Test 10
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

75 Terms
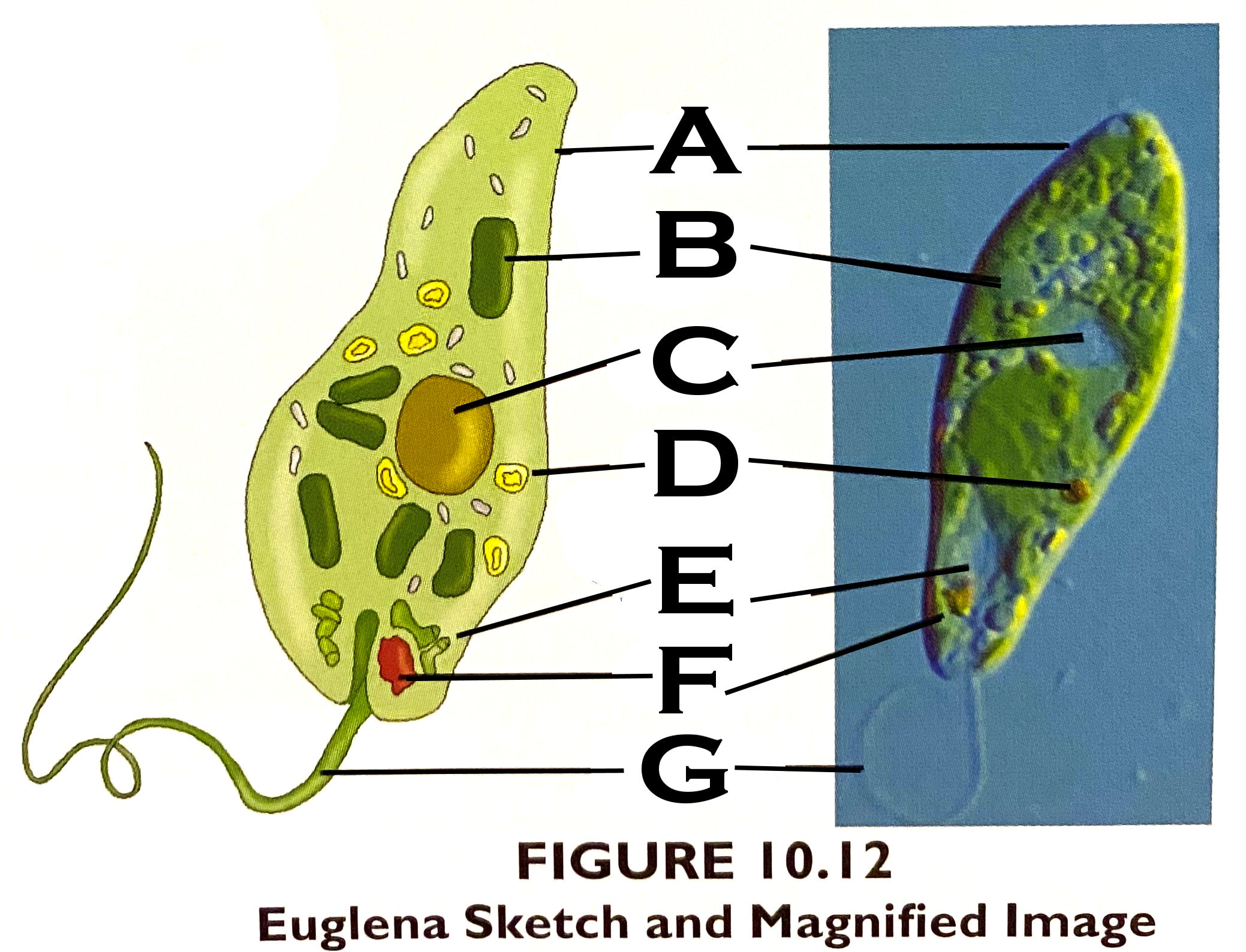
What organelle is A?
pellicle - A firm, flexible coating outside the plasma membrane
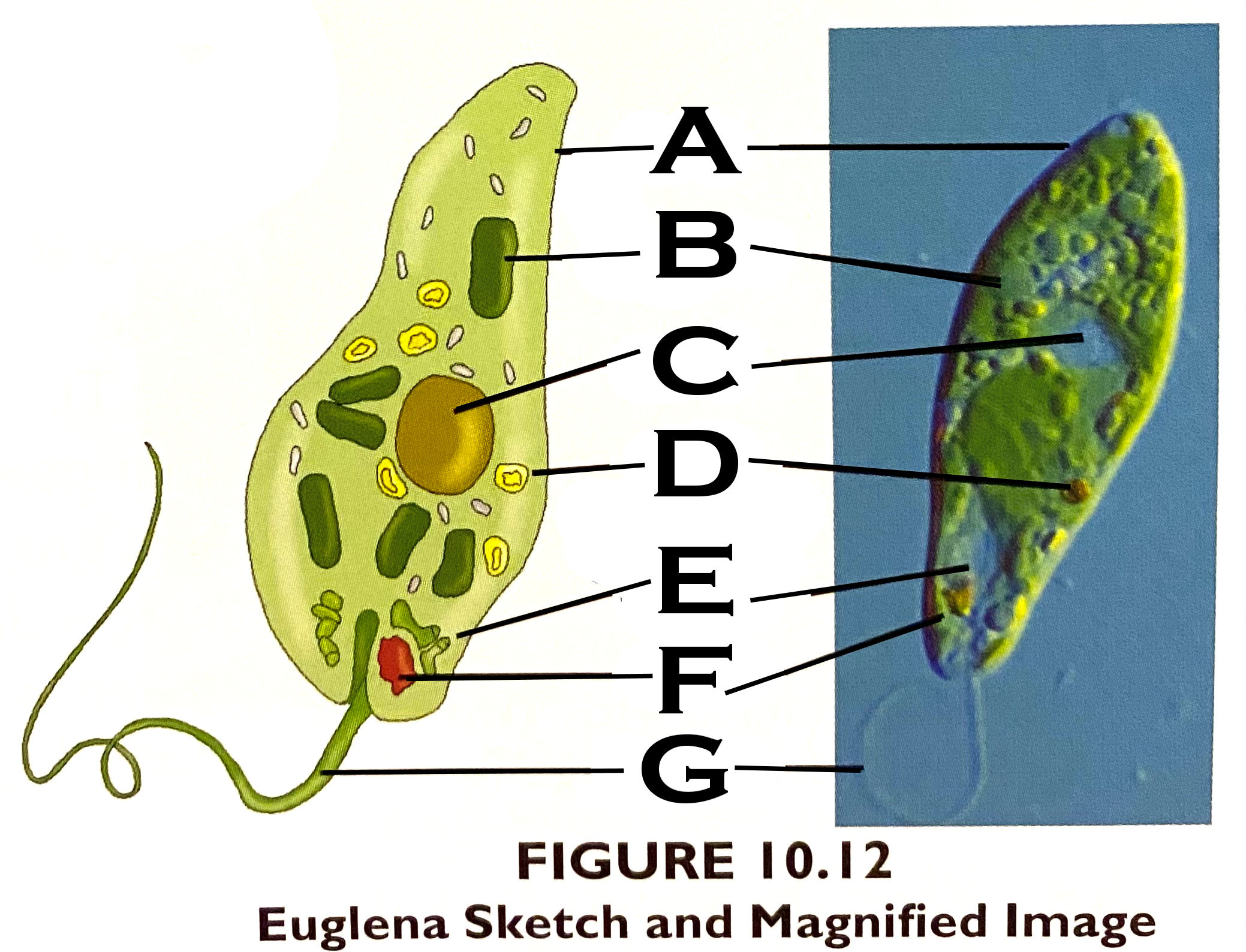
What organelle is B?
chloroplast
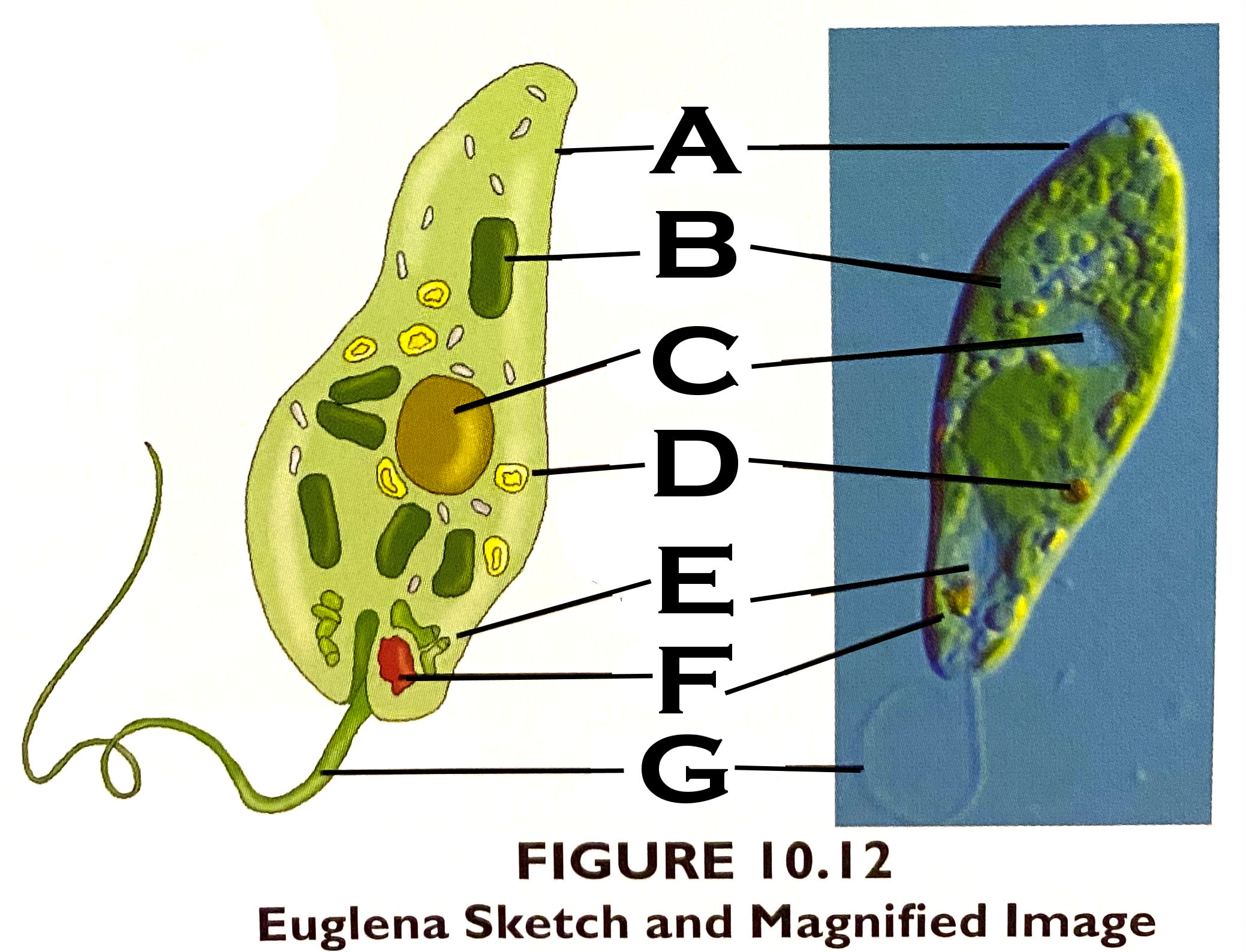
What organelle is C?
nucleus
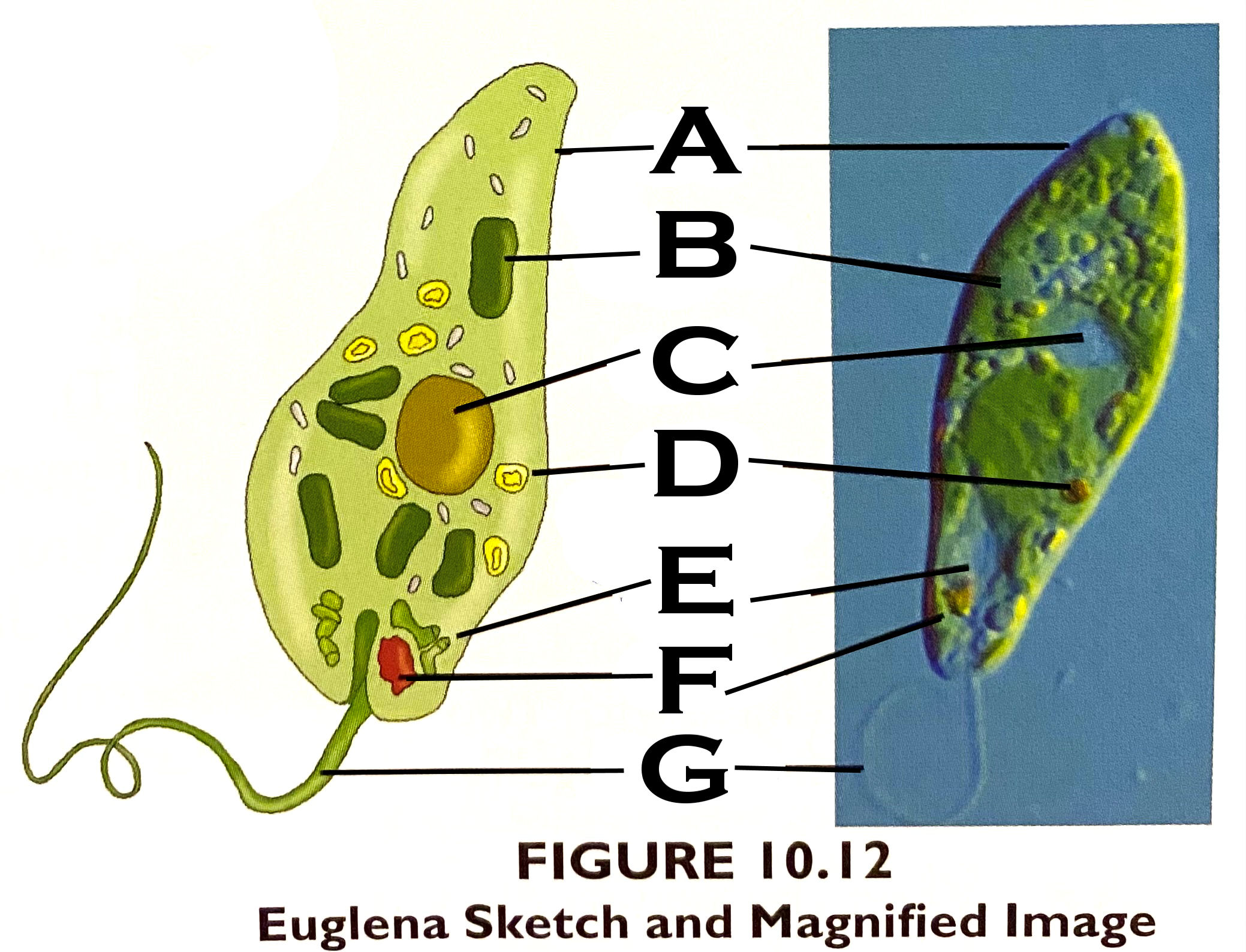
What organelle is D?
stored carbohydrate
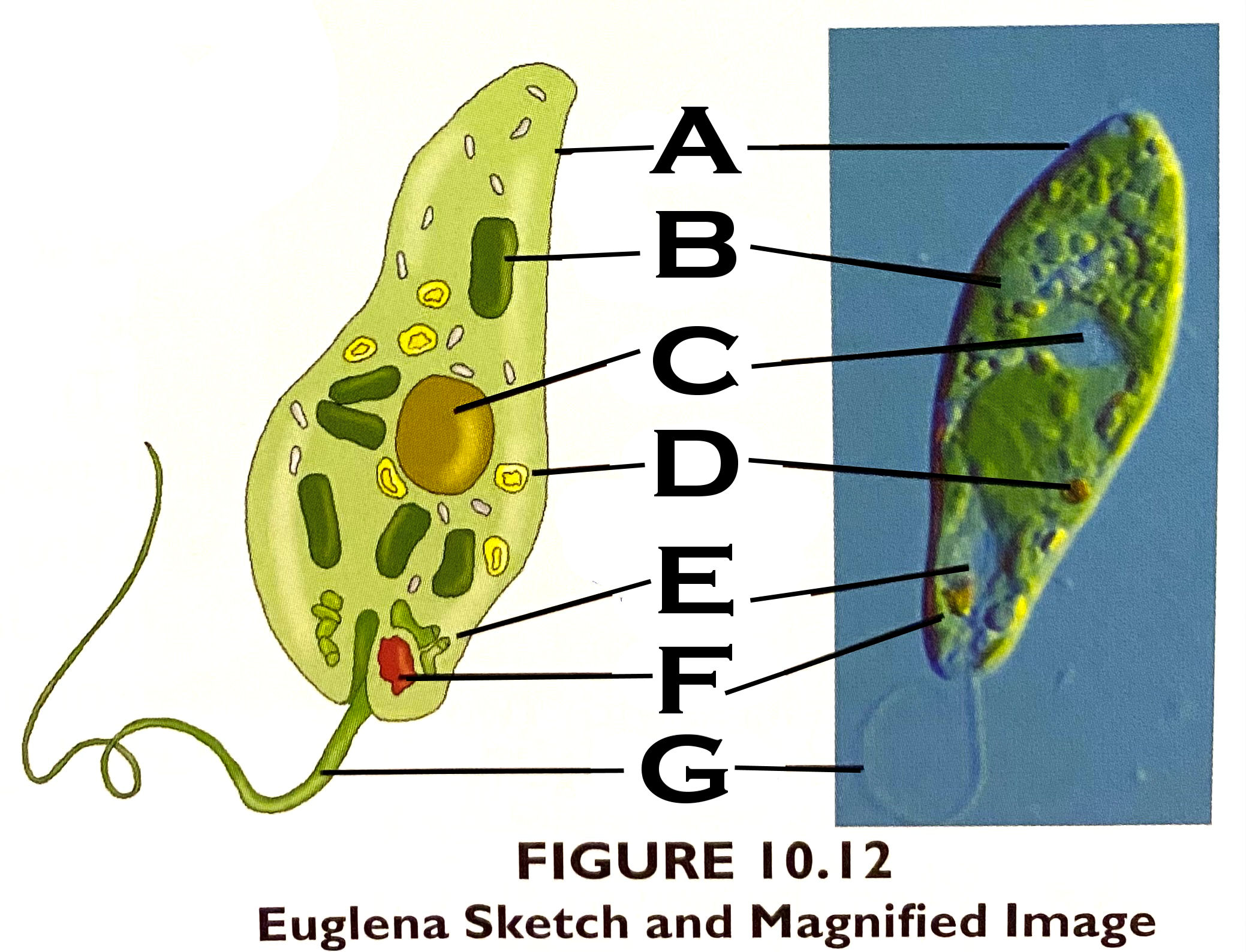
What organelle is E?
contractile vacuole
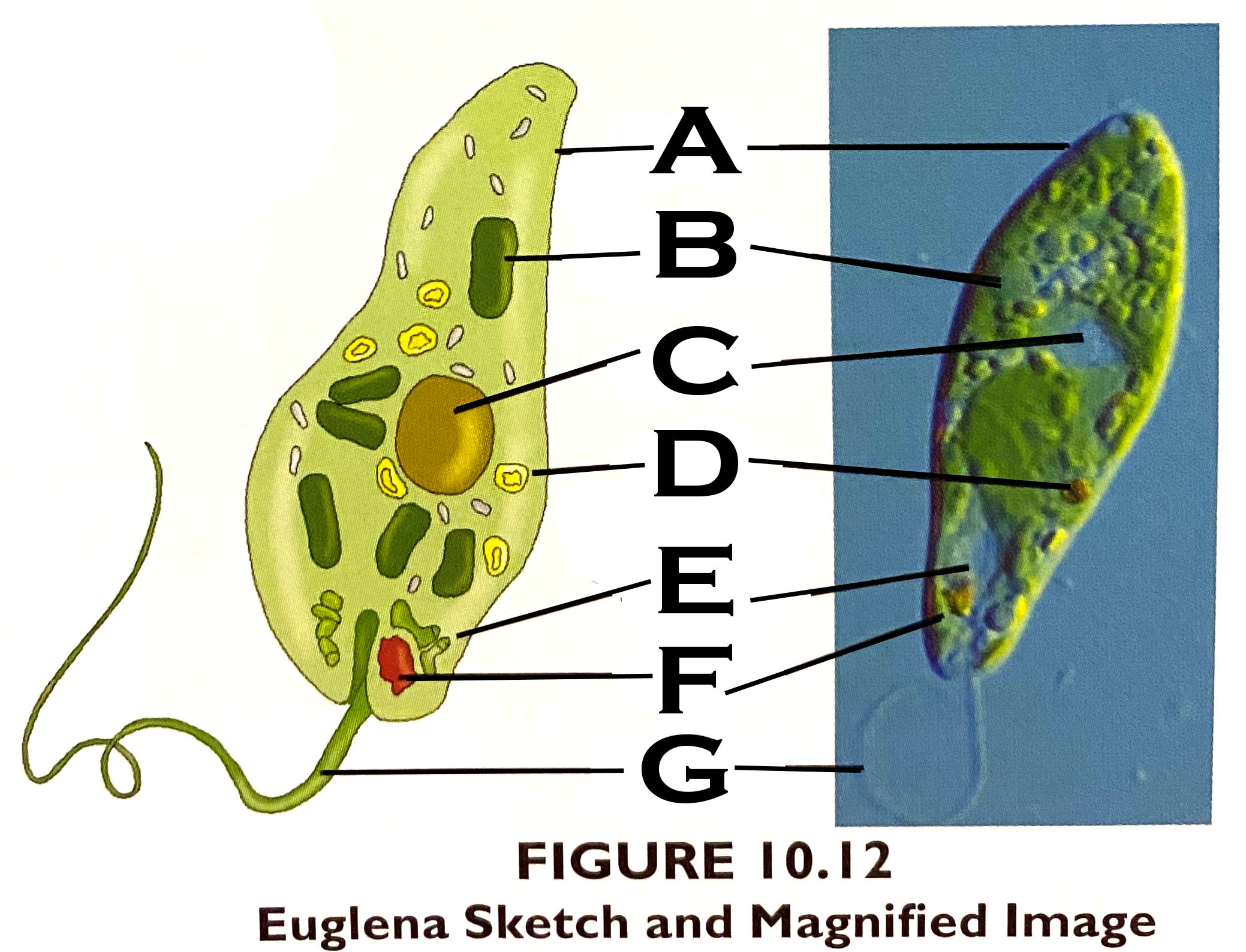
What organelle is F?
eyespot
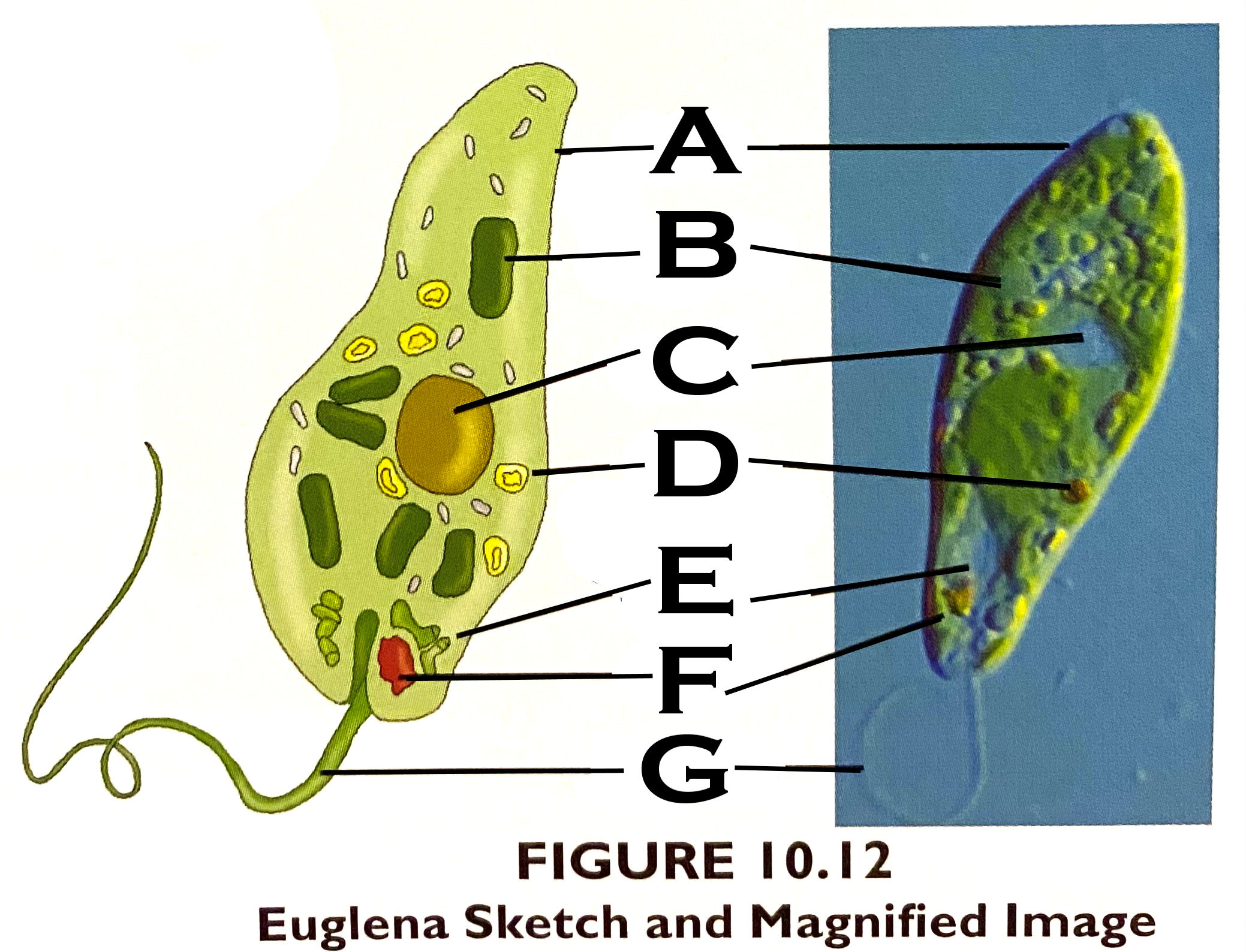
What organelle is G?
flagellum
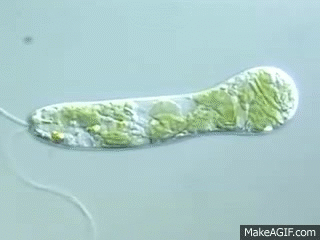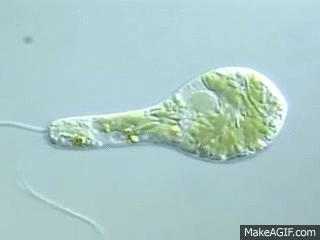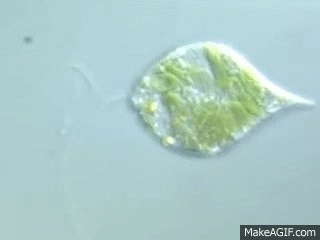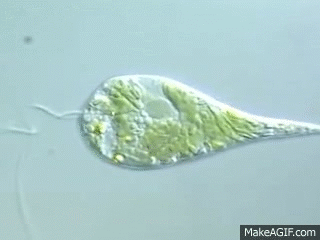
Which structure is responsible for the movement of a euglena?
The structure, flagellum
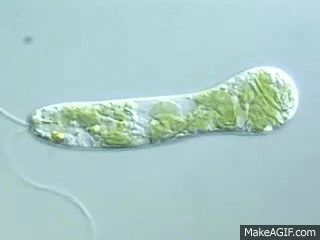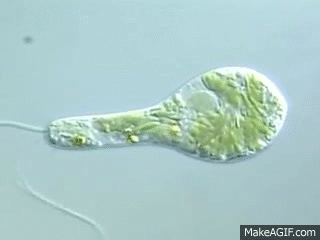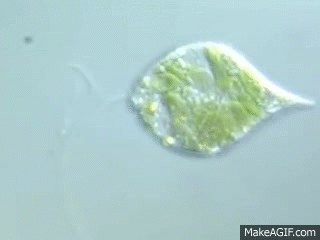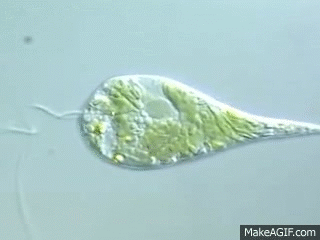
2 types of movement for euglena
Swimming with flagellum and amoeboid movement
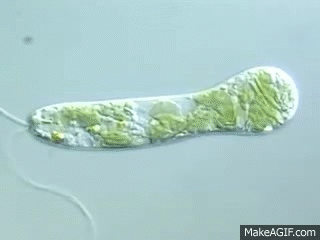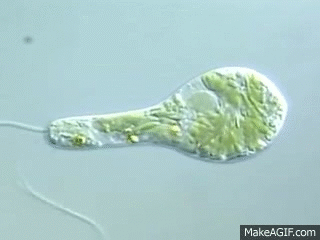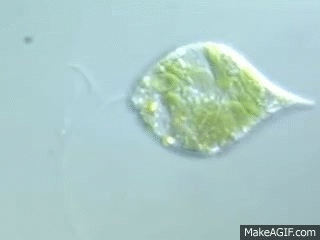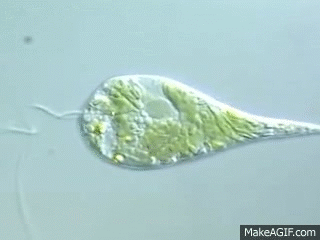
To which phylum does euglena belong?
Euglenophyta
The 3 types of Protists
Plant-like, animal-like, fungus-like
How the 3 types of Protists differentiate
how they get nutrients: autotrophic, heterotrophic, saprophytic

