MCDB 436 (12): Intracellular Signaling (II)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
transcription factors
proteins that regulate the transcription of genes
- turn on/off specific genes by binding to the DNA
- activator+enhancer and repressor+silencer
- turn on/off specific genes by binding to the DNA
- activator+enhancer and repressor+silencer
2
New cards
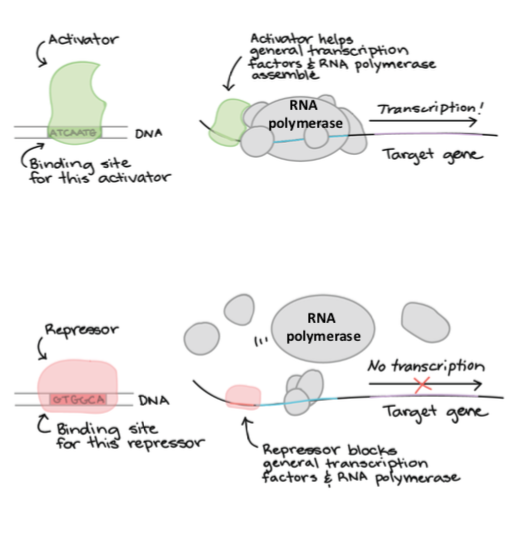
activators
bind to enhancer; activate the downstream gene expression. binds with specific DNA sequences and recruits RNA polymerase or other activators/protein complexes to make RNA
3
New cards
repressors
bind to silencers; TF acts as a repressor to prevent downstream transcription
4
New cards
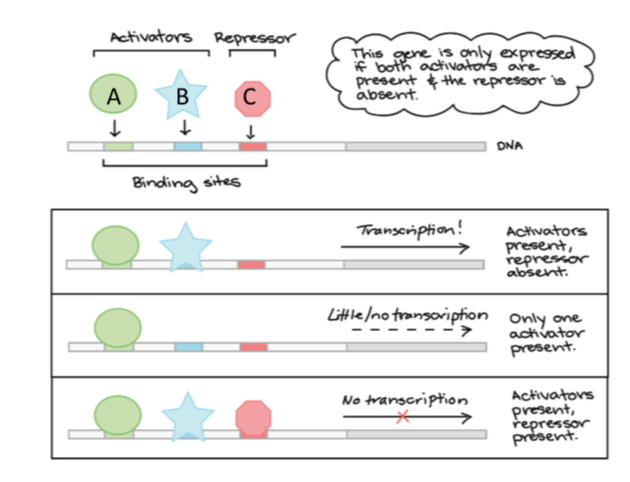
combinatorial regulation
TFs need to bind in a specific combination to turn on/off gene expression
- use of multiple TFs to regulate a gene means that different sources of info can be integrated into a single outcome
- use of multiple TFs to regulate a gene means that different sources of info can be integrated into a single outcome
5
New cards
NFkB TFs
central regulators of innate and adaptive immune functions; consist of NFkB1, NFkB2, ReIA, ReIB, and c-Rel
6
New cards
NFkB1 and NFkB2
p50/p52; lack transcriptional activation domains; their homodimers act as repressors
7
New cards
Rel-A, Rel-B, c-Rel
carry transcriptional activation domains
- can form homo- and heterodimers with other members of Rel (except Rel-B)
- can form homo- and heterodimers with other members of Rel (except Rel-B)
8
New cards
activation of NFkB signaling pathway
most common inducible NFkB binding activity: p50/p65 homodimers (NFkB1 and RelA)
- unstimulated cell: NfkB dimers inactive in cytoplasm because of IkB (kB inhibitors)
- ligand binding (TNFa, IL-1, CD40L, LPS) -> begin recruitment and activation of IKKs -> phosphorylate IkB -> degradation of IkB by ubiquitin -> NFkB activation
- unstimulated cell: NfkB dimers inactive in cytoplasm because of IkB (kB inhibitors)
- ligand binding (TNFa, IL-1, CD40L, LPS) -> begin recruitment and activation of IKKs -> phosphorylate IkB -> degradation of IkB by ubiquitin -> NFkB activation
9
New cards
IKKs
IkB kinases; phosphorylate IkB to signal for ubiquitin degradation, allowing for NFkB activation
10
New cards
IkB
kB inhibitors; present in unstimulated cells on NFkB dimers
11
New cards
NFkB - epithelial cells
IL-8, adhesion molecules, IL1, IL2, TNFa, IL-12
- important components of innate immune response to invading microorganisms; required for ability of inflammatory to migrate where NFkB is activated
- important components of innate immune response to invading microorganisms; required for ability of inflammatory to migrate where NFkB is activated
12
New cards
T-bet
immune cell-specific member TF
