11 E
d. 24/12 E & 25/12 E
d. 24/12 E & 25/12 E
Which of the following isotope symbols indicates a Neon isotope with 10 neutrons
a. 22/10 Ne
b. 21/10 Ne
c. 20/10 Ne
d. 10/20 Ne
c. 20/10 Ne

How many protons and neutrons does iron-56 have?
a. 26 protons and 56 neutrons
b. 26 protons and 26 neutrons
c. 30 protons and 56 neutrons
d. 26 protons and 30 neutrons
d. 26 protons and 30 neutrons
Which of the following could be determined from the following symbol of a neutral atom? m/a X
a. mass number & atomic number
b. number of neutrons
c. number of electrons and number of protons
d. all of these
d. all of these
The atomic mass of silicon is 28.086 amu. Silicon-28, silicon-29, and silicon-30 are three isotopes of silicon. Which is more abundant given the atomic mass?
a. silicon-28
b. silicon-30
c. silicon-29
d. all are equally abundant
a. silicon-28
Which of the following is true about isotopes?
a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes
b. Isotopes have different chemical properties from each other
c. Isotopes have different numbers of protons in the nucleus
d. all of these are true about isotopes
a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes
In the Isotopes Gizmo activity, you noted that the most stable isotopes have _________
a. double the number of protons compared to neutrons
b. double the number of neutrons compared to protons
c. close to the same number of protons and neutrons
d. half the amount of neutrons compared to protons
c. close to the same number of protons and neutrons
Because there are different isotopes of elements, all having different masses, which mass is put on the periodic table for each element?
a. the mass number of the heaviest isotope
b. the mass number of the most common isotope
c. an average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes
d. a weighted average mass of all of the naturally occurring isotopes
d. a weighted average mass of all of the naturally occurring isotopes
Two isotopes for nitrogen are nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15. Given the atomic mass of nitrogen is 14.007, which is more abundant?
a. nitrogen-14
b. nitrogen-15
c. both are equally abundant
a. nitrogen-14
An atom with 2 protons and 2 neutrons weighs
a. 2 amu
b. 8amu
c. 4 amu
d. 10amu
c. 4 amu
It is possible for two different elements to have the same mass number because____________________
a. their numbers of protons and neutrons can add up to the same number
b. their numbers of protons and electrons can add up to the same number
c. their numbers of protons can be the same
d. it is not possible for two different elements to have the same mass number
a. their numbers of protons and neutrons can add up to the same number
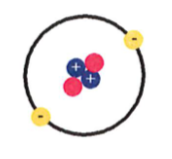
What element is represented by this neutral atom?
a. boron
b. helium
c. beryllium
d. chlorine
b. helium
Which of the following is NOT an example of how unstable isotopes are used in our world?
a. nuclear energy/ weapons
b. archaeological dating of artifacts
c. food/ medical equipment sterilization
d. all of these are ways we use unstable isotopes
d. all of these are ways we use unstable isotopes
The atomic mass of an element is calculated by multiplying the mass of each isotope by its natural abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then__________________
a. subtracting the products
b. dividing the products
c. adding the products
d. getting the arithmetic mean of the products
c. adding the products
In the Atomic Mass Gizmo, you were able to determine the weighted average atomic mass of various sample sizes of a neutral isotope mix. As the sample size increases, the weighted average atomic mass ___________
a. gets closer to the average atomic mass found on the periodic table
b. gets further away from the average atomic mass found on the periodic table
c. is not affected by the sample size
a. gets closer to the average atomic mass found on the periodic table
What is the most reasonable inference you could make about chromium (Cr), which has four stable isotopes and an average atomic mass of 52.057 amu?
a. Approximately 10% of chromium atoms have a mass of 52 amu
b. All of chromium’s isotopes have a mass of between 52 and 53 amu
c. the most common isotope of chromium has a mass of exactly 52.057 amu
d. the most common isotope of chromium is Cr-52
d. the most common isotope of chromium is Cr-52
Assume element X has 2 isotopes: X-125 and X-126. For every 100 atoms of X, 70 of them have a mass of 125.0 amu and 30 have a mass of 126.0 amu. What is the average atomic mass of X?
a. 125.3u
b. 125.7u
c. 126.3u
d. 126.7u
a. 125.3u
(125*.70)+(126*.30)=87.5+37.8=125.3
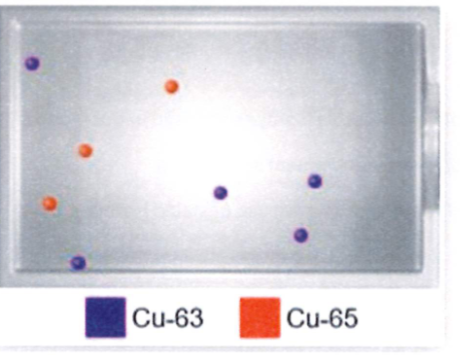
Calculate the average atomic mass for the sample atoms shown below
a. 63.50 amu
b. 63.75 amu
c. 64.25 amu
d. 64.50 amu
b. 63.75 amu
3/8=0.375 5/8=0.625
(.625×63)+(.375×65)=63.75
Given the following sample data collected for the “Bean Bag” isotope lab, calculate the atomic mass of Bg
a. 0.563 g
b. 5.630 g
c. 0.420 g
d. 4.200 g
c. 0.420 g
(0.183*.123)+(0.371*.361)+(0.511× 0.516)=0.420116=0.420