Organism that contains both a macronucleus and a micronucleus
Paramecium
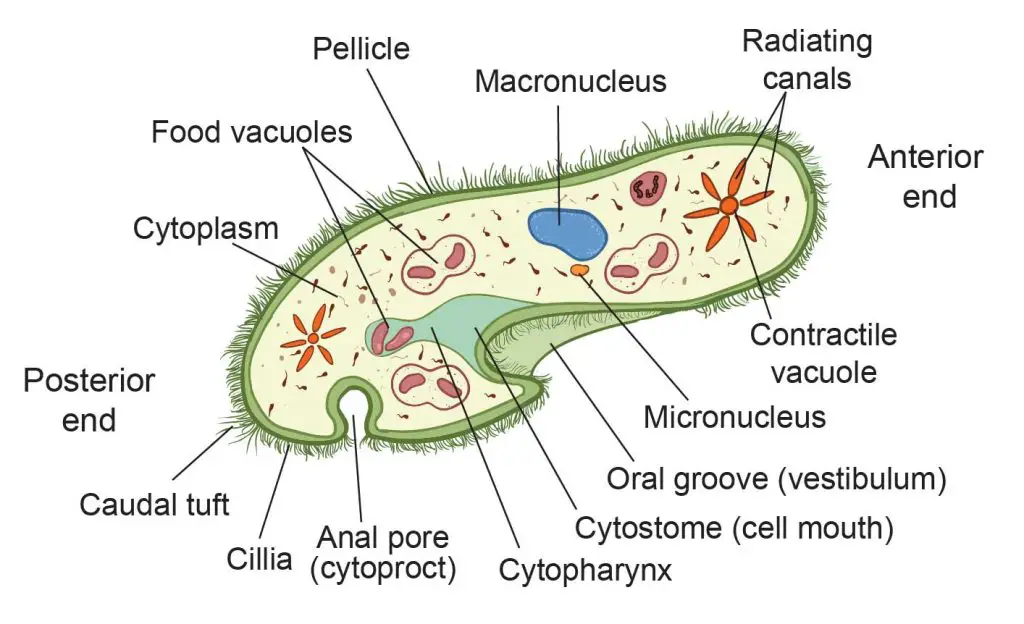
Function of the macronucleus in Paramecium
Control of metabolism
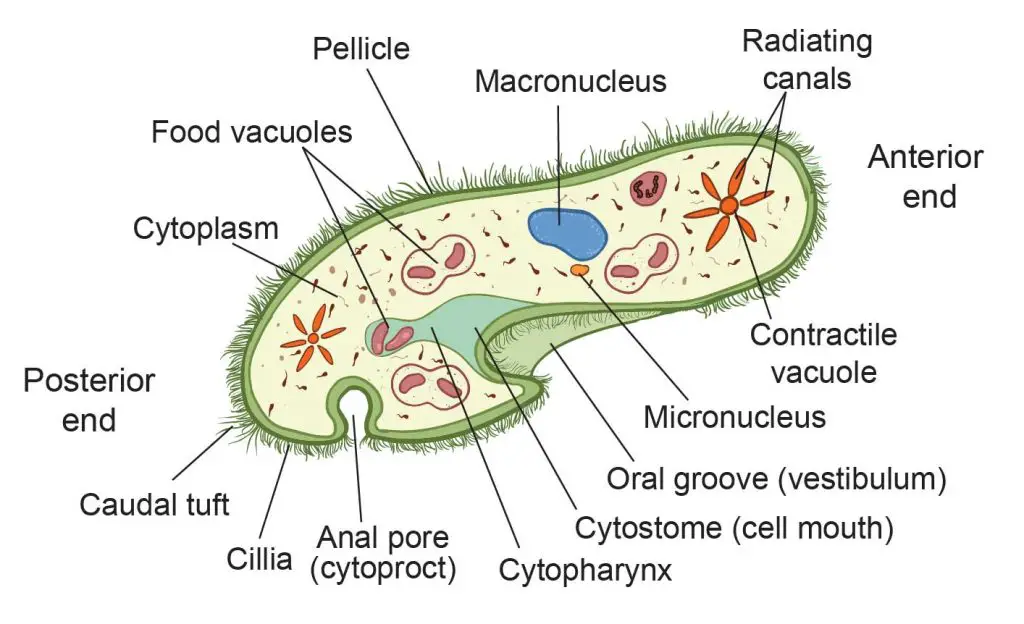
Function of the micronucleus in Paramecium
Reproduction
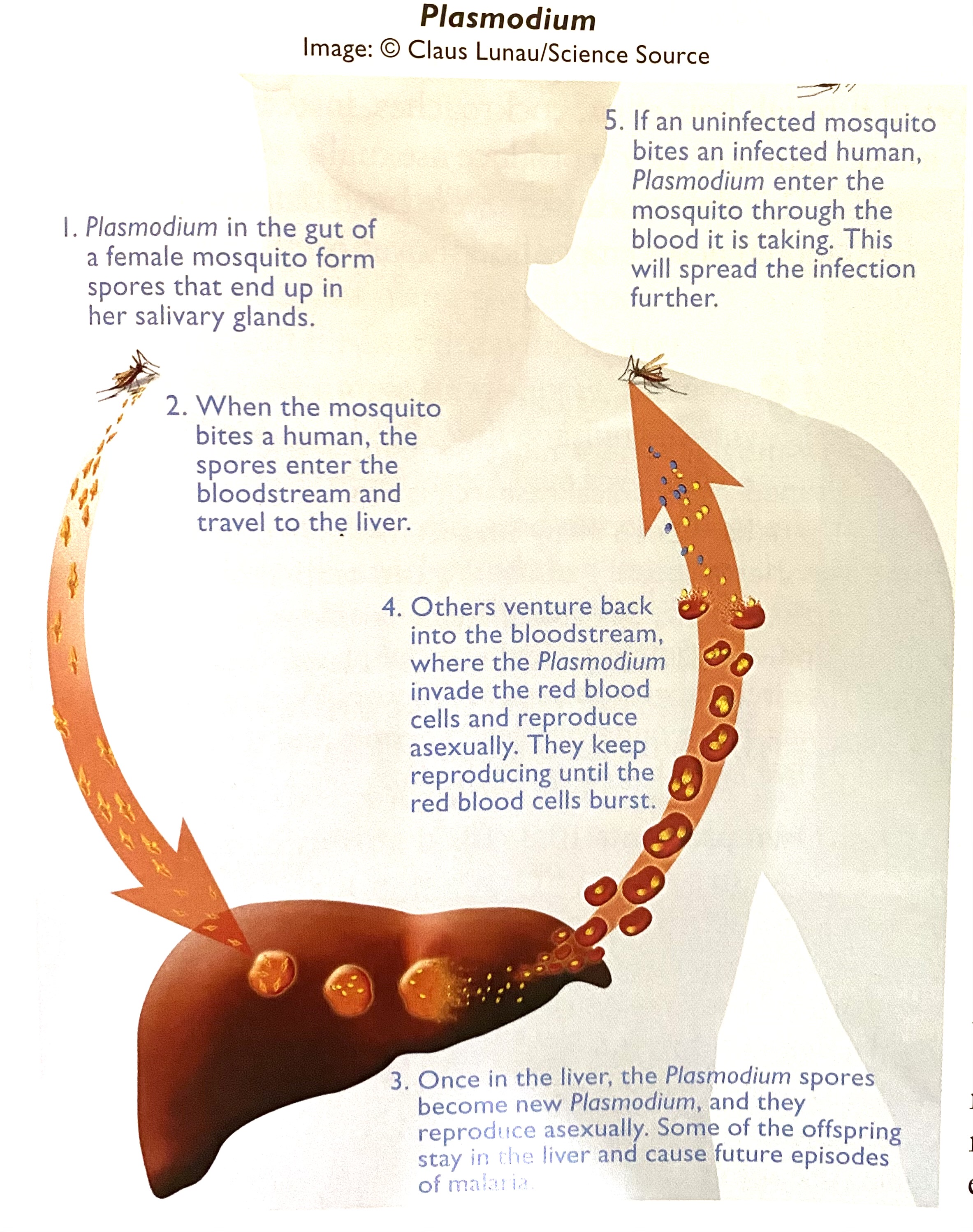
Protist that causes malaria?
Plasmodium
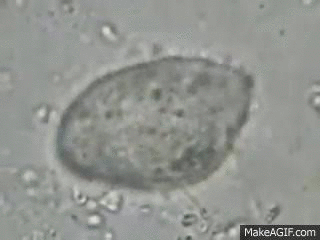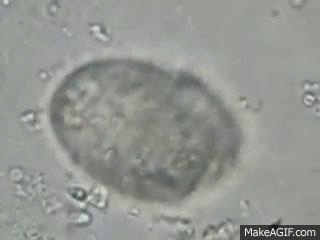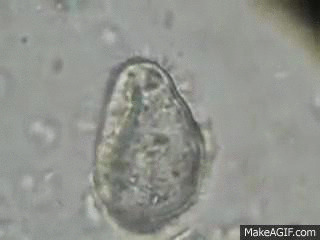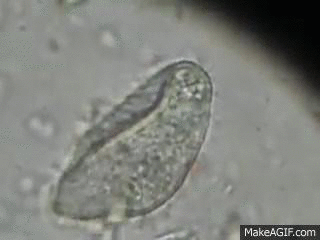
Protist known to cause dysentery
Balantidium coli
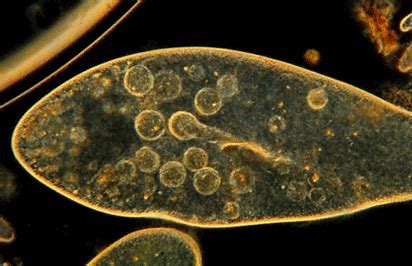
What is always part of the life cycle of Sporozoa?
spore formation
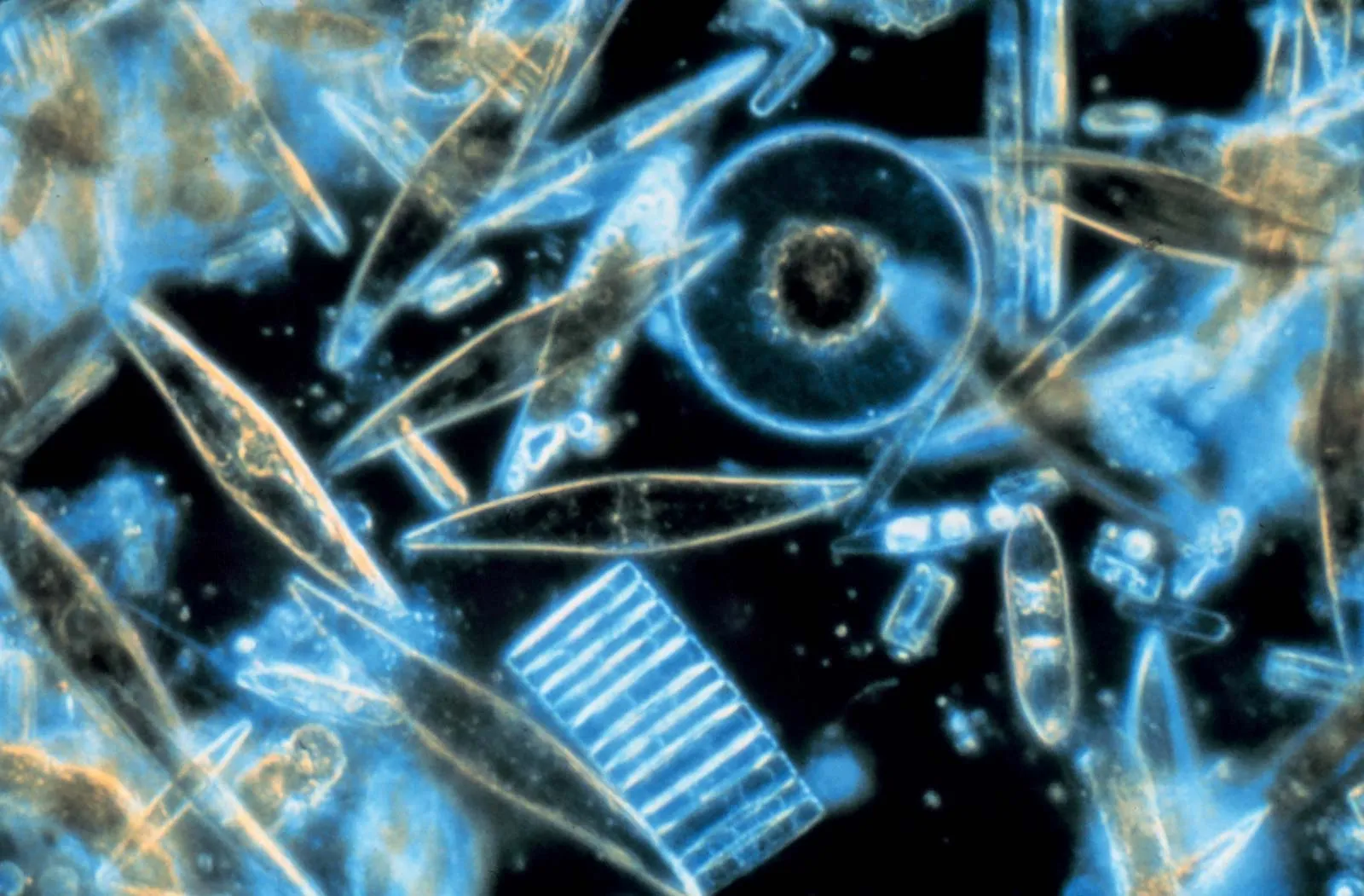
What is the unique component of a diatom’s cell wall?
Silicon dioxide
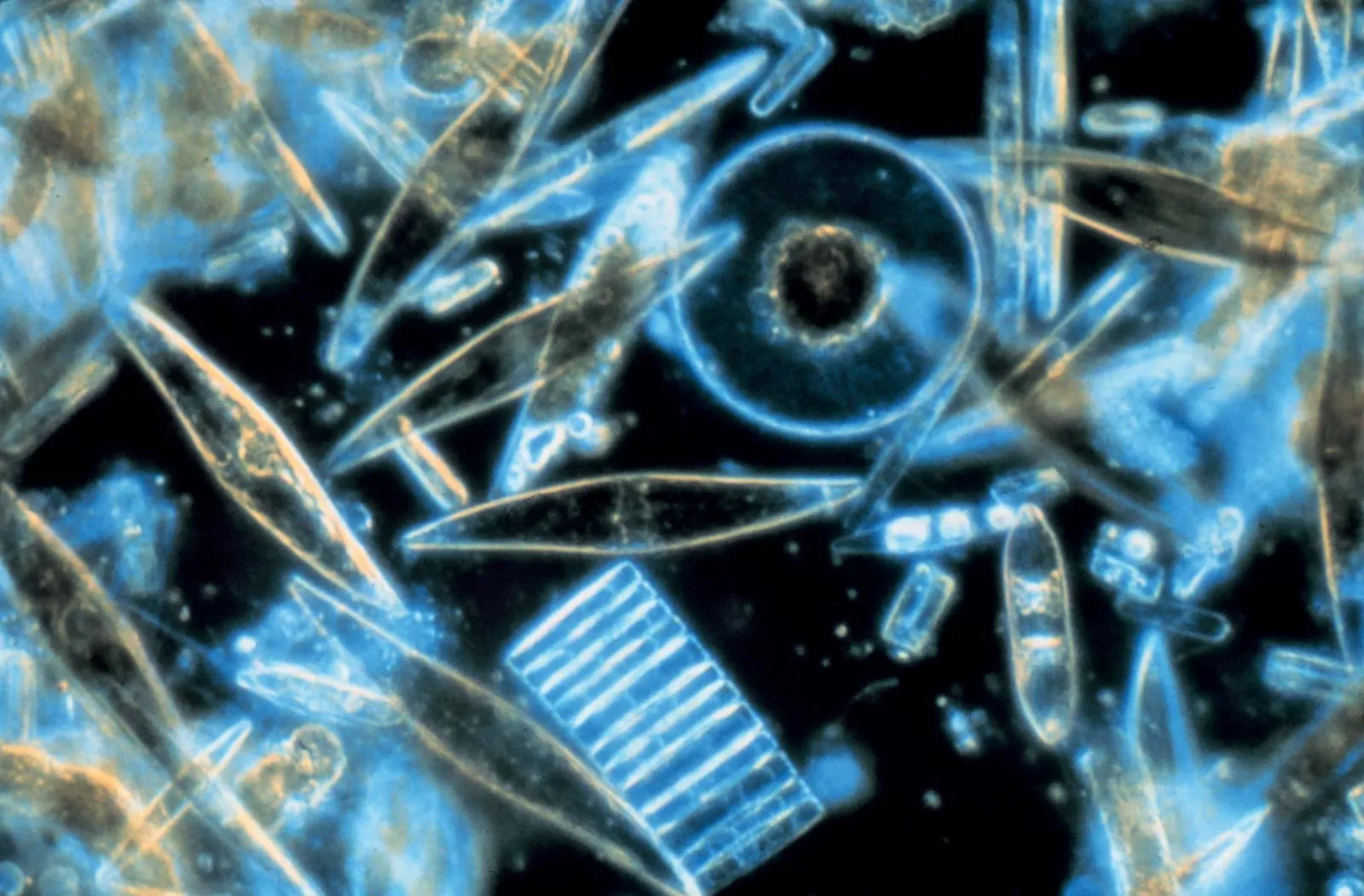
Commercial uses for diatoms
Toothpaste abrasive
Pest control
Filtering liquids

