EEB2244E Final
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
295 Terms
fragmentation
asexual reproduction: organism splits into two mature individuals
adiabatic cooling
warm air rises, expands, cools holds less water vapor so it rains (equator/ITCZ)
tropical rainforest biome
- annual temp >20C
- ITCZ (equator)
- biodiverse
- poor soil (rapid cycling nutrients)
temperate rainforest biome
- annual temp 5-20C
- wet
boreal forest biome
- annual temp
climate envelope
suitable climate conditions constraining a species geographic range
sequential hermaphrodites
animals where one sex functions then switches to the other through physiological transformation; takes days, irreversible
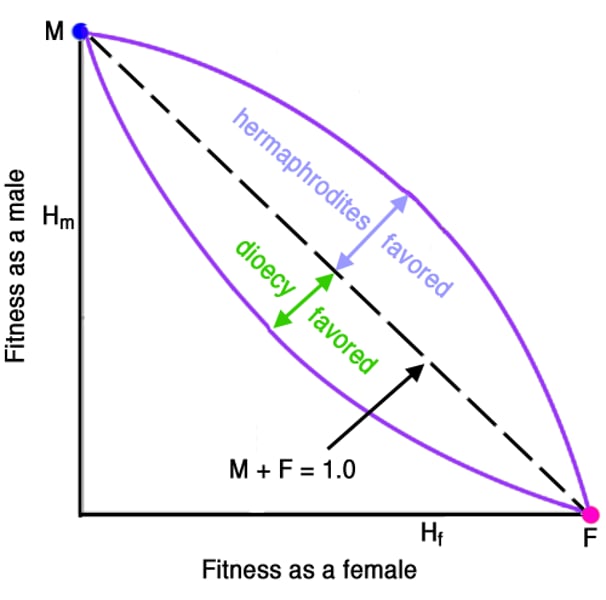
Hermaphrodism occurs when
cost of reproductive failure > cost of producing male and female functions
monogamy
- one male, one female; serial or life long
- favored by equal parental contribution, even resource distribution, inability to monopolize >1 female
social behavior: altruism
(-,+) cost to donor, benefit to recipient; does not lead to direct fitness
apparent competition
impacts resembling competition but not due to shared resources
- shared predator or parasite
time delays in population cycles
- τ
- degree of cycling=r*τ
- period of cycle=4τ
- between breeding and offspring addition (gestation)
- storage of resources
- anything causing population growth to be impacted by density in the past
true predators
consume whole, live animals or plants: mostly carnivores, seed-predators, and filter feeders; short association, many victims
