Chapter 16: Fishes (Chondrichthyes and Actionoptergyii)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the Phylum, Subphylum and class of Sharks, skates and rays? What are the special characteristics in this class?
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Chondrichthyes
This class has cartilaginous skeletons, paired fins, and jaws.

Function of the lateral line and spiracles in dogfish? (sharks)
Lateral line: movement and vibrations
Spiracles: behind the eye. second entrance for water. More oxygen to gills.

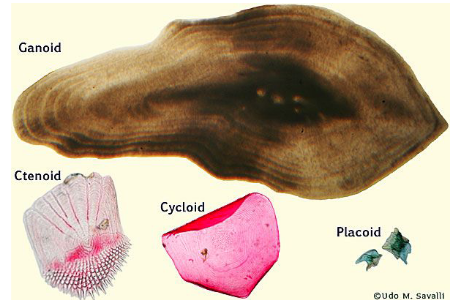
What type of scales do cartilaginous fishes have? How would they feel rubbing your hand down the shark vs up the shark?
Placoid scales. AKA “Dermal Denticles”. spiny, toothlike projections.
Rub hand down shark towards tail: smooth
Rub shark up towards head: sandpaper feeling, rough

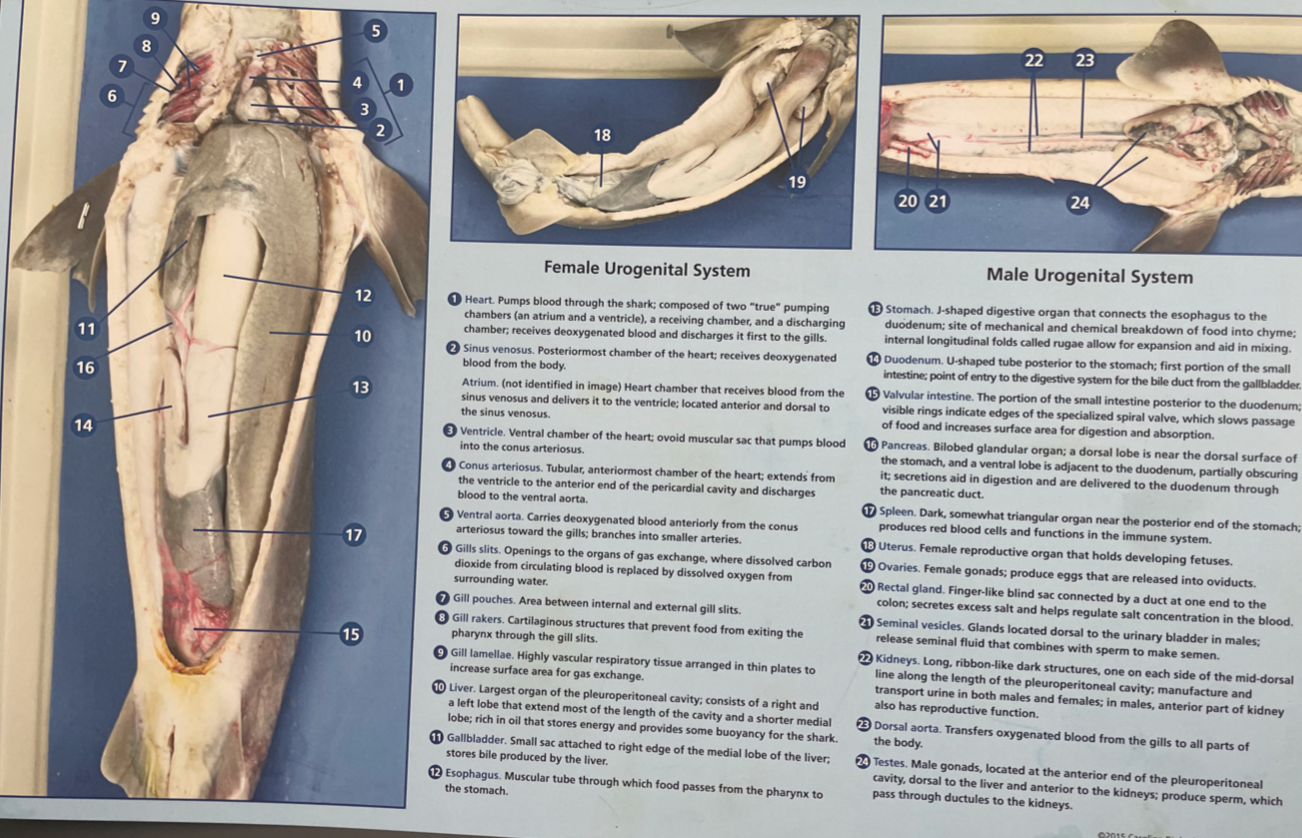
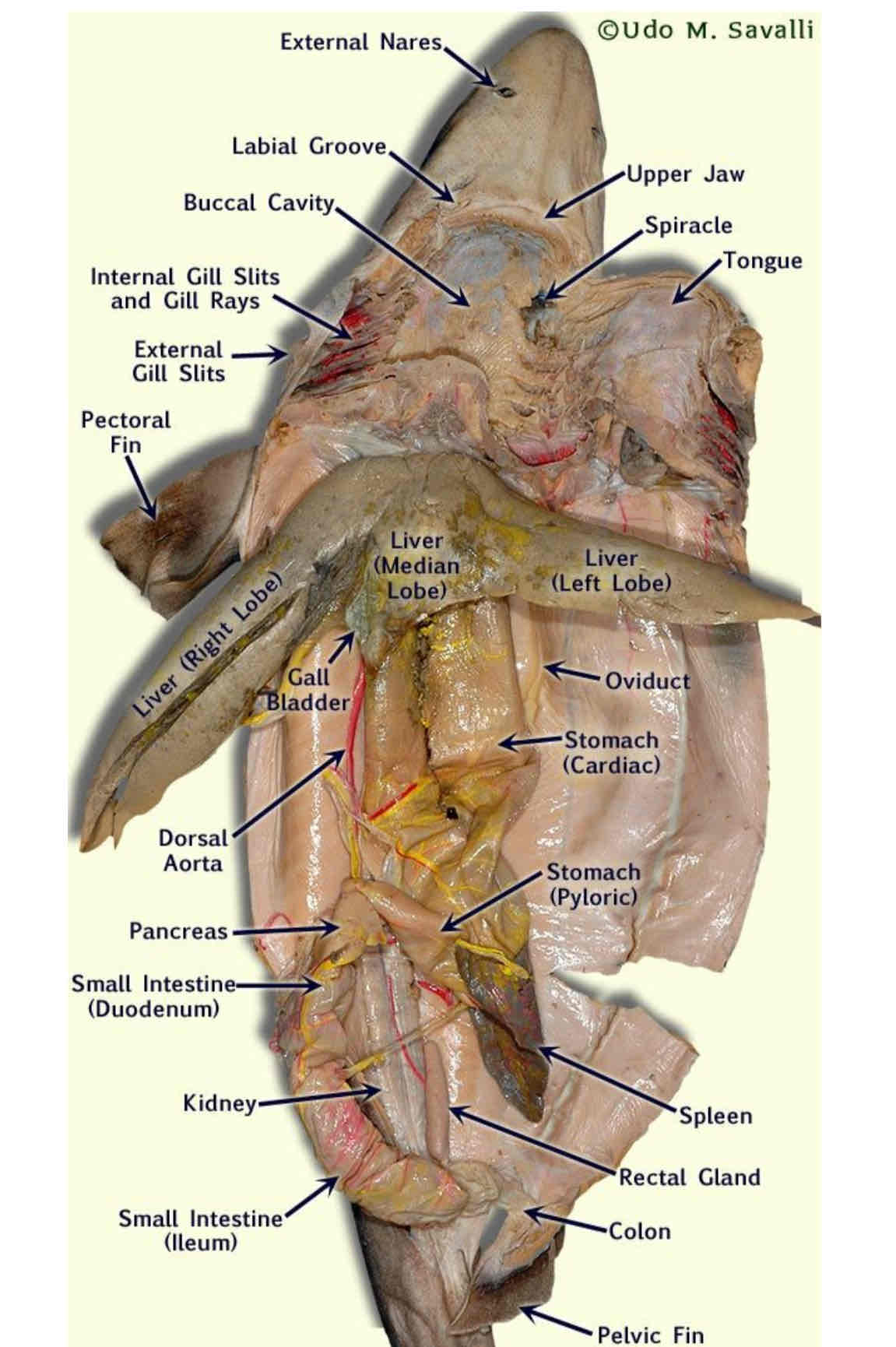
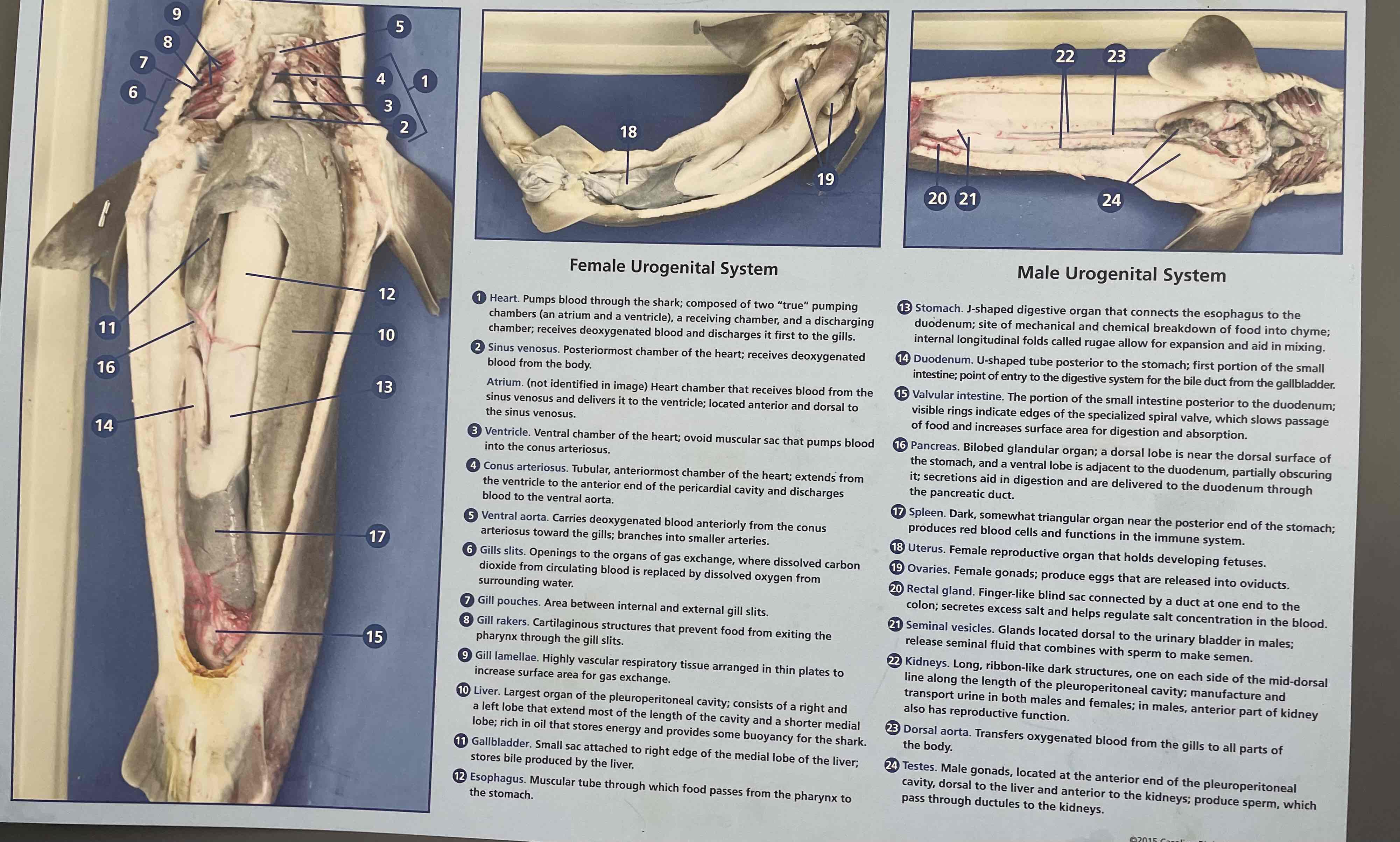
Identify Internal structures of a dogfish and their functions.
gills
heart (and # of chambers)
liver
stomach (with rugae)
intestines (with spiral organ)
Spiral Valve
rectal gland
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Spleen
Kidney
Gonads
Gills: respiration
Heart: 2 chambered. Circulation
Liver: filled with oil to maintain buoyancy
Stomach: digestion.
Rugae: Inside the stomach. Dark with many folds, allows stomach to expand.
Intestine: digestion
Spiral Valve: Spiral structure inside intestine. Slows the passage of food and increases surface area. Aids in digestion.
Rectal Gland: excretion. excretes excess salt for osmoregulation
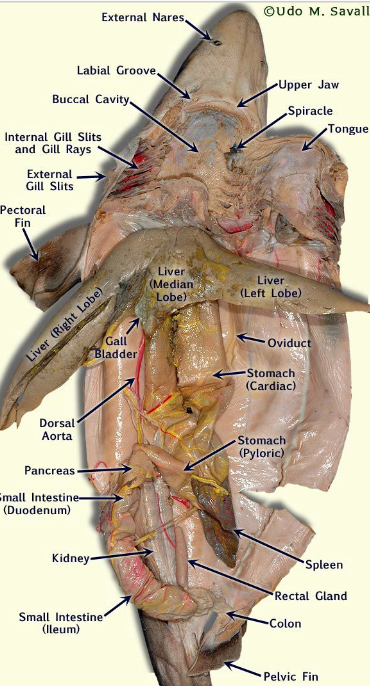
Internal Anatomy dissection. Number these internal structures:
Gills
Heart & # of chambers
Stomach & rugae
Intestine
Spiral valve
Rectal gland
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Spleen
Kidney
Gonads
6-9, 1, 13, 14-15, inside 15, 20, 10, 11, 16, 17, 22, 18+19 or 24.
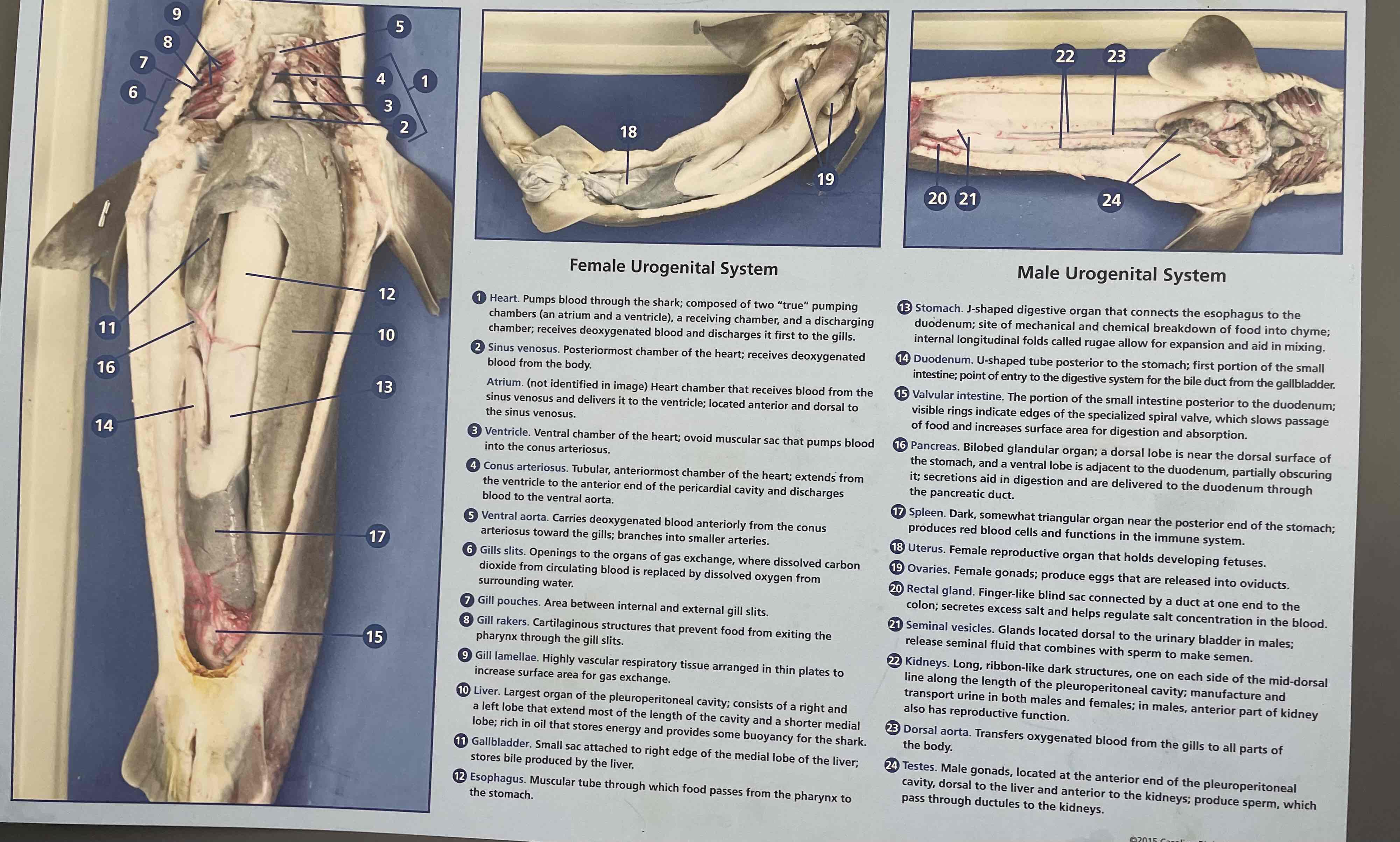
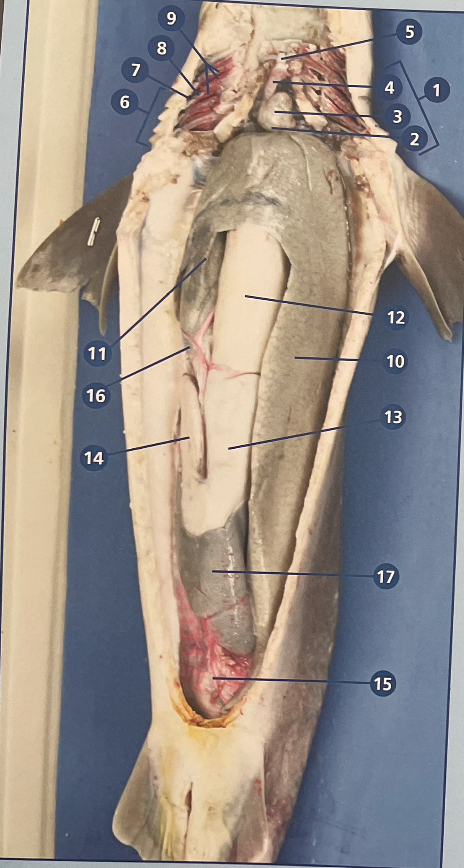
Internal and External Anatomy of dissection. Number these Internal structures:
liver
Stomach (& rugae)
Intestine (& spiral valvue
rectal gland
heart
gonads
10,13,15,20,1, (gonads are 18+19 or 24)


