Anatomy
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
Brain Stem
has 3 divisions
10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves are from the brain stem
10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves are from the brain stem
2
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
attaches to spinal cord
forms the lowest part
includes control for cardiac and respiratory autonomic functions
forms the lowest part
includes control for cardiac and respiratory autonomic functions
3
New cards
Pons
lies above medulla oblongata and midbrain
also composed of white matter ( myelin) and reticular formation
also composed of white matter ( myelin) and reticular formation
4
New cards
Midbrain
forms the uppermost part of the brain
forms the midsection of the brain
lies above the pons and below the cerebrum
forms the midsection of the brain
lies above the pons and below the cerebrum
5
New cards
Functions of the Brainstem
perform sensory, motor, and reflex functions
6
New cards
Nuclei in the Medulla
contain a number of reflex centers including cardiac and respiratory centers
ex- vomiting, coughing, sneezing
ex- vomiting, coughing, sneezing
7
New cards
What does the pons contain?
center for reflexes
8
New cards
The Midbrain, likes the Pons
contains cranial nerve reflexes like eye movement
9
New cards
Structure of the Cerebellum
means “little brain”
2nd largest part of the brain, but has more neurons than all other parts of the nervous system combined
2nd largest part of the brain, but has more neurons than all other parts of the nervous system combined
10
New cards
Arbor vitae
internal white matter
also means tree of life
also means tree of life
11
New cards
What does the cerebellum consist of
2 large lateral masses
right cerebellar hemisphere + a central section called the vermis
right cerebellar hemisphere + a central section called the vermis
12
New cards
Function of the Cerebellum
1. acts with the cerebral cortex to produce skilled movements by planning and coordinating the activities of muscle groups
2. helps control muscle functions below the conciseness to make movement smooth
3. control skeletal movement to maintain balance