Batesian mimicry
harmless organism looks like harmful one; mimic benefits, model does not
Mullerian mimicry
two or more distasteful or poisonous species come to resemble one another; all poisonous
infection resistance
the ability of a host to prevent an infection from occurring
hydrologic cycle
movement of water through ecosystems and atmosphere, driven by evaporation, transpiration, precipitation
phosphate cycle: aquatic
- phosphate assimilated and excreted/decomposed
- phosphate precipitates and forms sediment
- sedimentary rock is later uplifted moving phosphate back to terrestrial systems
circulation in ponds and lakes
- summer stratification: surface water heats up and floats
- autumn overturn: surface water cools and sinks
- winter stratification: surface freezes and floats, 4C water densest at bottom
- spring overturn: surface water warms to 4C and sinks
*4C water densest
wetland biomes
- freshwater: swamps (emergent trees), marshes (emergent non-woody vegetation), bogs (acidic water, low nutrients)
- saltwater: marshes (non-woody vegetation, highly productive) and mangrove swamps (salt tolerant trees, roots in water, prevent erosion) estuaries
detrivores
break down dead organic matter (detritus)
microcosm
isolated community; manipulative study; has control and treatment
solar equator vs geographic equator
- solar equator: latitude receiving direct sun rays
- geographic equator: 0 degrees latitude