Skate eggs
Be able to identify the skate egg case as a reproductive structure
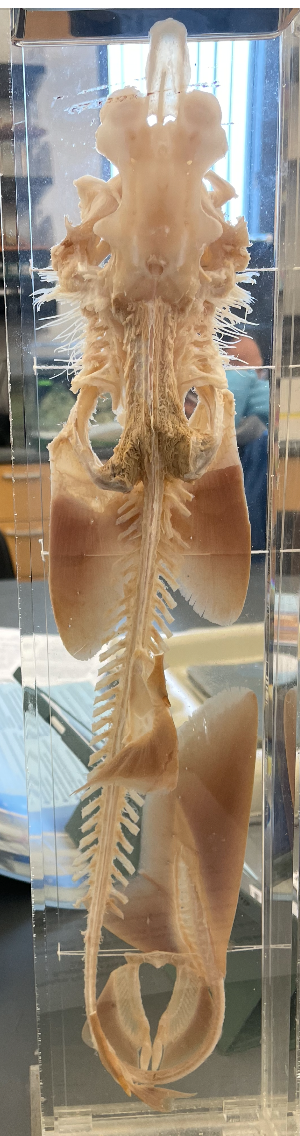
What is this skeleton made of? What class would it be found in?
Cartilage. Class Chondrichtyes. Picture is of a dogfish skeleton (shark)
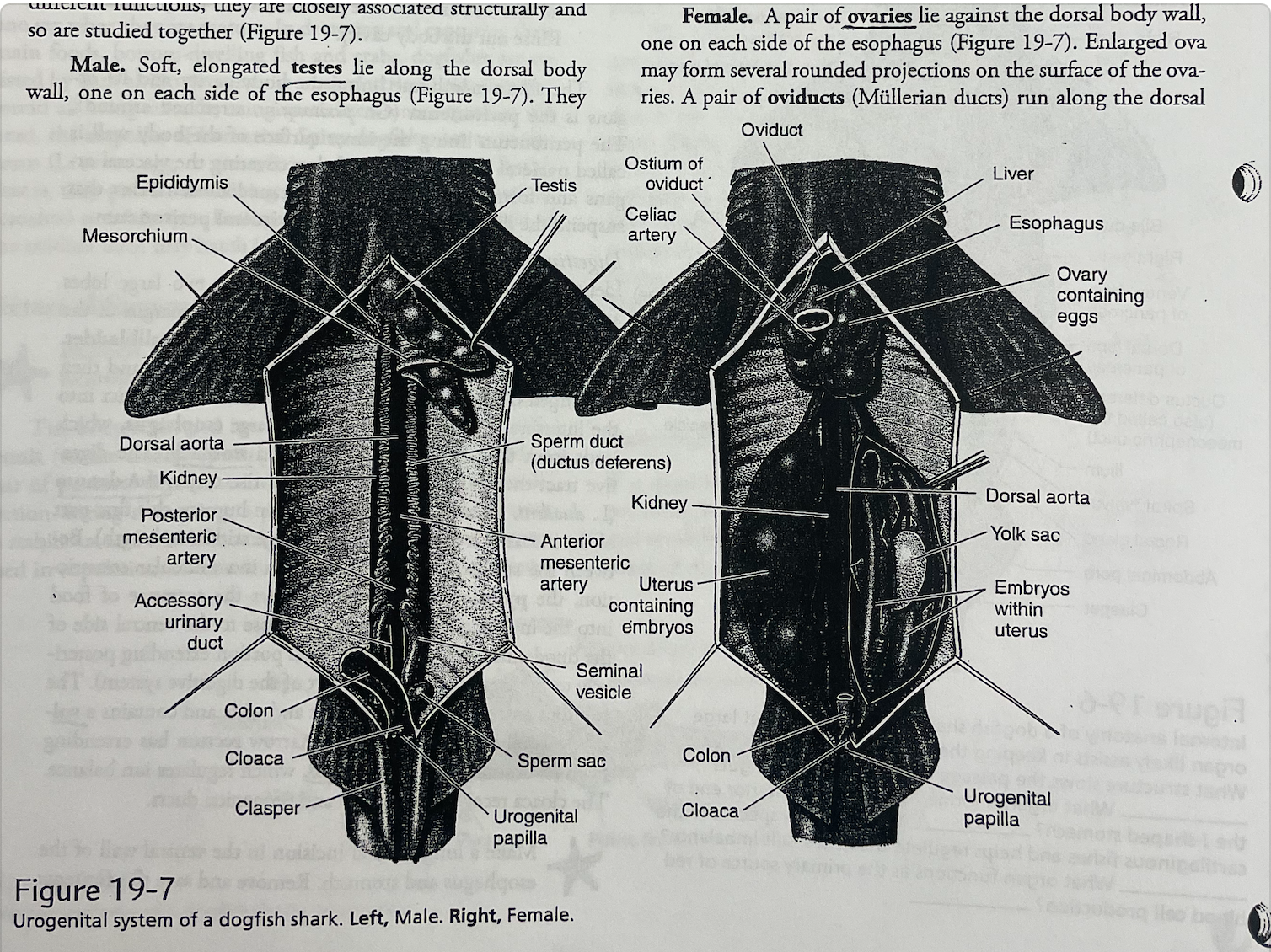
How can you tell the difference between a male and female shark? (in this image, Left is male, Right is Female)
Male sharks have a pair of round/oblong claspers. Females have flat shape around cloaca, no claspers.
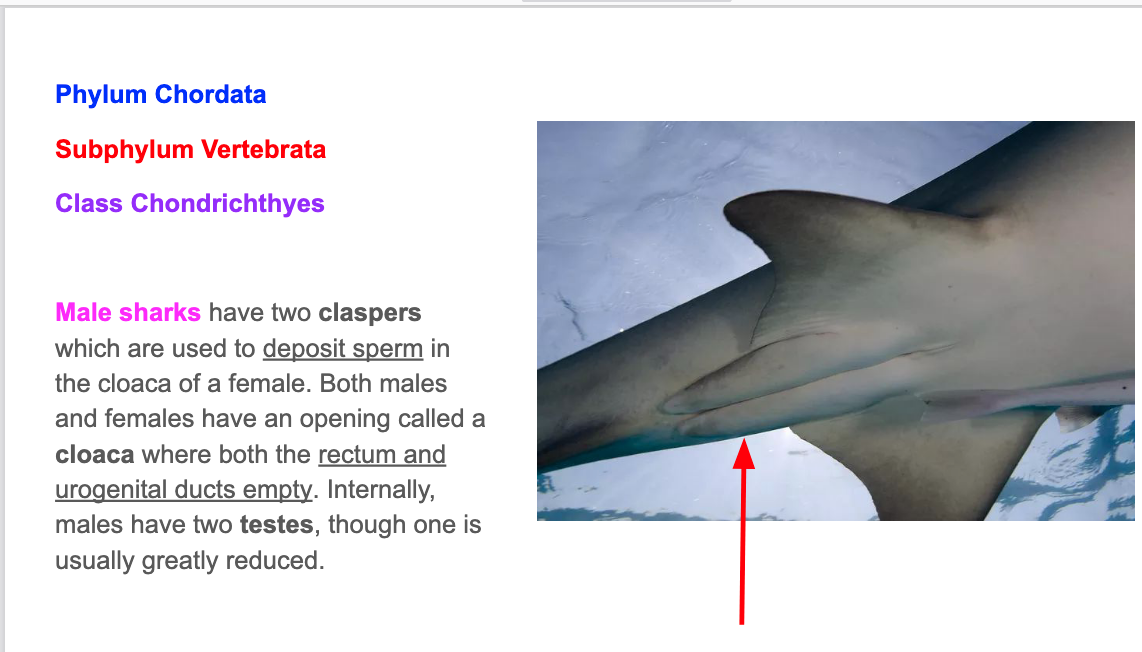

Is this shark male or female?
Female. No claspers, only cloaca

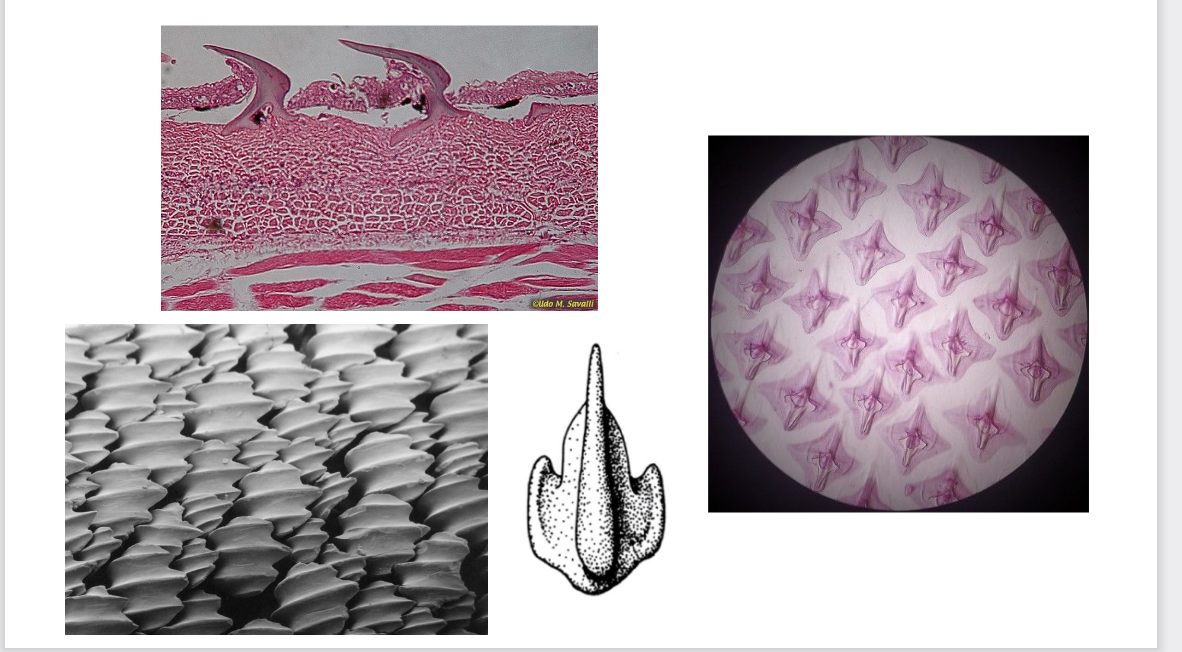
What is shown in these cell slides?
Placoid scales/ Dermal Denticles. Found in sharks
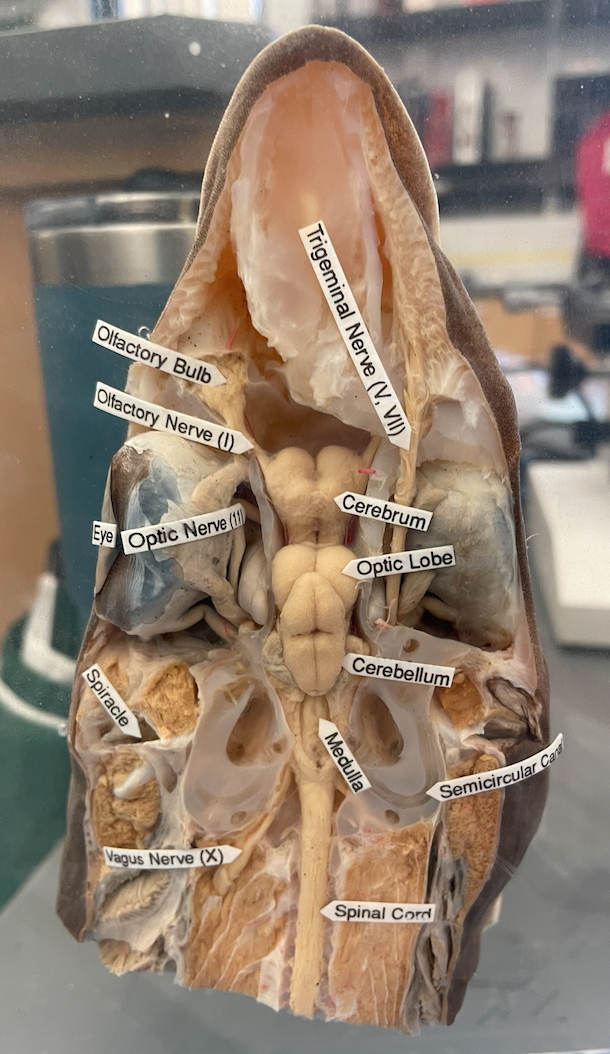
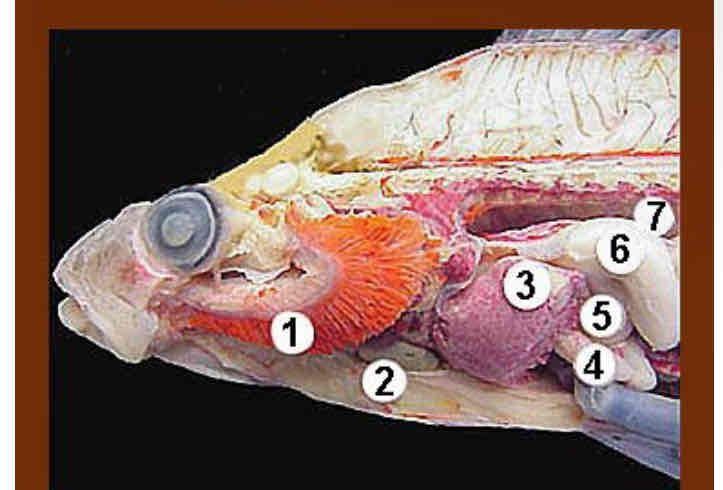
Dogfish shark dissected head. Be able to identify following structures and functions
Eye
Spiracle
Spinal cord
Eye: sight.
Spiracle: Another way for water to come in and ring oxygen over gills. Respiration
Spinal Cord: sensory