- induced in T cells (with many methods)
- induced in B cells through STAT1 after BcR and/or IFNyR ligation
regulates TH1 differentiation; balances terminal differentiation and memory cell potential in CD4 and CD8 T cells; in CD8, prevents cell exhaustion
- induced in T cells (with many methods)
- induced in B cells through STAT1 after BcR and/or IFNyR ligation
regulates TH1 differentiation; balances terminal differentiation and memory cell potential in CD4 and CD8 T cells; in CD8, prevents cell exhaustion
13
New cards
immune receptor types
- Ig: ligand binding
- transmembrane signaling protein: with ITAM/ITIMs, proximity to Src family kinase
- transmembrane signaling protein: with ITAM/ITIMs, proximity to Src family kinase
14
New cards
ITAMs
activating tyrosine containing motif attached to cytoplasmic tails of transmembrane signaling proteins
contains TWO tyrosine residues
contains TWO tyrosine residues
15
New cards
ITIMs
inhibiting tyrosine containing motif attached to cytoplasmic tails of transmembrane signaling proteins
16
New cards
TcR complex
- signaling: initiated by ITAMs in CD3 epsilon, gamma, delta, and zeta (3) chains - 10 total
- motif also on BcR, NKcR
- motif also on BcR, NKcR
17
New cards
CD4 and CD8
- CD8: alpha-beta heterodimer (or alpha-alpha), each contains one Ig domain
- CD4: monomeric, contains 4 Ig domains
- cytplasmic tail binds to Lck
- CD4: monomeric, contains 4 Ig domains
- cytplasmic tail binds to Lck
18
New cards
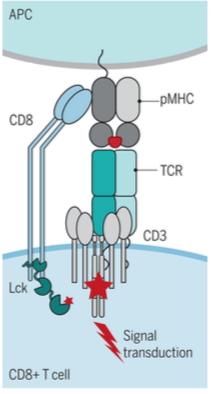
Lck
mediates ITAM phosphorylation and downstream transcription regulation
- Src family kinase
- attached to CD4 and CD8 cytoplasmic tails
- Src family kinase
- attached to CD4 and CD8 cytoplasmic tails
19
New cards
ITAM phosphorylation pathway
TcR and co-receptor brought together by binding to peptide:MHC complexes ->
recruit Lck (on CD4/8 tail) ->
phosphorylation of ITAMs in CD3 chains (y, d, e, z) ->
recruit PTKs + ZAP-70 ->
ZAP-70 binds to phosphorylated ITAMs through SH2 domains ->
enables ZAP-70 phosphorylation and Lck activation ->
phosphorylates SLP-76 and Lat ->
joined by Gads to create LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex ->
downstream effects
recruit Lck (on CD4/8 tail) ->
phosphorylation of ITAMs in CD3 chains (y, d, e, z) ->
recruit PTKs + ZAP-70 ->
ZAP-70 binds to phosphorylated ITAMs through SH2 domains ->
enables ZAP-70 phosphorylation and Lck activation ->
phosphorylates SLP-76 and Lat ->
joined by Gads to create LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex ->
downstream effects
20
New cards
ZAP-70
PTK Syk family protein associated with the zeta chain of CD3
phosphorylates LAT and SLP-76
phosphorylates LAT and SLP-76
21
New cards
ITAM:SH2 domains
ITAM has 2 tyrosine residues, providing sites for recruitment of SH2 domains - such as ZAP-70
