11.3: Membrane Transport
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:26 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Define simple diffusion.
The movement of a solute through a permeable barrier along its concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached.
2
New cards
Define facilitated diffusion.
The movement of solutes through a permeable barrier, aided by a membrane protein without the usage of ATP, along its concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached.
3
New cards
Describe active transport vs. passive transport.
Active transport requires ATP, because it involves moving solutes against their concentration gradient.
Passive transport does not require ATP; it involves moving solutes along their concentration gradient.
Passive transport does not require ATP; it involves moving solutes along their concentration gradient.
4
New cards
Define primary active transport
The energetically unfavorable movement of solutes against their concentration gradient, using the hydrolysis of ATP as their source of energy.
5
New cards
Name two types of primary active transport mechanisms?
ATPase transports and ABC transporters
6
New cards
What are the three types of ATPases?
P-type, V-type, and F-type
7
New cards
What is P-type ATPase? What does it do?
P-type ATPase is an integral transmembrane multi-domain polytopic protein. Its is reversibly phosphorylated by ATP and its function is the transport of CATIONS across membranes.
8
New cards
What region of P-type ATPases are phosphorylated?
The critical Asp is phosphorylated, which generates a conformational change that drives membrane transport.
9
New cards
Give two examples of P-type ATPase transporters. Are they uniport, symport, or antiport?
SERCA: uniport transporter of Ca2+ ions.
Na+,K+: antiport transporter of Na+ and K+ ions.
Na+,K+: antiport transporter of Na+ and K+ ions.
10
New cards
What is a V-type ATPase? What does it do?
V-type ATPases are integral transmembrane multi-domain polytopic proteins that are involved with the movement of PROTONS across a membrane.
The V stands for vacuolar, because usually intracellular compartments (such as vacuoles) need to be acidified for proper function.
The V stands for vacuolar, because usually intracellular compartments (such as vacuoles) need to be acidified for proper function.
11
New cards
What is an F-type ATPases? What does it do?
F-type ATPases are extremely similar to V-type ATPases in both structure and function. However, the F relates to "energy-coupling Factors," meaning that it couples the movement of protons to the hydrolysis and synthesis of ATP.
12
New cards
What is the key difference between F-type and V-type ATPases?
F-type ATPases, when working in their reverse direction (all depending on proton gradients), they actually catalyze the synthesis of ATP.
13
New cards
What is an ABC transporter? What does it do? Describe its molecular characteristics. How does the mechanism work?
ATP-Binding-Cassette
ABC transporters actively move many types of molecules across membranes, including amino acids, polypeptides, salts, and lipids.
ABC transport proteins have two ATP-binding domains, and two transmembrane domains. Each intermembrane domain is comprised of 6 transmembrane helices.
The mechanism works via the interconversion between two conformations, dependent on ATP hydrolysis. Either conformation has the binding site facing either the inside or outside of the cell.
ABC transporters actively move many types of molecules across membranes, including amino acids, polypeptides, salts, and lipids.
ABC transport proteins have two ATP-binding domains, and two transmembrane domains. Each intermembrane domain is comprised of 6 transmembrane helices.
The mechanism works via the interconversion between two conformations, dependent on ATP hydrolysis. Either conformation has the binding site facing either the inside or outside of the cell.
14
New cards
Define secondary active transport
The energetically unfavorable movement of solutes against their concentration gradient, coupled to a very energetically favorable reaction to have a net negative delta G.
15
New cards
What is a key secondary active transporter in most living cells? How does it work?
The sodium-glucose symporter.
Works by coupling the energetically favorable movement of Na+ into a cell with the energetically unfavorable movement of glucose into a cell.
Works by coupling the energetically favorable movement of Na+ into a cell with the energetically unfavorable movement of glucose into a cell.
16
New cards
For an uncharged ion, ΔG = ?
