AP Psychology Unit 5 - Mental and Physical Health
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
American Psychological Association
A scientific and professional organization that represents psychology in the United States. It's responsible for setting ethical guidelines for psychological research
Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
A handbook published by the American Psychiatric Association that provides standardized criteria and classification for diagnosing mental disorders
World Health Organization (WHO)
The United Nations' specialized agency for international public health responsible for providing leadership on global health matters, shaping the health research agenda, and monitoring and assessing health trends worldwide
International Classification of Disorders (ICD)
A comprehensive system used to classify and code various medical conditions, including psychological disorders. It serves as a standardized diagnostic tool for professionals worldwide
Dysfunction
An impairment or disturbance in an individual’s behavior
E.g. your cleaning habits interfere with your work and relationships
Distress
Emotional or mental suffering, typically caused by life stressors or internal conflicts
E.g. not being able to clean your room causes anxiety and panic
Deviant
Not typical of one’s society’s normal behavior
E.g. cleaning your room when you wake up, right before school, after school, after dinner, before you go to bed
Stigma
Negative social attitudes or beliefs associated with a particular characteristic or condition, often leading to discrimination and prejudice against individuals or groups
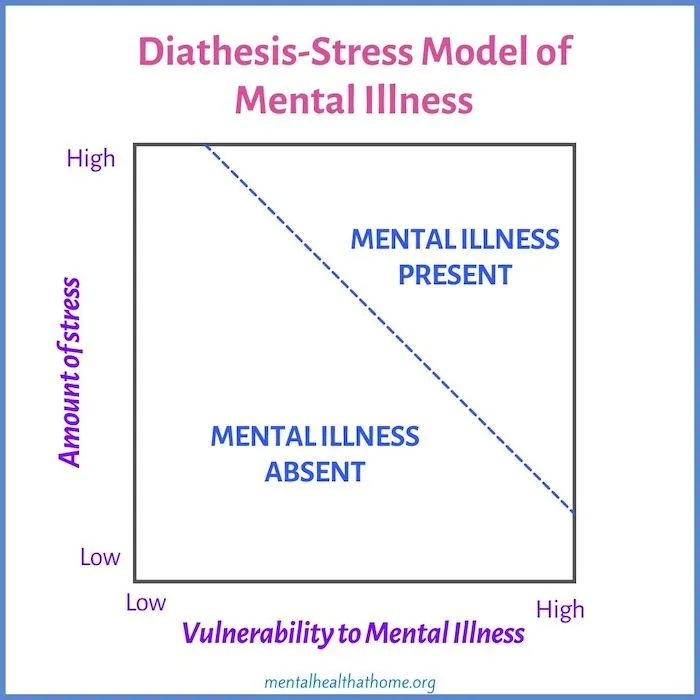
Diathesis-Stress Model
A psychological concept that suggests that the development of psychological disorders is influenced by both a genetic predisposition (diathesis) and environmental stressors (stress)
Diathesis
Genetic predisposition (In the Diathesis-Stress Model)
Stress
Environmental stressors or life events (In the Diathesis-Stress Model)
Racism
Prejudice, stereotyping, and discrimination directed towards individuals or groups based on their race or ethnicity
Ageism
Prejudice, stereotyping, and discrimination directed towards individuals or groups based on their age
Discrimination
The negative behavior or action taken against an individual based on their group membership
Eclectic
A therapeutic approach that combines techniques from various forms of therapy based on the individual's specific needs and circumstances
Maladaptive Behavior
Actions or patterns of behavior that are ineffective, disruptive, or harmful to an individual's well-being and ability to function in society
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
A group of conditions characterized by impairments in brain function that affect cognitive, emotional, social, and behavioral development
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
A neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity
Boys are more likely to be diagnosed with it than girls
Autism Spectrum Disorder
A neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by problems with social interaction and fixed patterns of behavior, interests, and activities
Anxiety Disorders
A group of mental disorders characterized by significant feelings of anxiety and fear
Specific Phobia
An anxiety disorder characterized by fear or anxiety towards a specific situation or object. Includes symptoms such as intense fear, avoidance behavior, physical symptoms, and distress
Agoraphobia
An anxiety disorders characterized by intense fear of specific social situations, especially ones where escape may be difficult. Includes symptoms such as fear of open or crowded spaces, avoidance, panic symptoms, and functional impairment
Panic Disorder
An anxiety disorder characterized by unanticipated and reoccurring panic attacks. Includes symptoms such as panic attacks, persistent concern, and behavior changes
Social Anxiety Disorder
An anxiety disorder characterized by an intense fear of social situations where the person may be exposed to potential embarrassment. Includes symptoms such as intense fear, physical symptoms, avoidance, and distress
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
An anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life. Includes symptoms such as persistent worry, restlessness, muscle tension, sleep disturbances, and irritability
Acrophobia
A specific phobia characterized by a fear of heights
Arachnophobia
A specific phobia characterized by a fear of spiders
Panic Attack
An abrupt surge of intense fear or discomfort that reaches its peak within minutes and includes symptoms like heart palpitations, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath
Culture-Bound Syndromes
Psychological or behavioral disorders that are specific to particular cultural or ethnic groups, often influenced by the beliefs and practices of that culture
“Ataque de Nervios” (Attack of Nerves)
