ashlyn copy_NEED TO KNOW
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
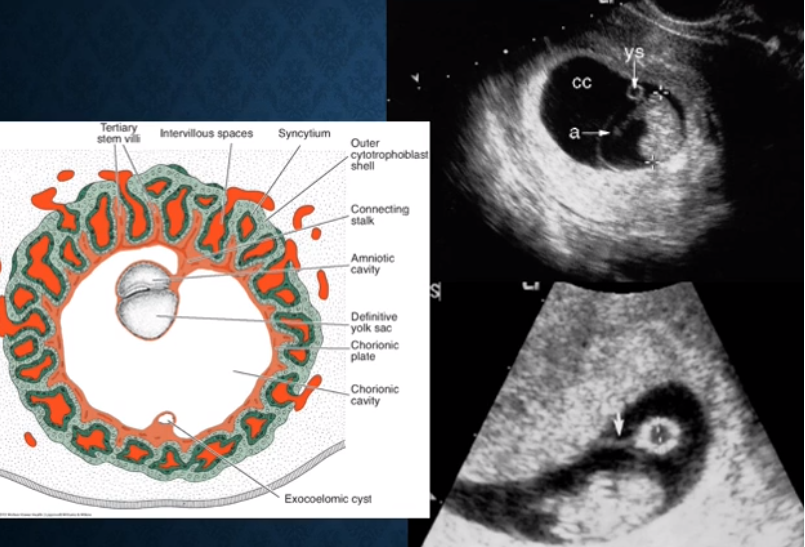
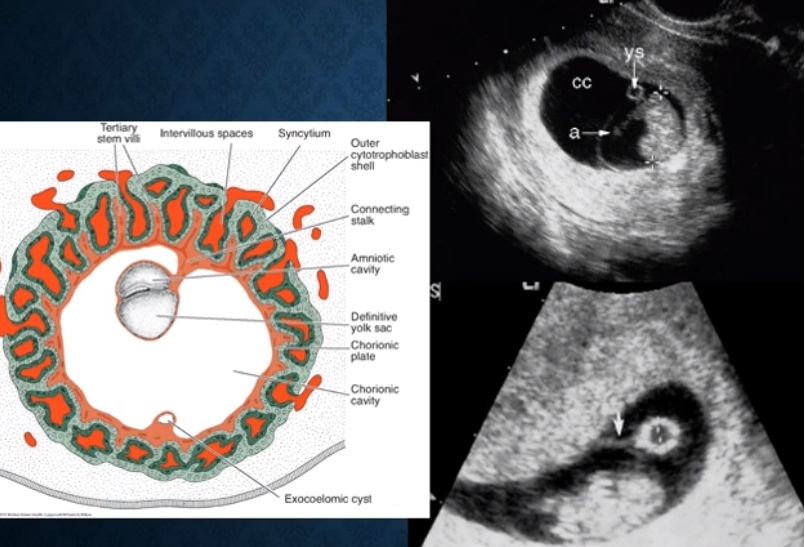
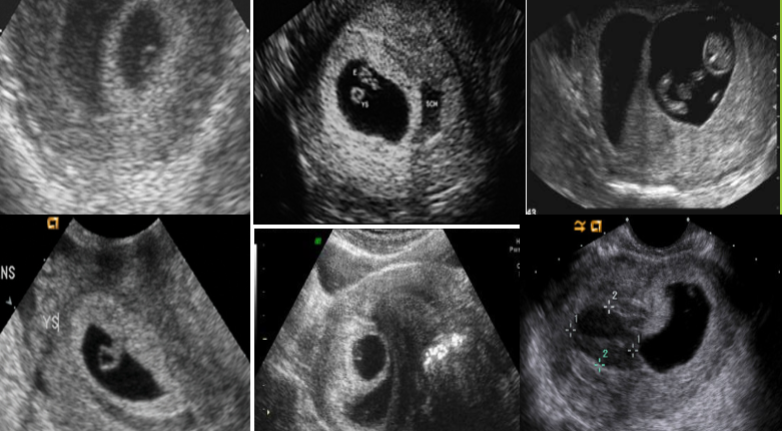
identify: embryo, secondary yolk sac, and amnion in this photo!