- solar equator at geographic equator on equinoxes, at 23.5N (Tropic of Cancer) on June solstice, at 23.5S (Tropic of Capricorn) on December solstice
adiabatic heating
cool air sinks, condenses, warms holds more water vapor so its dry (30*N/S)
Hadley cells
atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at 30° N/S
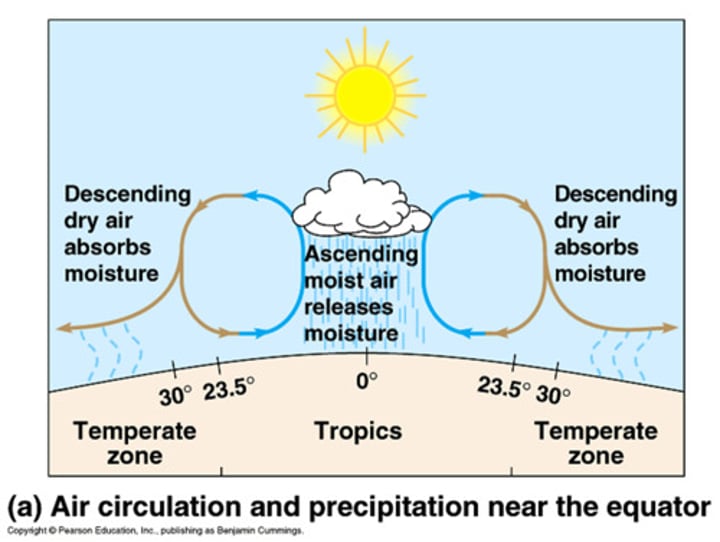
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
solar equator where Hadley cells meet
trade winds, westerlies, and easterlies
- global winds caused by Hadley cells, Ferrel cells, Polar cells
- wet at 0, dry at 30N/S
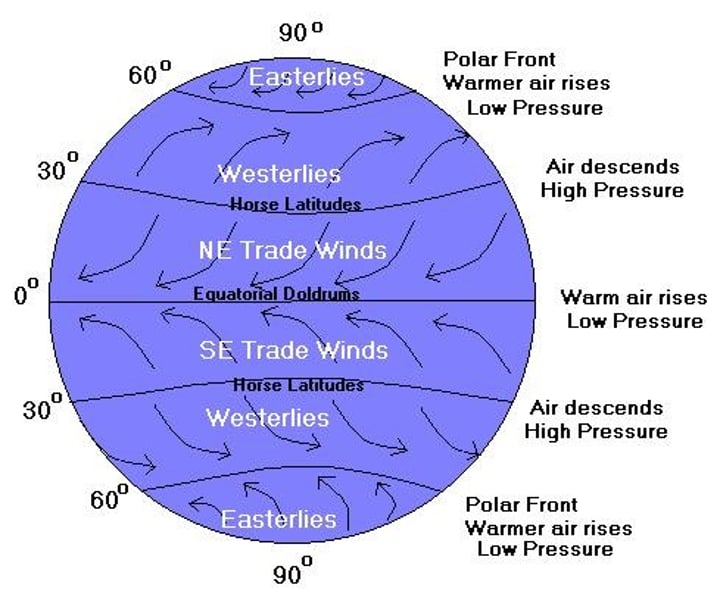
Coriolis effect
Causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere
ocean gyres
- gravity pulls water away from equator
- clockwise in N hemisphere, counterclockwise in S hemisphere
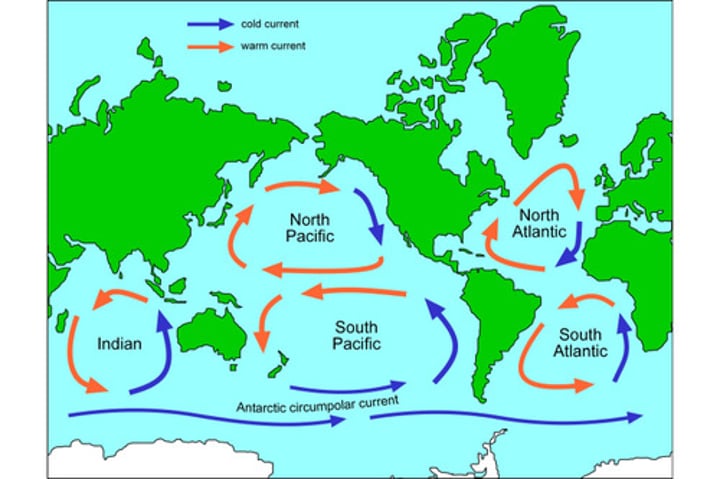
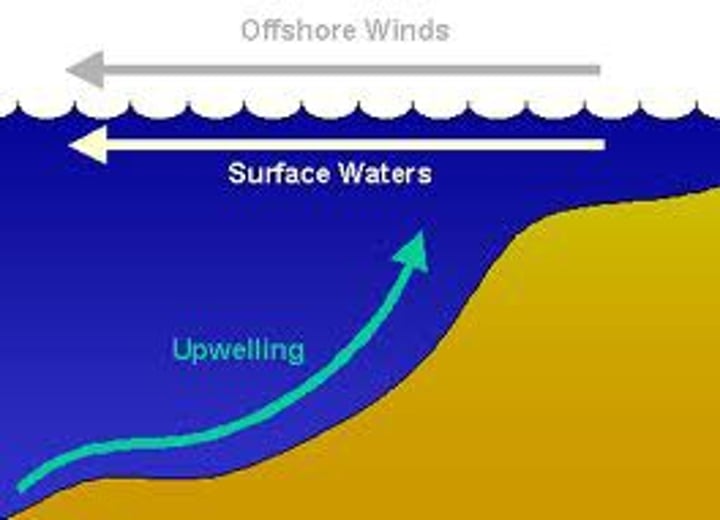
ocean upwelling
upward movement of ocean water where surface currents move away from western coastlines; cold high nutrient water brought to the surface of west coasts = high productivity
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
every 3-7 years trade winds reverse/oscillate causing warm water to move in opposite direction and cold water upwelling to be opposite
maritime vs continental climates
maritime more stabilized (less seasonal temp variation) and higher rainfall
continental more extreme variation and lower rainfall
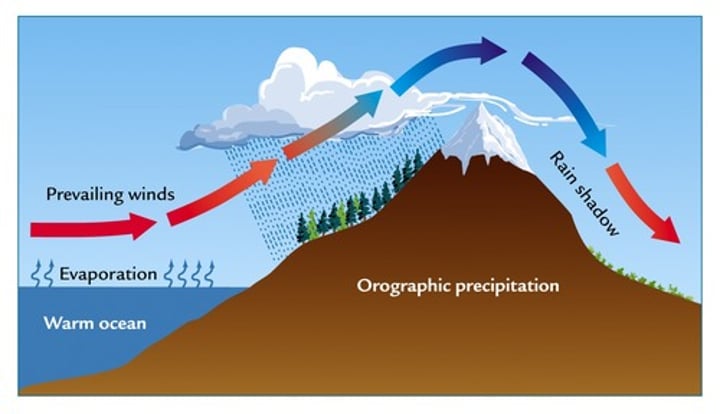
rain shadow effect
wet, warm air moves up windward side of mountain causing cooling air and rain, air falls down leeward side of mountain absorbing moisture as it warms drying the land