A culture-specific syndrome observed in Latin American/Caribbean communities. Characterized by sudden onset of emotional distress and physical symptoms, often in response to a traumatic/stressful event
Taijin kyofusho
An anxiety disorder unique to Japanese culture. It is characterized by an intense fear of offending or embarrassing others through one’s appearance or behavior. Includes symptoms such as preoccupation with appearance/behavior, avoidance of social situations, physical symptoms, persistent worry, and fear of negative evaluation
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
A mental health disorder characterized by the presence of obsessions, compulsions, or both. Includes symptoms such as obsessions, compulsions, and avoidance
Obsessions
Persistent, intrusive thoughts, images, or urges that cause significant anxiety or distress
Compulsions
Repetitive behaviors or mental acts performed in response to an obsession or according to rigid rules. These are intended to reduce anxiety or prevent a feared event
Hoarding Disorder
A mental health disorder characterized by persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value. Symptoms include excessive accumulation (of items), difficulty discarding items, emotional distress, functional impairment, and indifference towards/denial of the disorder
Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorders
Mental health disorders characterized by abnormalities in perceptions or expressions of reality, often involving hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and speech
Schizophrenia
A schizophrenic spectrum disorder characterized by disturbances in thinking, emotional responsiveness, and behavior. Involves symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking/speech, and disorganized motor behavior
Delusions
Beliefs that a person firmly holds onto, despite clear evidence to the contrary. These beliefs are not influenced by reality and remain persistent even when they're irrational
Delusions of Grandeur
Delusions where a person believes that they have exceptional abilities
Delusions of Persecution
Delusions where a person believes that they are going to be harmed by someone or something
Disorganized thinking or speech
A positive symptom of schizophrenia characterized by fragmented or illogical thoughts and speech patterns or when an individual's speech becomes incoherent, illogical, or difficult to follow
Hallucinations
A positive symptom of schizophrenia characterized by false perceptions
Word Salad
A positive symptom of schizophrenia characterized by severely disorganized and incomprehensible speech or writing
Disorganized Motor Behavior
Unusual and atypical movements or actions exhibited by individuals, often seen in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia
Negative Symptoms
A reduction or absence of normal behaviors and functions that are typically present in healthy individuals
Positive Symptoms
Abnormal experiences or behaviors that are added to a person's normal repertoire of thoughts and actions
Flat Affect
A negative schizophrenia symptom characterized by a lack of emotional reactivity on the part of an individual
Catatonic Excitement
A subtype of catatonia (and a positive schizophrenia symptom) characterized by extreme agitation, hyperactivity, and an inability to control movements or behaviors
Catatonic Stupor
A subtype of catatonia (and a negative schizophrenia symptom) characterized by a marked decrease in responsiveness to the environment, often seen in individuals experiencing severe forms of schizophrenia
Acute
A sudden onset of very intense symptoms
Chronic
When symptoms persist over a long period of time
Dopamine Hypothesis
A theory that suggests an excess of dopamine activity in certain brain areas is associated with the development and symptoms of schizophrenia
Depressive Disorders
Mental health disorders characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and worthlessness and a lack of desire to engage in formerly pleasurable activities
Major Depressive Disorder
A depressive disorder that includes symptoms such as a depressed mood, loss of pleasure in normally pleasurable activities (Anhedonia), sleep disturbances, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness, cognitive impairment, psychomotor agitation, and suicidal ideation
For a person to be diagnosed with this disorder, they must meet 5 requirement from the DSM-5, and they must last for at least 2 weeks
Persistent Depressive Disorder
A depressive disorder that includes symptoms such as chronic depressed mood, appetite and weight changes, sleep disturbances, fatigue, low self esteem, difficulty concentrating, and hopelessness
For a person to be diagnosed with this disorder, they must meet 2+ requirements from the DSM-5, and they must last for at least 2 years
Bipolar Disorders
Brain disorders that cause changes in a person's mood, energy and ability to function. These disorders cause people to have extreme and intense emotional states that occur at distinct times, called mood episodes