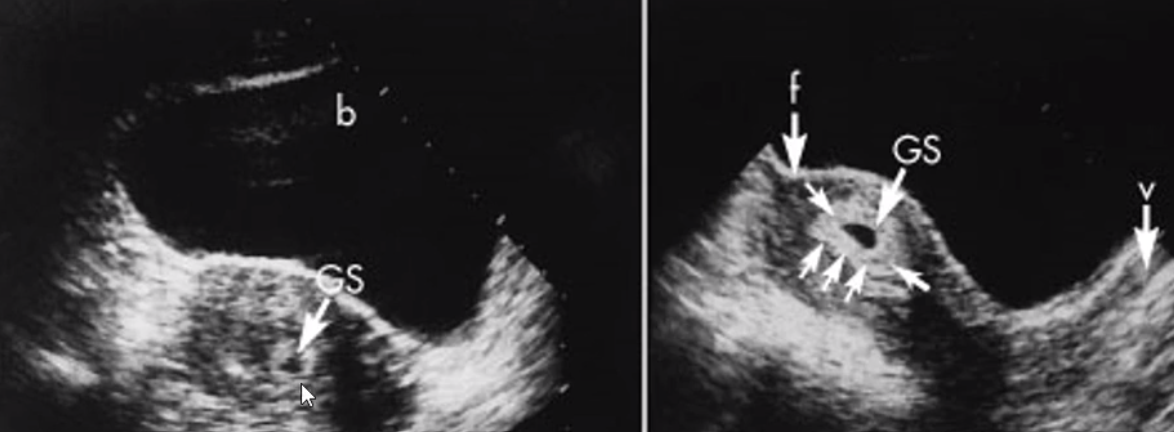
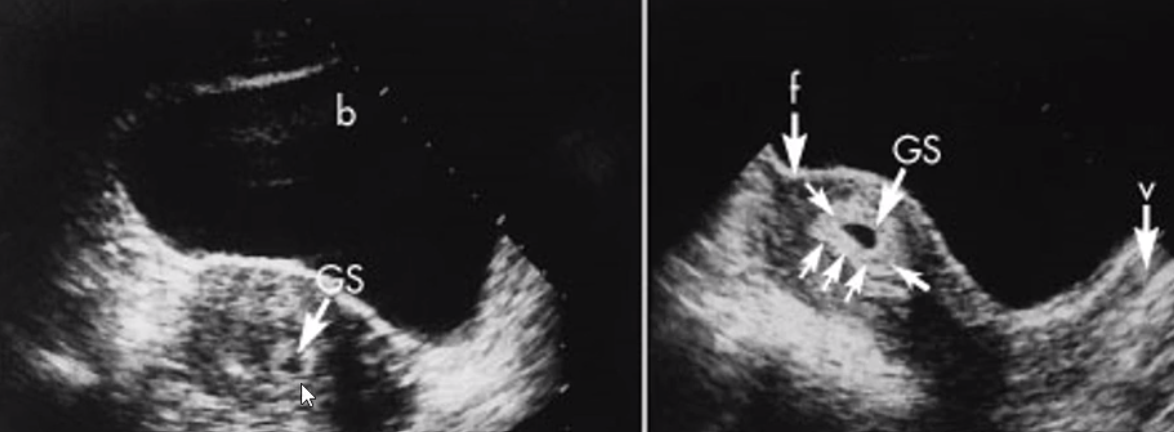
identify decidua in this photo!
What contributes to the maternal portions of the placenta
Decidua Basalis
What is the normal number of chromosomes for Ova, sperm, and embryo
Ova = 23X
Sperm= 23X or 23Y
Embryo = 46XX or 46XY
The order of which structures appear on ultrasound (yolk sac, gest sac, embryo)
Gestational sac: 4-5 weeks
Yolk sac: 5-6 weeks
Embryo (fetal pole) with heartbeat: 6 weeks
Qualitative and Quantitative HCG levels:
which one is more accurate for determining gestational age
know the difference!