4. coordinate incoming sensory info
13
New cards
Diencephalon
between brain
includes the structure thalamus, hypothalamus, and the pineal glands
includes the structure thalamus, hypothalamus, and the pineal glands
14
New cards
Thalamus
responsible for sensations
introduces conscious recognition of the pain, temperature, touch
relays all kinds of sensory impulses except smell
introduces conscious recognition of the pain, temperature, touch
relays all kinds of sensory impulses except smell
15
New cards
hypothalamus
functions as a higher autonomic center and relay station between the cerebral cortex and lower autonomic centers
make possible mind influence over the body
synthesizes the hormones(arousal) released by pituitary glands
make possible mind influence over the body
synthesizes the hormones(arousal) released by pituitary glands
16
New cards
Pineal Gland
respond to **light and dark** and secretes melatonin and regulates circadian rhythmes and sleep-wake cycle
17
New cards
Gray Matter
the darker outer portion
primary composed of neurons, somas, cerebral cortex of cerebrum
primary composed of neurons, somas, cerebral cortex of cerebrum
18
New cards
White Matter
lighter section underneath
mostly made of axons wrapped in myelin
mostly made of axons wrapped in myelin
19
New cards
brain
60% of fat
20
New cards
Spinal nerves
31 pairs of peripheral spinal nerves
merge from the spinal cord through spaces between the vertebrae