ΔG = RT * ln(C2/C1)
Where:
R = ideal gas constant, 8.314 J/mol*K
T = temperature, K
C2/C1 = ratio of final conc : initial conc
Where:
R = ideal gas constant, 8.314 J/mol*K
T = temperature, K
C2/C1 = ratio of final conc : initial conc
17
New cards
For a charged ion, ΔG = ?
ΔG = RT * ln(C2/C1) + ZF(ΔV)
Where:
R = ideal gas constant, 8.314 J/mol*K
T = temperature, K
C2/C1 = ratio of final conc : initial conc
Z = charge of ion
F = Faraday's constant, 96480 J/mol*V
ΔV = membrane potential, V
Where:
R = ideal gas constant, 8.314 J/mol*K
T = temperature, K
C2/C1 = ratio of final conc : initial conc
Z = charge of ion
F = Faraday's constant, 96480 J/mol*V
ΔV = membrane potential, V
18
New cards
For movement across a membrane, rate of transport Vo = ?
Remember Michaelis-Menten equation for enzyme kinetics.
Vo = Vmax * [Sout] / (Kt + [Sout])
Vo = Vmax * [Sout] / (Kt + [Sout])
19
New cards
What are the 3 hallmarks of passive transport?
1. High rates of diffusion down a concentration gradient.
2. Saturability: conformational changes occur.
3. Stereospecificity: there is a very specific binding site.
2. Saturability: conformational changes occur.
3. Stereospecificity: there is a very specific binding site.
20
New cards
What's the difference between ion channels and ion transport?
Channels have much higher rates of diffusion, because they are only gated and do not depend on conformational changes. Thus, they are not saturable. It is like a bottomless water cup with a lid as a "gate."
Transporters on the other hand have lower rates of diffusion, because they have a capacity; that is to say, they are saturable. This is because they rely on conformational changes that occur when their substrate binds to move across the membrane.
Transporters on the other hand have lower rates of diffusion, because they have a capacity; that is to say, they are saturable. This is because they rely on conformational changes that occur when their substrate binds to move across the membrane.
21
New cards
Describe 6 examples/methods of passive transport.
Chloride-bicarbonate exchanger
ionophore
aquaporin
ion channels
ion transporters
GLUT(1-4)-transporters
ionophore
aquaporin
ion channels
ion transporters
GLUT(1-4)-transporters
22
New cards
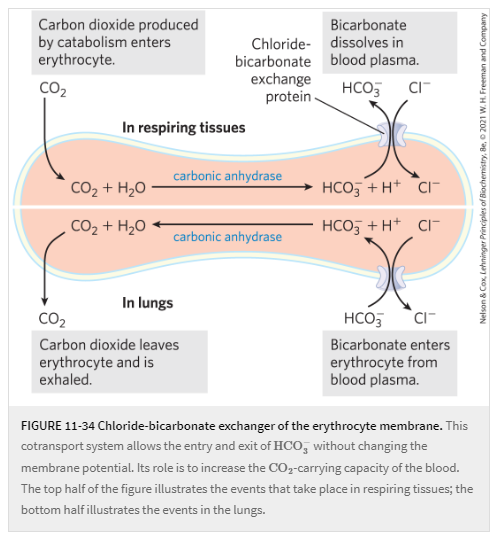
Describe the function and method of the Chloride-Bicarbonate Exchanger.
Is it passive or active transport? Why?
Is it uni/sym/anti-port?
Is it passive or active transport? Why?
Is it uni/sym/anti-port?
Function: Antiport passive exchange of anions across a plasma membrane.
Specifically, bicarbonate (HCO3-) and Chloride (Cl-) are moved antiport to one another, both along their concentration gradient.
Method: Tissues
>CO2 from metabolism enters the cell.
>Cell doesn't want CO2 bubbles, so it converts CO2 to HCO3-. (via carbonic anhydrase)
>HCO3- needs to travel to the blood because it is a pH buffer.
>HCO3- travels to Chloride-Bicarbonate Exchange protein.