22
New cards
ZAP-70 phosphorylation + LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex
phosphorylates LAT and SLP-76; linked by Gads
LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex
1) Akt activation -> increased cellular metabolic activity
2) PLC-gamma activation -> TF activation
3) Vav activation -> actin polymerization and cytoskeletal reorganization
4) ADAP recruitment -> enhanced integrin adhesiveness and clustering
LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex
1) Akt activation -> increased cellular metabolic activity
2) PLC-gamma activation -> TF activation
3) Vav activation -> actin polymerization and cytoskeletal reorganization
4) ADAP recruitment -> enhanced integrin adhesiveness and clustering
23
New cards
LAT
linker for activated T cells; transmembrane protein with large cytoplasmic domain (scaffold proteins)
- multiple docking sites; can serve as a docking site for other proteins
- multiple docking sites; can serve as a docking site for other proteins
24
New cards
PLC-gamma signaling
splits into
1) stimulation of Ca2+ entry
2) activation of Ras
3) activation of protein kinase C (PKC)
1) stimulation of Ca2+ entry
2) activation of Ras
3) activation of protein kinase C (PKC)
25
New cards
PLCgamma1 - Ca2+ and PKC signaling pathway
Lck -> ZAP-70 -> LAT -> PLCgamma1 -> PIP2 breakdown
1) IP3 -> Ca2+ -> stimulates STIM1, CRAC/ORAI1, calmodulin (CaM), calcineurin (CaM-dependent protein phosphatase), NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells)
2) DAG -> PKC, NFkB, Ras
1) IP3 -> Ca2+ -> stimulates STIM1, CRAC/ORAI1, calmodulin (CaM), calcineurin (CaM-dependent protein phosphatase), NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells)
2) DAG -> PKC, NFkB, Ras
26
New cards
ORAI1
plasma membrane calcium channel (aka Ca release-activated Ca channel)
PLC-gamma -> catalyze PIP2 breakdown -> DAG + IP3 -> less ER Ca2+ -> STIM1 binds to ORAI1 -> Ca2+ enters cytosol from ECF
PLC-gamma -> catalyze PIP2 breakdown -> DAG + IP3 -> less ER Ca2+ -> STIM1 binds to ORAI1 -> Ca2+ enters cytosol from ECF
27
New cards
DAG
confined to the membrane; product of PIP2 by PLC-gamma catalyzation
- diffuses in the plane of the membrane and serves as a molecular target that recruits other signaling molecules to the membrane
- diffuses in the plane of the membrane and serves as a molecular target that recruits other signaling molecules to the membrane
28
New cards
IP3
diffuses into the cytosol; product of PIP2 by PLC-gamma catalyzation
- binds to IP3 receptors on ER
- binds to IP3 receptors on ER
29
New cards
STIM1
transmembrane protein that clusters in the ER membrane as a result of low Ca2+ in the ER
- binds to ORAI1 -> Ca2+ channel opening -> Ca2+ enters cytosol from ECF
