Chapter 25- Macromolecules
- Macromolecule: A long chain molecule containing hundreds of atoms joined together by covalent bonds. It is also called a polymer.
- Monomers: Small repeating units that join to form a macromolecule.
- Polymerisation: the process of joining together a large number of monomers to make a polymer.
- Addition polymeristion: the type of polymeristion where no atoms are lost so just one product is formed.
- Condensation polymeristion: the type of polymerisation where a small molecule, usually water, is also produced as a byproduct.
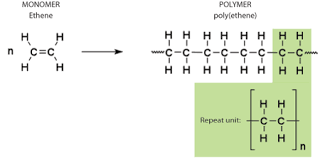
ADDITION POLYMERISATION
At high temperature and pressure, thousands of alkenes join together to form an addition polymer.
The double bonds in monomers break at such high temperature and pressure, forming single bonds with two other monomers.
Ethene is used to manufacture the polymer, poly(ethene), commonly known as polythene.
Addition polymers are used to make disposable containers, PVC pipes, raincoats and gloves etc.
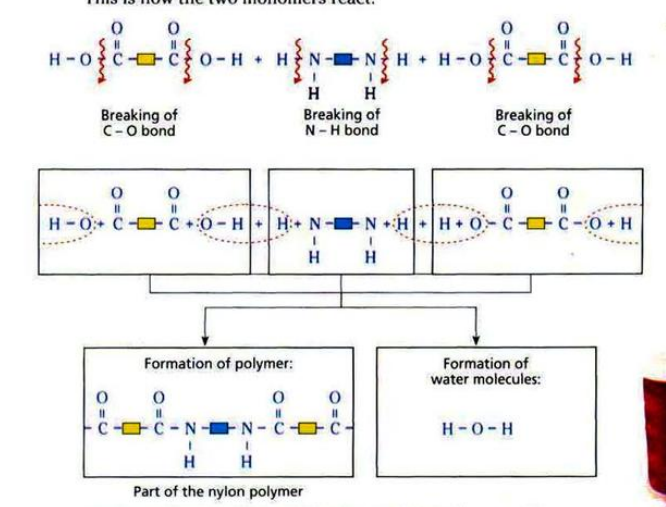
CONDENSATION POLYMERISATION
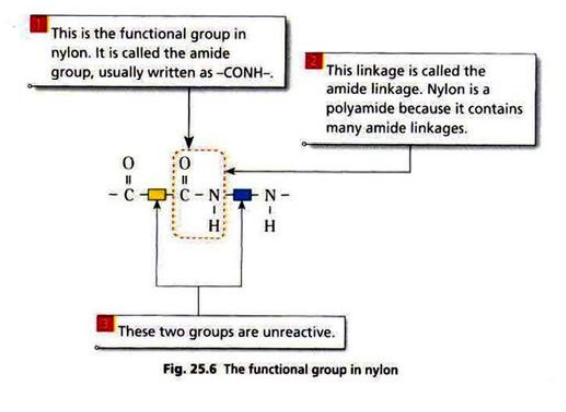
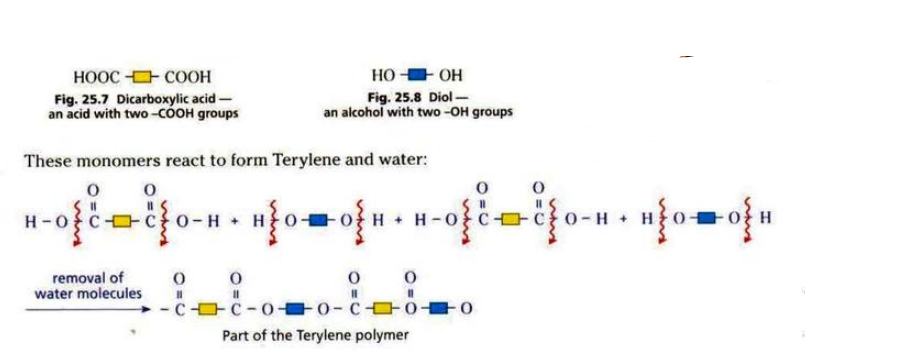
- There are two groups of condensation polymers: polyamides and polyesters.
Nylon is made from diamine and dicarboxylic acid.
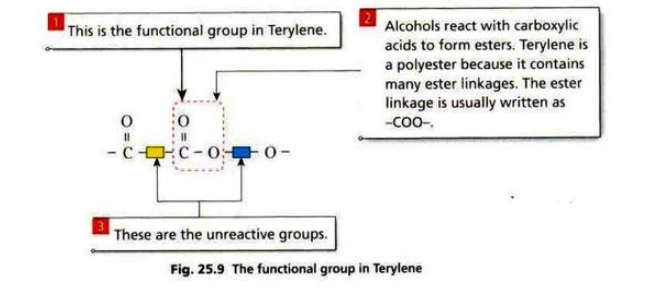
Terylene is made from diol and dicarboxylic acid.
- Plastics and polymers are non-biodegradable and cause pollution problems.