Mania
A mood state characterized by abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level (Seen in bipolar disorders)
Depression
A mood state characterized by periods of persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, and other symptoms similar to major depressive disorder (Seen in bipolar disorders)
Rapid Cycling
A pattern of mood episodes in bipolar disorder where a person experiences four or more distinct mood swings within a year
Bipolar 1
A bipolar disorder characterized by the occurrence of at least one manic episode which may or may not be followed by one hypomanic or depressive episode
Bipolar 2
A bipolar disorder characterized by patterns of depressive and hypomanic episodes but does NOT include full blown manic episodes
Hypomania
A mood state characterized by persistent disinhibition and pervasive elevated (euphoric) or irritable mood but generally less severe than full mania
Dissociative Disorders
Mental disorders that involve experiencing a disconnection and lack of continuity between thoughts, memories, surroundings, actions and identity
Dissociative Amnesia
A dissociative disorder characterized by an inability to remember important personal information, often related to trauma/stress. Involves symptoms such as localized amnesia, selective amnesia, and generalized amnesia
Dissociative Fugue
A rare condition in which a person suddenly, without planning or warning, travels far from home or work and leaves behind their past life. They may even assume a new identity
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)
A dissociative disorder characterized by the presence of 2+ distinct personality states within a single person. Includes symptoms such as the presence of multiple identities, recurrent gaps in memory, and disruptions in identity
Trauma and Stressor Related Disorders
A group of mental health disorders that includes any mental health condition that's triggered by a traumatic event
Posttraumatic-Stress Disorder (PTSD)
A trauma and stressor related disorder characterized by persistent and distressing symptoms that interfere with an individual’s ability to function in daily life. Includes symptoms such as re-experiencing, distressing dreams, avoidance of trauma-related stimuli, emotional numbness, negative beliefs, persistent distorted thoughts, reduced positive emotions, hypervigilance, irritability or aggression, difficulty with sleep, and difficulty concentrating
Personality Disorders
Types of mental disorders characterized by enduring patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that deviate from societal expectations. These patterns often lead to significant distress or impairment in various areas of an individual's life
Cluster A
A cluster of personality disorders characterized by odd or eccentric behaviors. Includes Paranoid Personality Disorder, Schizoid Personality Disorder, and Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Cluster B
A cluster of personality disorders characterized by dramatic, emotional, or erratic behaviors. Includes Antisocial Personality Disorder, Histrionic Personality Disorder, Narcissistic Personality Disorder, and Borderline Personality Disorder
Cluster C
A cluster of personality disorders characterized by anxious and fearful behaviors. Disorders involve patterns of thinking and behaving that are pervasive, inflexible, and maladaptive, leading to significant distress or impairment. Includes Avoidant Personality Disorder, Dependent Personality Disorder, and Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder
Paranoid Personality Disorder (PPD)
A Cluster A personality disorder marked by pervasive and unjustified mistrust and suspicion of others. Includes symptoms like suspicion, misinterpretation, reluctance to confide, defensiveness, and grudges
Schizoid Personality Disorder (SPD)
A Cluster A personality disorder characterized by a pervasive pattern of detachment from social relationships and a restricted range of emotional expression. Includes symptoms such as detachment, indifference to social norms, restricted emotional range, solidarity preference, and lack of pleasure
Schizotypal Personality Disorder (STPD)
A Cluster A personality disorder characterized by eccentric behavior, unusual beliefs or magical thinking, and social anxiety. Includes symptoms such as unusual beliefs, odd behavior, social anxiety, cognitive or perceptual distortions, and inappropriate affect
Antisocial Personality Disorder (ASPD)
A Cluster B personality disorder marked by a pattern of disregarding and violating the rights of others that includes problems such as deceitfulness, impulsivity, aggressive behavior, recklessness, lack of conscience, irresponsibility, and viewing other as prey
Histrionic Personality Disorder (HPD)
A Cluster B personality disorder characterized by a consistent pattern of pervasive attention-seeking behaviors and exaggerated emotional displays. Includes symptoms such as excessive emotionality, attention-seeking behavior, dramatic presentation, suggestibility (easily influenced), overemphasis on physical appearance, and shallow interpersonal relationships
