Chapter 18: Competition and Monopoly
A monopoly is a market with only one seller of a good or service.
Profit is the difference between a firms total revenue and its total cost.
The ^^total revenue earned by a firm comes from the sale of the firm's goods or services.^^
The total cost for a firm comes from expenses that a firm must pay in order to produce its products.
Total cost includes spending on resources like labour and materials plus the opportunity cost of the firm owner.
Total cost of production include the direct costs and opportunity costs associated with producing a given level of output.
Marginal cost of production is the change in total cost incurred when an additional unit of output is produced.
<<Total revenue is the amount of money earned when a supplier sells a given quantity of a good. It is equal to the price of the good (P) multiplied by the quantity of the good sold (Q).<<
<<Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue earned when an additional unit of output is produced and sold.<<
Producing the level of output that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost generates the maximum profits.
In perfectly competitive markets, there are many buyers and sellers, and the price for the good is determined by the intersection of the market demand and supply for the good.
The profit-maximizing output level for a firm occurs where MR(Marginal revenue) = MC(Marginal cost).
- If MR> MC, increasing output will increase profits.
- If MR < MC, decreasing output will increase profits.
Perfect competition is a type of market that has several distinguishing characteristics: identical products, complete information, many buyers and sellers, and easy entry and exit from the market.
- IDENTICAL PRODUCT- Each firm in a perfectly competitive market produces a product that is identical to that produced by all the other firms in the market.
- The products produced by perfectly competitive firms are indistinguishable from one another as far as the buyer is concerned.
- COMPLETE INFORMATION- A second characteristic of perfect competition is that buyers and sellers have complete information about the prices charged by each firm.
- If one firm is charging more than another firm, buyers will know about it and will move their business to the lower-priced firm.
- When buyers have complete information about each firm's prices, any one firm will not be able to charge more for their product without losing customers to competitors.
- MANY BUYERS AND SELLERS- A third characteristic of perfect competition is that perfectly competitive markets are made up of many buyers and sellers of a good or service.
- When there are many sellers of a product, each individual seller plays too tiny a role in the market to have any influence on the product's price.
- Each firm's supply is only a small part of the overall market supply, so changes in one firm's supply do not cause a change in the market supply or price of the good.
Taking an example here, the figure below illustrates the relationship between the market demand and supply and the price that the company Econoweb can charge for its reports.
In our example, Econoweb charged its clients $37 for each report produced. In a perfectly competitive market, this price would have come from the intersection of the market supply and demand for web reports.
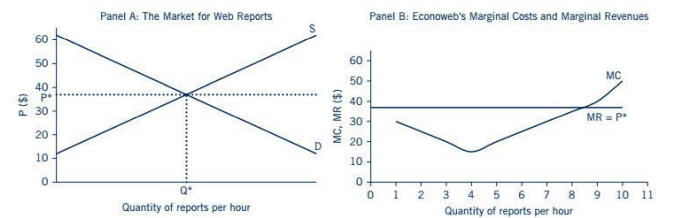
Panel A of the figure shows the market demand and supply of web reports.
The intersection between the demand and supply curves generates an equilibrium price of $37 per report.
At the equilibrium price P*, a total of Q* reports are sold Because there are a large number of firms in the market, each firm produces a small fraction of this total equilibrium quantity of reports.
Panel B of the figure shows Econoweb's marginal cost and marginal benefit curves.
The price that Econoweb charges for its web reports is P* = $37, which is exactly the same price charged by the other firms in the market.
If Econoweb tried to charge more than $37, its customers would simply move their business to another firm.
If Econoweb tries to charge less than $37 for its reports, it would lose revenues to other competitors.
The reduction in revenues would reduce Econoweb's profits and make it less competitive than other firms.
Over time, Econoweb's competitors could use their higher profits to drive Econoweb out of the market.
Price takers are firms that cannot set the price of their good, but instead must take the market price as given.