How amoeba move
By contracting and extending pseudopods

Phylum for paramecium
Ciliophora

How does a paramecium move?
By cilia beating rhythmically
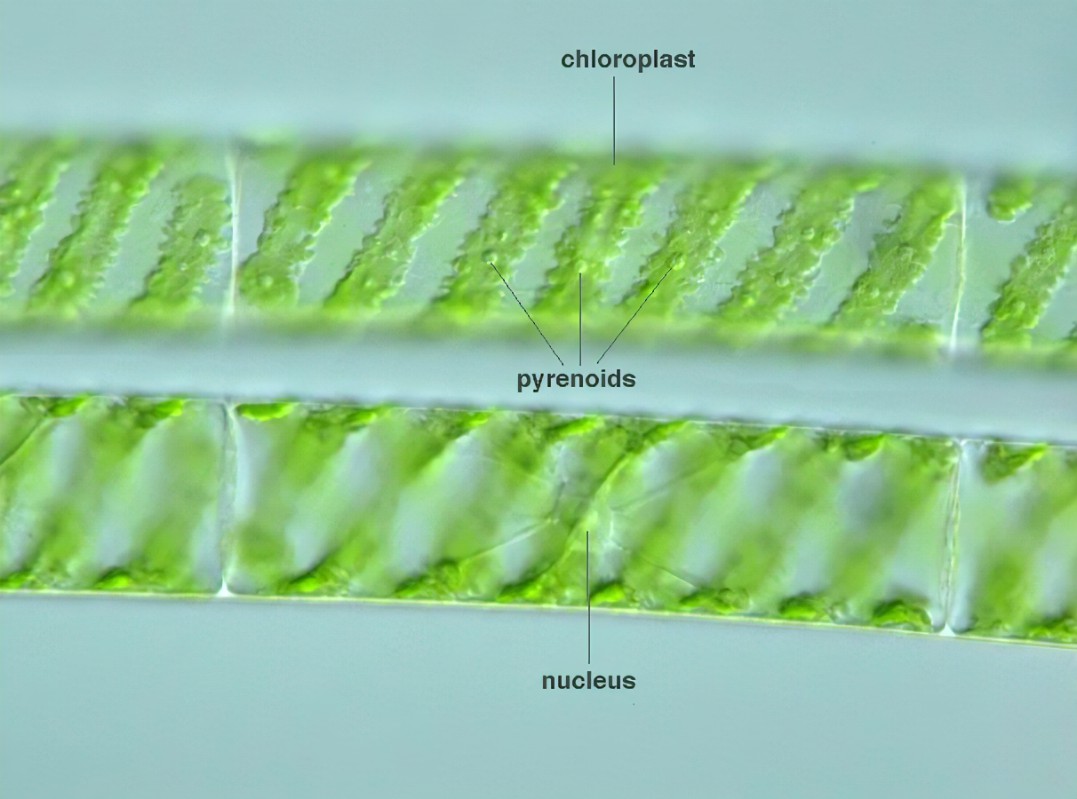
Shape of the chloroplasts in spirogyra
Spiral or helical-shaped
Where is chlorophyll found in plant cells?
Chloroplasts

Color of Rhodophyta
Red

Algin uses
A thickening agent; used in ice cream and pudding
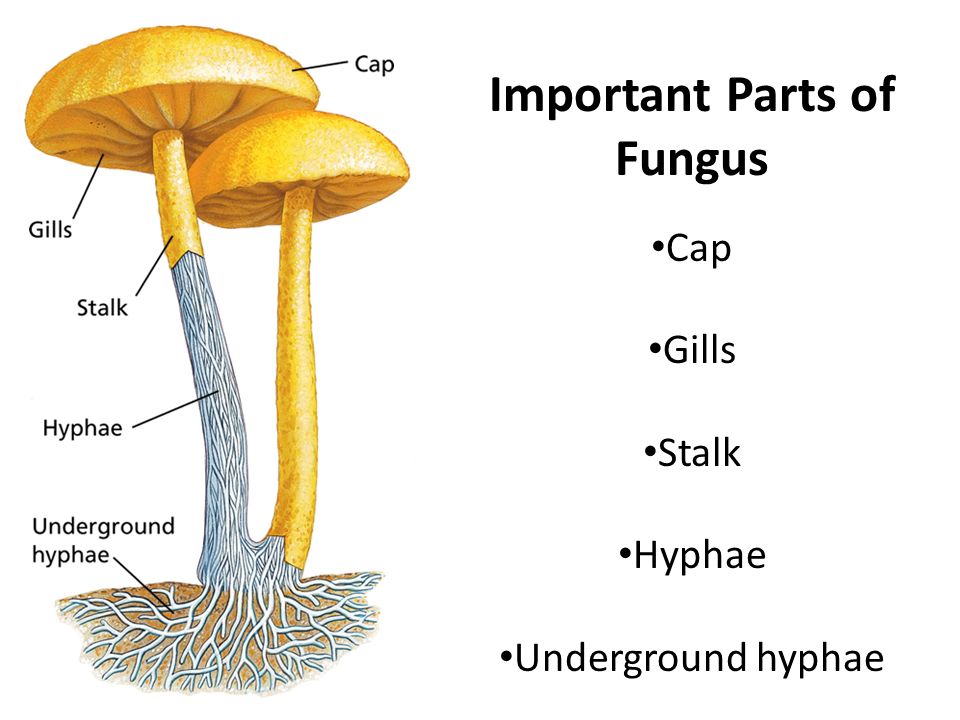
Characteristics of kingdom Fungi
Eukaryotic
Cell walls have chitin
Multicellular (most)
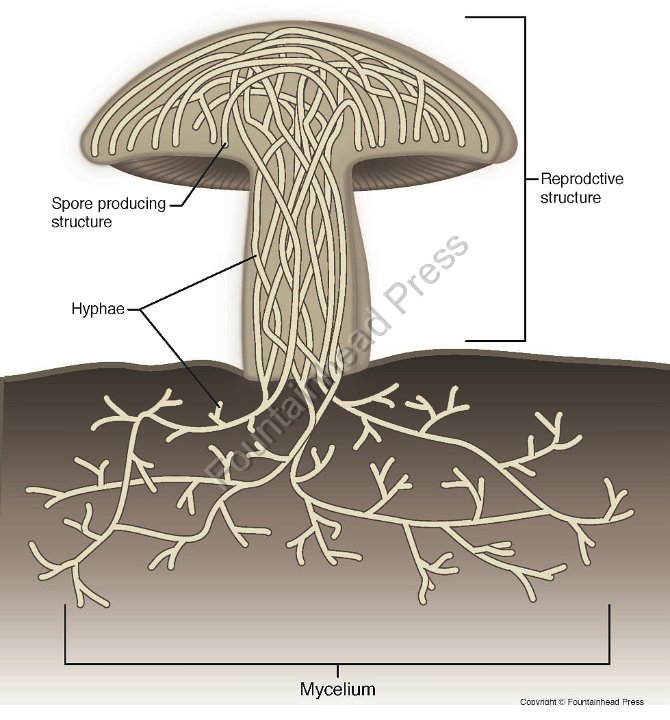
mycelium v. hyphae
Mycelium is the main part; hyphae are filaments
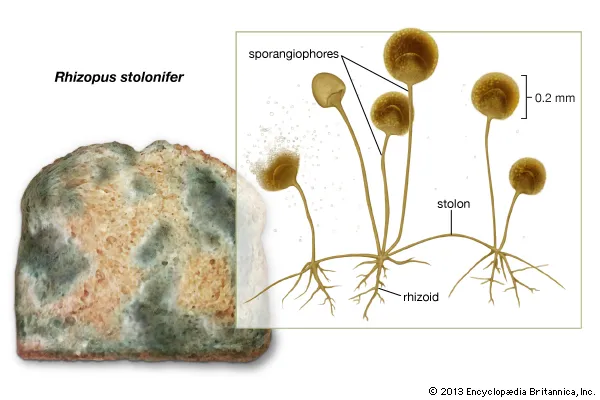
Function of rhizoids in fungi
Support and anchor the fungus
Extracellular digestion
Digestion occurs outside the organism
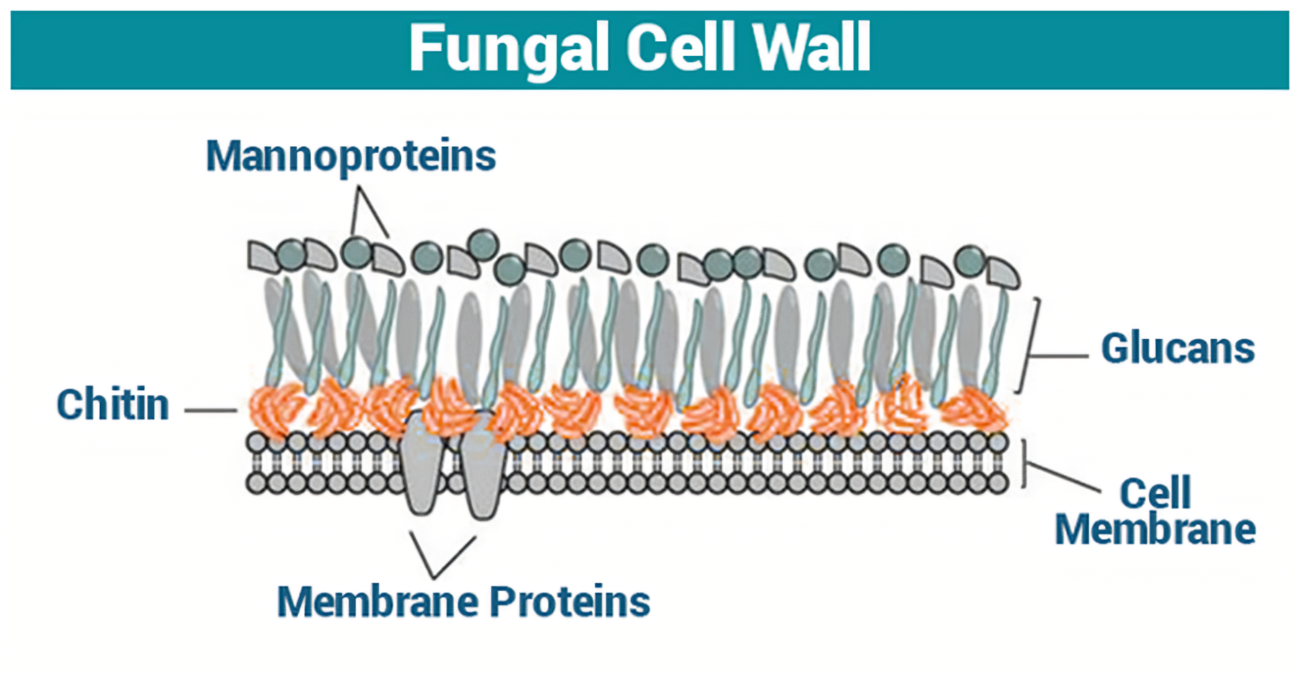
Chitin
A chemical providing toughness and flexibility

Phylum of fungi characterized by sac-like structures
Ascomycota
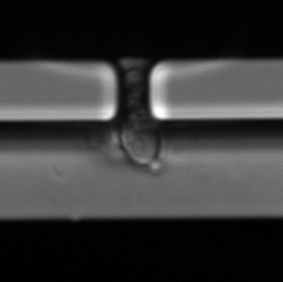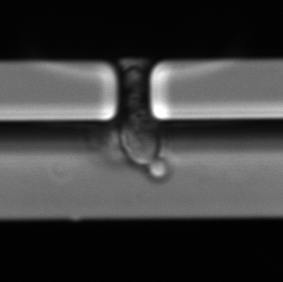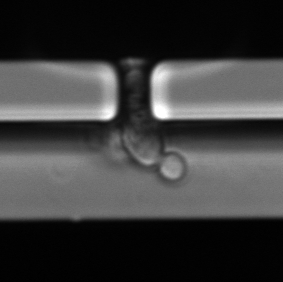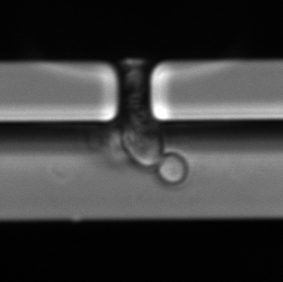
Budding in yeast
A form of asexual reproduction
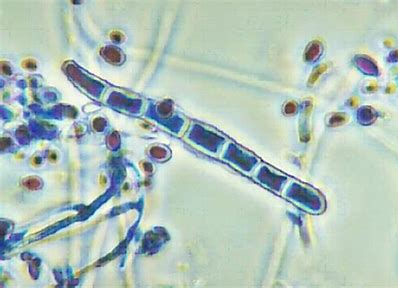
Fungus that causes athlete's foot
Trichophyton rubrum
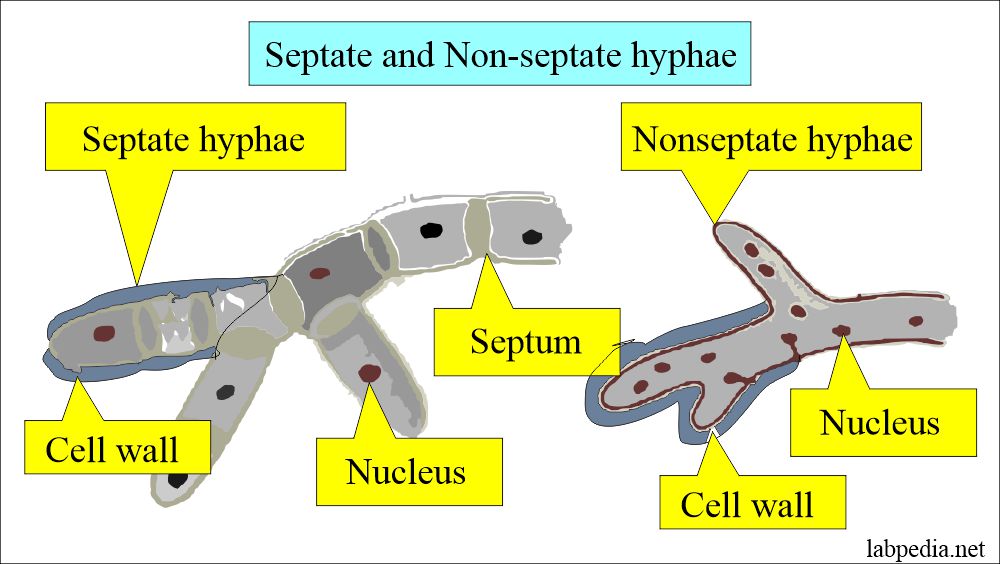
Septate v. nonseptate hyphae
Septate hyphae have cell walls; nonseptate do not
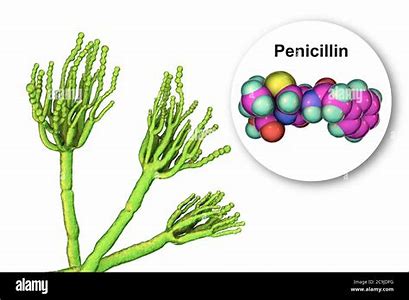
Antibiotic produced by fungi in the genus Penicillium
Penicillin

