Chapter 5: Basic Economic Concepts
5.1 Scarcity
Scarcity: occurs because unlimited desire for goods and services exceeds limited ability to produce them due to constraints on time and resources
Resources
- Also sometimes called inputs or factors of production
- Examples
- Capital (physical capital): manufactured goods that can be used in the production process
- Ex) Tools, machinery, equipment
- Labor: physical and mental effort of people
- Includes human capital: knowledge and skill acquired through training and experience
- Entrepreneurship: ability to identify opportunities and organize production, and willingness to accept risk to pursue rewards
- Natural resources: refers to any productive resource existing in nature
- Ex) Wild plants, wind, water
- Acronym: Crazy Leopards Envy Narwhals → Capital, Labor, Entrepreneurship, Natural resources/land
- Energy and technology are considered to be byproducts
- Production models often just includes labor and capital
5.2 Resource Allocation and Economic Systems
- Economics: study of how societies allocate scarce resources among competing ends
- Positive economics: describes the way things are
- Ex) “The unemployment rate hit a three-year high”
- Normative economics: way things should be
- Ex) “The Fed should lower the federal funds rate”
5.3 The Production Possibilities Curve
Opportunity cost: value of the best alternative sacrificed compared to what actually takes place
- Ex) Opportunity cost of studying is losing sleep
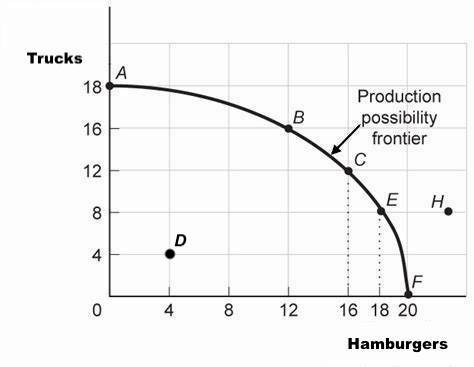
Production-possibilities frontier: illustrates the opportunity cost of making one good rather than another one
- Abbreviated as PPF
- Frontier: curve that represents all of the combinations that could be produced using available resources
- If a point is outside the frontier, the good cannot be produced since it needs more resources than the economy has
- If a point is inside the frontier, it can be obtained but is inefficient
- Efficiency: all of the resources are used productively
- Resources are wasted
- Can determine opportunity cost from PPF
- Greater absolute value of slope = greater opportunity cost
Consumer goods: products for sale in a retail or consumer market used directly by consumers
Capital goods: things purchased to produce other goods
5.4 Comparative Advantage and Gains From Trade
- Specialization
- More efficient → increases productivity
- Division of labor: allows people to develop expertise in certain tasks, where practice improves performance
- Absolute advantage: when a country can produce a good using fewer resources per unit of output compared to another country
- Comparative advantage: when a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost compared to another country
- Consumption possibilities frontier
- With trade, countries can have a consumption possibilities frontier that exceeds its own production possibilities frontier
- Slope is determined by terms of trade
5.5 Cost-Benefit Analysis
Business project factors
- Cost of implementing project
- Resulting benefits
Cost-benefit analysis: comparing value of cost vs. benefits
5.6 Marginal Analysis and Consumer Choice
- Distributive efficiency (efficiency in exchange): those who place the highest relative value on goods should receive them
- Ex) Auctions
- Achieved when marginal rate of substitution is equal for every consumer
- Marginal rate of substitution: ratio of marginal utility for two goods