Qualitative: Pregnancy test, simple positive or negative
Quantitative: Measures amount of HCG in maternal blood; more diagnostic info; much more accurate
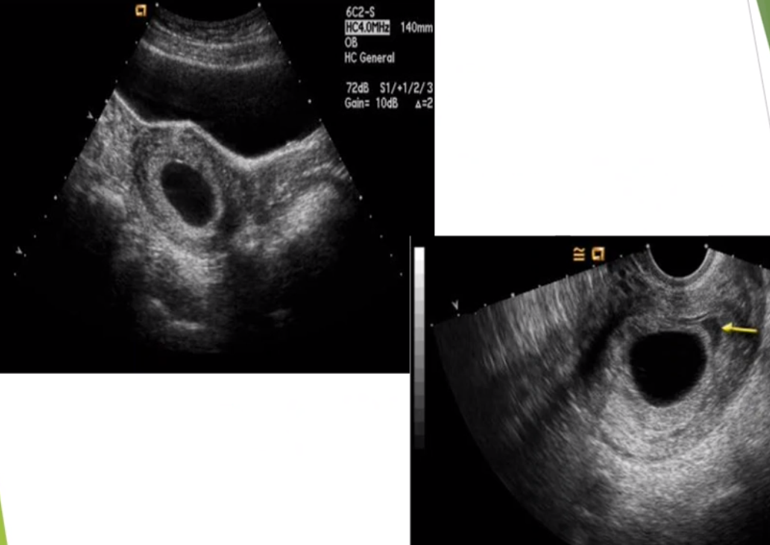
what is shown?
anembryonic pregnancy aka blighted ovum
blighted ovum on US?
empty gestational sac
may see double ring BUT NO EMBRYO OR YOLK SAC
may see debris in sac that looks similar to yolk sac
will see trophoblastic flow (ring of fire)
sac grows more slowly than expected
Know about the anembryonic pregnancy aka blighted ovum:
pregnancy failed to occur prior to development of an identifiable embryo/ embryonic tissue has been resorbed after early embryo demise
caused by sperm that fertilizes an ovum that is abnormal
there is no/ never was an actual baby
What size would the empty gestational sac be diagnose a blighted ovum?
Empty gestational sac with MSD > 25mm
Which anomaly is most commonly associated with cystic hygroma
most predominant by mid pregnancy= Turner syndrome
Also associated with autosomal trisomy’s and trisomy 21.
What does molar pregnancy look like?
difference between partial and complete?
definition of complete molar pregnancy?
They appear as complex intrauterine mass early on.
Complete molar -
no maternal chromosomes= proliferation of swollen chorionic villi and the absence of identifiable embryonic structures
stays as empty gest sac.
Partial molar -
One maternal and two paternal sets of chromosomes, leading to development of an abnormal embryo and placenta
becomes abnormal fetus
What are the findings of an embryonic demise on ultrasound
Empty amnion sign
Absence of cardiac activity when CRL >5mm
Know the definition of missed abortion
Embryo/fetus has died but gestational sac and contents remain within the uterus
Know the definition of inevitable abortion
Conceptus located within uterus but cervix is open and gestational sac is in the process of exiting the uterine cavity. Embryo may or may not be alive
Know the definition of incomplete abortion
Embryo has died and part of the products of conception have been expelled but some parts still remain within the uterus
Know the definition of complete abortion
All of the products of conception leave the body
Know what a subchorionic hemorrhage looks like on an ultrasound image
Fluid collection between gestational sac and uterine wall
Fetal heart rate rule, what’s a normal level, what is low, what is high
Normal is 120-180 bpm
Below 100-110 is bad
Above 160-180 is bad
DO NOT use anything but M-Mode on a fetus 12 weeks or less; DO NOT use PW or Color Doppler
When is fertilization possible?
24-48 hours after ovulation
Where does fertilization almost always occur in?
Ampulla of the fallopian tube
What does a trophoblast secrete?
hCG
What forms the point of exchange of maternal and fetal blood components
Chorionic villi
What type of yolk sac can be seen on ultrasound
Secondary
What is the first embryonic structure visible on ultrasound?
Secondary yolk sac
Most common type of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia
Hydatidiform Mole