Mount of Dogfish Shark. Be able to identify following INTERNAL structures and functions:
Nares/Nostrils
mouth
gills
heart + # of chambers
liver
stomach & rugae
Intestine
Rectal gland
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Spleen
Kidney
Gonads
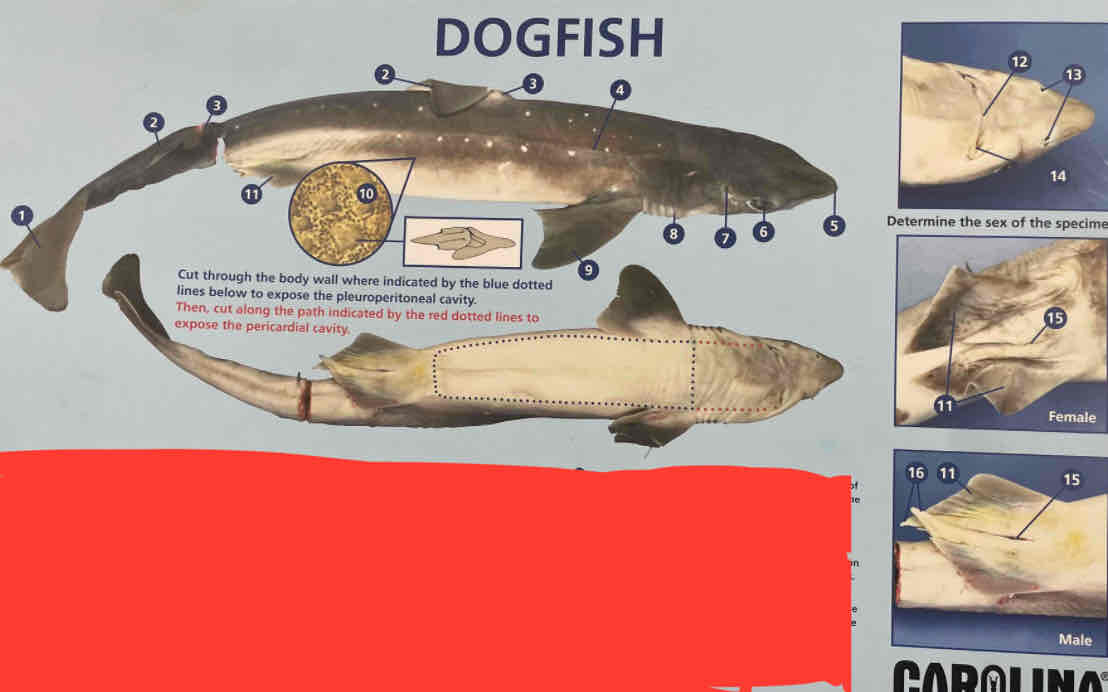

Dogfish shark external anatomy
Identify which numbers are these structures:
Rostrum
Eye
Spiracle
Gill slits
Mouth
Nostrils
Lateral line
Fin spine
Dorsal, pectoral, and caudal fins
Pelvic fin
Cloaca
Placoid scales
5, 6, 7, 8, 14, 13, 4, 2, 9, 1, 11, 15,10
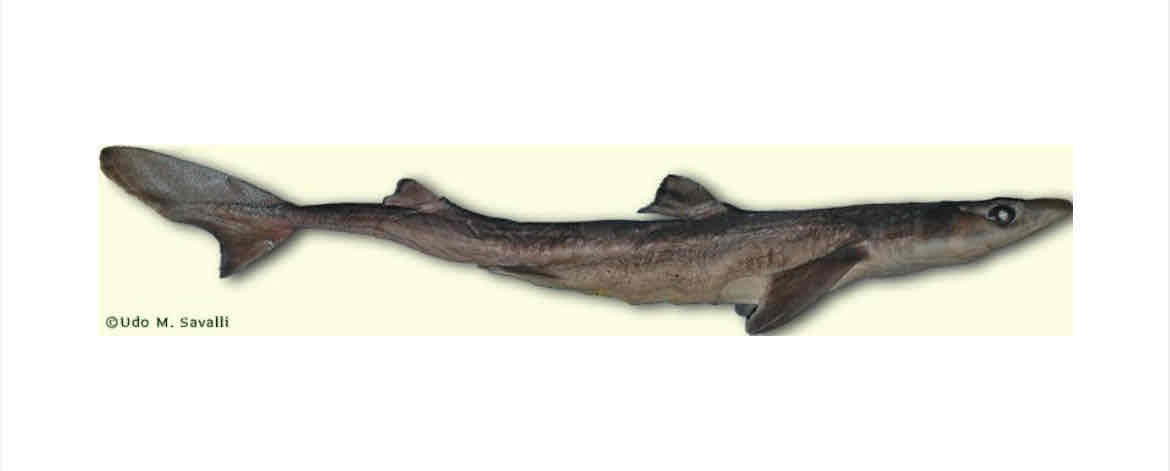


Dogfish external anatomy. Identify
eyes
Spiracles
Mouth
Nares
Lateral line
External gill slits
Spine
Pectoral fin
Anterior and posterior Dorsal fin
Pelvic fin
Clasper
Caudal fin
Know function of lateral line as well

Dogfish anatomy overview. Identify and describe the function of the following structures in your dogfish shark dissection
External Anatomy | • Internal Anatomy: | |
• Rostrum | • Gills | |
• Eye | • Liver* | |
• Spiracle* | • Stomach (indicate rugae)* | |
• Gill slits* | • Intestine | |
• Mouth | • Spiral Valve* | |
• Nostrils | • Rectal gland* | |
• Lateral line* | • Spleen* | |
• Placoid scales/ dermal | • Heart* | |
denticles | • Gonads |
Rostrum: sensory, helps in navigation.
Gills: respiration – exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Eye: sight.
Liver: buoyancy, filled with oil.
Spiracle: respiration, allows water intake for gills.
Stomach (with rugae): digestion; rugae allow for stomach expansion.
Gill slits: water exits after passing over gills.
Intestine: digestion and nutrient absorption.
Mouth: intake of food.
Spiral Valve: increases surface area for absorption.
Nostrils: sense of smell.
Rectal gland: excretion; regulates salt concentration.
Lateral line: detects movement and vibrations in water.
Spleen: involved in circulation; filters blood.
Placoid scales/Dermal Denticles: protection, reduce drag in water.
Heart: circulatory function; typically 2 chambers.
Gonads: reproduction.


What phylum, subphylum, and class are perch & 99% of fish species found? How are they characterized ?
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Actinopterygii (Ray finned fishes)
Characterized by their fins which are entirely supported by fin rays.