merge from the spinal cord through spaces between the vertebrae
21
New cards
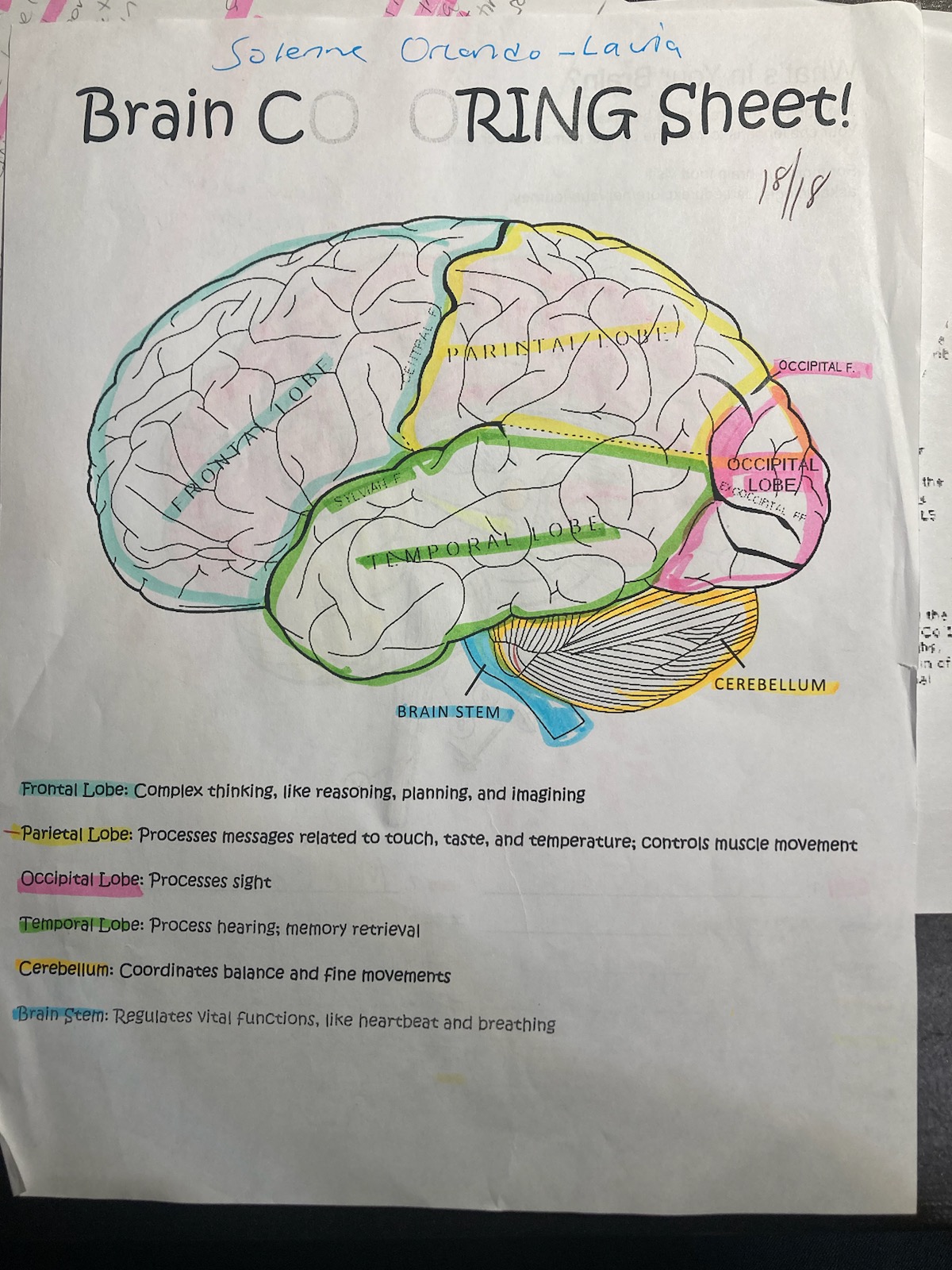
blue
frontal lobe
22
New cards
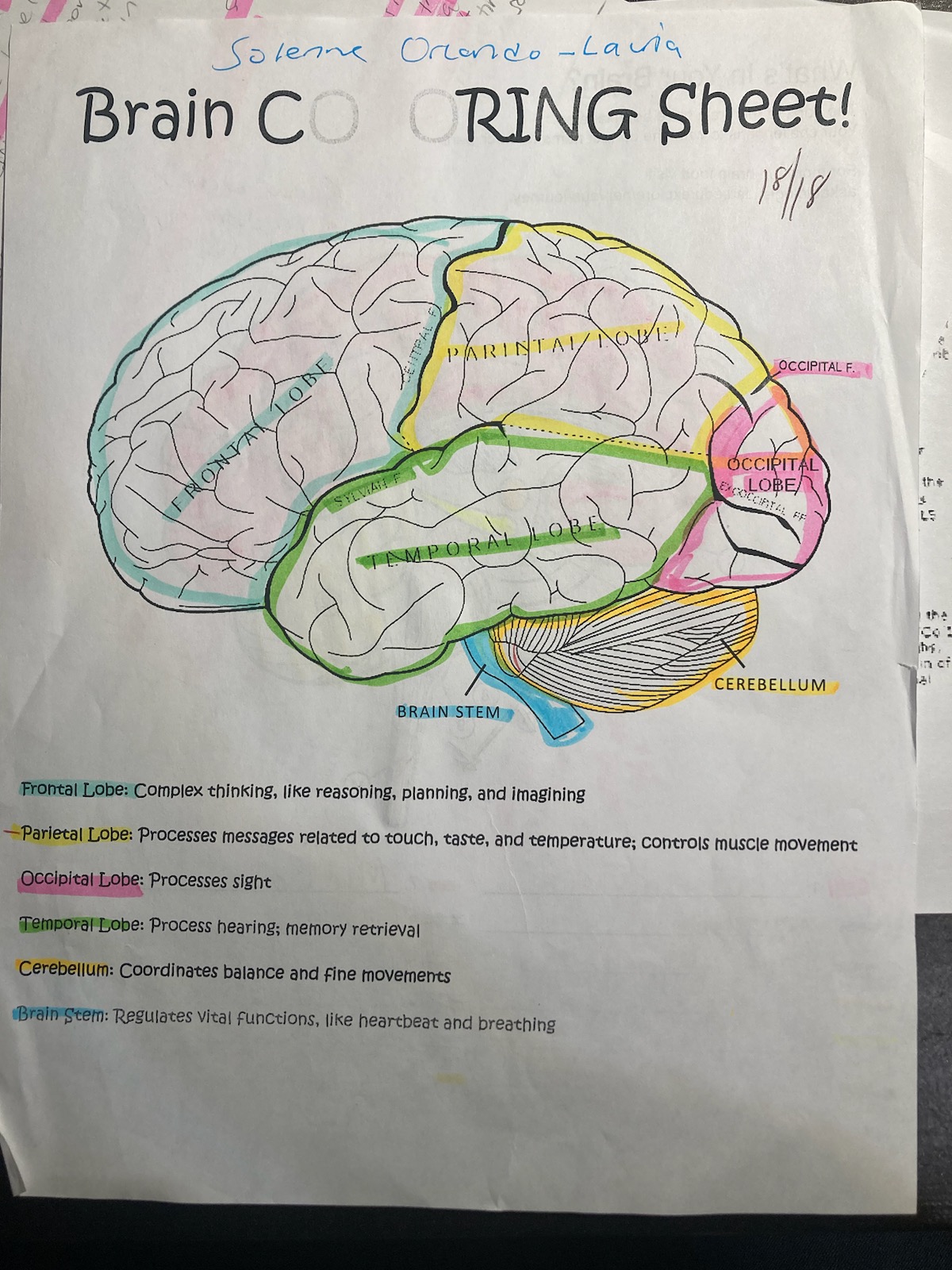
pink
occipital
23
New cards
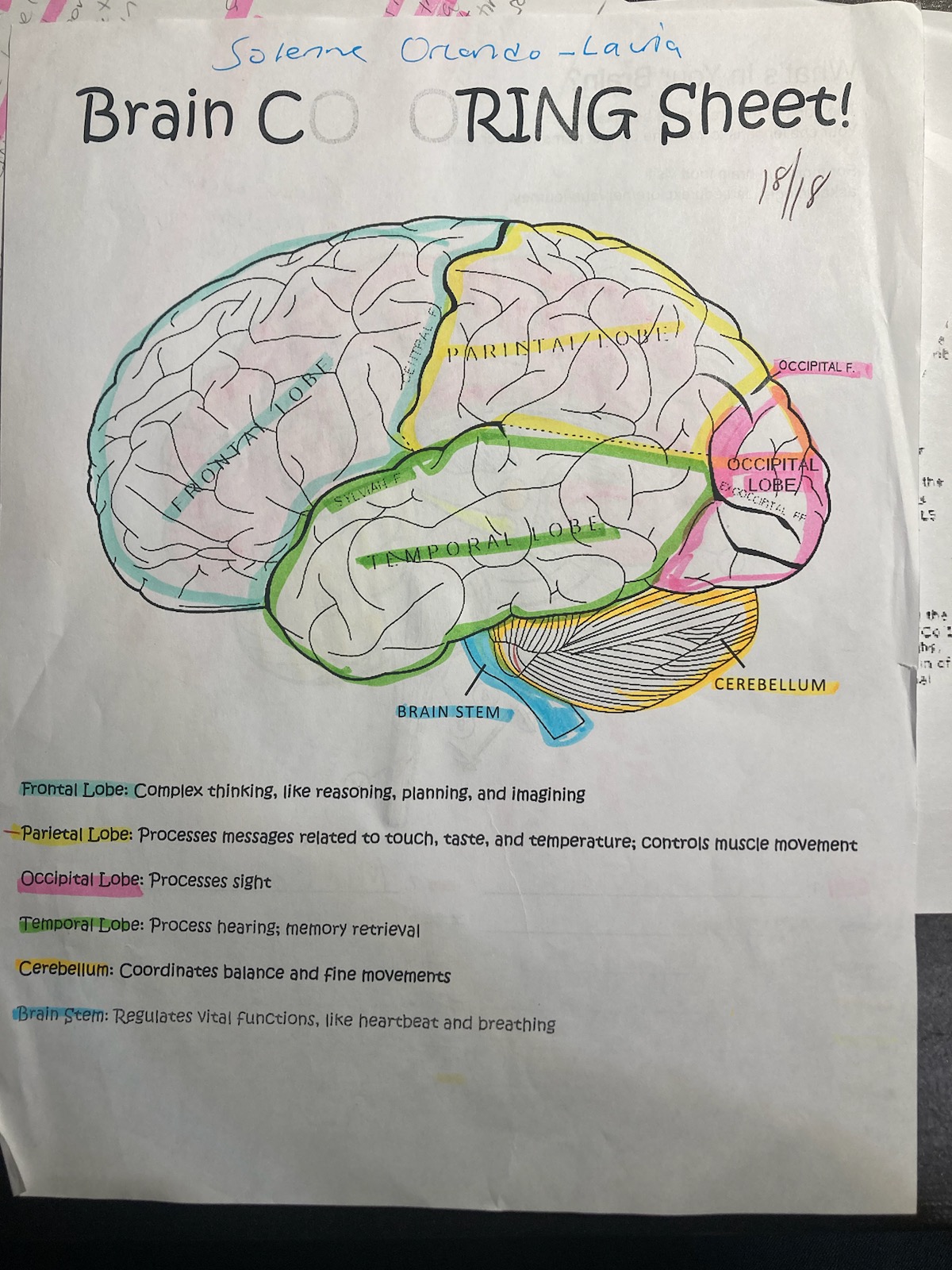
yellow
pariental
24
New cards
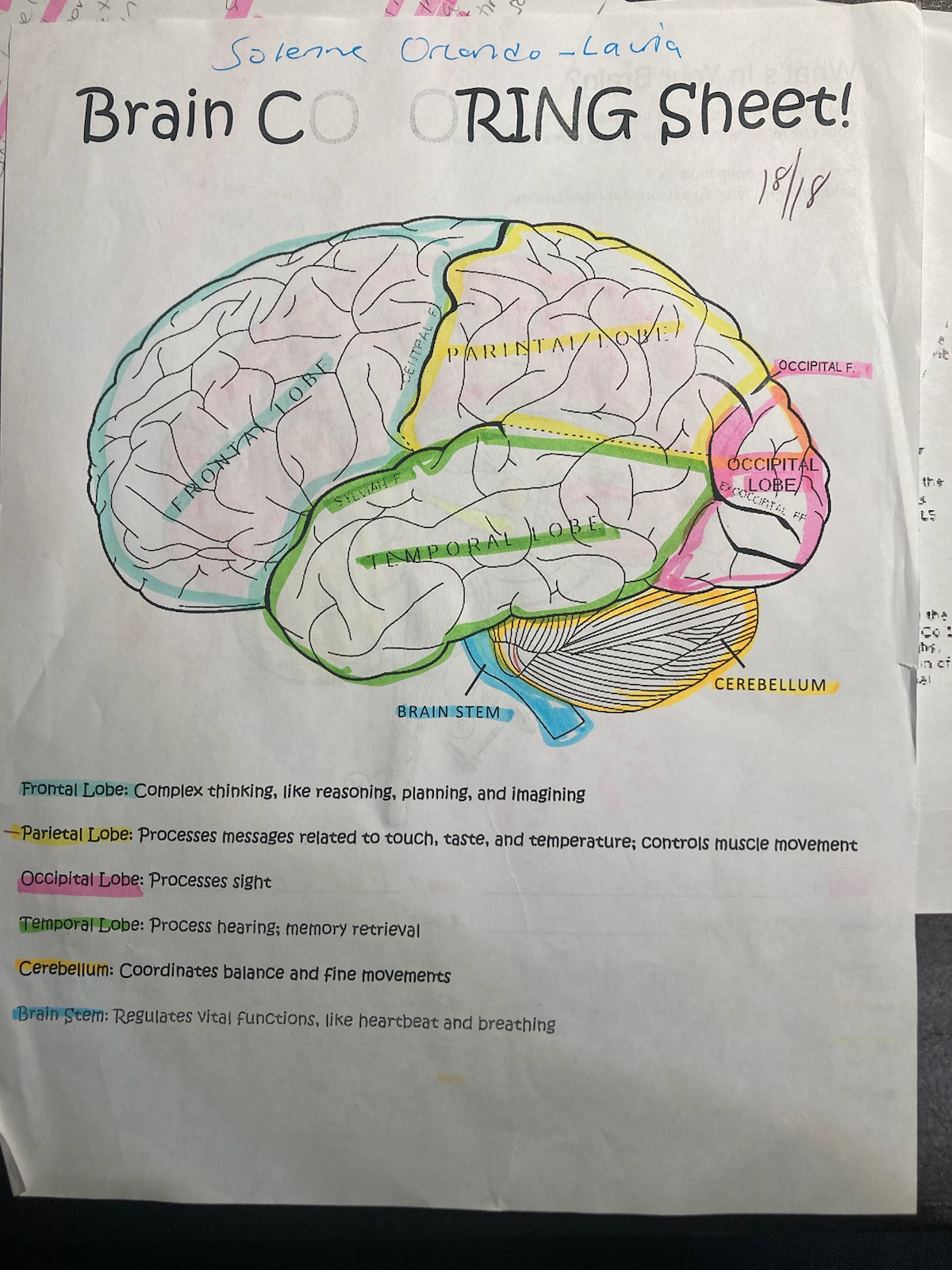
green
temporal
25
New cards
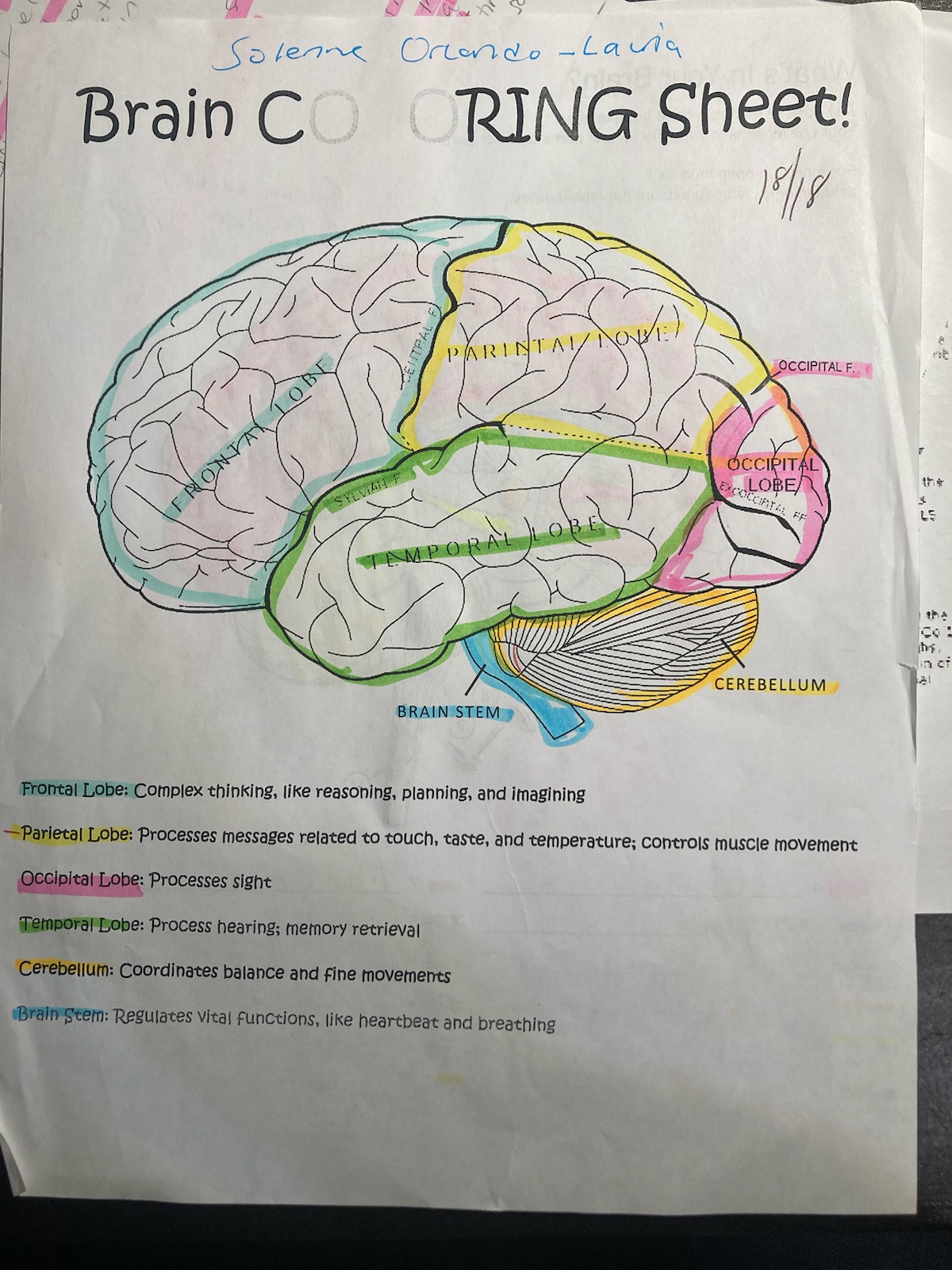
orange
cerebellum
26
New cards
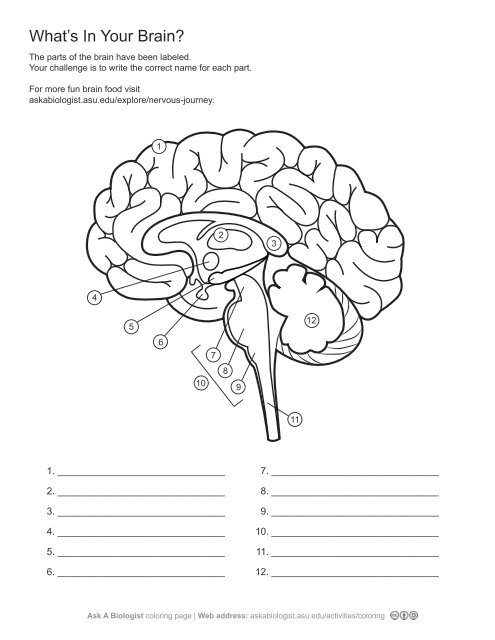
1\.
cerebral cortex
27
New cards
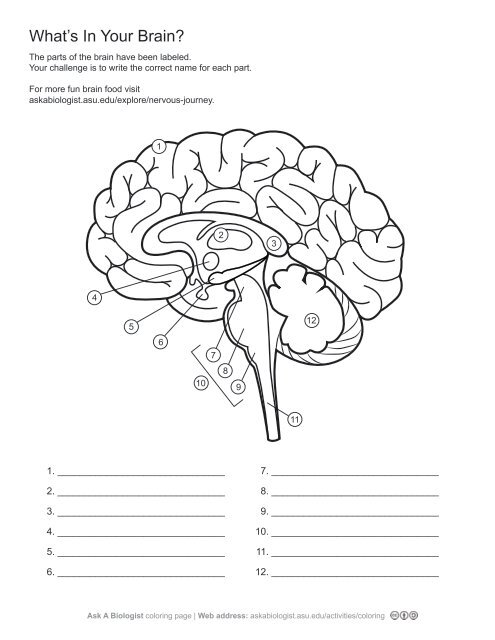
2\.
thalamus
28
New cards
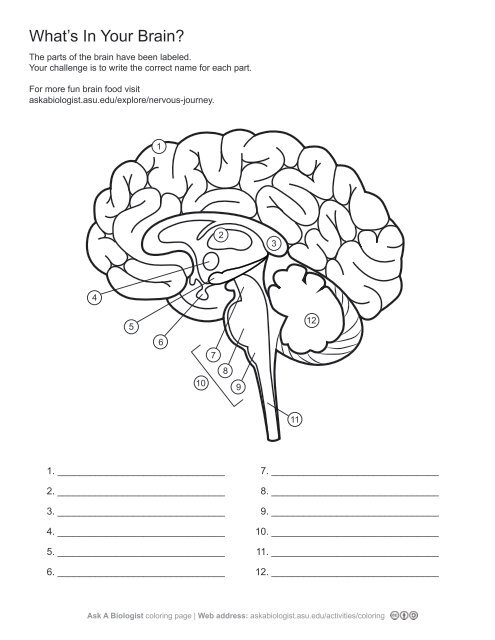
3,
corpus callosum
29
New cards
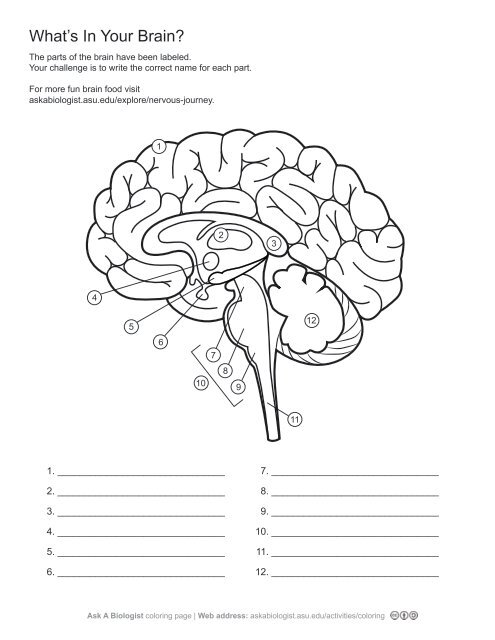
4\.