Who discovered penicillin?
Alexander Flemming
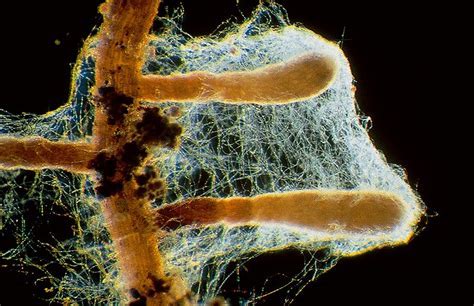
Mycorrhizae
Fungi that live on plant roots in a symbiotic relationship
How do mycorrhizae help plants?
By sharing minerals in exchange for food
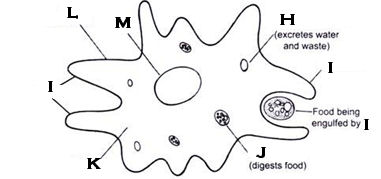
What organelle is H?
contractile vacuole; amoeba
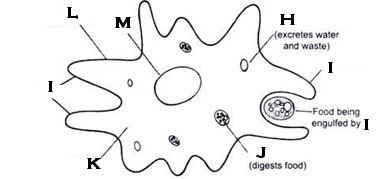
What organelle is I?
pseudopod
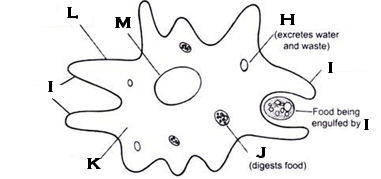
What organelle is J?
food vacuole
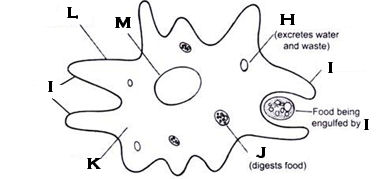
What organelle is L?
cell membrane
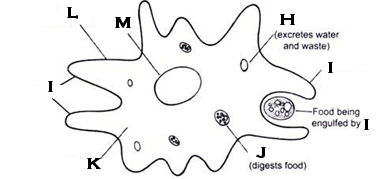
What organelle is M?
nucleus; amoeba