tropical seasonal forest/savanna biome
- consistently >20C
- very seasonal precipitation
subtropical desert biome
- annual temp >20C
- dry
- not seasonal
- low plant life
woodland biome
- annual temp 5-20C
- dry summers
temperate seasonal forest biome
- annual temp 5-20C
- acidic soil
- trees lose leaves
- seasonal precipitation
cold desert/temperate grassland biome
- annual temp 5-20C
- dry season
tundra biome
- annual temp
soil determining factors
- climate
- organisms
- relief (topography)
- parent material (bedrock)
- time
soil layers
O: organic matter
A: broken down organic material, fine rock
E: leached inorganic material
B: weathered rock, inorganic materials
C: less weathered, large parent rock
R: bedrock
exponential growth model
- continuous population growth, unlimited resources
- Nt=N0e^rt
- r=growth rate=births-deaths
geometric growth model
- seasonal population growth, unlimited growth
- Nt=N0λ^t
- λ=e^r
- lnλ=r
- doubling time=time it takes to double population=t2=ln2/r
negative density dependence
increase in population density causes decrease in population growth
- due to competition
positive density dependence
decrease in population density causes decrease in population growth
- Allee effect
- due to not being able to find mate or poor foraging
optimal population growth
- K/2
- population growing at highest rate
logistic model
- population growth model with limited resources and competition
- dN/dt=rN(1-N/K)
- K=carrying capacity