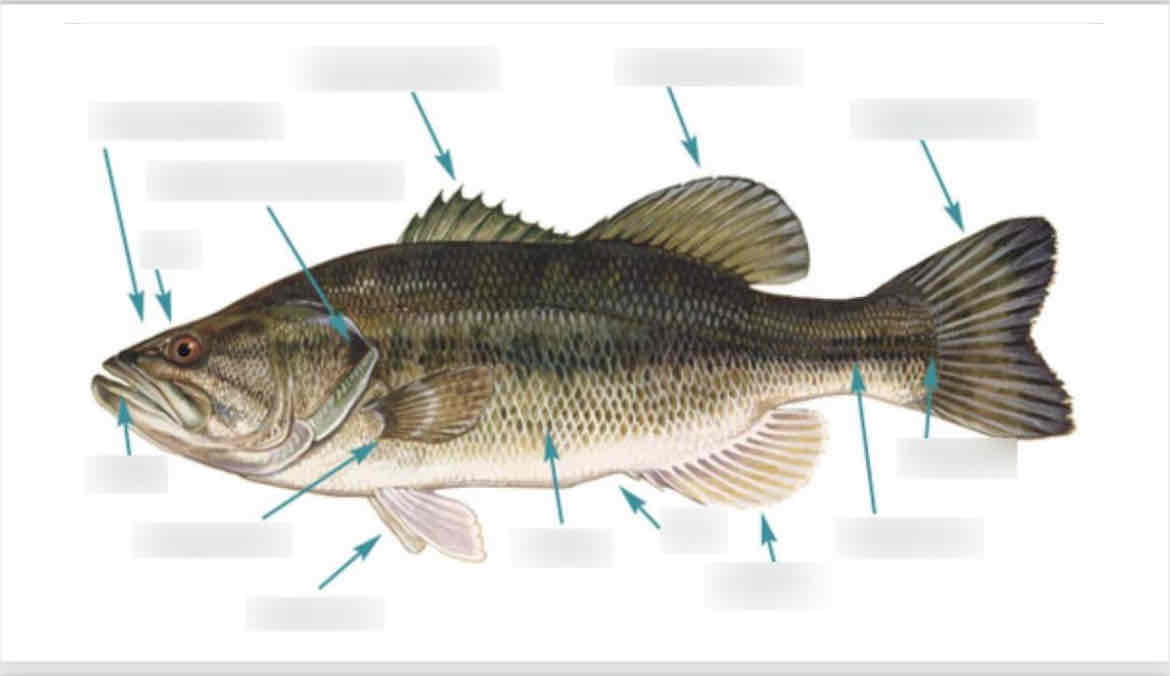
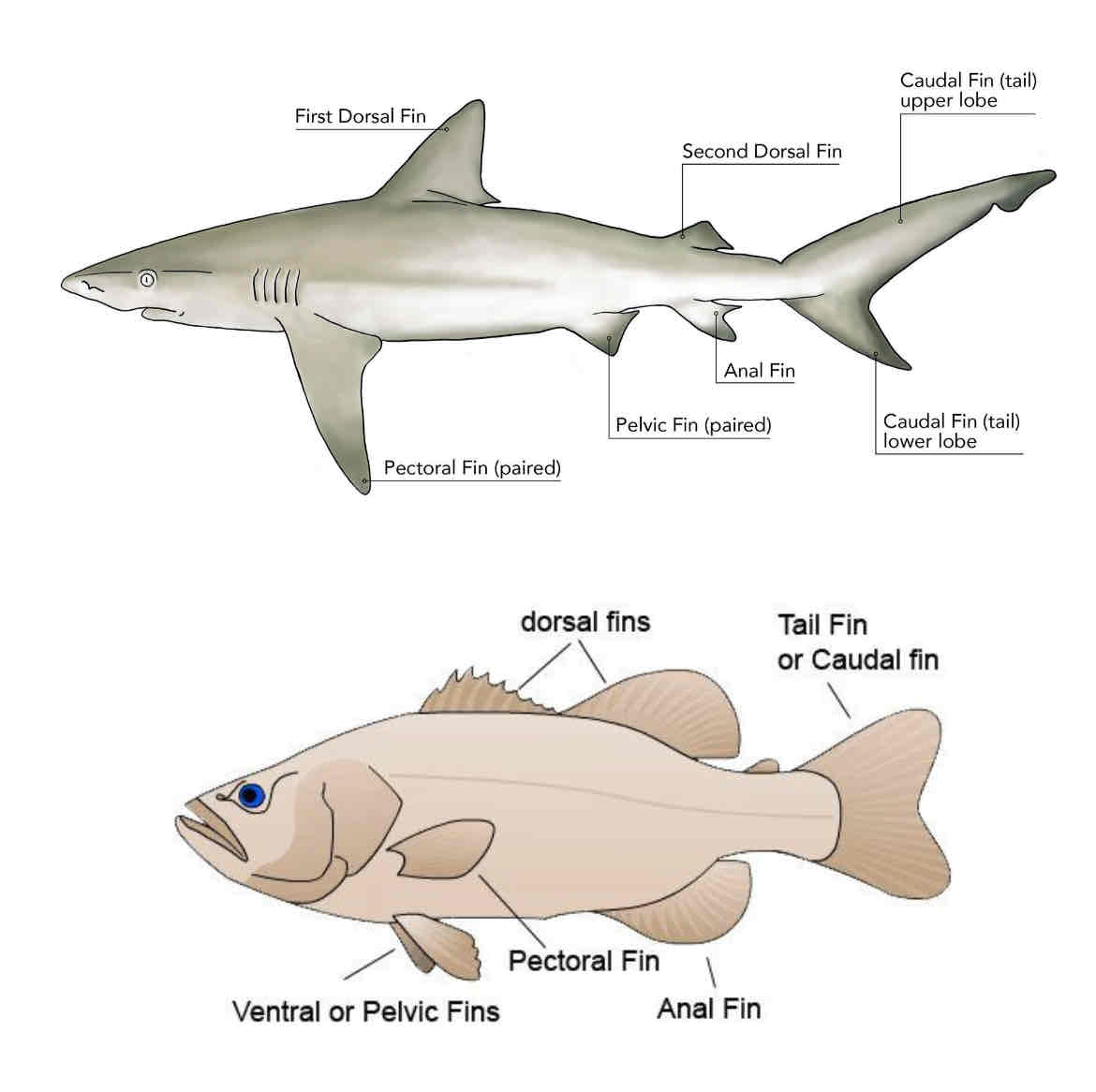
External perch anatomy. Identify the following external structures :
Mouth
Eyes
Nostrils
Fins: dorsal, pectoral, pelvic, anal, and caudal
Fin rays
Operculum
lateral line
Anus
Notice the difference between cartilaginous fish fins and ray finned/bony fish .
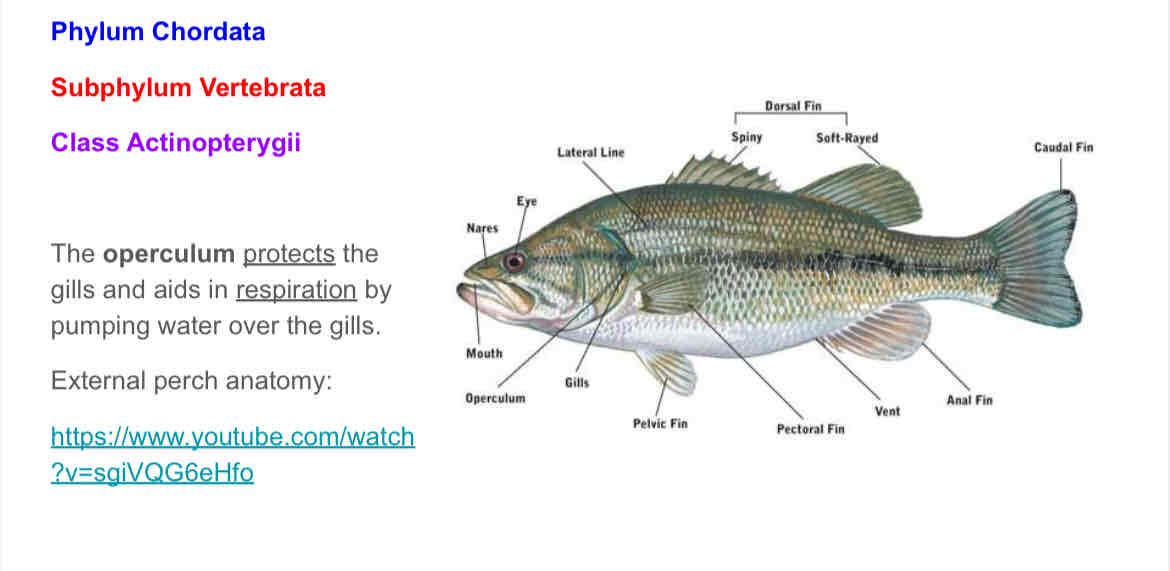
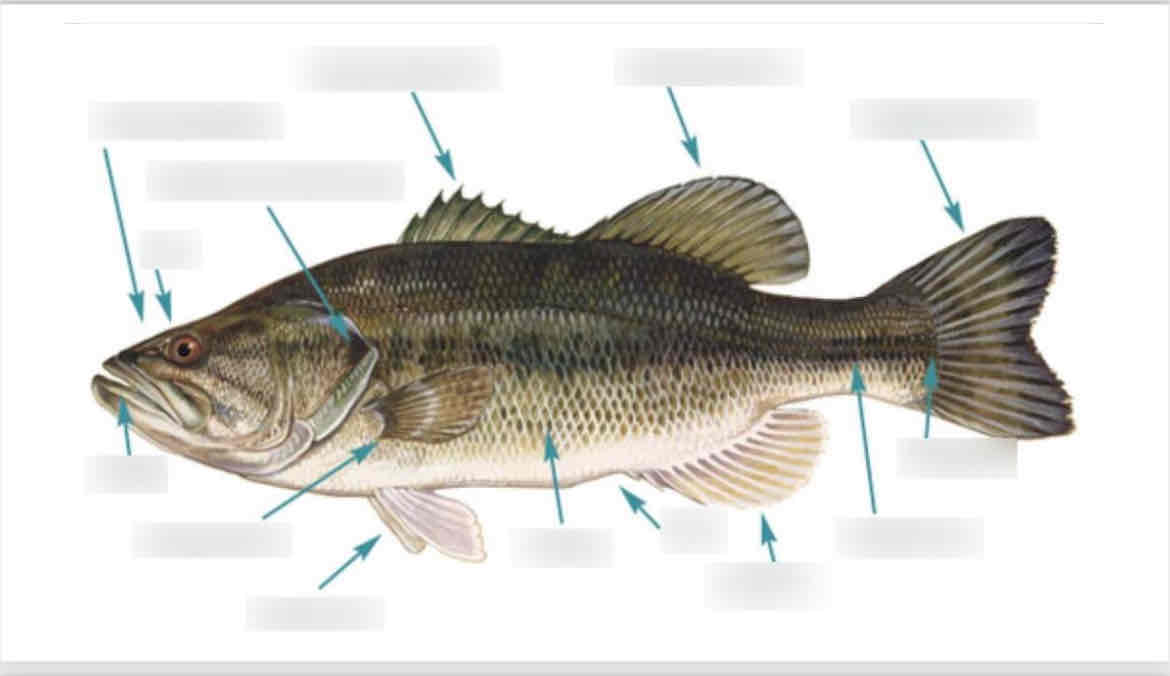
What is the function of the operculum and where is it located?
Operculum: protection and respiration. Protects the gills and aids in respiration by pushing water over them.
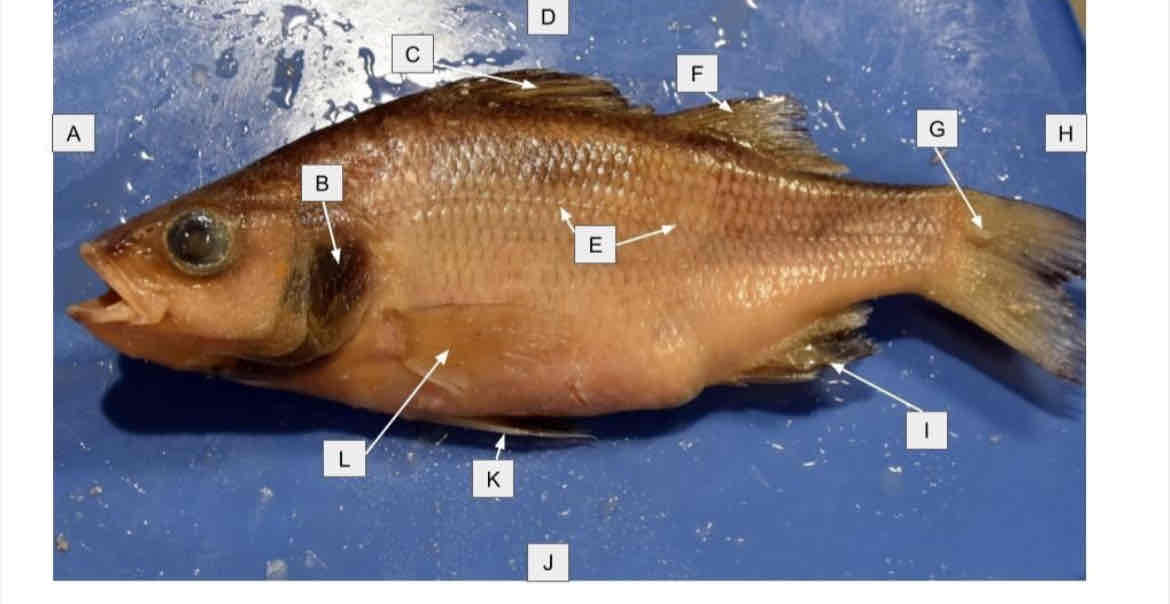
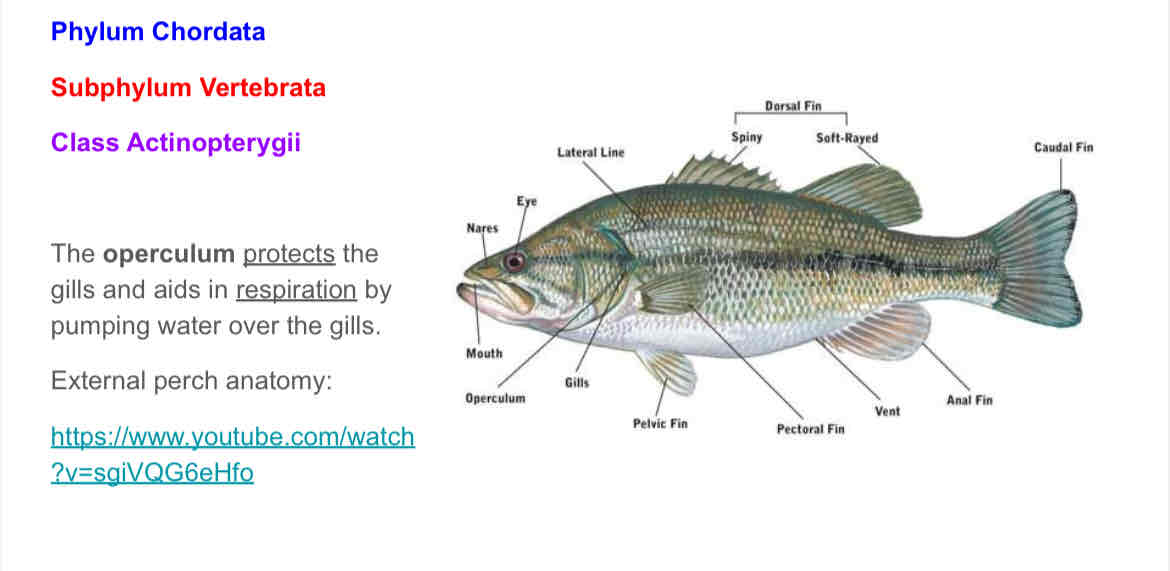

Perch external anatomy
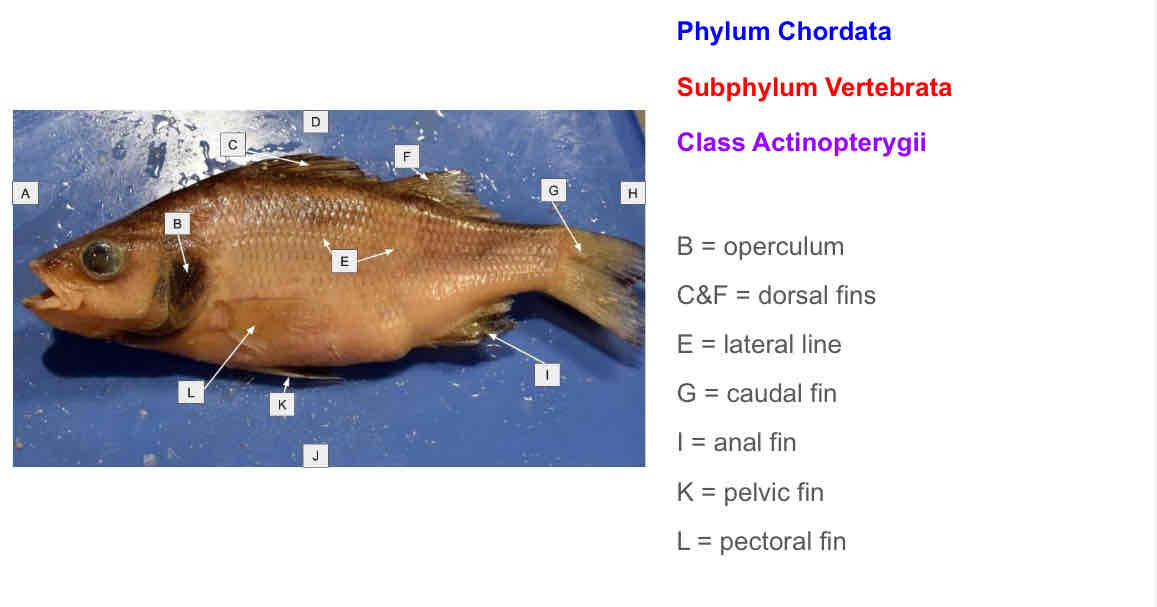
Match the letter to the structure:
operculum
Dorsal fins
Lateral line
Caudal fin
Anal fin
Pelvic fin
Pectoral fin
Note that sharks dont have operculums