What organelle is N?
food vacuole (it’s forming)
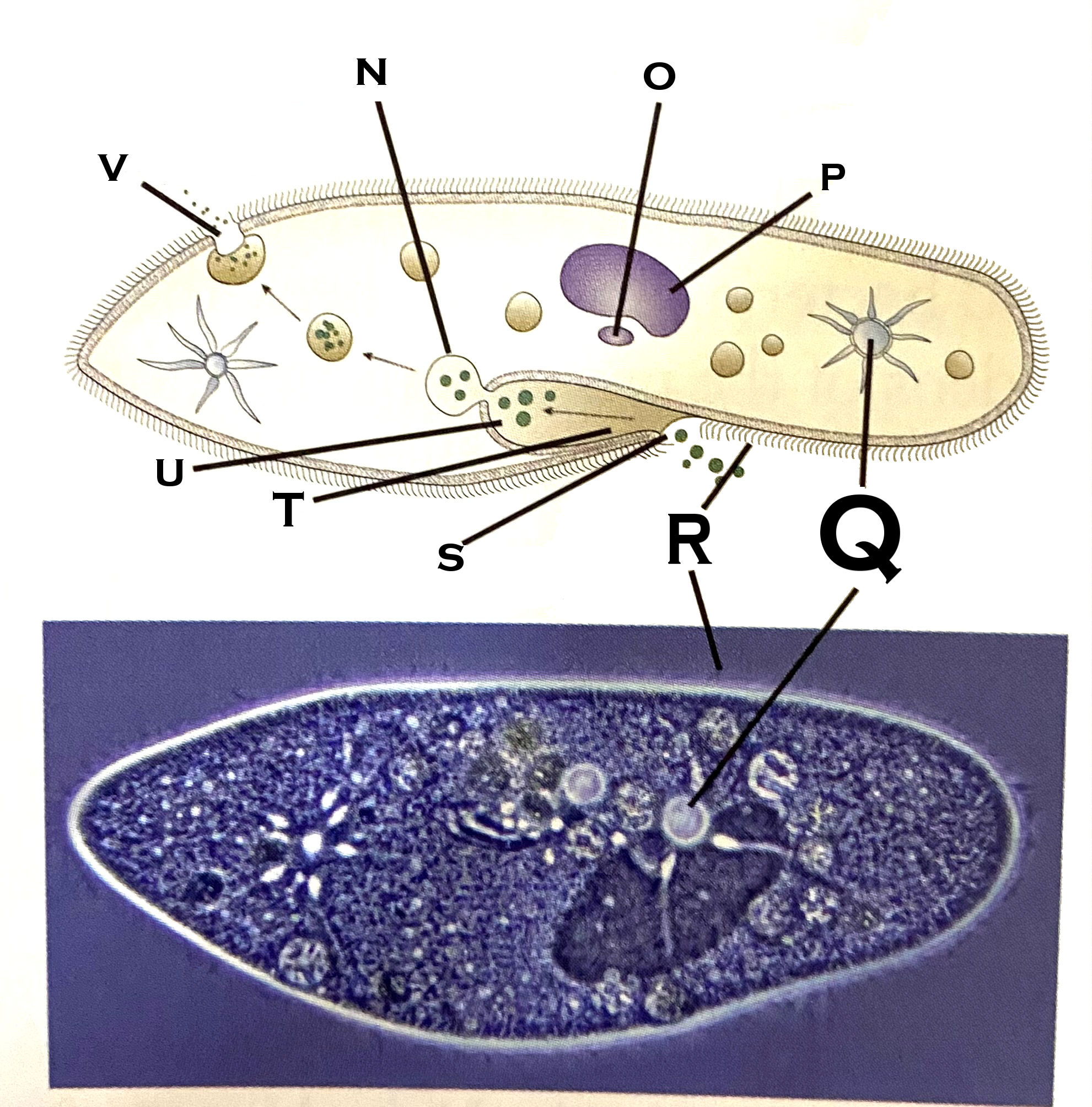
What organelle is O?
micronucleus
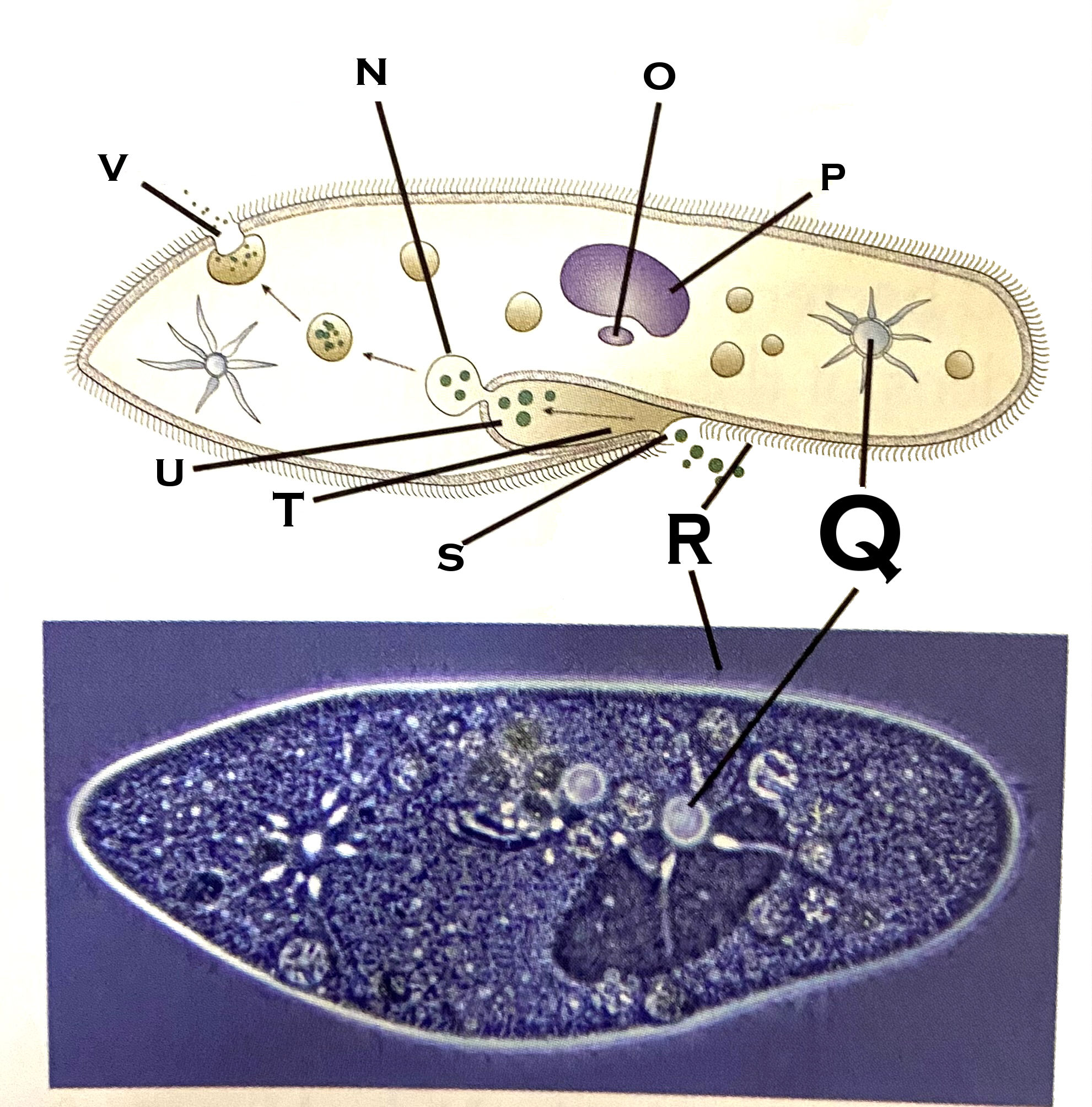
What organelle is P?
macronucleus
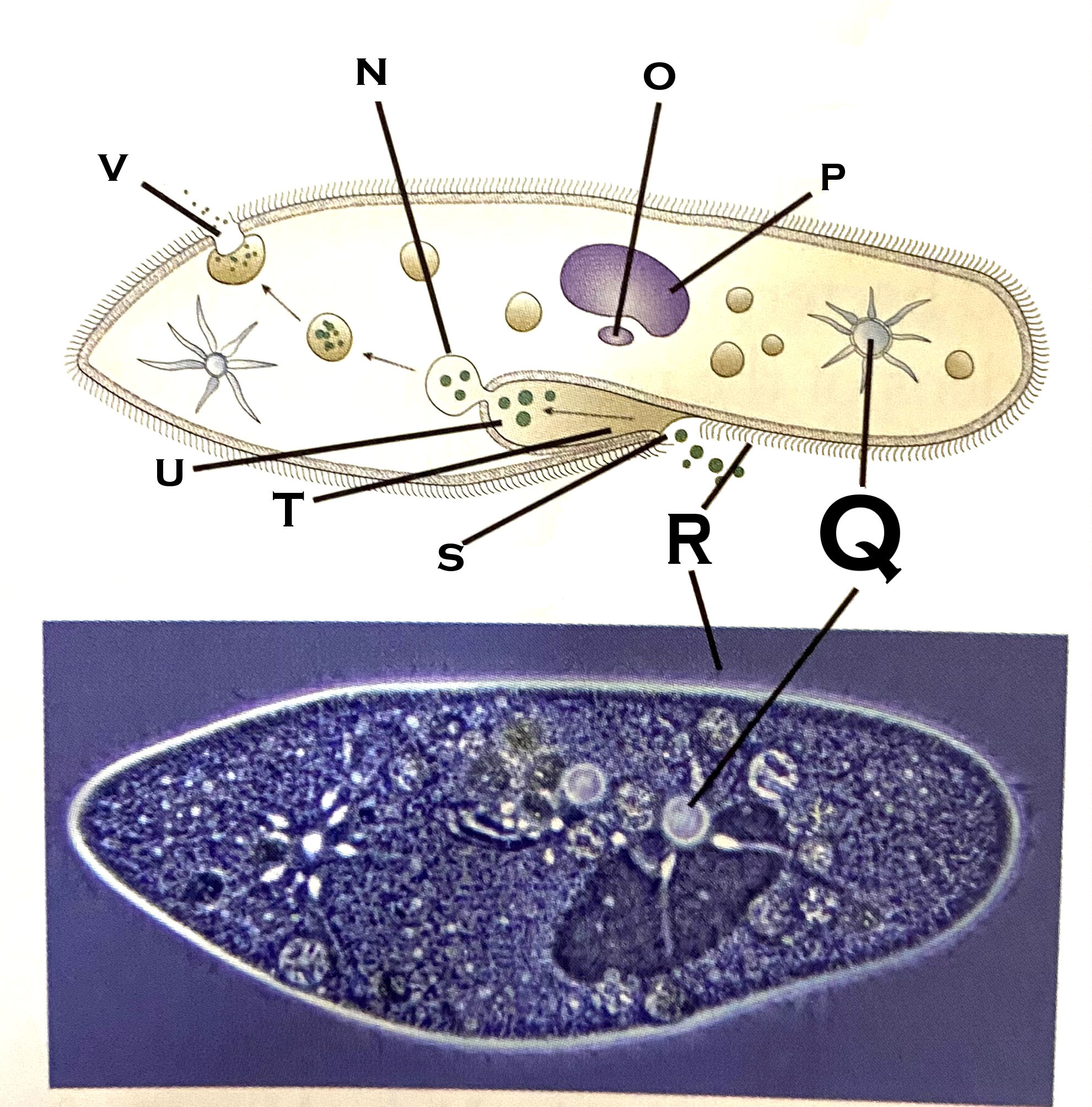
What organelle is Q?
contractile vacuole (paramecium)
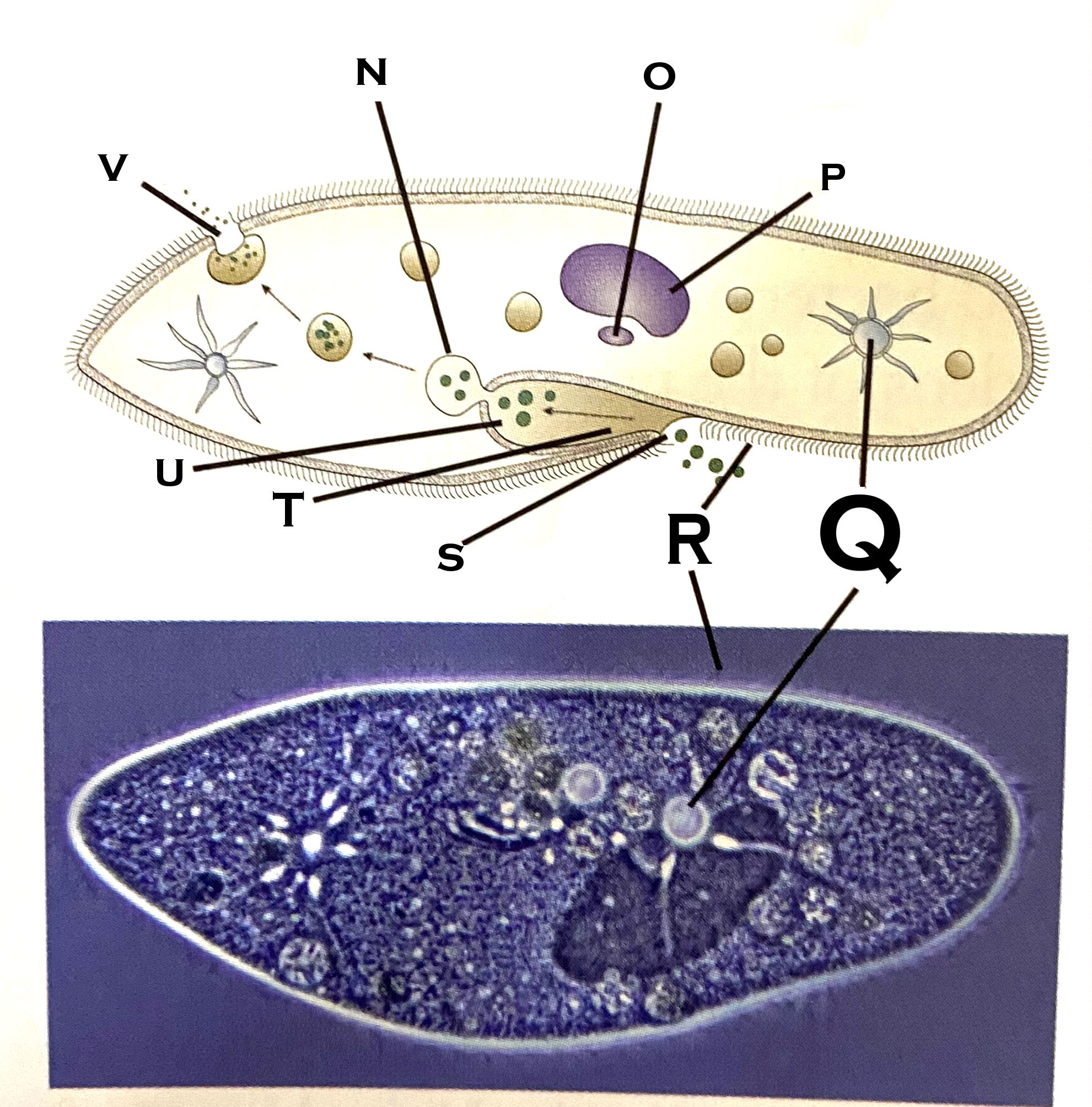
What organelle is R?
cilia
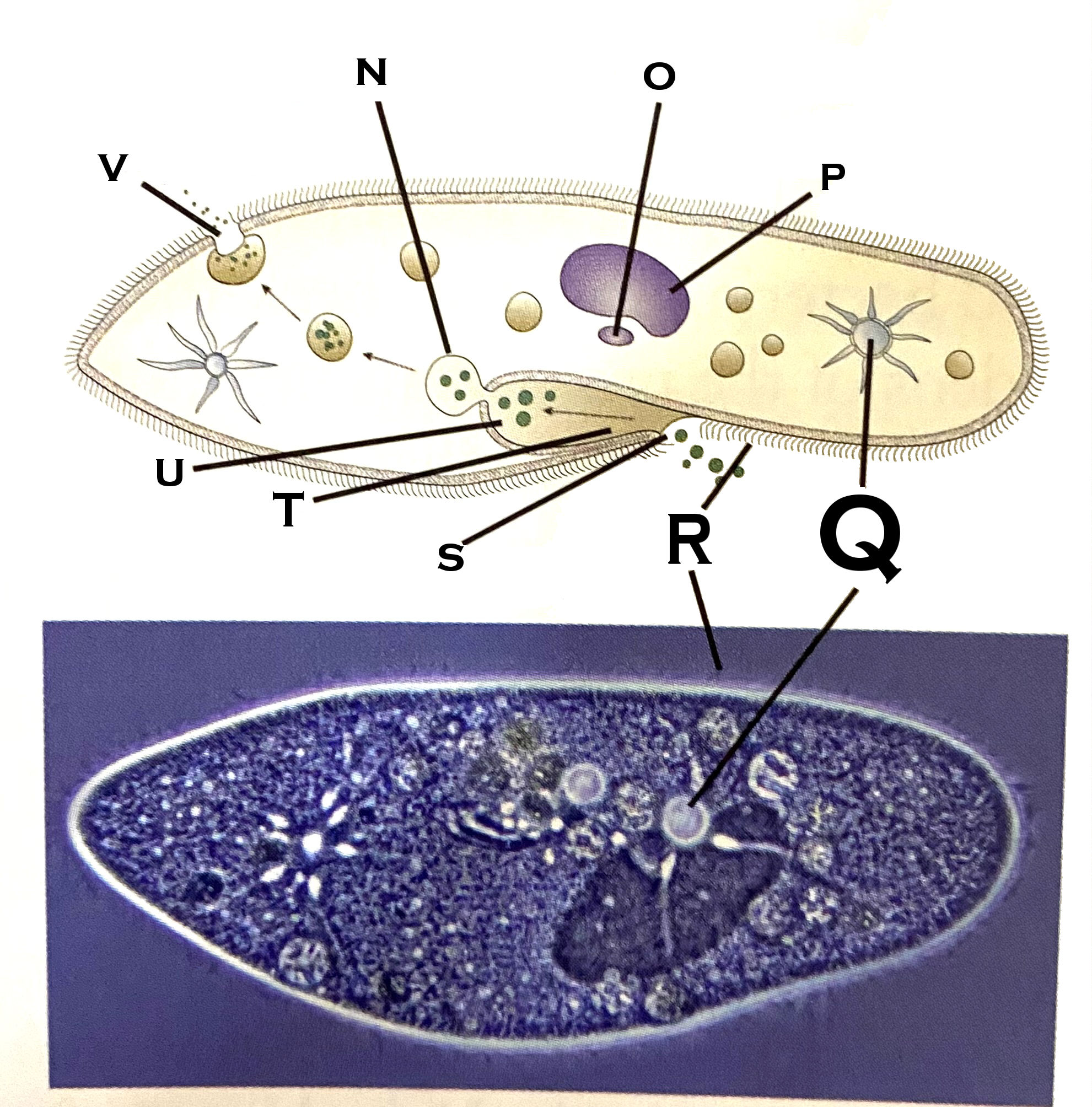
What organelle is S?
Oral pore
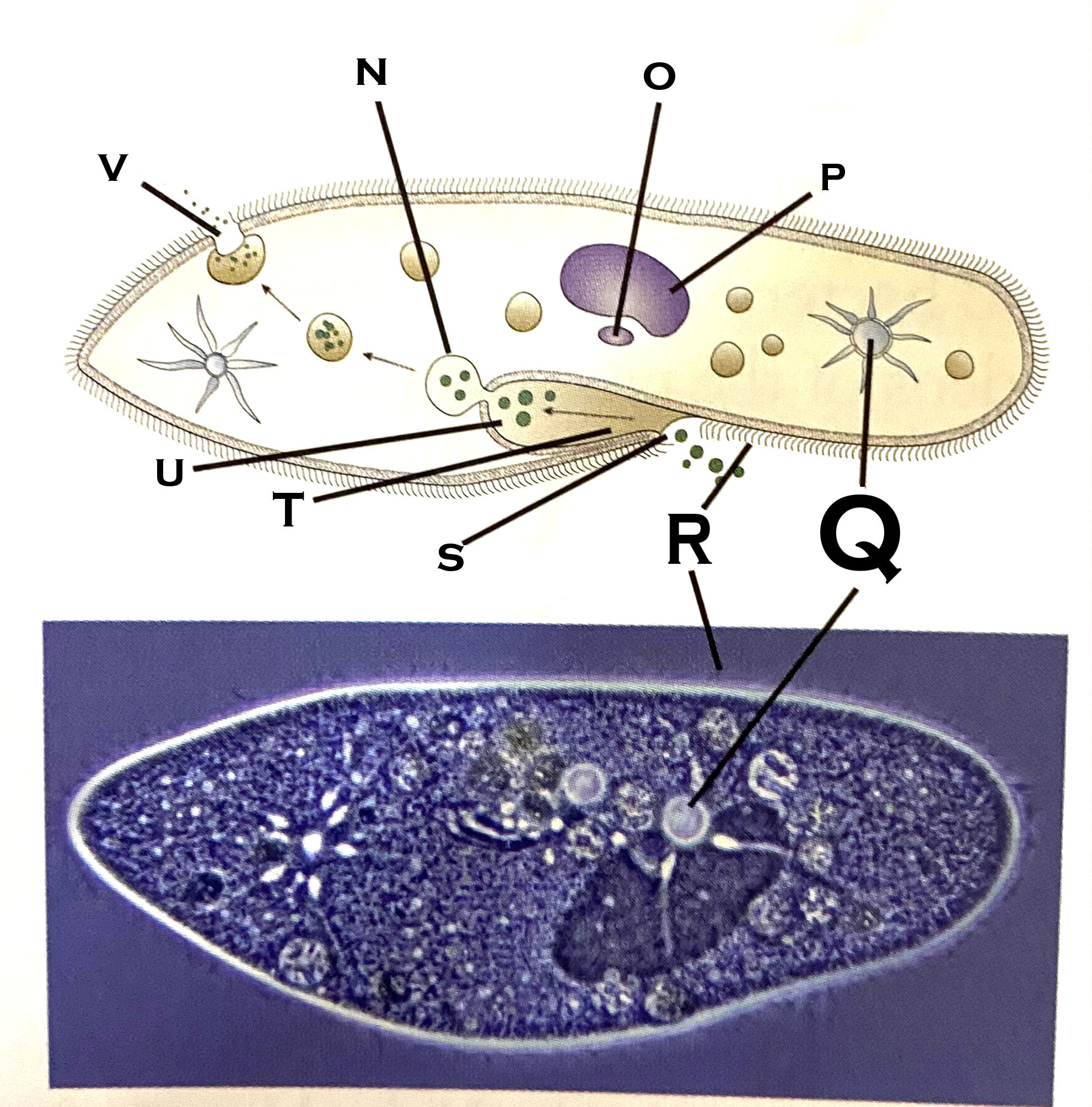