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
A Cluster B personality disorder characterized by exaggerated ideas of self-importance and achievements, preoccupation with fantasies of success, and arrogance. Includes symptoms such as grandiosity, need for admiration, lack of empathy, exploitative relationships, arrogant attitudes, and envy
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
A Cluster B personality disorder characterized by a pervasive pattern of instability in interpersonality relationships, self-image, and affect, along with marked impulsivity. Includes symptoms such as fear of abandonment, unstable relationships, unstable self-image, impulsivity, emotional instability, and self-harm
Avoidant Personality Disorder (AVPD)
A Cluster C personality disorder marked by chronic feelings of inadequacy and extreme sensitivity to criticism. Includes symptoms like social inhibitions, feelings of inadequacy, hypersensitivity to negative evaluation, and reluctance to engage in new activities
Dependent Personality Disorder (DPD)
A Cluster C personality disorder characterized by an excessive and pervasive need to be taken care of, leading to clinginess and fear of separation. Includes symptoms like excessive need for care, submissive and clinging behavior, fear of separation, and difficulty making decisions
Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD)
A Cluster C personality disorder characterized by a spectrum of obsessions with rules, lists, schedules, and order, among other things. Includes symptoms like preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, rigidity and stubbornness, and over-commitment to work
Eating and Feeding Disorders
Mental disorders defined by abnormal eating habits that negatively affect a person's physical or mental health
Anorexia Nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight and a distorted body image, leading to severe restriction of food intake. Includes symptoms such as extreme restriction of food intake, intense fear of weight gain, distorted body image, excessive exercise, preoccupation with food and weight, physical symptoms
Bulimia Nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by repeated episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors to prevent weight gain. Includes symptoms such as binge eating, purging behaviors, excessive exercise, preoccupation with body and weight, and physical symptoms
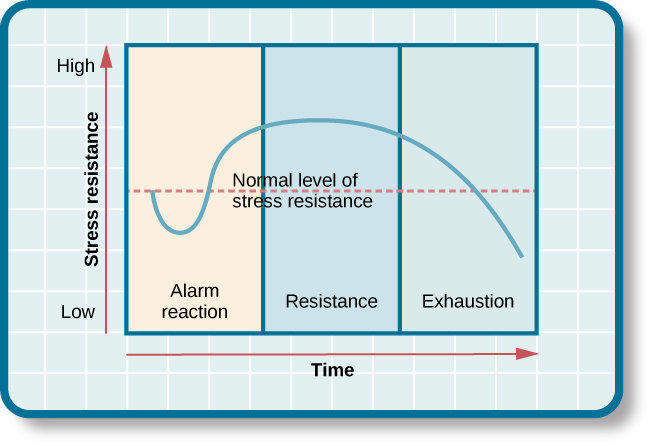
General Adaptation Syndrome
The body's three-stage response to stress, proposed by Hans Selye. The stages include alarm reaction, resistance, and exhaustion
Alarm Reaction
According to the GAS, this is the initial response of your body when faced with a stressful situation
Resistance Stage
The second stage in the GAS where your body adapts and tries to cope with ongoing stress
Exhaustion Stage
The final stage of GAS when prolonged or severe stress depletes your body's resources
Problem-Focused Coping
A strategy used to deal with stressors by taking direct action to solve the problem causing the stress. It involves identifying and addressing the root cause of the problem
Emotion-Focused Coping
A stress coping strategy aimed at managing the emotional distress associated with a stressful situation rather than addressing the problem itself
Acute Stress
A type of stress that is immediate and intense but short-lived. It's like a sudden heavy downpour - it can be overwhelming, but it doesn't last forever
Chronic Stress
Long-term stress that persists over extended periods. It's like a constant drizzle - not as intense as acute stress, but its persistence can lead to serious health problems
Eustress
Positive stress, a motivational force that can enhance performance and lead to feelings of achievement and fulfillment
Distress
Negative stress that can be overwhelming, debilitating, and have detrimental effects on physical and mental well-being
Insight Therapy
Therapy that attempts to help a person understand their underlying motivations and defenses
Psychodynamic Therapy
Based on Freud’s ideas of Id, Ego, and Supergo, it is a type of therapy where a therapist tries to release and interpret repressed feelings in a patient by analyzing dreams, resistances, free associations, and transferences
Free Association
A method used in psychodynamic therapy where patients are encouraged to share whatever comes into their mind, regardless of how irrelevant or nonsensical it may seem
Often used through the Inkblot or TAT tests
Dream Analysis
A form of psychodynamic therapy that involves talking about your dreams and attempting to dissect what they mean
Psychoanalytic Therapy
A therapy similar to psychodynamic therapy, but it is less about Id/Ego/Superego and more about childhood and general relationships that unconsciously impact a person’s life experiences