Normal profit is the profit that business owners could earn if they applied their resources and skills in their next best business alternative.
- Normal profit is total revenue minus total cost, including opportunity cost.
Economic profit occurs when a firm earns more than $O in normal profits.
- A firm owner earning economic profit earns more than she would if she chose her next best alternative.
Barriers to entry are obstructions that make it difficult for new firms to enter a market. Barriers to entry can include control over resources, high start-up costs, government regulations, and patents.
Unless a monopoly can discriminate among its buyers and charge them each different prices, when a monopoly tries to sell a higher quantity of its good, it has to lower its price for all the units it sells.
The figure below illustrates Econoweb's demand and marginal revenue curves if it operates as a monopoly.

- The demand curve D is the market demand for web reports.
- The marginal revenue curve (MR) shows the change in total revenue earned when Econoweb expands its output.
- For monopoly firms, marginal revenue is less than price.
Price Setters are firms that are able to set the prices for their products.
Taking the Econoweb as an example, as a perfectly competitive firm, Econoweb took the market equilibrium price of reports ($37) as given and used a marginal revenue-marginal cost comparison to find its profit-maximizing output level (8 reports per hour).
- As a monopoly, the profit-maximizing level of output for Econoweb was 4 reports per hour, and the profit-maximizing price was $42 per report.
- Thus, Econoweb produced less output and charged higher prices when it operated as a monopoly than when it operated as a perfectly competitive firm.
- This result, that monopolies produce less output and charge higher prices than similar firms operating in perfect competition, is a general characteristic of monopolies.
- The figure below illustrates the price and output levels for monopolies and perfectly competitive firms more generally.
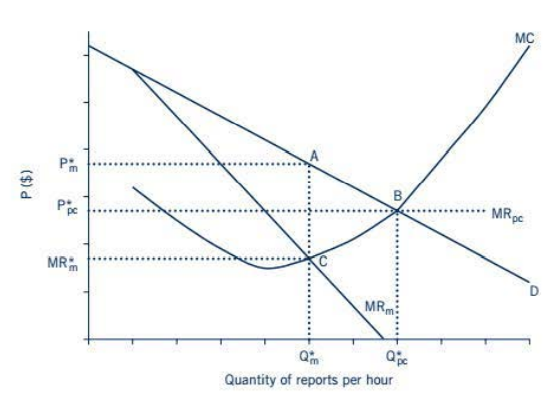
- The demand curve for reports is shown by D, and marginal costs are shown by curve MC.
- If Econoweb were operating as a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal revenue curve MR(pc) would be the same as the market equilibrium price of reports, P*(pc).
- The marginal revenue curve MR(pc) intersects the marginal cost curve at point B, so tile optimal level of output for the perfectly competitive firm is Q*(pc).
- The price of reports is P*(pc).
- If Econoweb operates as a monopolist, MR(m) represents its marginal revenue curve.
- MR(m) intersects the marginal cost curve at point C, so the profit-maximizing level of output for tile monopolist is Q*(m).
- At this level of output, Econoweb will determine the price of reports by finding the price on the demand curve D that indicates how much consumers are willing and able to pay for Q*(m) reports.
- Point A on the demand curve shows the price that corresponds to Q*(m), so the monopolist's profit maximizing price is P*(m).
- When Econoweb operates as a monopoly, its level of output is lower and tile price it charges is higher than when it operates as a perfectly competitive firm.
Antitrust laws are laws that promote competition between businesses and prohibit anti-competitive behaviour by firms with large control over markets.
^^Firm entry and exit into perfectly competitive markets means that economic profits are difficult to sustain, so over the long term, perfectly competitive firms earn just enough to cover their opportunity costs.^^
- For monopoly firms, the optimal level of output also occurs where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, but monopoly firms can charge a higher price for their good than perfectly competitive firms can.
- The profit-maximizing level of output produced by a monopoly is lower than what would be produced by a competitive firm.
- Because monopoly firms generate dead weight losses, they are a form of market failure.