Describe the function of the following external anatomy structures: Mouth, Nostrils, Operculum, Pectoral fins, Pelvic fins, Anal fins, Dorsal fins, Caudal fin, Lateral line, Anus.
Mouth: intake of food; Nostrils: sense of smell; Operculum: protects gills and aids in respiration; Pectoral fins: maneuverability; Pelvic fins: stability and maneuverability; Anal fins: stability; Dorsal fins: stability; Caudal fin: propulsion; Lateral line: detects movement and vibrations in water; Anus: excretion.
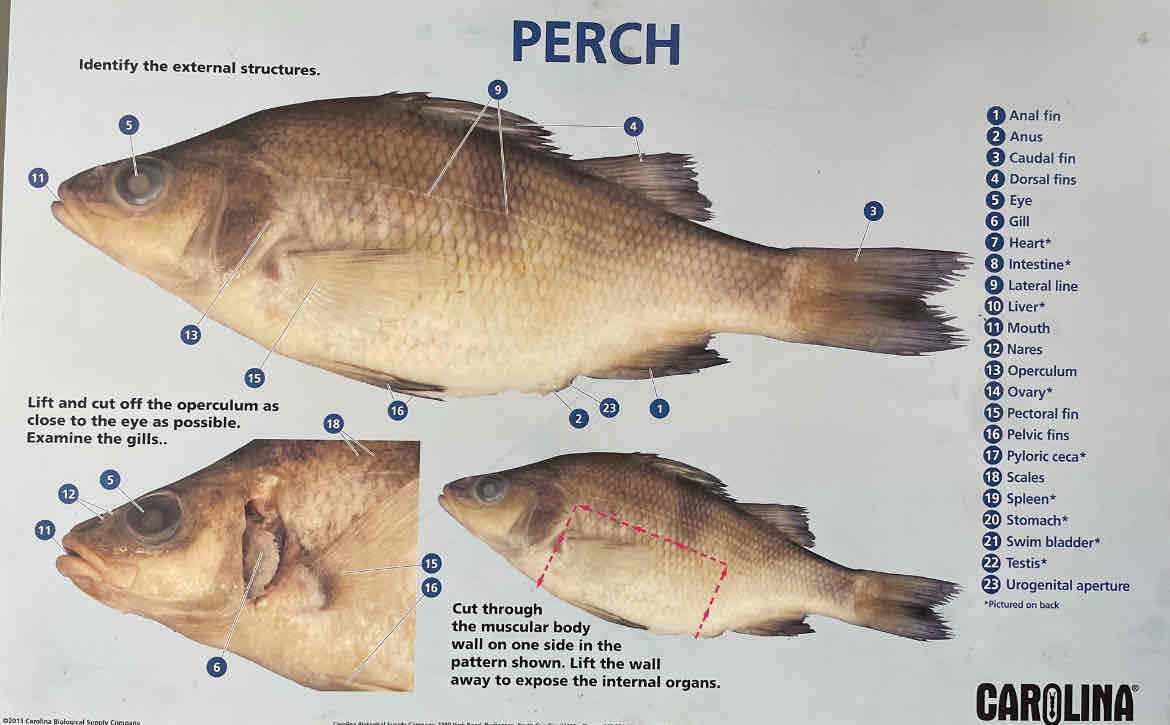
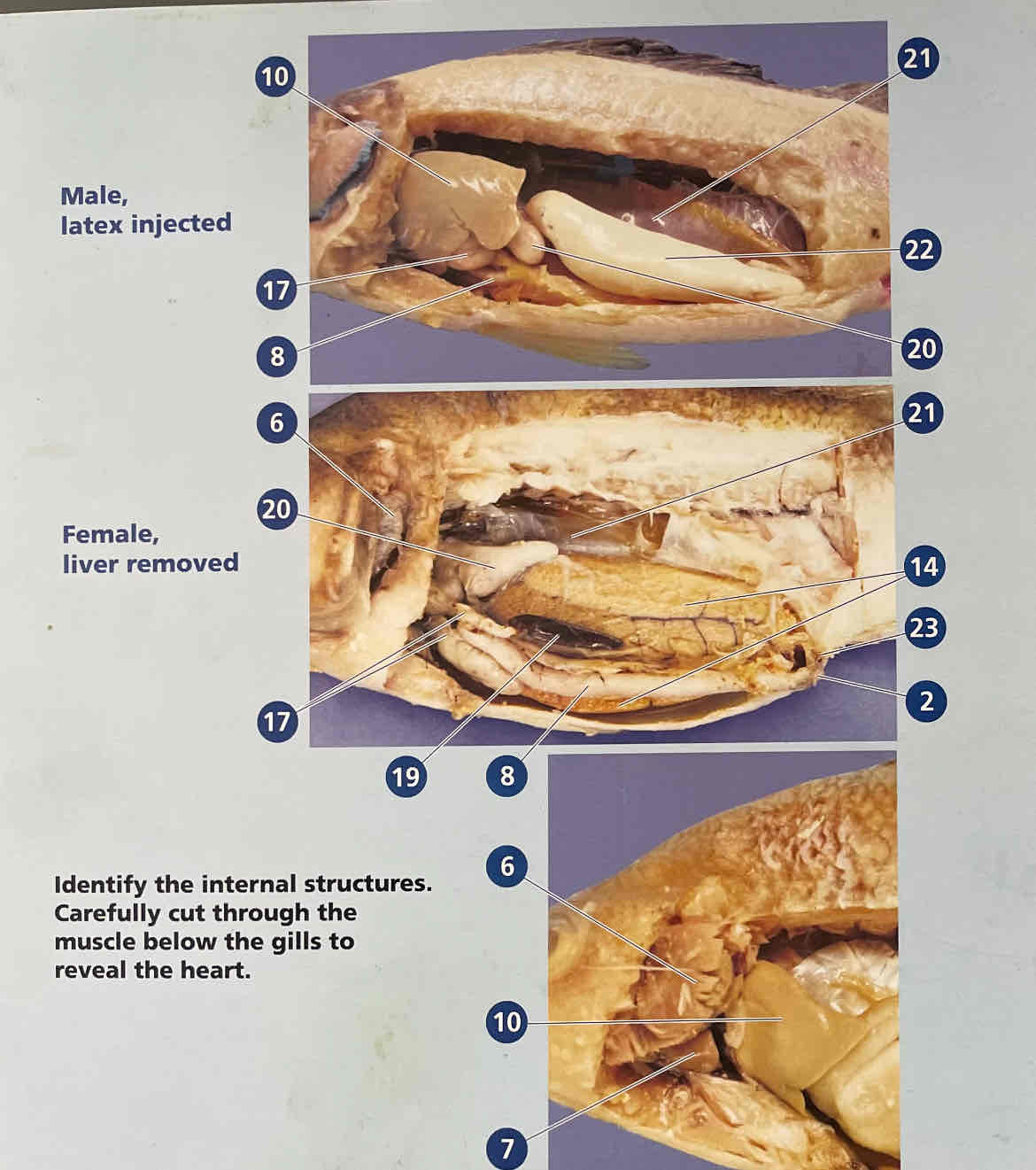
Identify and list function of Internal Anatomy: Gill filaments, Gill rakers, Intestine, Stomach, Liver, Gonads, Swim bladder, Heart, Brain
Gill filaments: respiration, increase surface area for gas exchange; Gill rakers: filter food from water; Intestine: digestion and nutrient absorption; Stomach: storage and digestion; Liver: bile production and detoxification; Gonads: reproduction; Swim bladder: buoyancy control; Heart: circulation; Brain: control center for sensory and motor functions.
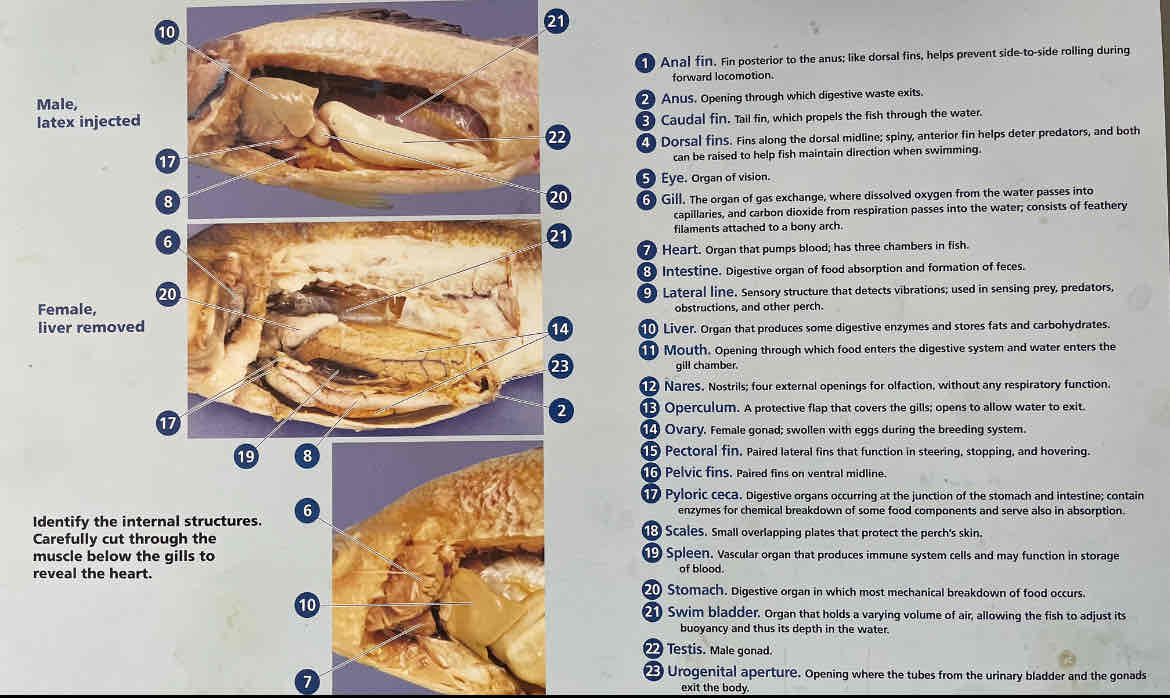
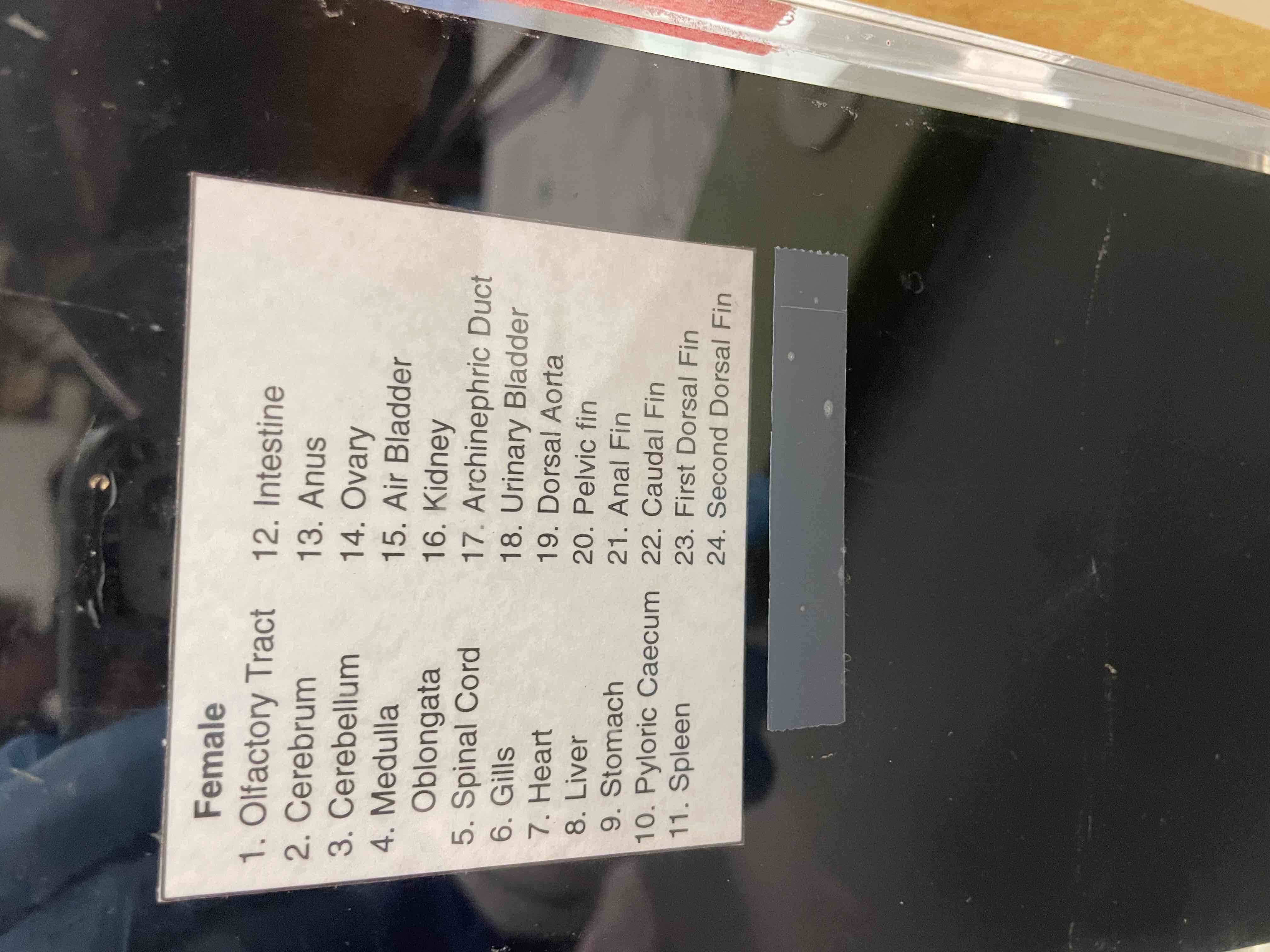
Internal perch anatomy. Identify the following:
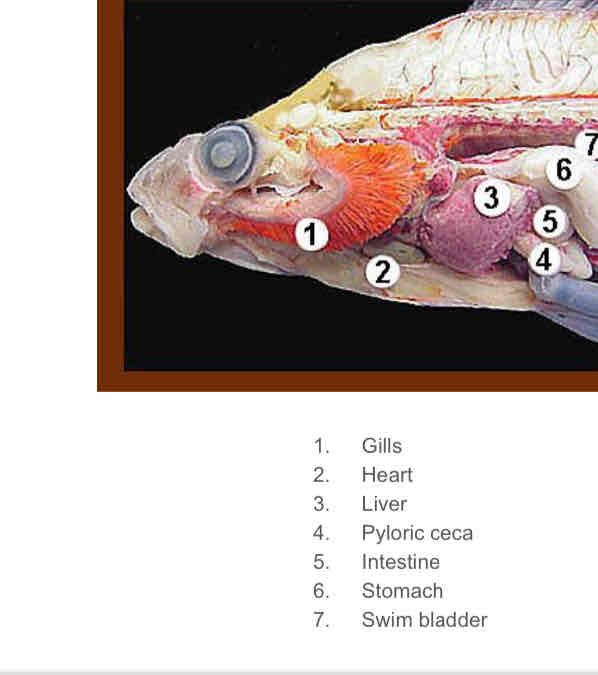
1. Gills
2. Heart
3. Liver
4. Pyloric ceca
5. Intestine
6. Stomach
7. Swim bladder
8.Gonads
Urinary bladder
Anus
Dorsal fin
Caudal fin
Pelvic fin
Anal fin
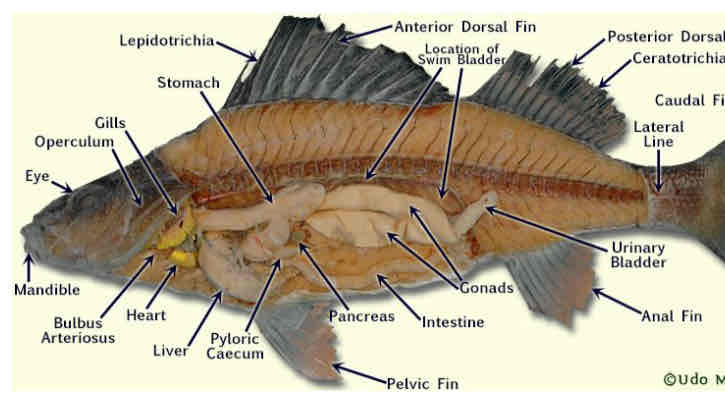
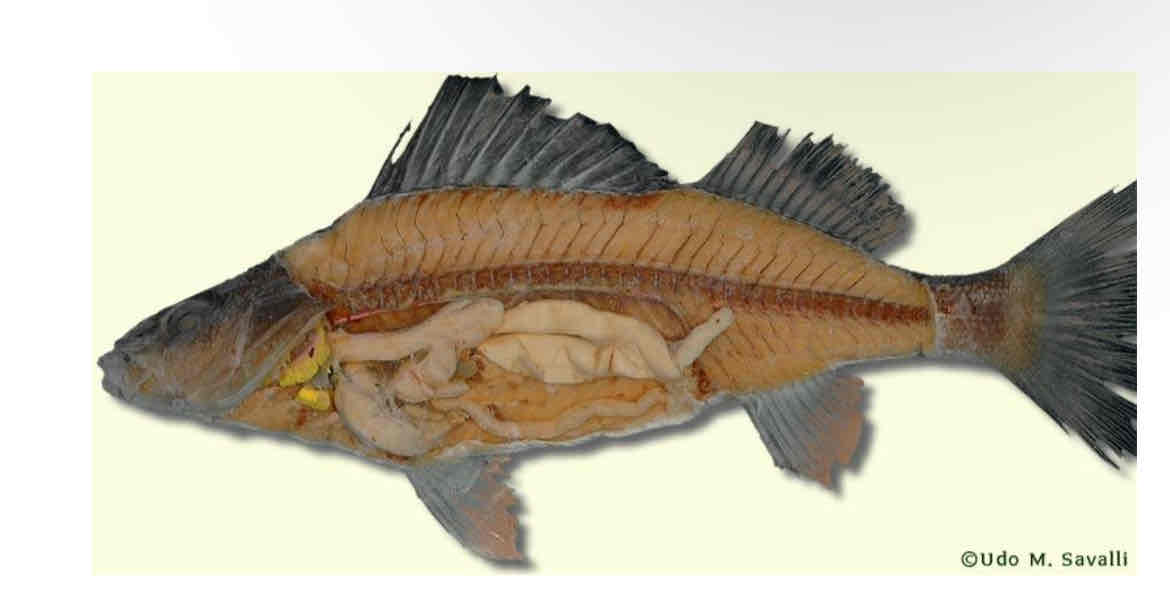
Identify the structures corresponding to the numbers. Internal perch anatomy
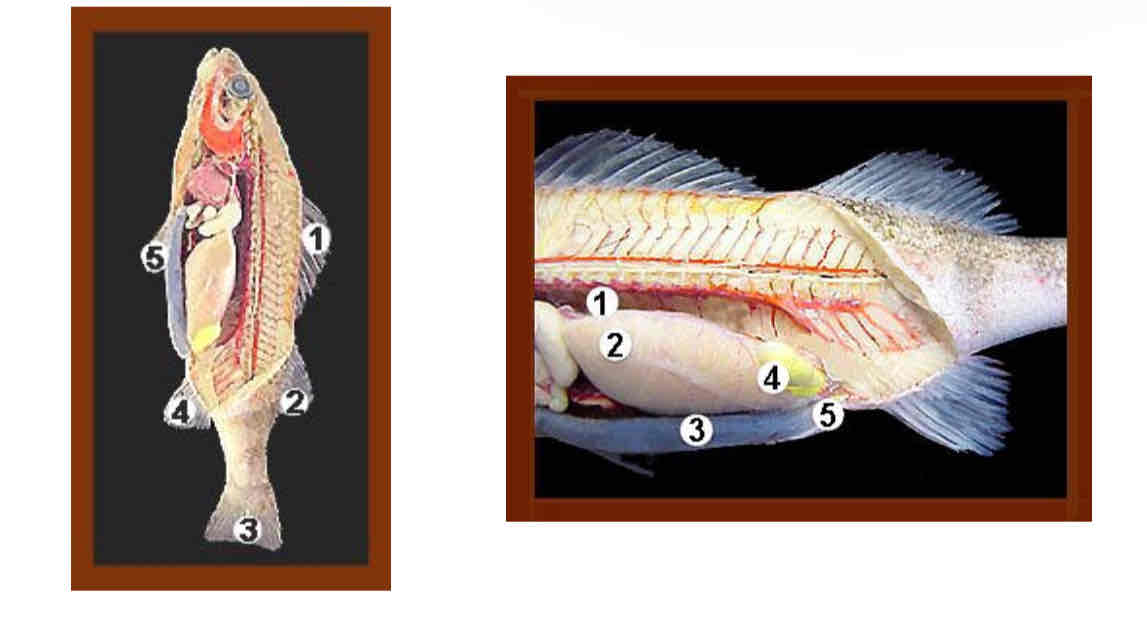
Identify the structures. Internal perch anatomy