hypothalamus
30
New cards
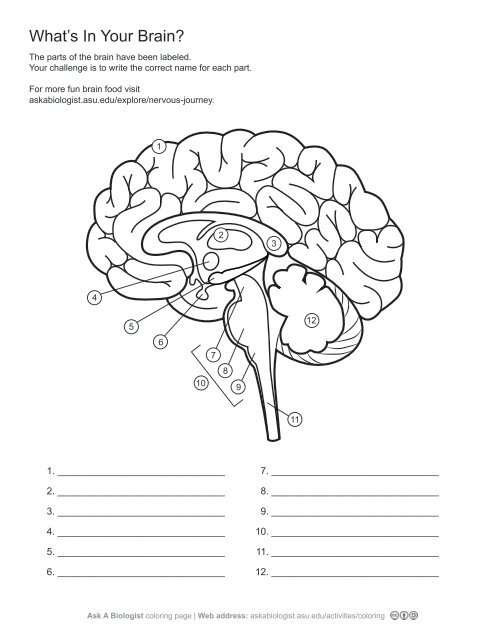
5. \
hippocampus
31
New cards
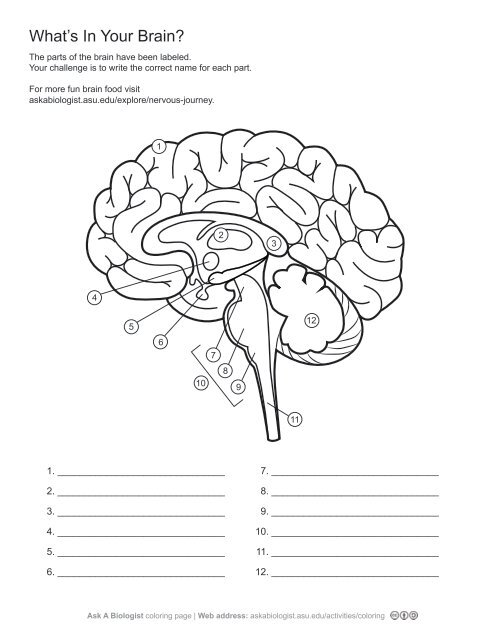
6\.
pituary gland
32
New cards
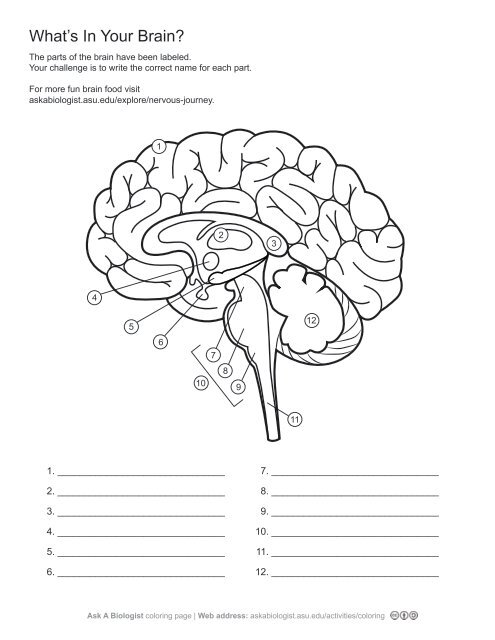
7\.
midbrain
33
New cards
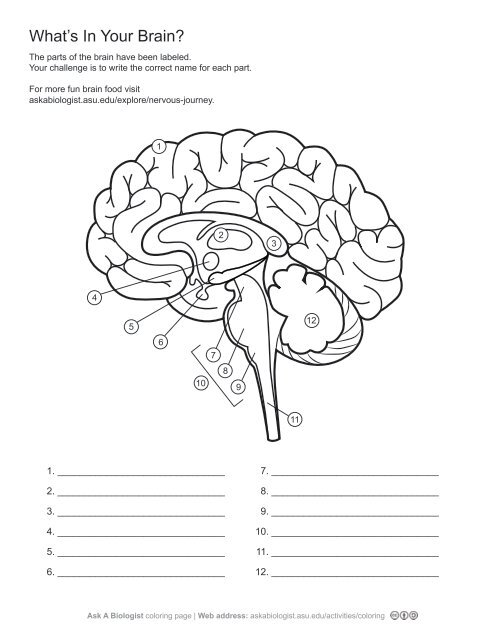
8\.