- inflection pt=max dN/dt= when N=K/2
survivorship curves
- Type I: high mortality late in life
- Type II: constant mortality (birds)
- Type III: high mortality early in life (oak tree)
cohort approach
follow a group of same aged individuals through lives
- sessile organisms
static approach
count all individuals of all ages at a point in time
- mobile and long lived organisms
- must be able to identify organisms
competitive exclusion
species with same niche cannot coexist
fundamental niche vs realized niche
- fundamental niche: range of abiotic conditions species can exist
- realized niche: range of abiotic and biotic conditions a species can exist; includes competition
endemic
species that is only found in a small area
capture mark recapture
capture and mark a number of animals (M), release, recapture a number of animals (n), record number with marks (x)
- M/N=x/n
clustered dispersion
- due to clustered resources, social behavior, limited dispersal
- V/M>1
evenly spaced dispersion
- due to depleted resources, competition, territoriality
- V/M
random dispersion
- no deterministic processes
- position of organisms independent of each other
- V/M=1
dispersal
movement of individual from one area to another
dispersal limitation
species limited geographically because it cannot physically get to another suitable area and no other factors
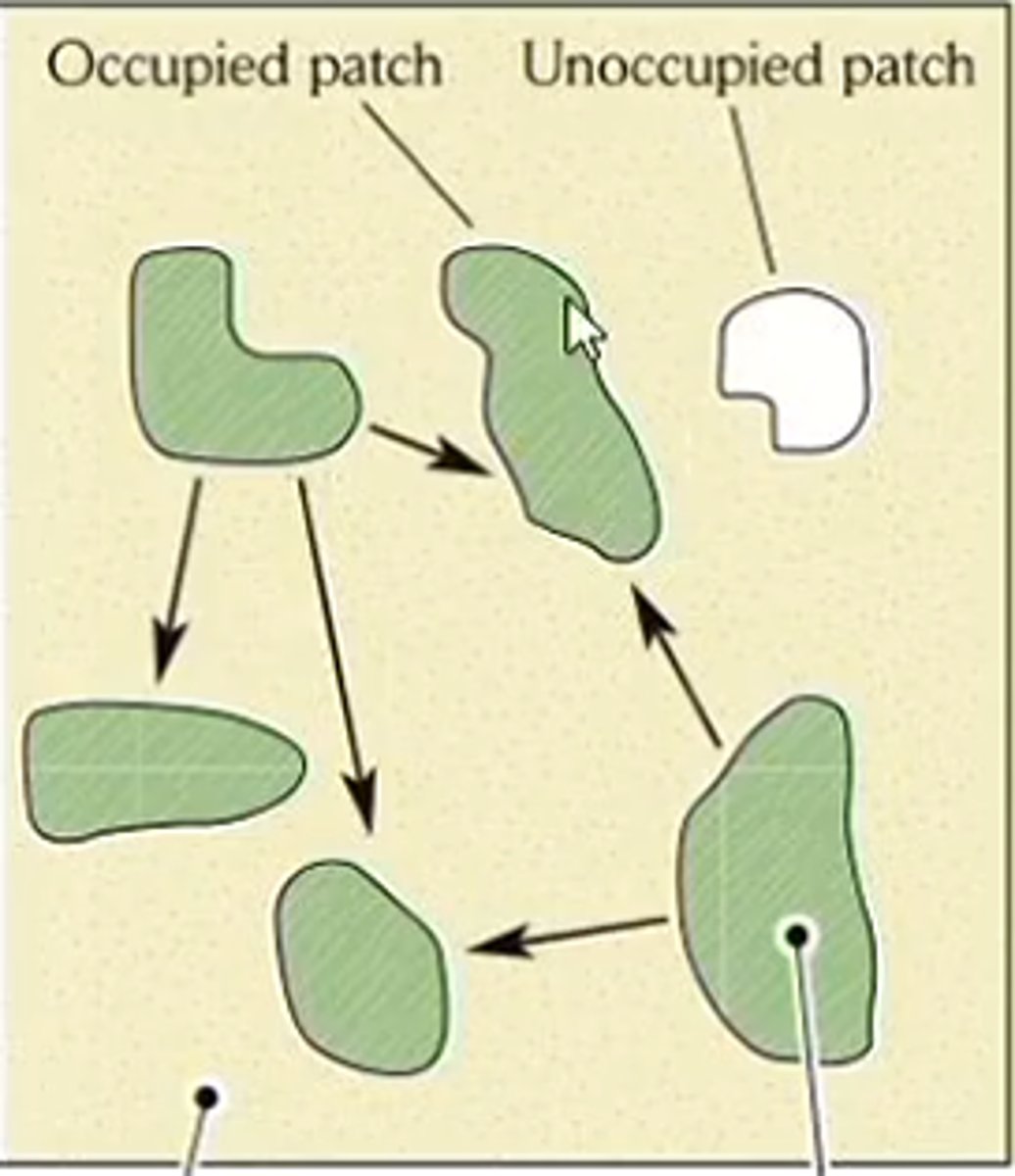
population structure
subdivision of organisms into subpopulations living in suitable habitat patches of habitat surrounded by matrix