What organelle is T?
Oral groove
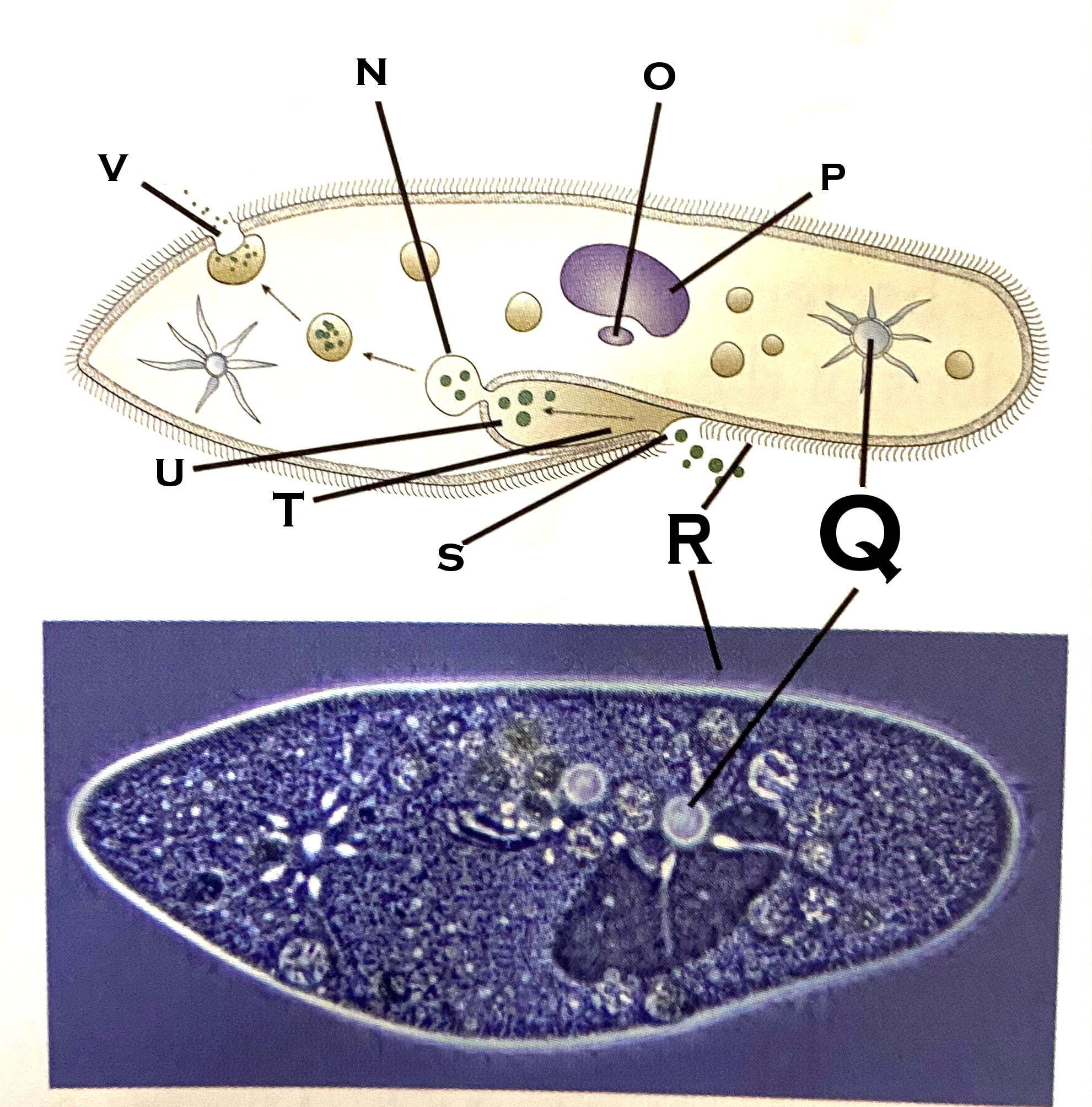
What organelle is U?
Gullet
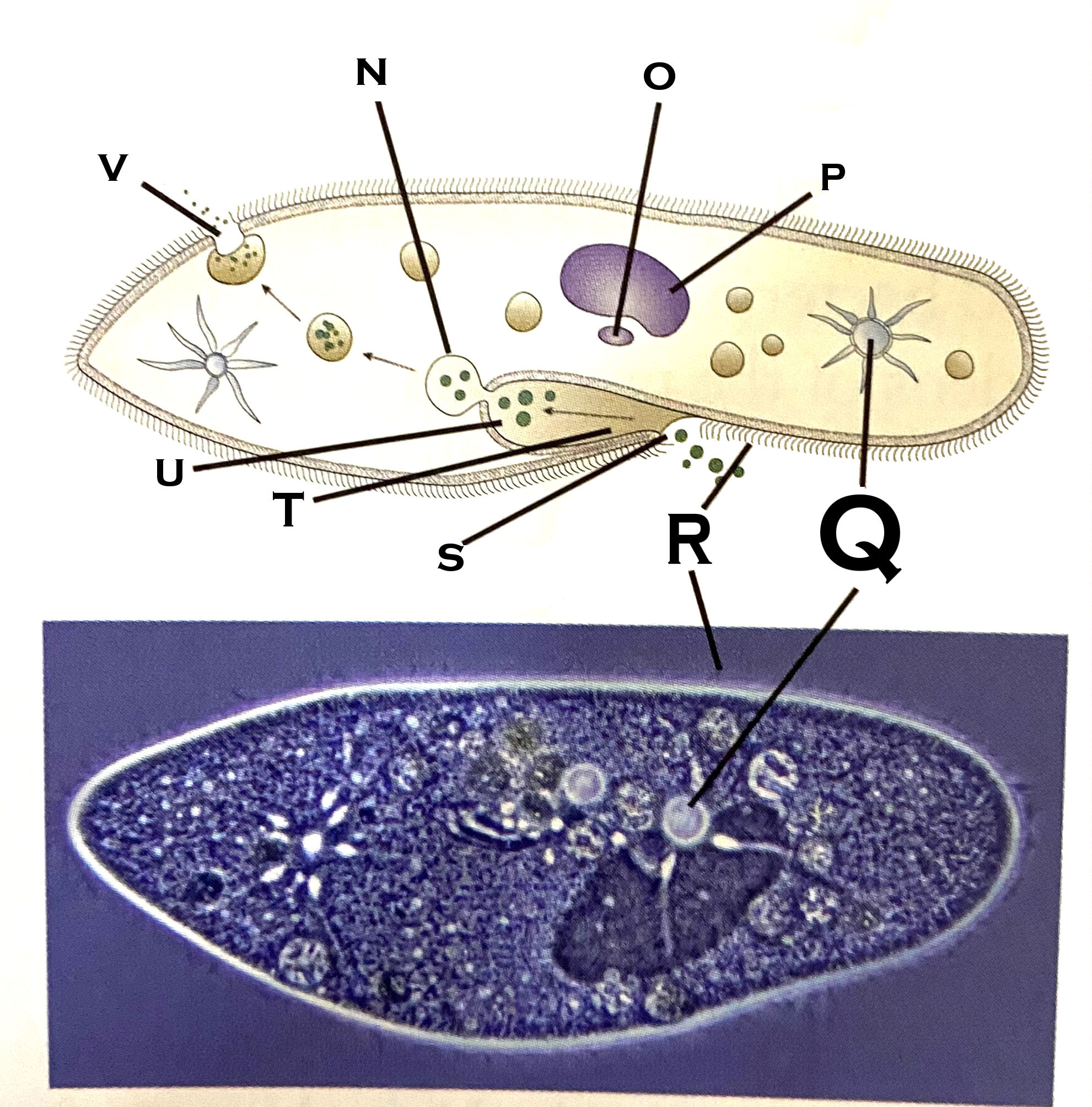
What organelle is V?
Anal pore
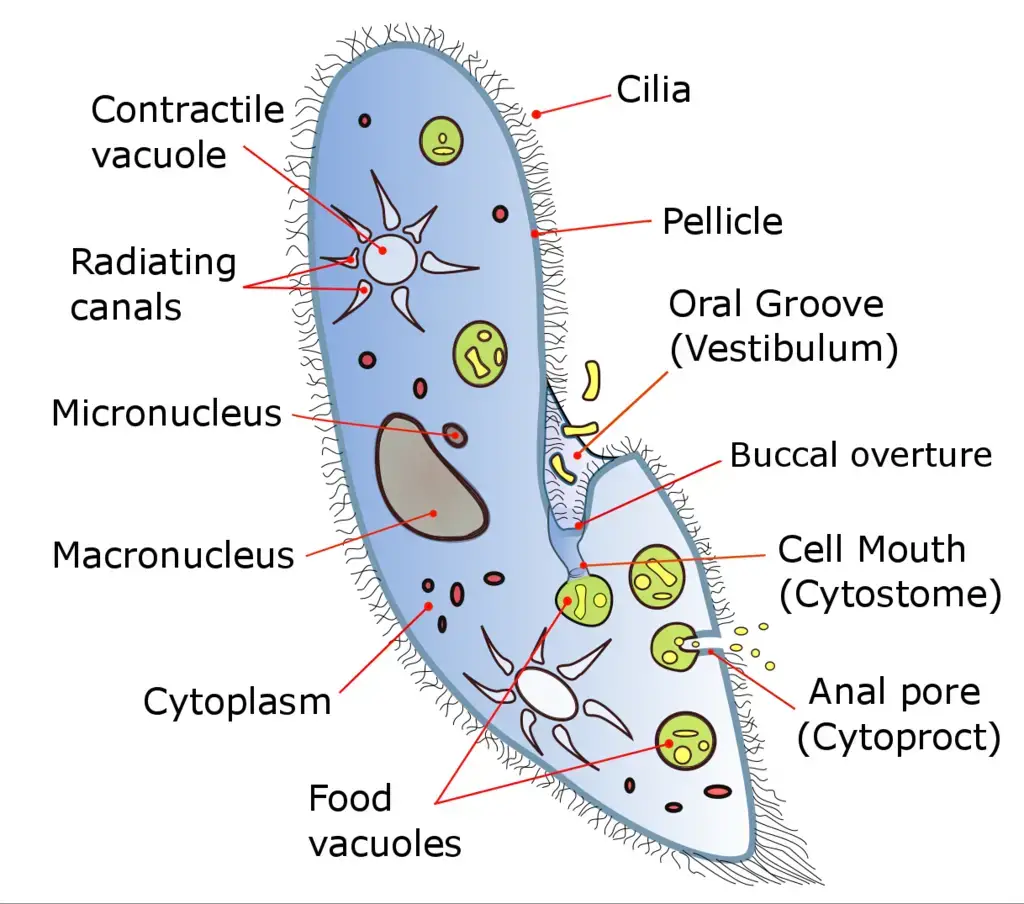
What type of organism is pictured?
a paramecium
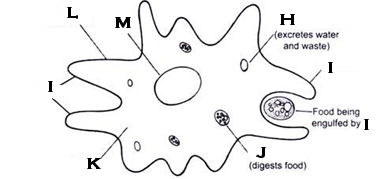
What type of organism is pictured?
an amoeba
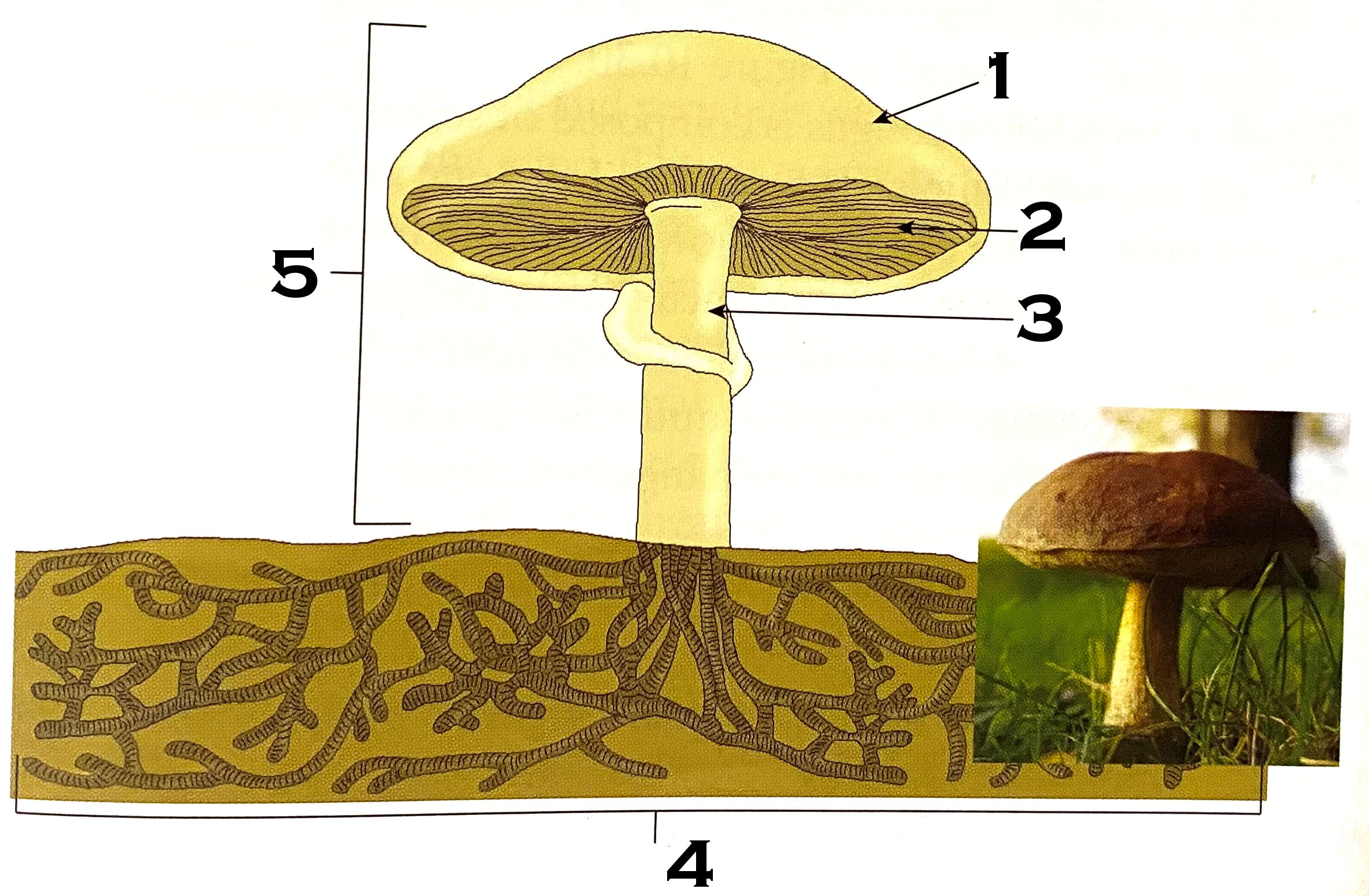
What part of the mushroom is #1?
cap
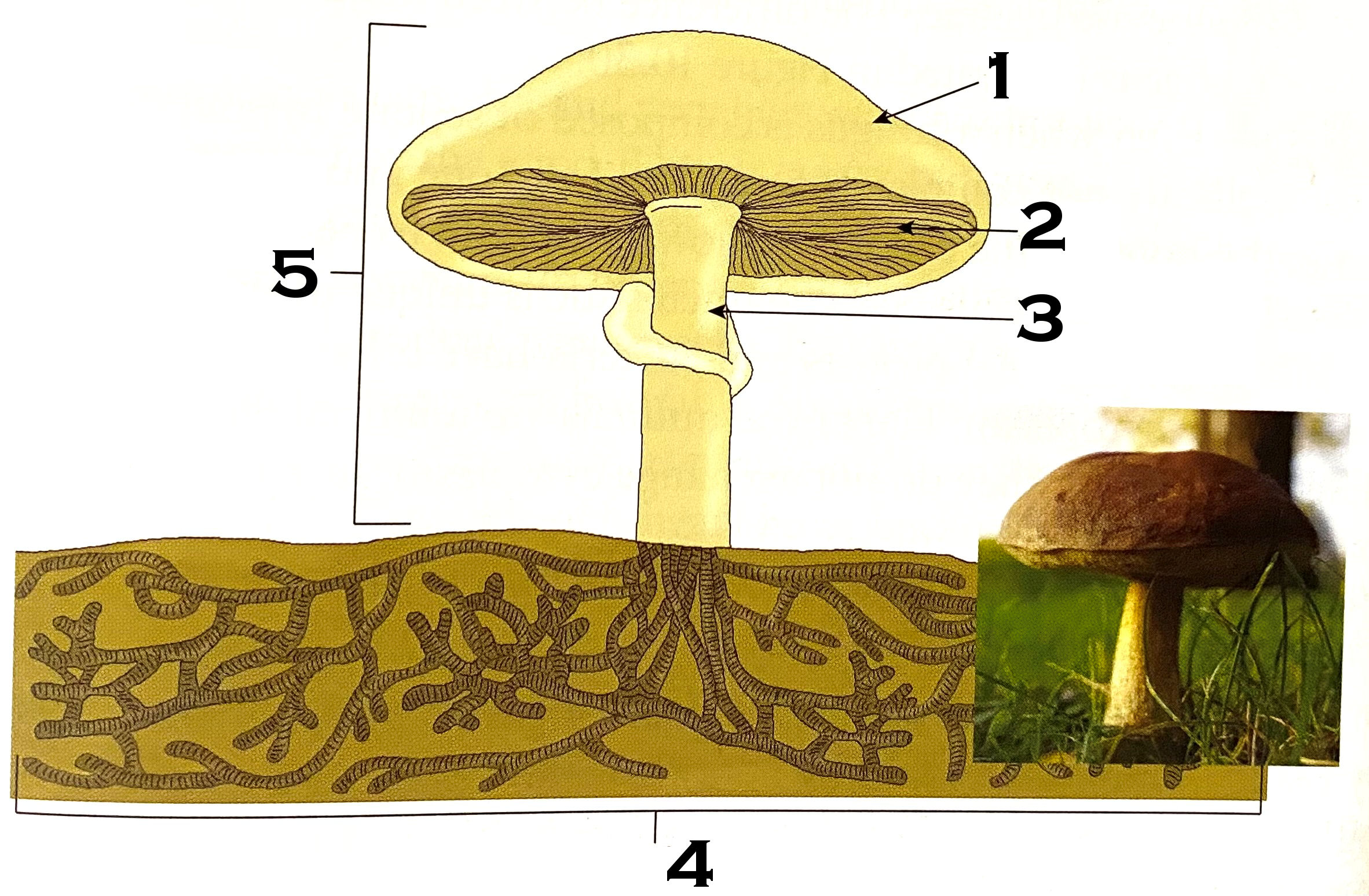