pons
34
New cards
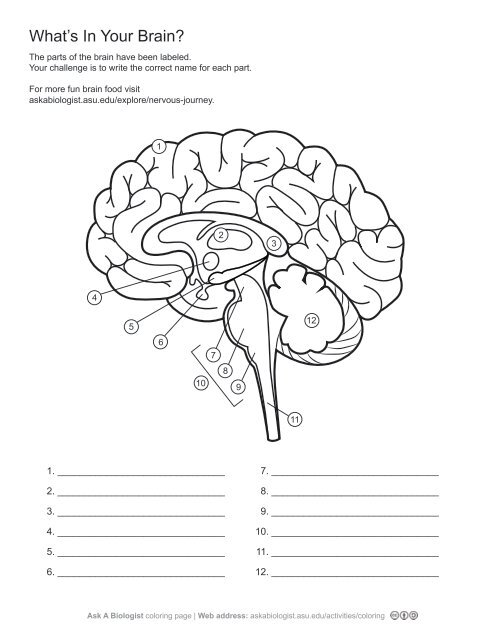
9\.
medulla oblangata
35
New cards
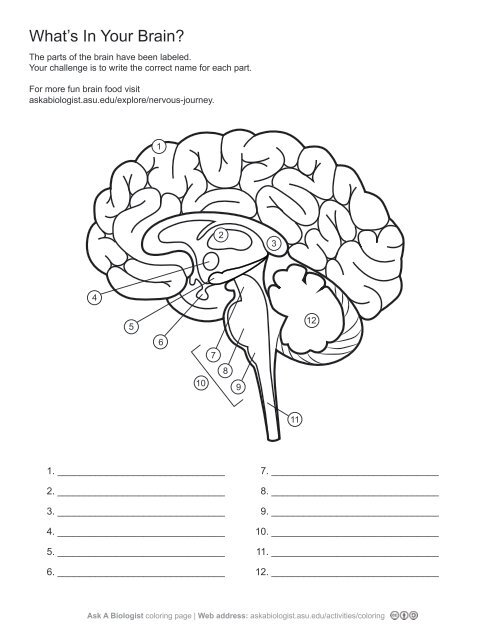
10\.
brainstem
36
New cards
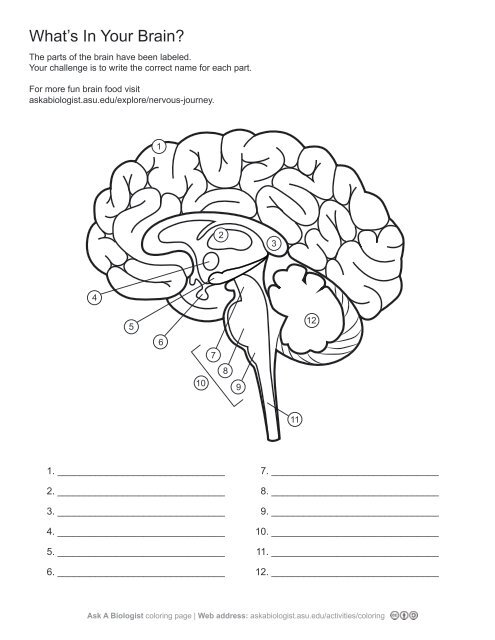
11\.
spinal cord
37
New cards
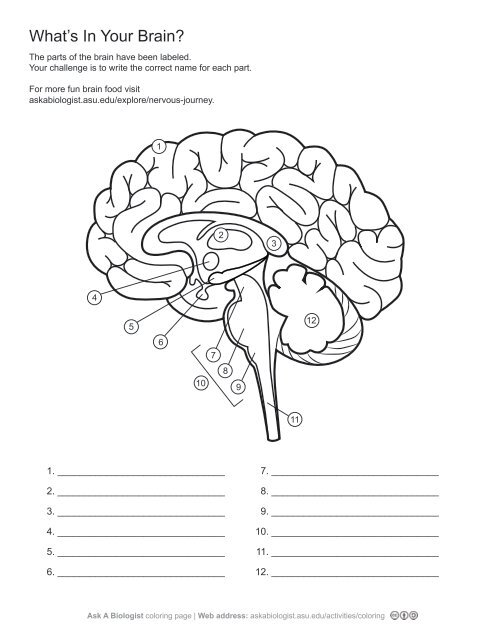
12. \
cerebellum