- binds to ORAI1 -> Ca2+ channel opening -> Ca2+ enters cytosol from ECF
30
New cards
NFAT
nuclear factor of activated T cells; regulated by Ca2+ signaling
1) phosphorylation on Ser and Thr residues keep NFAT in cytoplasm of unstimulated cells
2) Ca2+ entry activates Ser/Thr phosphatase calcineurin -> dephos's NFAT
3) dephos'd NFAT enters nucleus -> activate gene transcription
inhibited by cyclosporin A and FK506
1) phosphorylation on Ser and Thr residues keep NFAT in cytoplasm of unstimulated cells
2) Ca2+ entry activates Ser/Thr phosphatase calcineurin -> dephos's NFAT
3) dephos'd NFAT enters nucleus -> activate gene transcription
inhibited by cyclosporin A and FK506
31
New cards
Ras activation and MAPK pathway
Lck -> mediate ITAM phos -> ZAP-70 + LAT -> Grb2 + SOS (adaptor protein) -> Ras activation -> MAPK cascade -> AP-1
32
New cards
AP-1
transcription heterodimer composed of c-Fos and c-Jun
- participates in turning on transcription of many genes important for T-cell activation (ex: IL-2)
- participates in turning on transcription of many genes important for T-cell activation (ex: IL-2)
33
New cards
T cell signaling process
- receptor-ligand binding
- dimerize (cross-link or conformational change)
- signaling pathways
- activate transcription factors
- translocation to nucleus
- affect gene transcription
- dimerize (cross-link or conformational change)
- signaling pathways
- activate transcription factors
- translocation to nucleus
- affect gene transcription
34
New cards
T cell transcription factors
NFkB, NFAT, AP-1
35
New cards
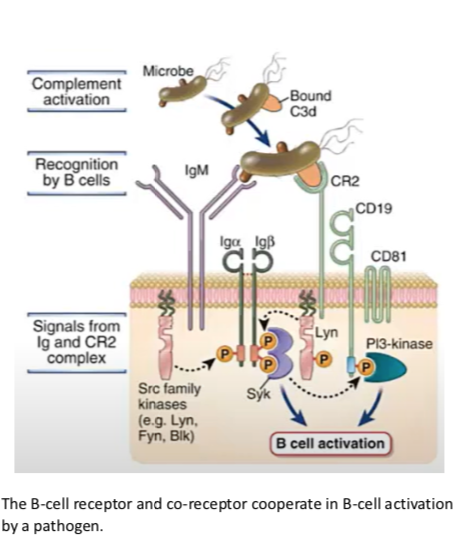
B cell signaling
BCR complex with co-receptor
- cross-linking of BCR; co-receptor of BCR; phosphorylation of ITAMs tyrosines by Src-family kinases (Lyn, Fyn, Blk)
- include adaptors and scaffold proteins
- PLC-gamma activation -> IP3 -> Ca2+ dependent enzymes
+ DAG -> PKC
- Ras pathway -> ERK, JNK
- cross-linking of BCR; co-receptor of BCR; phosphorylation of ITAMs tyrosines by Src-family kinases (Lyn, Fyn, Blk)
- include adaptors and scaffold proteins
- PLC-gamma activation -> IP3 -> Ca2+ dependent enzymes
+ DAG -> PKC
- Ras pathway -> ERK, JNK
36
New cards
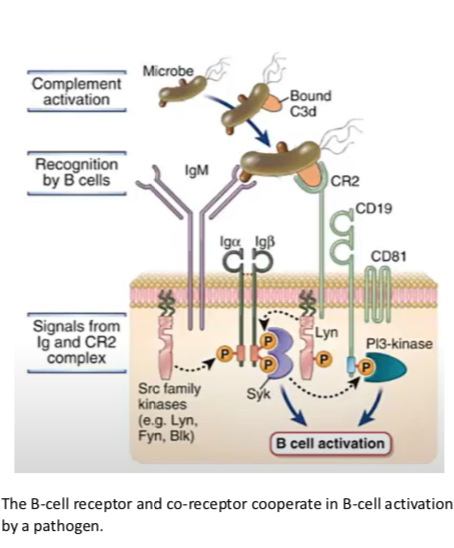
BCR complex
CR2-CD19-CD81 (C3d fragment attached to Ag)
cytoplasmic tail recruits Src family kinase; NOT Lck
cytoplasmic tail recruits Src family kinase; NOT Lck
37
New cards
B cell transcription factors
Myc, NFAT, NFkB, AP-1
38
New cards
co-stimulatory receptors
modulate Ag receptor signaling
- naive T: CD28
- naive T: TNFr CD40
- goal: enhance Ag receptor signals -> PI3K activation -> PIP3 -> T&B cell activation
- naive T: CD28
- naive T: TNFr CD40
- goal: enhance Ag receptor signals -> PI3K activation -> PIP3 -> T&B cell activation
39
New cards
CD28 signaling
CD28 with CD80/86 -> PI3-kinase -> PIP3 ->