What part of the mushroom is #2?
gills
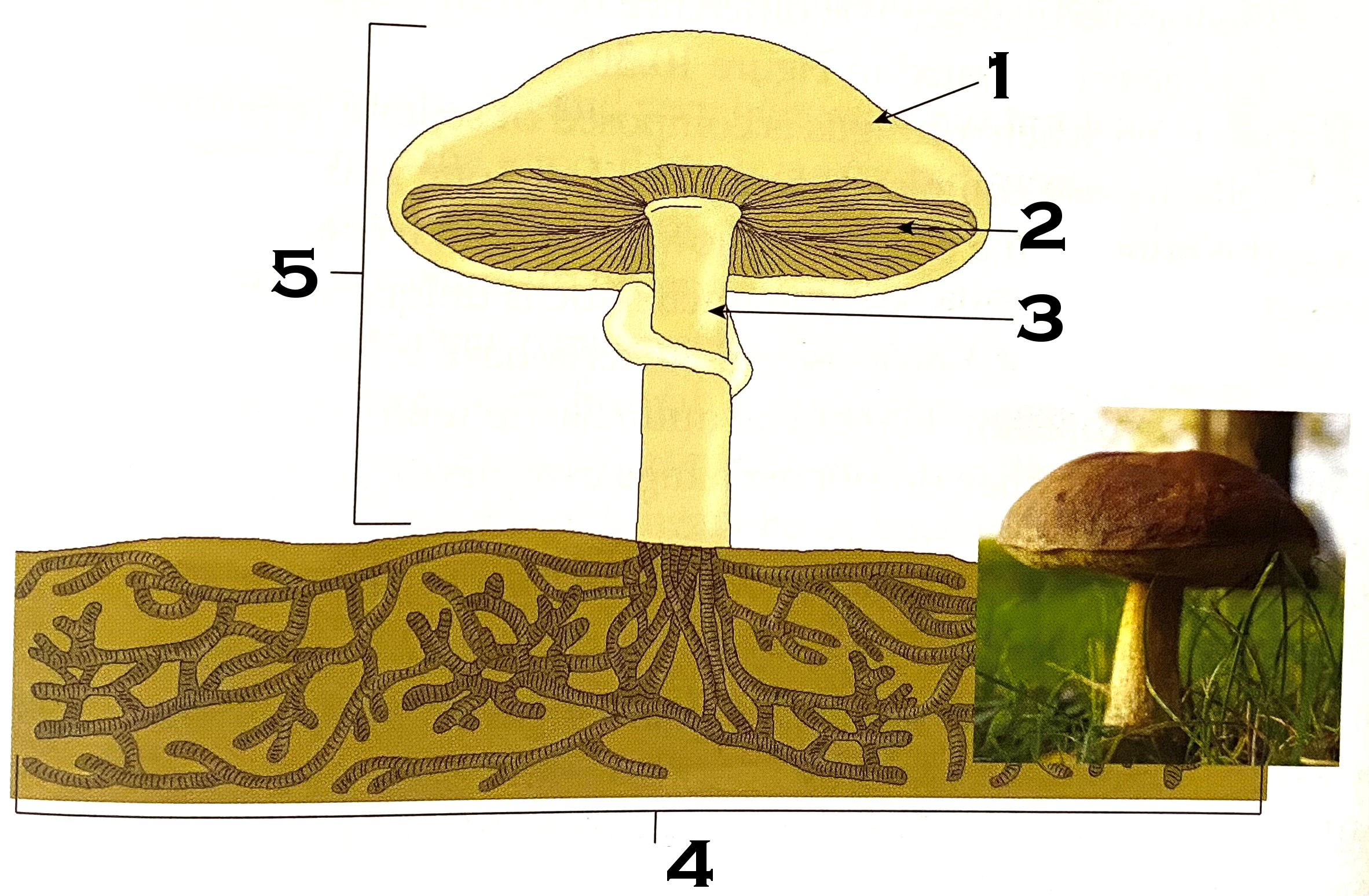
What part of the mushroom is #3?
stipe (commonly known as stalk or stem)
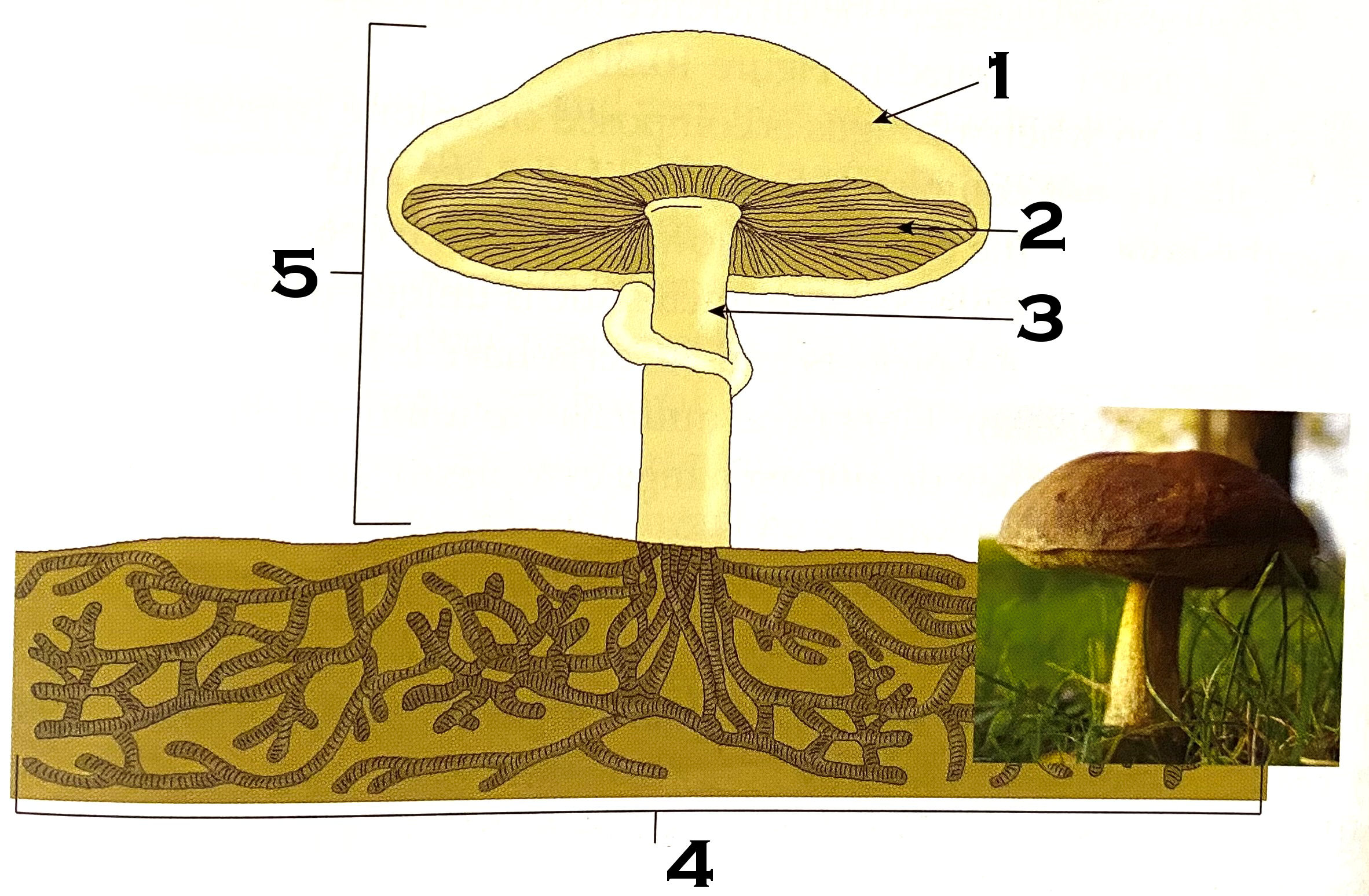
What part of the mushroom is #4?
mycelium
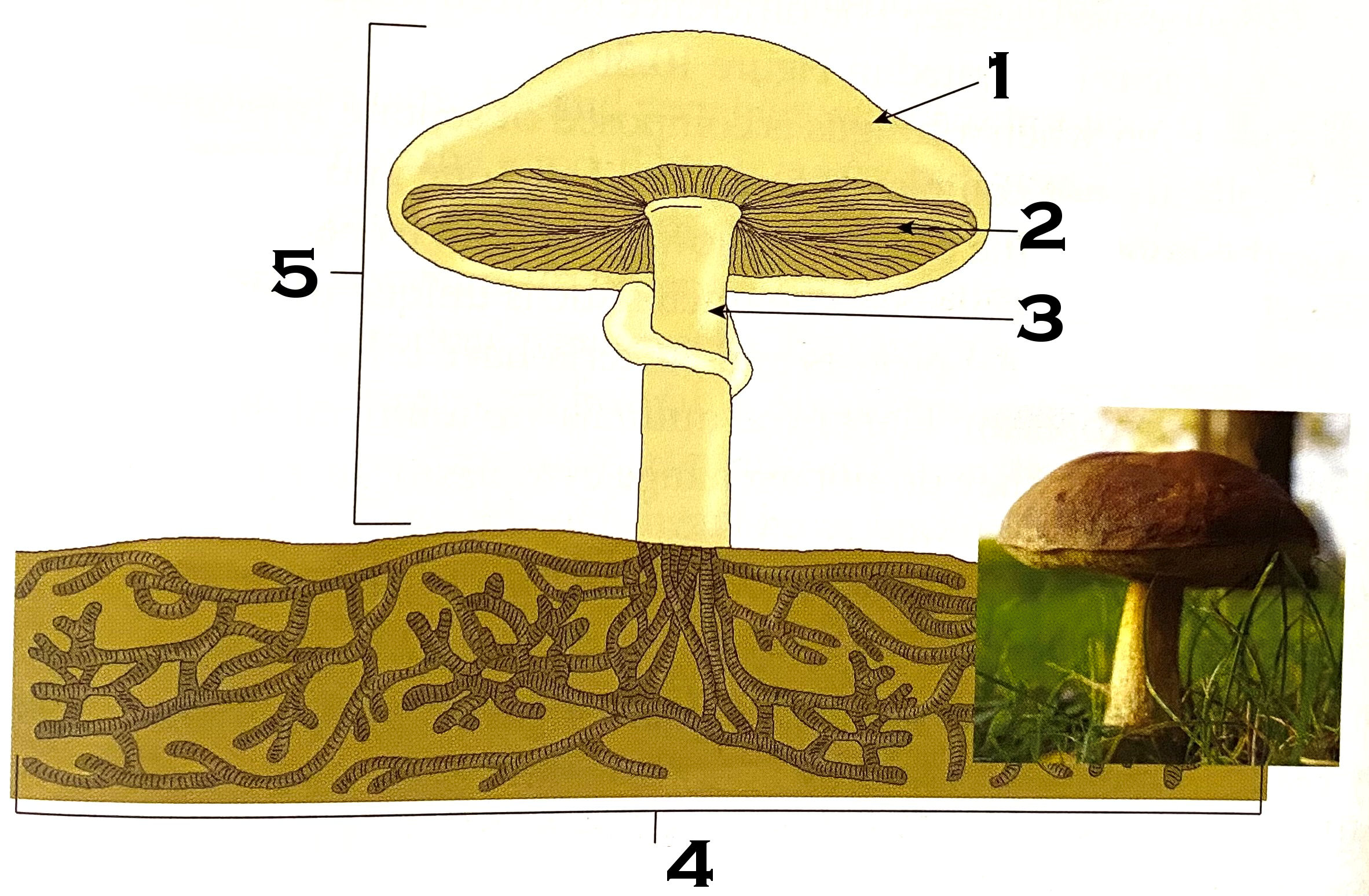
#4 on the mushroom, the mycelium, is made of what?
hyphae
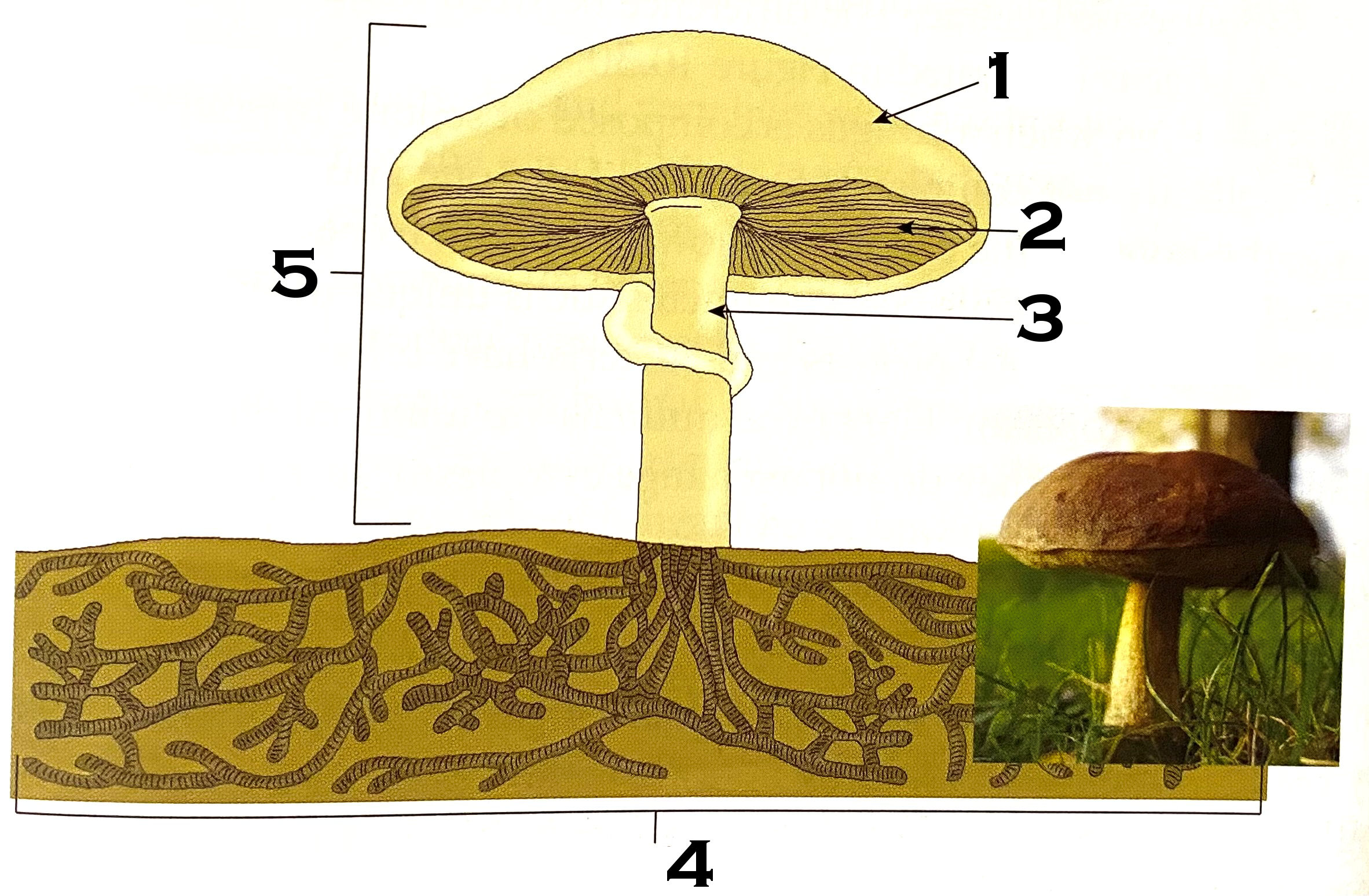
What is #5 of the mushroom?
fruiting body or reproductive structure

