Properties of Period 3 elements and their oxides
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3.2.4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Trend in atomic radius across period 3
Atomic radius decreases
Same shielding
Increase in nuclear charge
So outer shell is more strongly attracted to nucleus, compacting.
Trend in 1st ionisation energy across period 3
Overall Increase in 1st ionisation energy
Decrease in atomic radius
Increased nuclear charge
So stronger electrostatic attraction between nucleus and outer electron, requiring more energy to remove.
Al 1st ionisation energy lower than Mg
Mg outer electron in 3s orbital
Al outer electron in 3p orbital
3p is of higher energy than 3s
So more energy required to remove electron from 3s orbital.
S 1st ionisation energy lower than P
S has one spin pair in the 3p orbital which repel each other
So requires less energy to remove outer electron from S.
Trend in electronegativity across period 3
Increase in electronegativity
Atomic radius decreases
Nuclear charge increases
So stronger electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and electron in a bond.
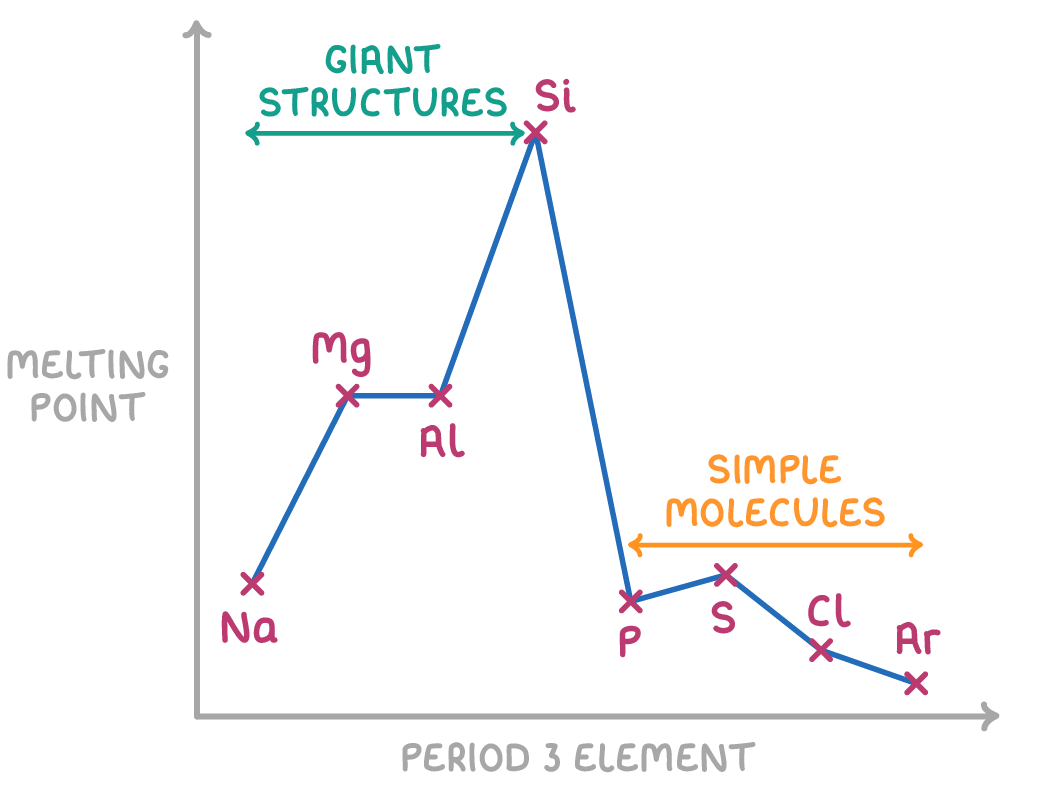
Trend in melting point across period 3
Na, Mg, Al are metallic lattices.
Strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charge ions.
Si is a giant covalent.
Many strong covalent bonds, require a lot of energy to overcome.
P, S, Cl are simple covalent molecules.
Van der Waal’s forces are stronger the larger the molecule.
S8 > P4 > Cl2
So S8 requires most energy to overcome VDW.
Ar exists as single atoms.
Explain the pH of solution of Al2O3
Has ionic lattice structure with covalent character.
Covalnt character means it is not water soluable.
So pH of solution remains at 7
Explain the pH of solution of SiO2
Macromolecular covalent
Many strong covalent bonds need to be broken for it to dissolve in water.
So solution remains at pH 7.
Explain the pH of solution of Na2O & MgO
Ionic lattices, Ions free to move, so solution is basic.
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) pH 14
MgO(s) + H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2(aq) pH 9
Mg2+ creates a stronger ionic bond than Na+, so MgO is less soluble, so less O2-, so lower OH-. Therefore MgO is a weaker base.
Explain the pH of solution of P4O10 , SO3, SO2
Simple covalent molecular
P4O10 (s) + 6H2O → 4H3PO4 (aq) pH 1
SO3 (g) +H2O → H2SO4 (aq) pH 1
SO2 (g) +H2O → H2SO3 (aq) pH 3
Forms strong acid so has lower pH.
Sulfuric acid and sulfate (VI) anion, SO42-
Phosphoric acid and Phosphate anion, PO43-
Sulfuric acid (IV) and Sulfate (IV) anion, SO32-
Melting points of period 3 oxides
Sodium and water
Rapid with cold water.
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2 (g)
Magnesium and water
Reacts slowly with cold water (l)
Faster with steam (g)
Mg(s) + 2H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Mg(s) + H2O(g) → MgO (aq) + H2 (g)
Which solution is a stronger alkali, Mg(OH)2 or NaOH?
NaOH is stronger as it is more soluble in water so release more OH-.
phophorus oxide
P4O10
Silicon oxide
SiO2
Aluminium oxide
Al2O3
Magnesium oxide
MgO
Sodium oxide
Na2O
Oxides of sulfur
SO3
SO2
Which period 3 oxides react with acids?
The basic oxides, magnesium oxide and sodium oxide
Which period 3 oxides react with bases?
The acidic oxides, phosphorus oxide, sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide, react with bases.
Does Aluminium oxide react with acids or bases?
Aluminium oxide is amphoteric, it reacts with solutions of strong bases and with solutions of strong acids.
Does SiO2 oxide react with acids or bases?
Silicon dioxide reacts with hot concentrated alkaline solutions
Aluminium oxide reacts with acid and base
Al2O3 + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH + 3H2O → 2Na+ + 2[Al(OH)4]-
Silicon dioxide reaction with base
SiO2 + 2NaOH → Na2SiO3 +H2O
Acid + Base
→ Salt + Water
P4O10 add base
P4O10 + 12NaOH → 4Na3PO4 + 6H2O
Al2O3 + H2O
Al2O3 is insoluble in water so no reaction occurs