>Coupled with H+, HCO3- exchanges with Cl-
Specifically, bicarbonate (HCO3-) and Chloride (Cl-) are moved antiport to one another, both along their concentration gradient.
Method: Tissues
>CO2 from metabolism enters the cell.
>Cell doesn't want CO2 bubbles, so it converts CO2 to HCO3-. (via carbonic anhydrase)
>HCO3- needs to travel to the blood because it is a pH buffer.
>HCO3- travels to Chloride-Bicarbonate Exchange protein.
>Coupled with H+, HCO3- exchanges with Cl-
23
New cards
What is an ionophore?
A small, amphipathic, and cyclic peptide that binds small ions.
It masks the ion's charge due to its charged interior, but it has an uncharged exterior.
Because it's a pretty small molecule, it effectively converts the ion to a nonpolar molecule and it's able to simply diffuse across membranes.
It masks the ion's charge due to its charged interior, but it has an uncharged exterior.
Because it's a pretty small molecule, it effectively converts the ion to a nonpolar molecule and it's able to simply diffuse across membranes.
24
New cards
What is an aquaporin?
Aqua = water, Porin = pore = tunnel
Water tunnel; aquaporins are essentially just channels across membranes that allow the free flow of water molecules across, reaching rates of transfer that approach free diffusion
Rate: 10^9 s^-1
Water tunnel; aquaporins are essentially just channels across membranes that allow the free flow of water molecules across, reaching rates of transfer that approach free diffusion
Rate: 10^9 s^-1
25
New cards
Briefly describe GLUT1, in both structure and function.
>What type of transport is it; what is it specific to; where does it transport?
>Describe characteristic structural features.
>What is it stabilized by?
>What type of transport is it; what is it specific to; where does it transport?
>Describe characteristic structural features.
>What is it stabilized by?
GLUT1 is a passive transporter that moves glucose into blood cells from blood plasma. "Supplies glucose to erythrocytes" -the book
It also is important for moving glucose across the blood brain barrier.
It is specific to D-glucose
Structurally, it's comprised of 12 hydrophobic transmembrane segments. These segments are hydrophobic on their exterior (where they contact the nonpolar lipid interior of the membrane) but hydrophilic on the interior (the tunnel where glucose travels through).
Overall, the entire structure is stabilized by the hydrophobic effect.
It also is important for moving glucose across the blood brain barrier.
It is specific to D-glucose
Structurally, it's comprised of 12 hydrophobic transmembrane segments. These segments are hydrophobic on their exterior (where they contact the nonpolar lipid interior of the membrane) but hydrophilic on the interior (the tunnel where glucose travels through).
Overall, the entire structure is stabilized by the hydrophobic effect.
26
New cards
Briefly describe GLUT2's function.
GLUT2 is is a passive uniport transporter that facilitates the downhill diffusion of glucose in intestinal, liver, and kidney cells.
27
New cards
Describe how the Na+-glucose symporter works together with GLUT2 and the Na+K+ ATPase. Describe what types of transport each of these transporters are.
Na+-glucose transporter: Secondary active transport
GLUT2: Passive transport (facilitated diffusion)
Na+K+ ATPase: P-type ATPase (Primary active transport)
From the intestinal lumen, glucose enters the cell via the Na+-glucose symporter.
The glucose leaves the cell and into the blood plasma via GLUT2, down its concentration gradient.
The Na+ leaves the cell via the Na+K+ ATPase, exchanging 2Na+ out for 3K+ in (leaving the inside of the cell more acidic)
GLUT2: Passive transport (facilitated diffusion)
Na+K+ ATPase: P-type ATPase (Primary active transport)
From the intestinal lumen, glucose enters the cell via the Na+-glucose symporter.
The glucose leaves the cell and into the blood plasma via GLUT2, down its concentration gradient.
The Na+ leaves the cell via the Na+K+ ATPase, exchanging 2Na+ out for 3K+ in (leaving the inside of the cell more acidic)