basic metapopulation model
suitable habitat patches of equal quality embedded within matrix
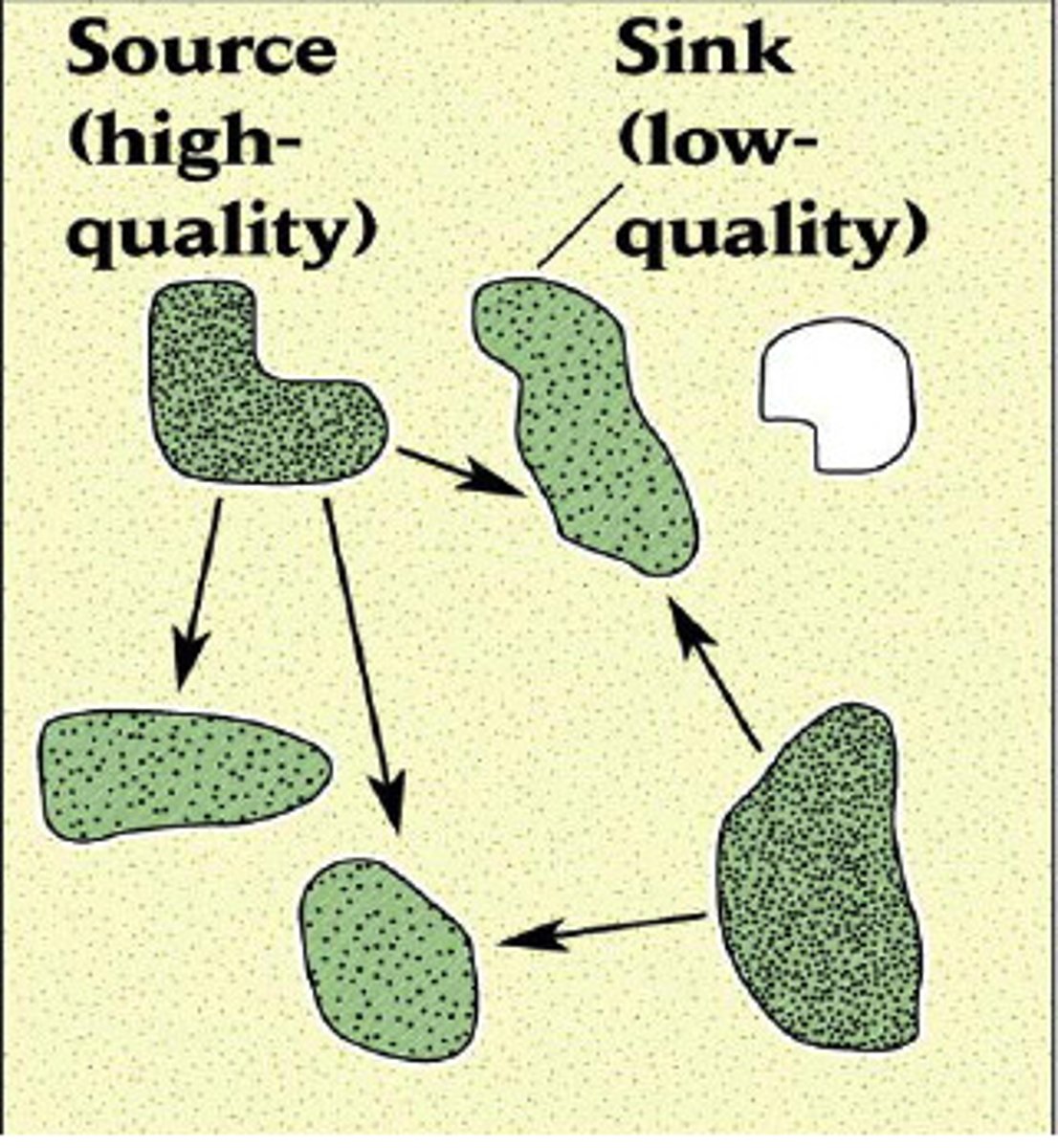
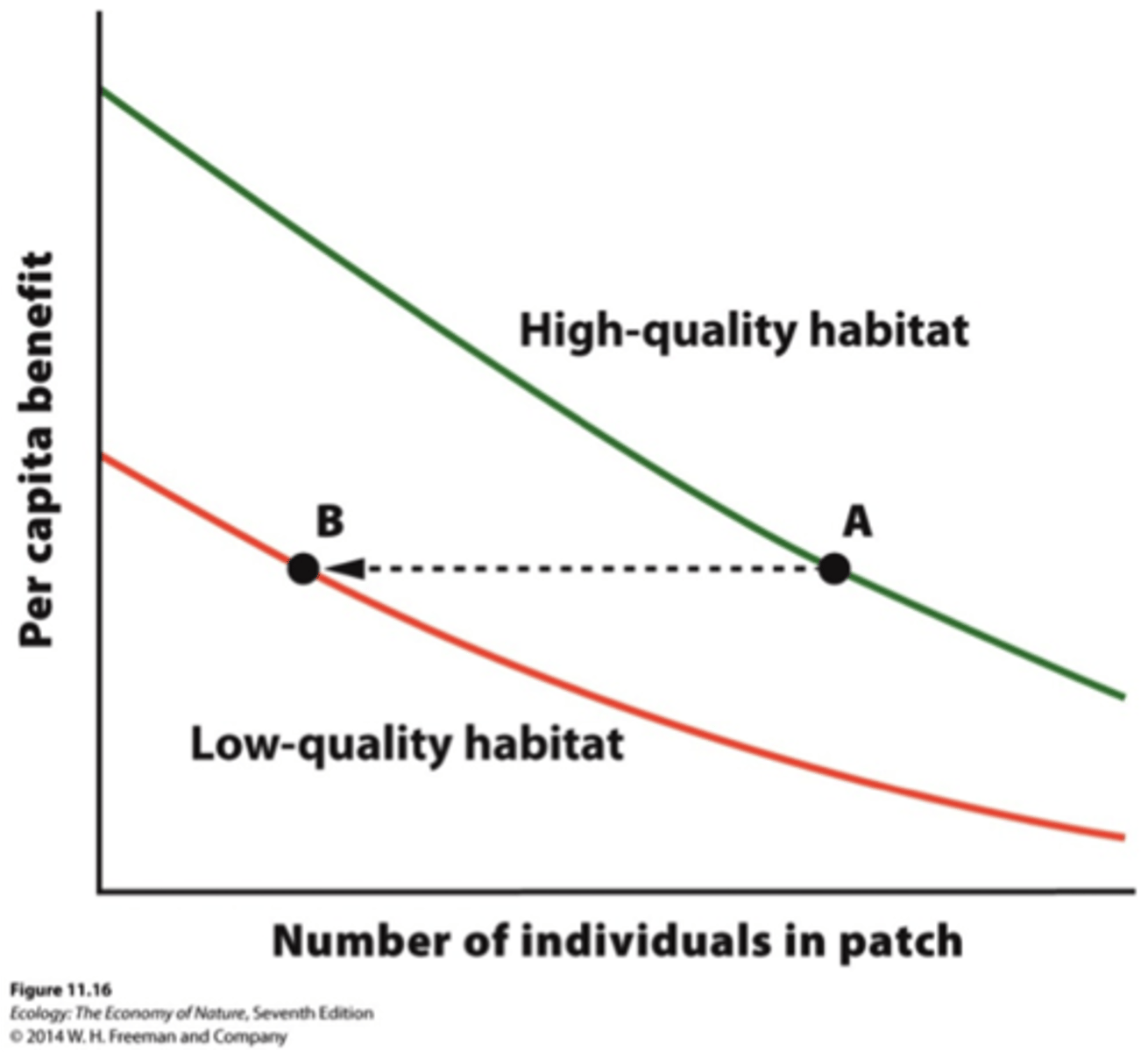
source-sink model
- source: high quality habitat, self sustaining, provides dispersers
- sink: low quality habitat, rely on dispersers
landscape model
variation in matrix quality and habitat conductivity
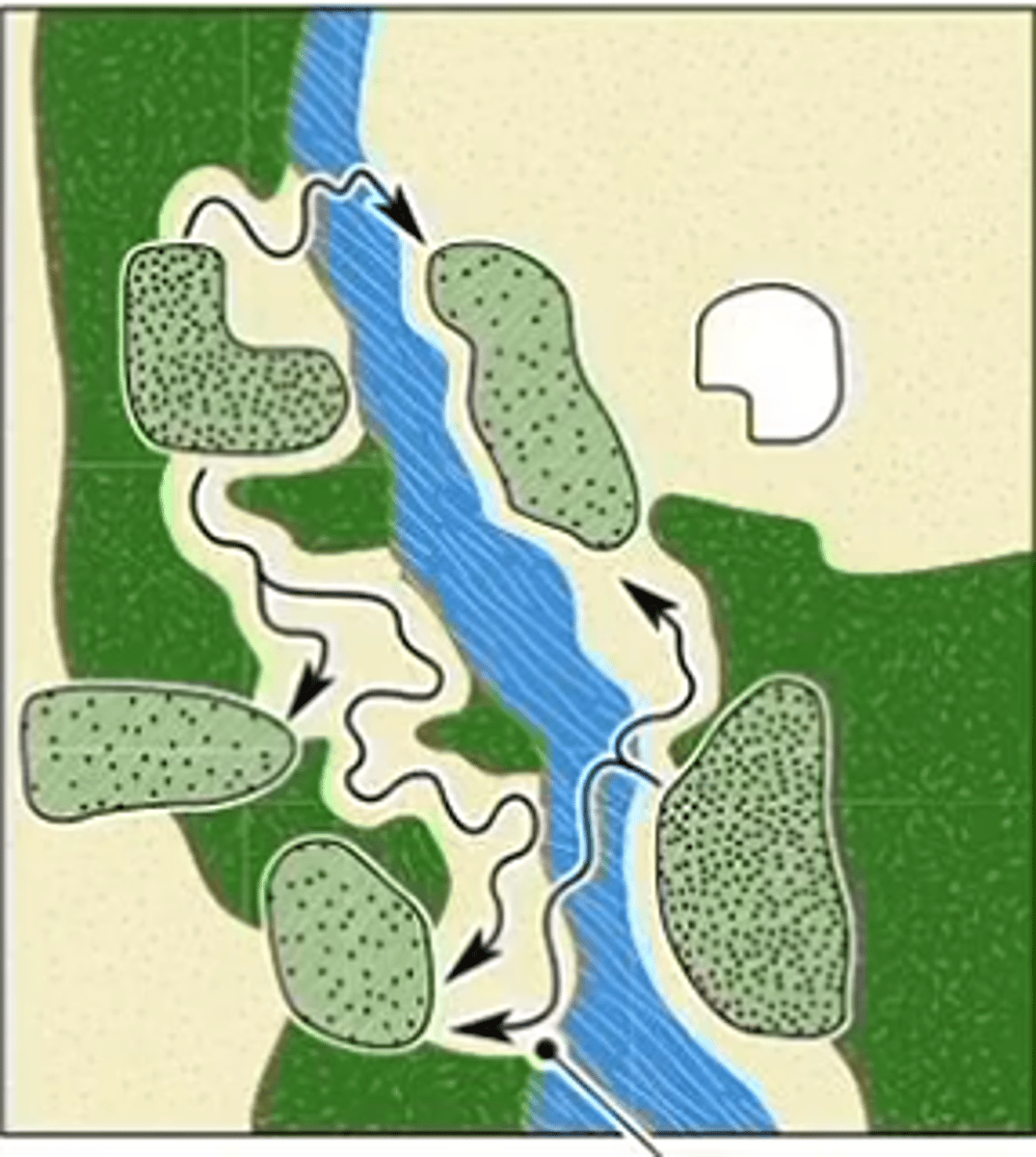
ideal free distribution
individuals distribute among different habitats in response to resources and competition
fast life history/r-selected
- early maturity
- short lifespan
- high number of offspring
- little parental care
- traits to increase population growth
slow life history/K-selected
- late maturity
- long lifespan
- small number of offspring
- high parental care
- traits to increase competitiveness
Grime's Plant Classification
- competitors: high competition, adjust resource allocation, fast growth, early reproduction, low energy to offspring, low stress and low disturbance environments (oak trees)
- ruderals: high disturbance, fast life history, fast growth, early reproduction, energy to producing more offspring, seeds long lived and well dispersed (weeds)
- stress tolerators: high stress, slow life history, slow growth, low energy to offspring, vegetative reproduction, resource conservation (tundra plants)
Lack's hypothesis
selection will favor the clutch size that produces the most surviving offspring
determinate growth vs indeterminate growth
- determinate growth: stops growing once it initiates reproduction
- indeterminate growth: continues growth after reproduction
senescence
gradual decline in fecundity and increase in mortality as an individual ages
semelparity
organisms reproduce only once during their life
- lots of energy required for reproduction, frequent catastrophic events
iteroparity
repeated reproduction throughout lifetime
phenological mismatch
climate change causing temperature rise before photoperiod change so species timing is out of sync
vegetative propagation
asexual reproduction: immature organisms from nonsexual organisms
spore formation
asexual reproduction: release of reproductive cells
binary fission
asexual reproduction: forms two daughter cells from one
advantages of asexual reproduction
- offspring assured without other organism
- adapted to parent's environment
- parent passes on all genes
budding
asexual reproduction: 1 mother (larger) and 1 daughter (smaller) organism (hydra and yeast)
parthenogenesis
asexual reproduction: parent produces embryo without fertilization
advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction
+ genetic variation
- sex organs and mating behavior costly
- mating behavior risky
- mating not guaranteed
- cost of meiosis: only half the genes passed on
red queen hypothesis
sex and genetic recombination provide moving targets for pathogen evolution
avoiding Muller's ratchet
asexual organisms cannot purge mutations, they accumulate
sexual organisms can avoid mutations: meiosis loses mutations
what biologically defines "male"?