(1) recruit PDK1 to phosphorylate and activate Akt
(2) recruit Itk to phosphorylate PLC-gamma
(3) recruit Vav -> Cdc24 activation
(1) recruit PDK1 to phosphorylate and activate Akt
(2) recruit Itk to phosphorylate PLC-gamma
(3) recruit Vav -> Cdc24 activation
40
New cards
CTLA-4
inhibitory receptor signal competing for CD80/86 over CD28
- induced on activated T cells
- function controlled largely by regulation of its surface expression
- induced on activated T cells
- function controlled largely by regulation of its surface expression
41
New cards
PD-1
programmed death-1; inhibitory T cell receptor
42
New cards
BTLA
B and T lymphocyte attenuator; inhibitory receptor on T and B cells
43
New cards
Ag-receptor signaling pathways - summary
tyrosine kinases -> adaptors and scaffold proteins -> phospholipases and lipid kinases -> GTPases, ser/thr kinases, phosphatases -> TFs, cytoskeletal changes, adhesion, metabolism
44
New cards
cytokine receptors
- type I: hematopoietin family
- type II: IFN family
- TNFr family
- IL-1R family: Ig superfamily
- chemokine receptors: GPCR
- type II: IFN family
- TNFr family
- IL-1R family: Ig superfamily
- chemokine receptors: GPCR
45
New cards
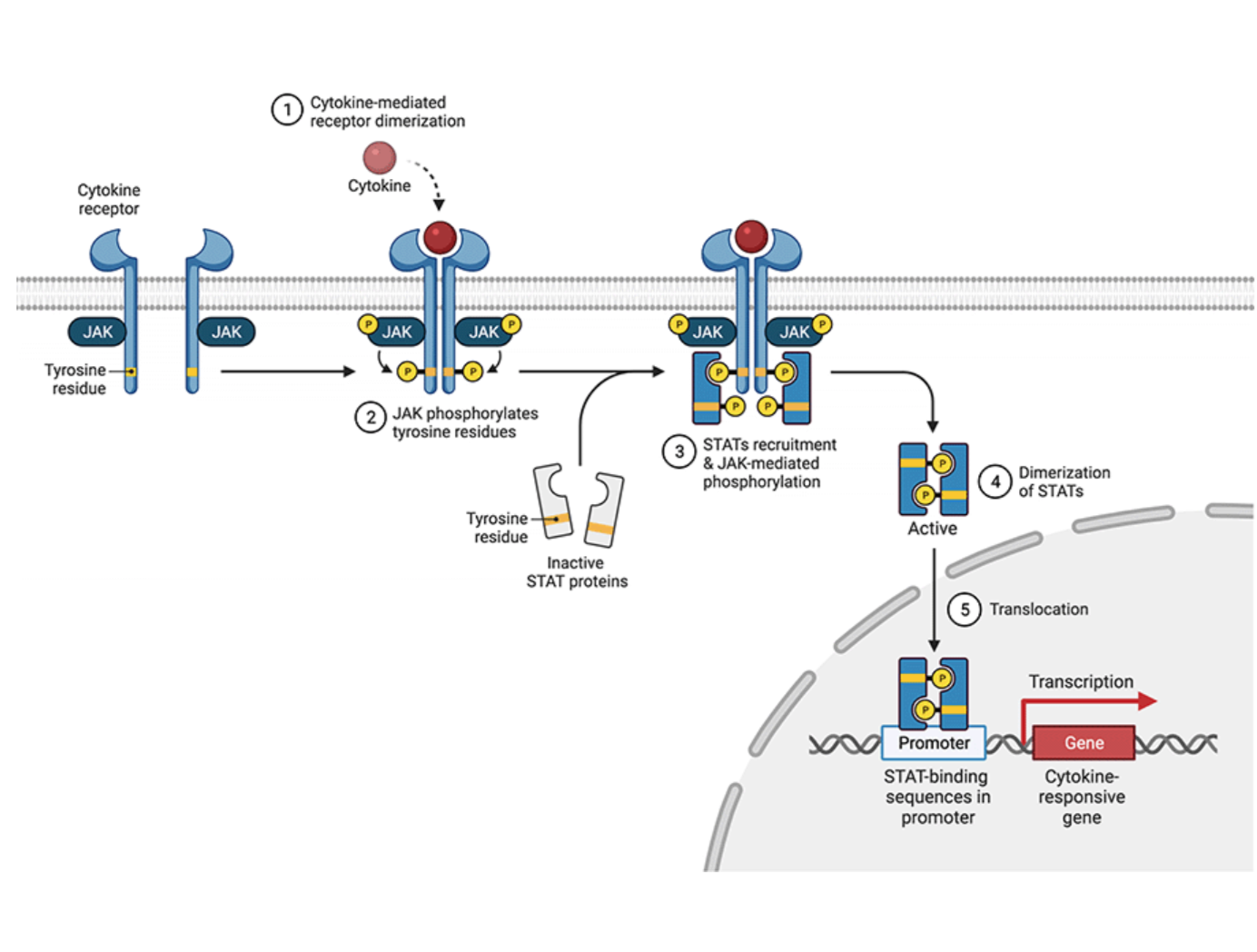
JAK-STAT signaling
JAK = signal transducer
STAT = transcription activator
1) cytokine-mediated receptor dimerization
2) JAK phosphorylates tyrosine residues of cytokine receptor
3) STATs recruitment and JAK-mediated phosphorylation
4) dimerization of STATs
5) translocation into nucleus
STAT = transcription activator
1) cytokine-mediated receptor dimerization
2) JAK phosphorylates tyrosine residues of cytokine receptor
3) STATs recruitment and JAK-mediated phosphorylation
4) dimerization of STATs
5) translocation into nucleus
46
New cards
JAK-STAT signaling in the immune system
- abnormal signaling = immune disorders
- regulated at different steps, such as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins, protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) proteins, and protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP)
- also regulated by post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, ubiquitylation)
- regulated at different steps, such as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins, protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) proteins, and protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP)
- also regulated by post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, ubiquitylation)
47
New cards
STAT1 and STAT4
TH1 cell differentiation
IFN-gamma -> STAT1 -> T-bet -> TH1
IL-12 -> STAT4 -> T-bet -> TH1
IFN-gamma -> STAT1 -> T-bet -> TH1
IL-12 -> STAT4 -> T-bet -> TH1
48
New cards
STAT6
TH2 cell differentiation
IL-4 -> STAT6 -> GATA-3 -> TH2
IL-4 -> STAT6 -> GATA-3 -> TH2