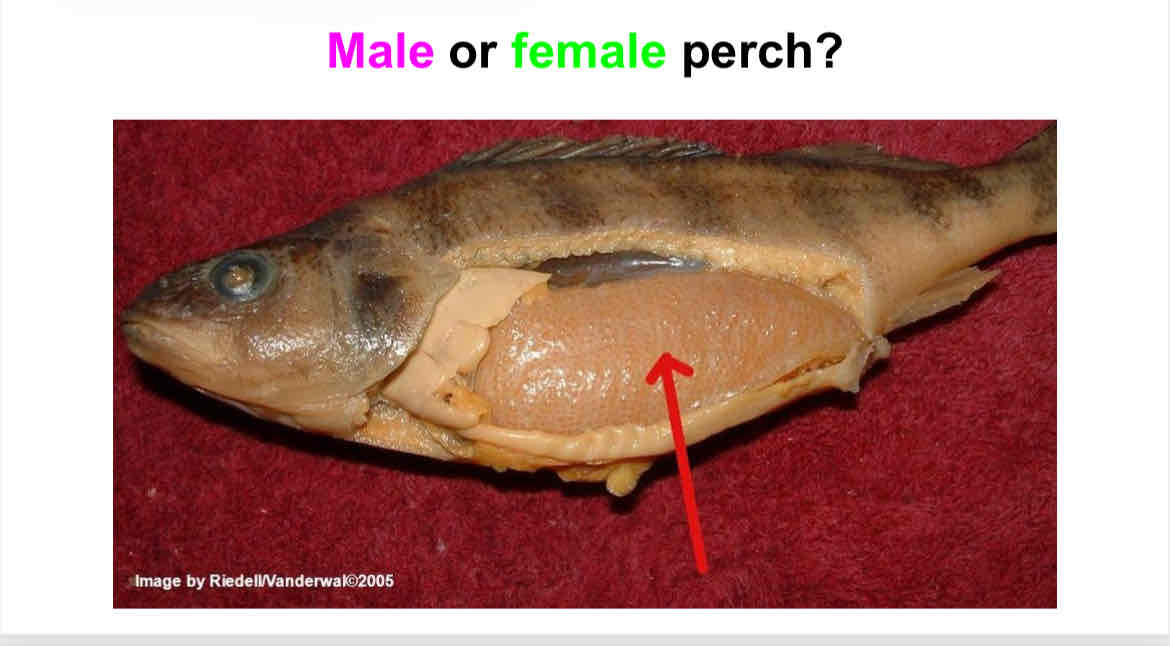
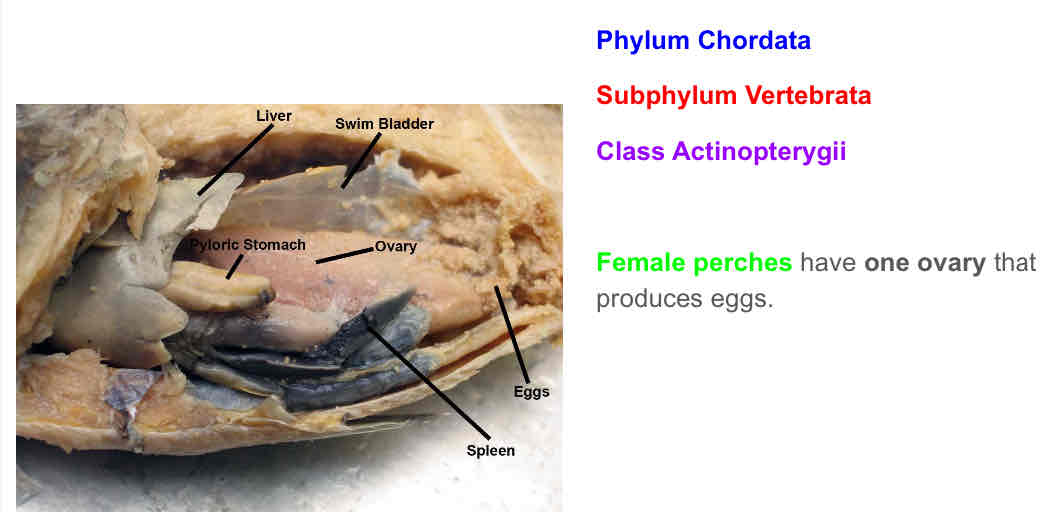
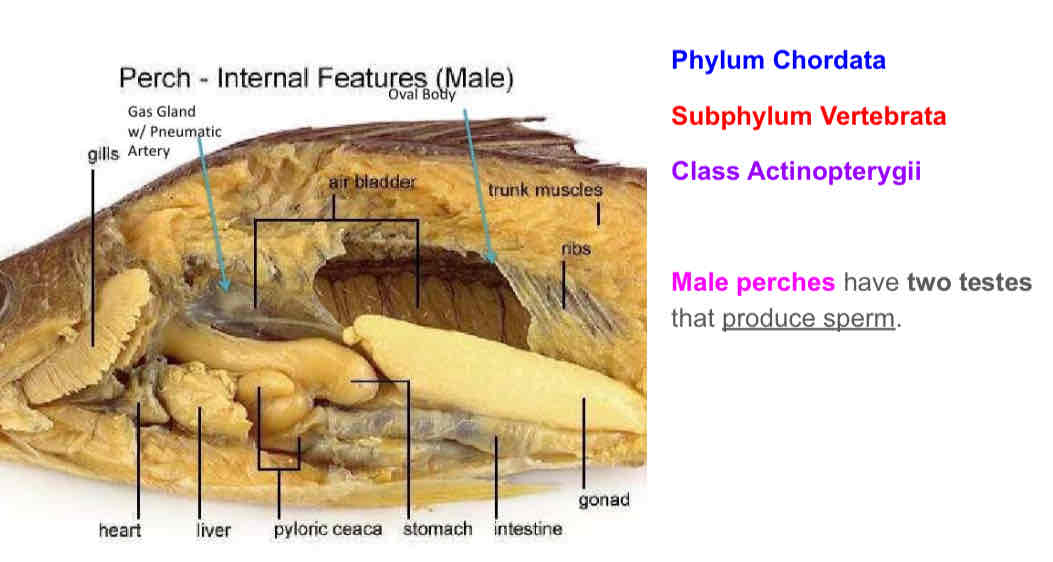
Is this a male or female perch? How can you tell?
Female. One large ovary
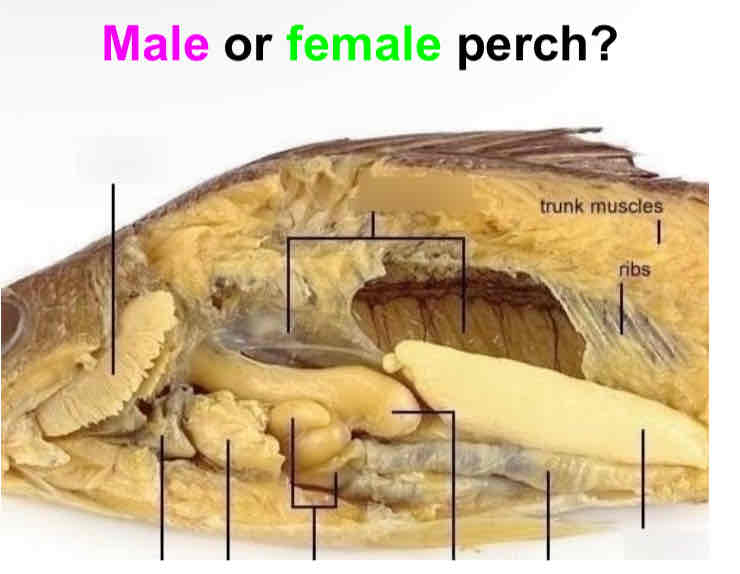
Is this a male or female perch? How can you tell?
Male. 2 testes for sperm
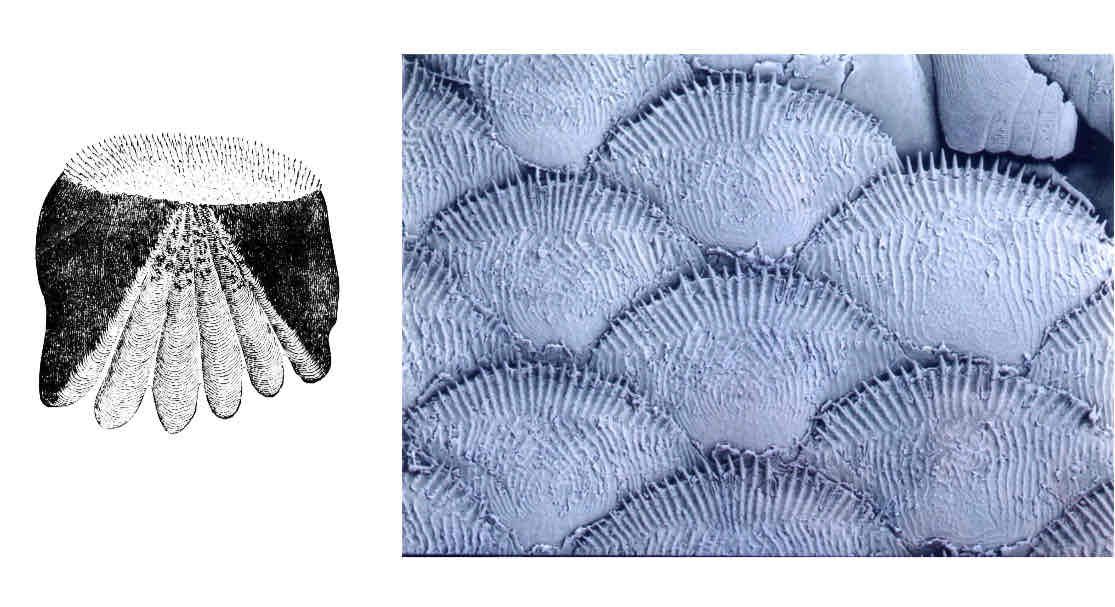
What type of scale cell is this? Are these found in Cartilaginous fish or bony fish?
Ctenoid scales . Found in ray finned bony fishes like perch.

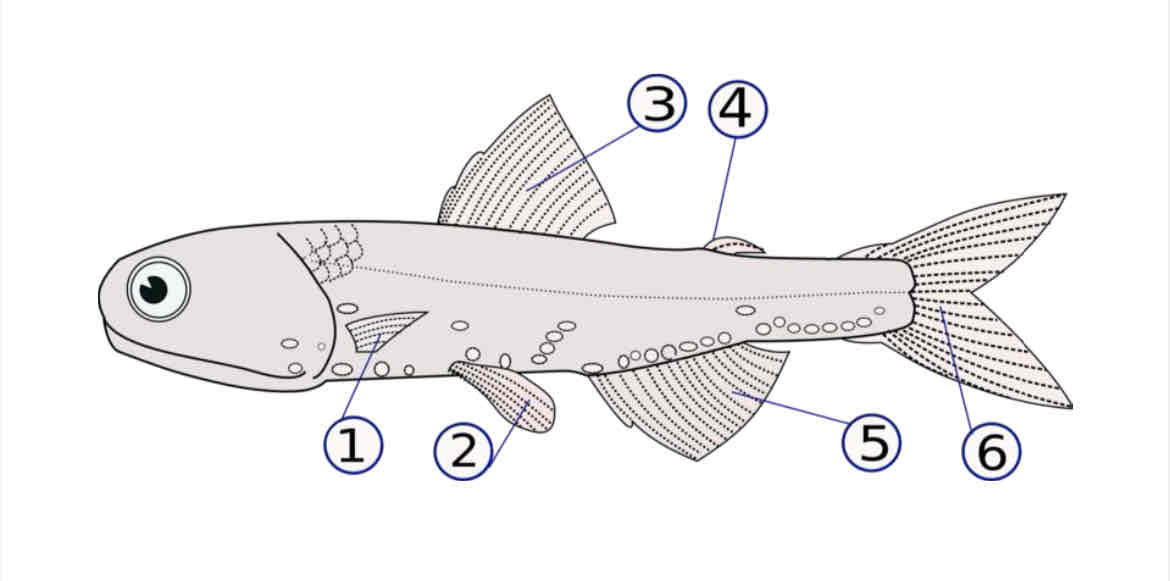
Identify each fin and its function. Compare and contrast to shark fins.
Pectoral fin: maneuverability
Pelvic fin: maneuverability
Dorsal fin: stability
Anal fin: stability
Caudal fin: propulsion , swimming
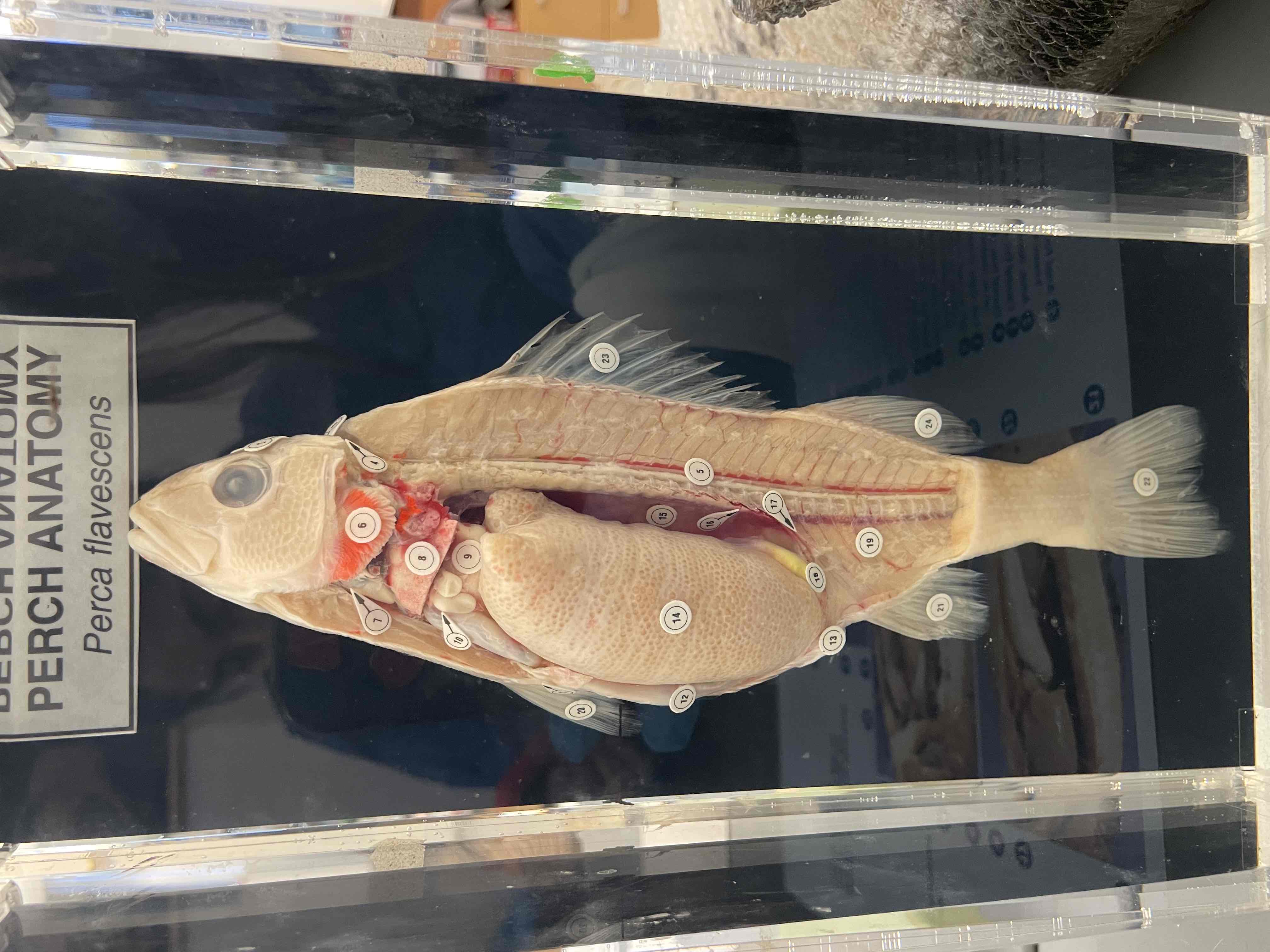