size and mobility of the gamete- smaller, more mobile
sex determination
genetic determination: chromosomes
environmental determination: temperature dependent
dioecious
separate male and female plants
hermaphrodism
reproductive organs of both sexes in the same individual; most plants
monoecious
one plant, separate male and female flowers
perfect flowers
one flower: male and female parts
simultaneous hermaphrodites
animals with both male and female functions at the same time
self-fertilization
an individual's male gametes fertilize its own female gametes; build up of mutations, unfavorable
out-crossing
breeding with other individuals
promiscuity
- both sexes have multiple partners
- favored by inability to monopolize resources, unpredictable environment
polygamy
- having more than one mate at a time
- favored by patchy resources
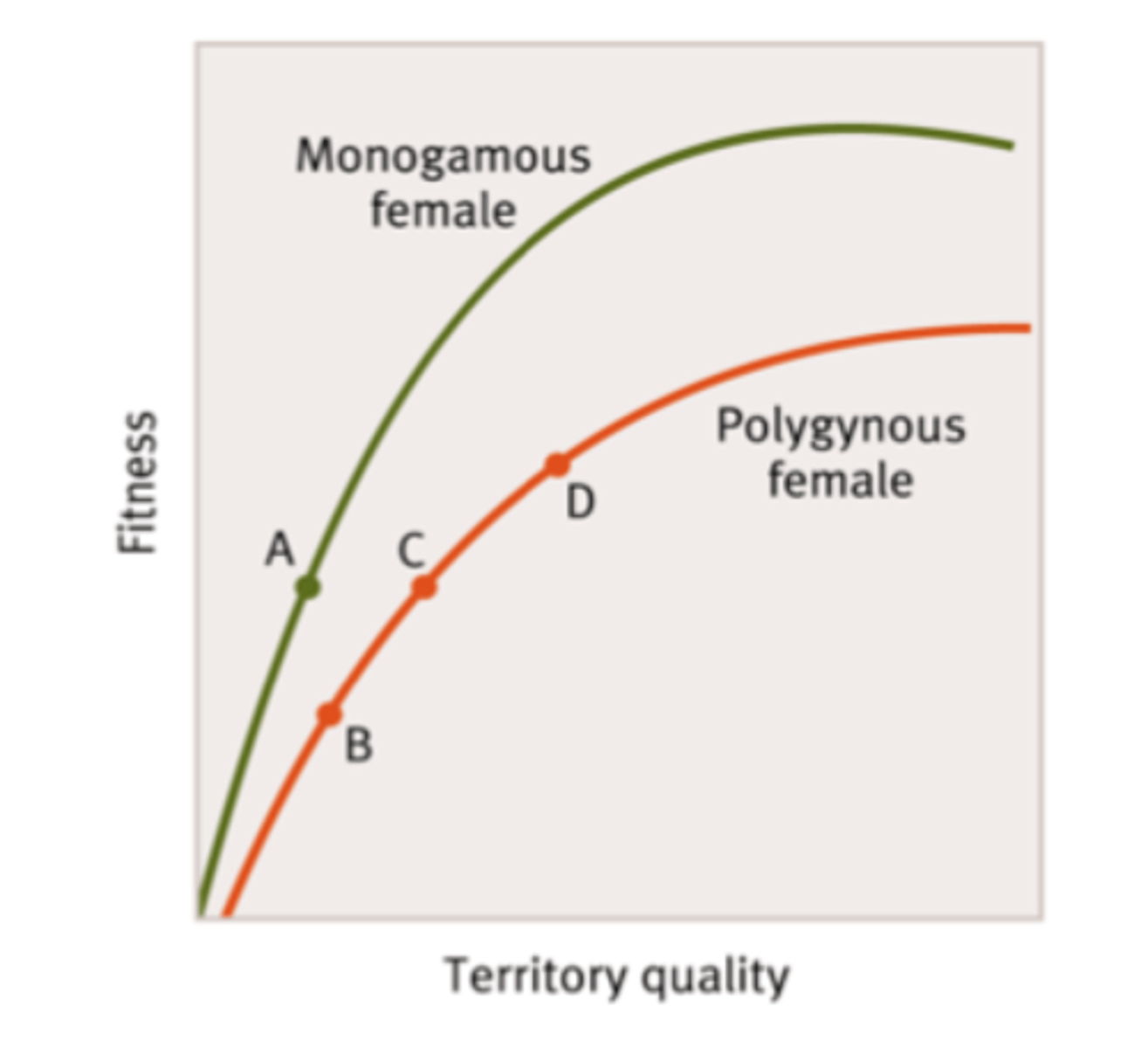
polygyny
- 1 male, many females
- females prefer few best males, males w best territory
polyandry
- 1 female, many males
- female looks for superior sperm or mating gifts, unpredictable environment-> maximize egg production
polygyny threshold model
polygyny when territory variation so great that some females better off in polygyny than monogamy
sexual dimorphism
phenotypic difference between males and females
- need for larger/more offspring or eggs -> females larger
- males compete physically for mates -> males larger
sexual selection
individuals differentiate among potential mates based on traits; sex that makes larger investment will be more discriminating
- intrasexual: within sex competition for mates
- intersexual: mate choice
good genes hypothesis
choose a mate with superior genotype
good health hypothesis
choose the healthiest mate