What color are members of Phaeophyta?
brown

What color are members of Chlorophyta?
green (or yellow-green)
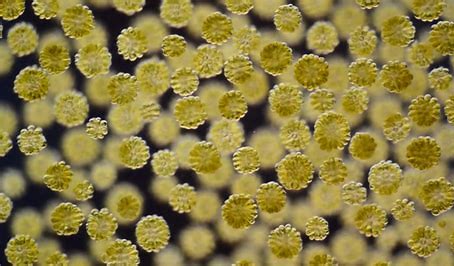
Usually, what color are members of Chrysophyta?
golden
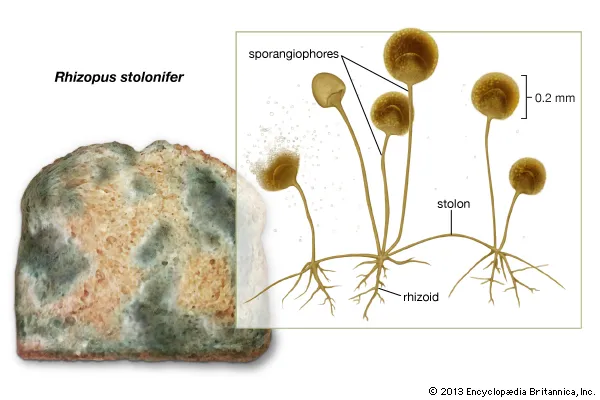
Stolons
‘connector’ aerial hyphae
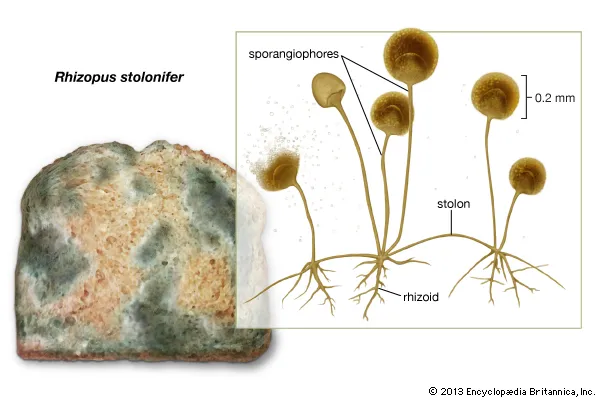
Sporangiophores
specialized enclosures or sacs made out of hyphae that have sporangia on their tips where spores are produced
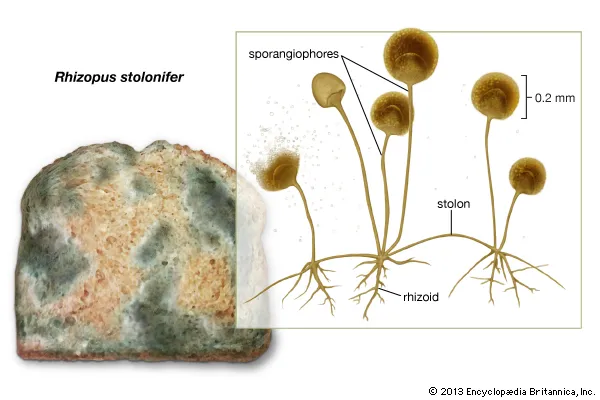
3 types of hyphae
Rhizoids
Stolons
Sporangiophores
The 5 phyla of fungi
Zygomycota
Ascomycota
Basidiomycota
Chytridiomycota
Deuteromycota

Zygomycota
1. Spores formed in small structures that exist where hyphae fuse with one another for the purpose of reproduction
2. These spores are called zygospores
3. No fruiting bodies are formed in reproduction

Ascomycota
1. Spores formed in sac-like structures (look like globes, flasks, or dishes) called asci
2. These spores are called ascospores
3. Some members are unicellular: yeasts
4. Sexual reproduction – fusion of hyphae of different mating types, and a fruiting body is formed

Basidiomycota
1. Spores formed in club-like structures called basidia
2. These spores are called basidiospores
3. Saprophytic (most)
4. Parasitic (a few)
5. Sexual reproduction between mycelia
Chytridiomycota
1. Spores have flagella
2. Saprophytic (most); some are parasitic
3. Inhabit muddy or aquatic areas, feeding on decaying water plants
Deuteromycota
1. Assume they have a form of sexual reproduction, but scientists have not discovered it yet
2. Called imperfect fungi
Name two pathogenic fungi and the maladies they cause.
Claviceps purpurea – causes ergot of rye, a plant disease
Synchytrium endobioticum – causes potato wartmycorrhizae