Perch internal anatomy mount

Trout life stages
Note difference in young between classes of fish
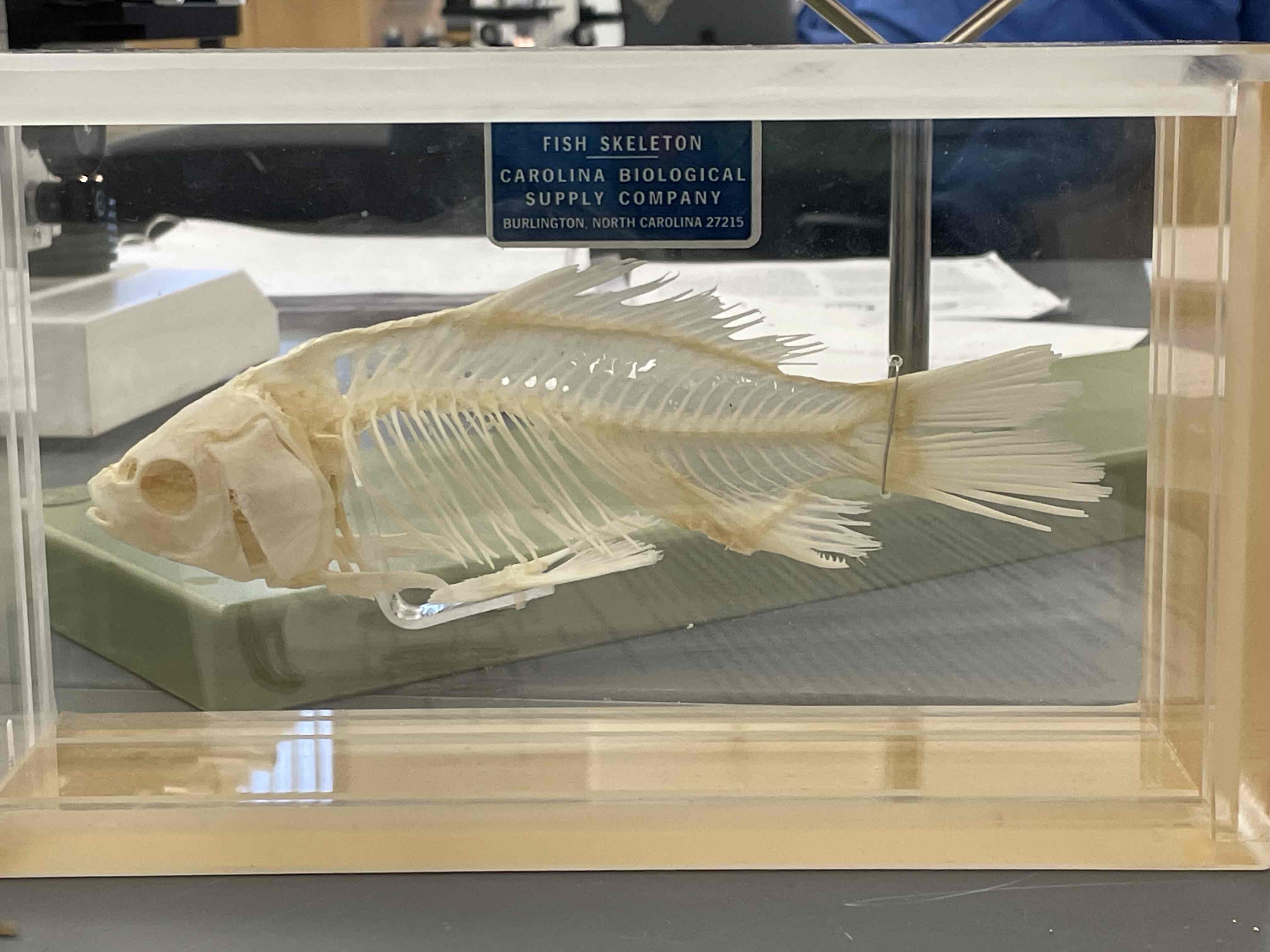

Perch skeleton. Cartilaginous or bony fish? What class is this ?
Perch are bony fish. Class Actinopterygii, aka Ray-finned bony fishes.
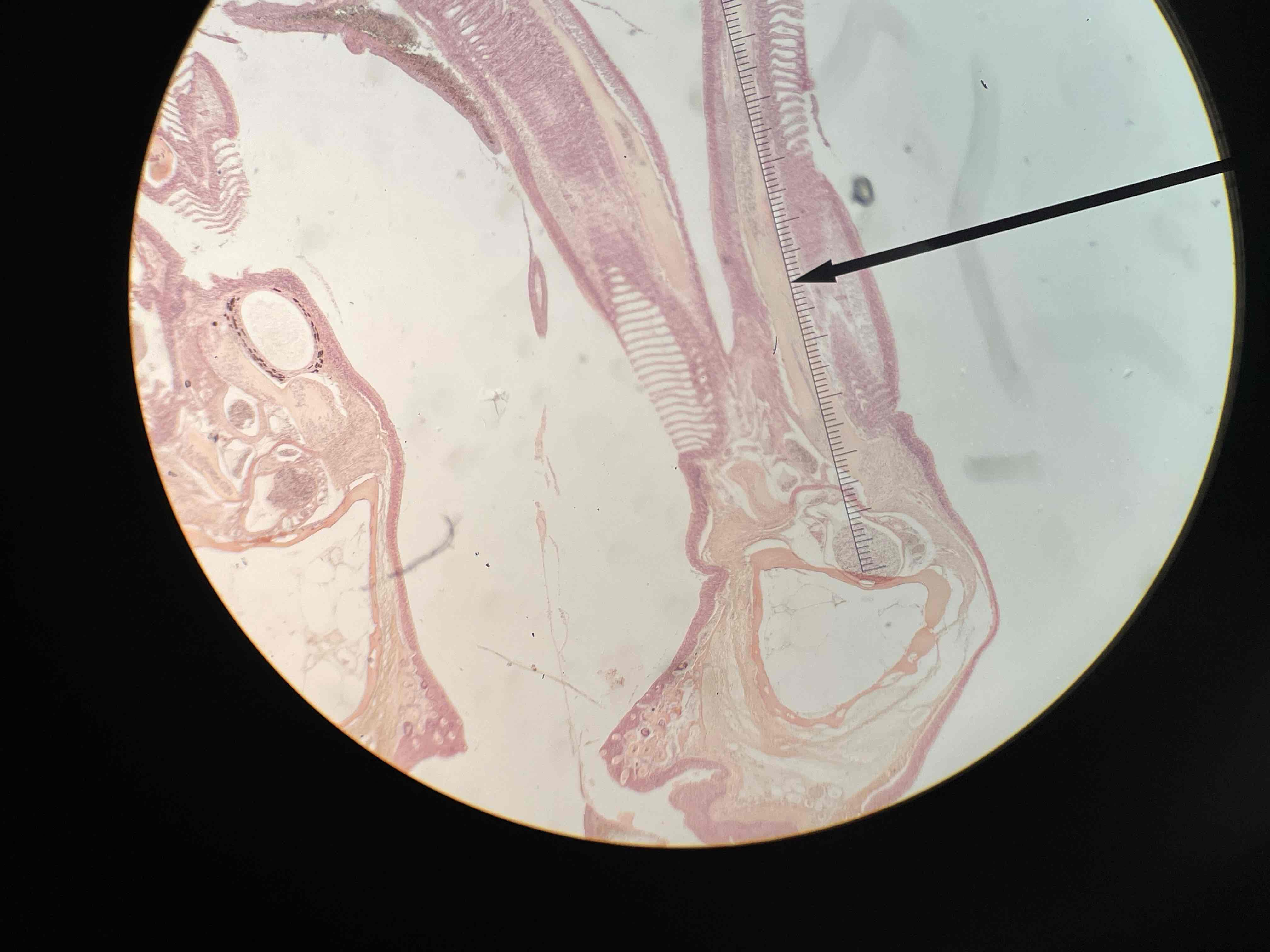
What is in this slide? Identify and describe the function.
Fish gills slide. Function for respiration.
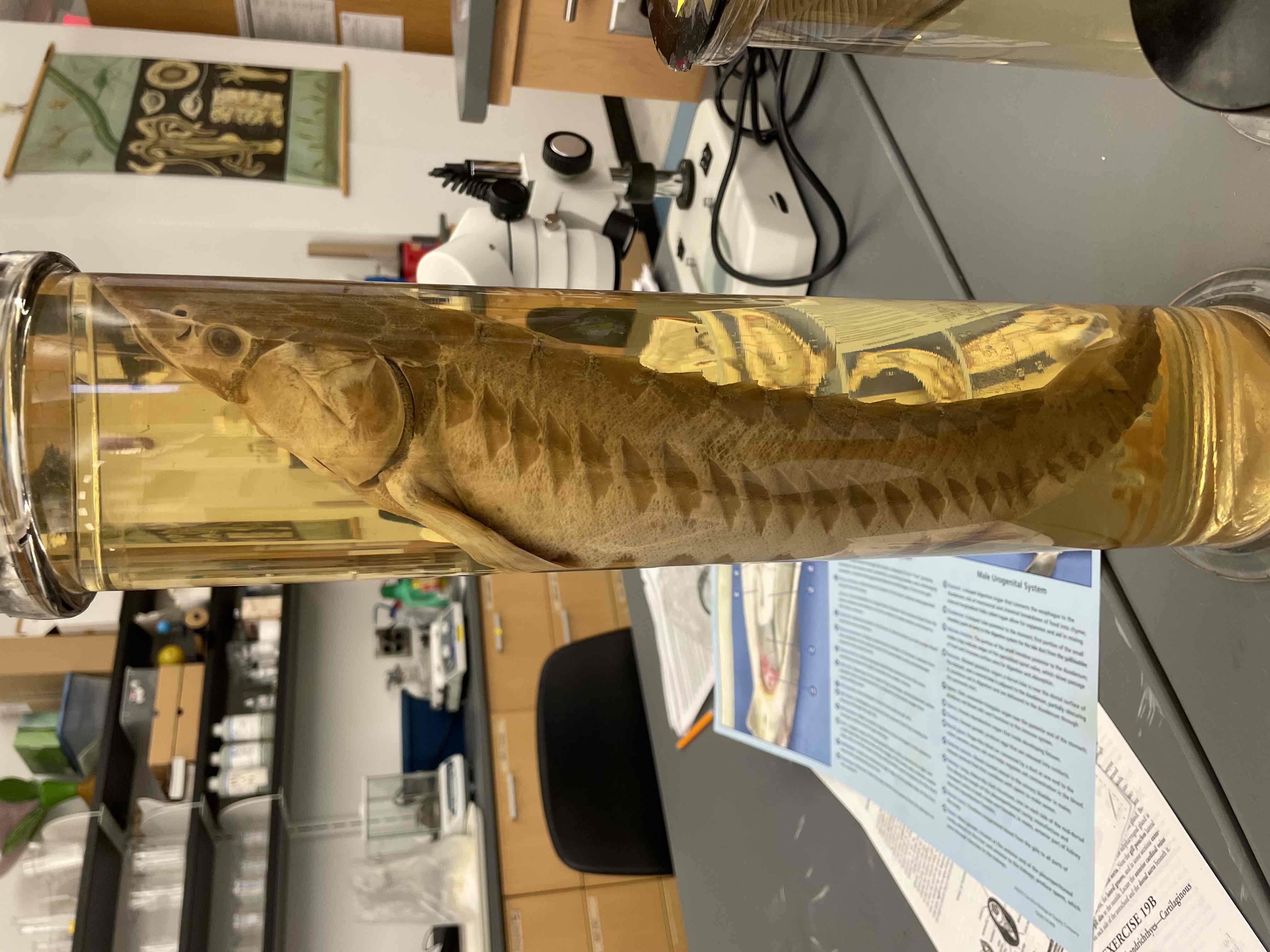


What phylum, subphylum, and class are the following fish found? ( Know the general features of members of the Class): sea horse, elephant fish, flying fish, sharksucker (remora), stargazer, blowfish, sturgeon.
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Actinopterygii
General features: Members of this class, known as ray-finned fishes, have an elaborate structure of fins supported by bony rays, a swim bladder for buoyancy, and gills covered by an operculum. They inhabit a range of environments from freshwater to marine
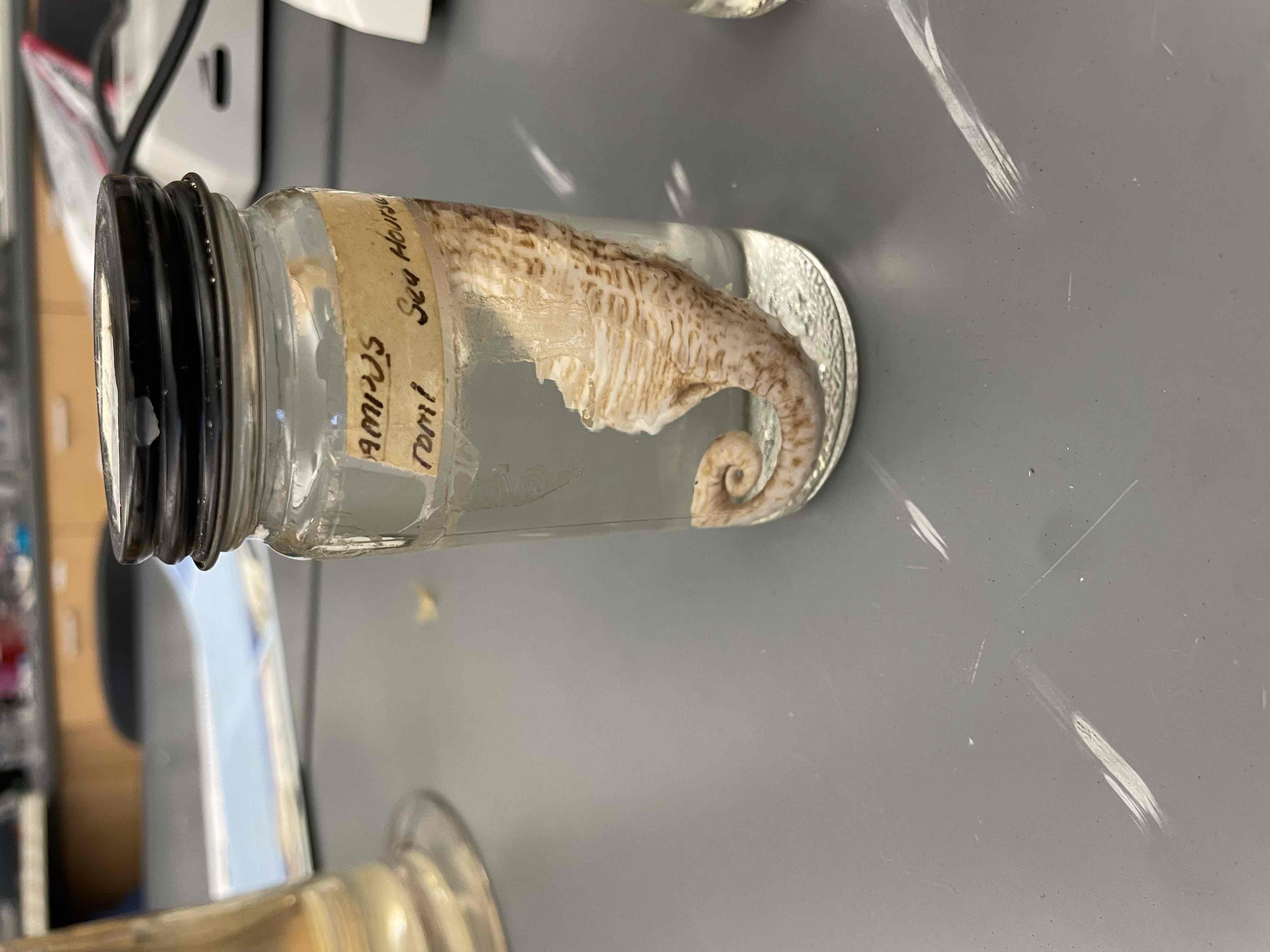
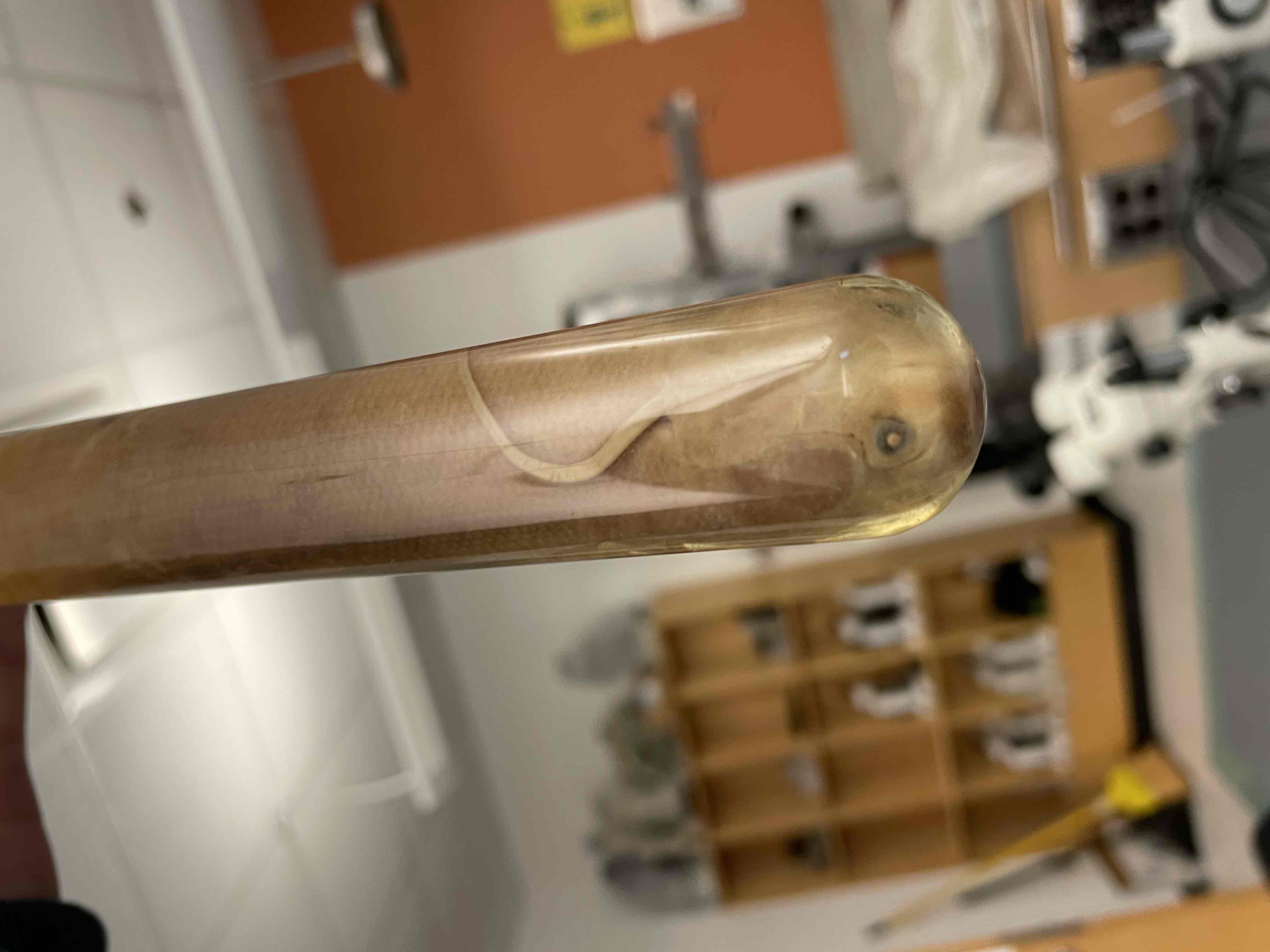


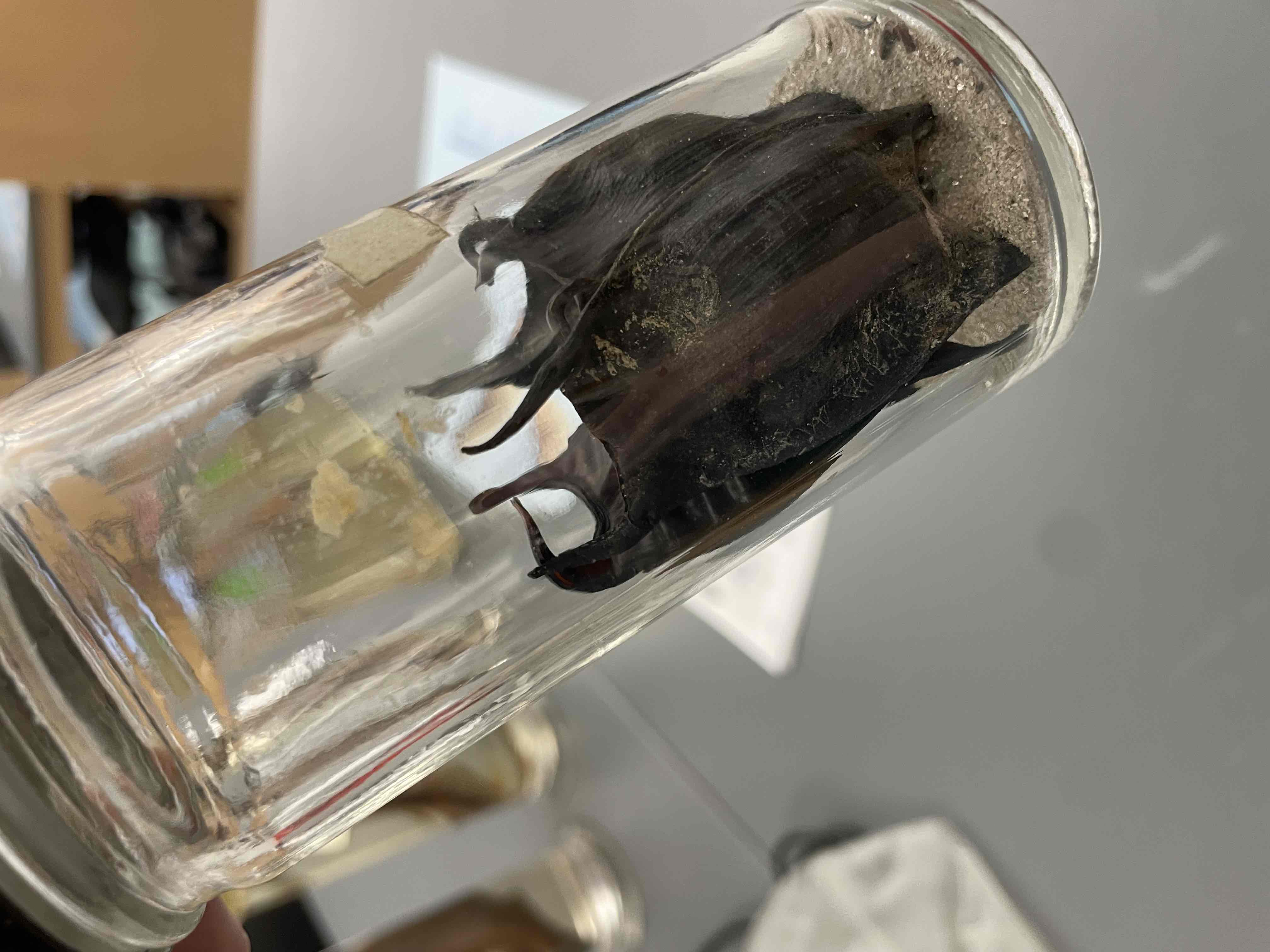
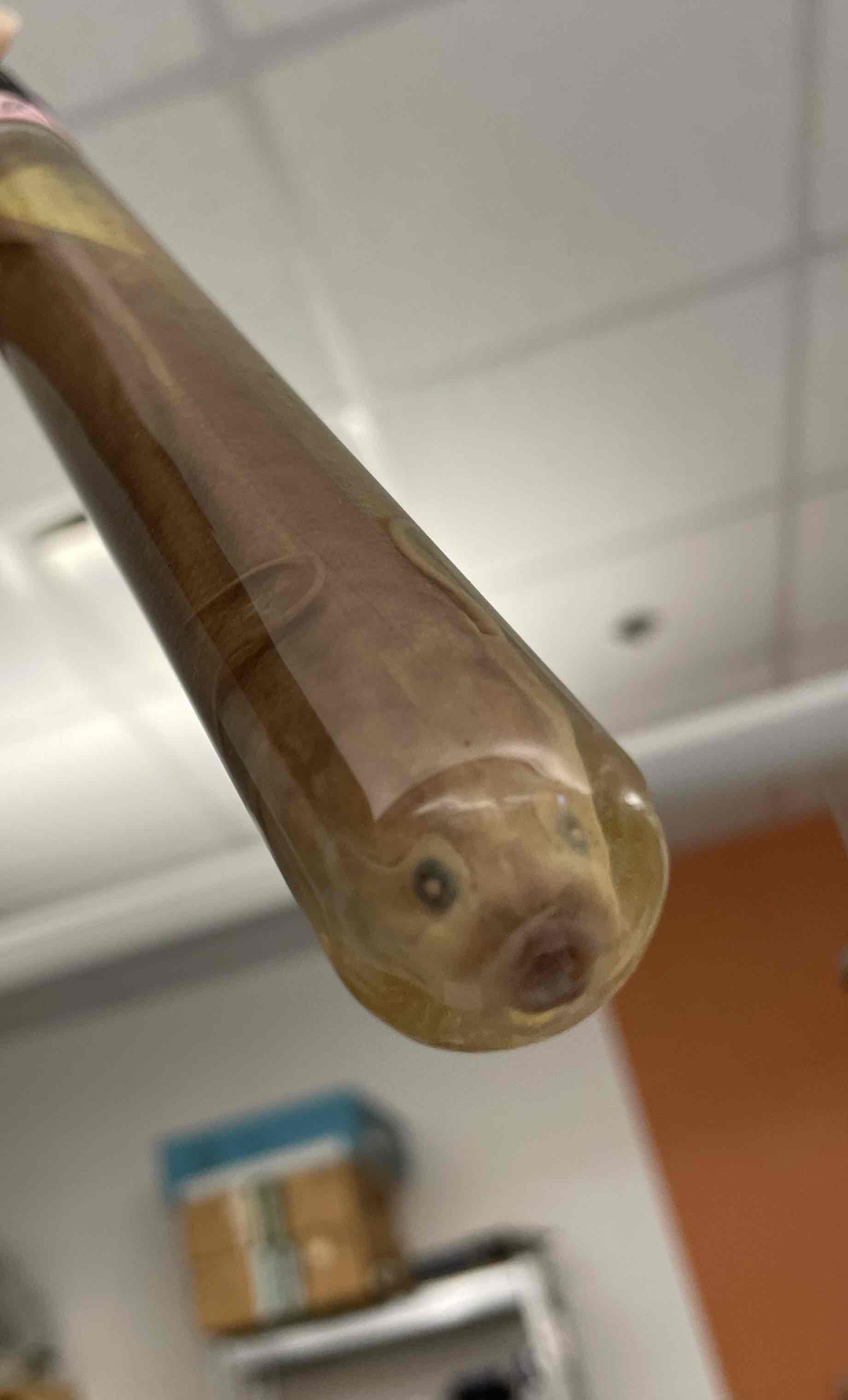
What is the specimen in this vial?
Be able to identify the phylum and subphylum for this specimen
Recognize that this specimen shares a common ancestor with tetrapod (4 legged) vertebrates
Lungfish.
Phylum: chordata
Subphylum; vertebrata
“Lobe-finned fishes”. Don’t need to know specific class name.
How many chambers do Fishes heart’s have? Same as any other classes?
2 chambers. No, only group this unit with 2 chambers.

How do sharks and perches compare in the way they maintain buoyancy?
perches use a swim bladder to control their position in the water, while sharks primarily rely on a large, oily liver to provide lift, as they lack a swim bladder