Exam 3 - Brain, Cranial Nerves, Nervous System, Spinal Nerves
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lott :( 🤯🤯🤯🤯🤯
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
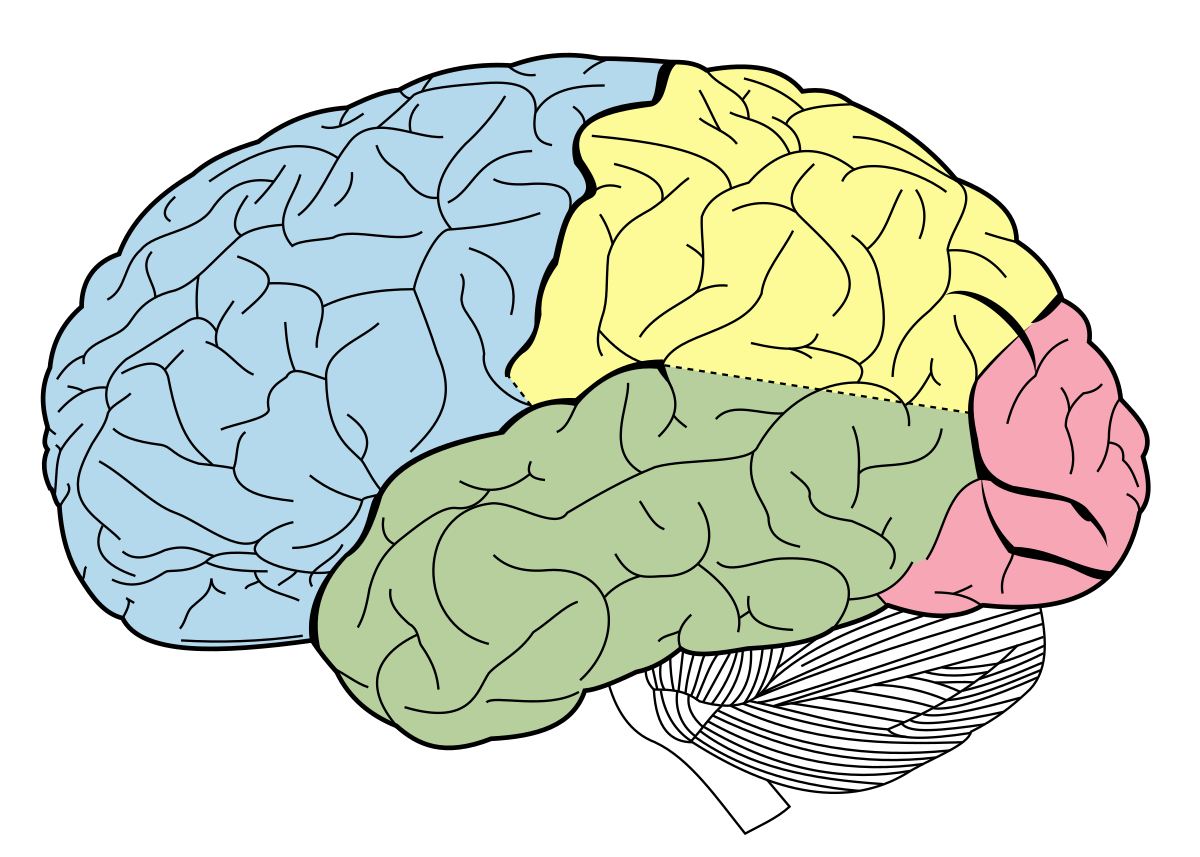
Cerebrum
2 Hemispheres, 4 Lobes Each Side
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital
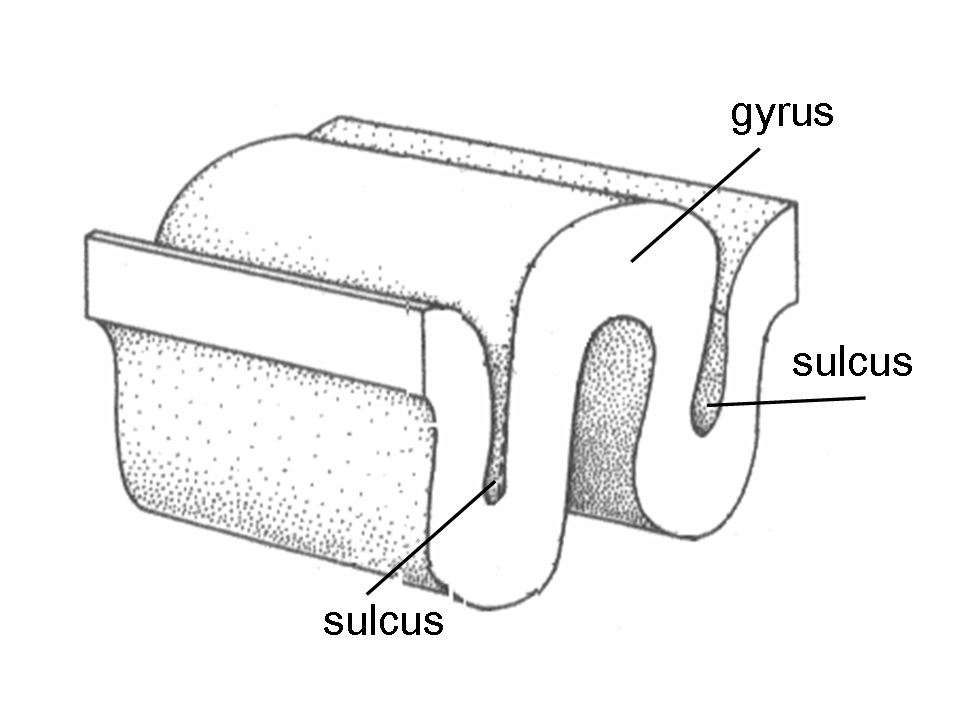
Gyri
Wrinkles of the Brain
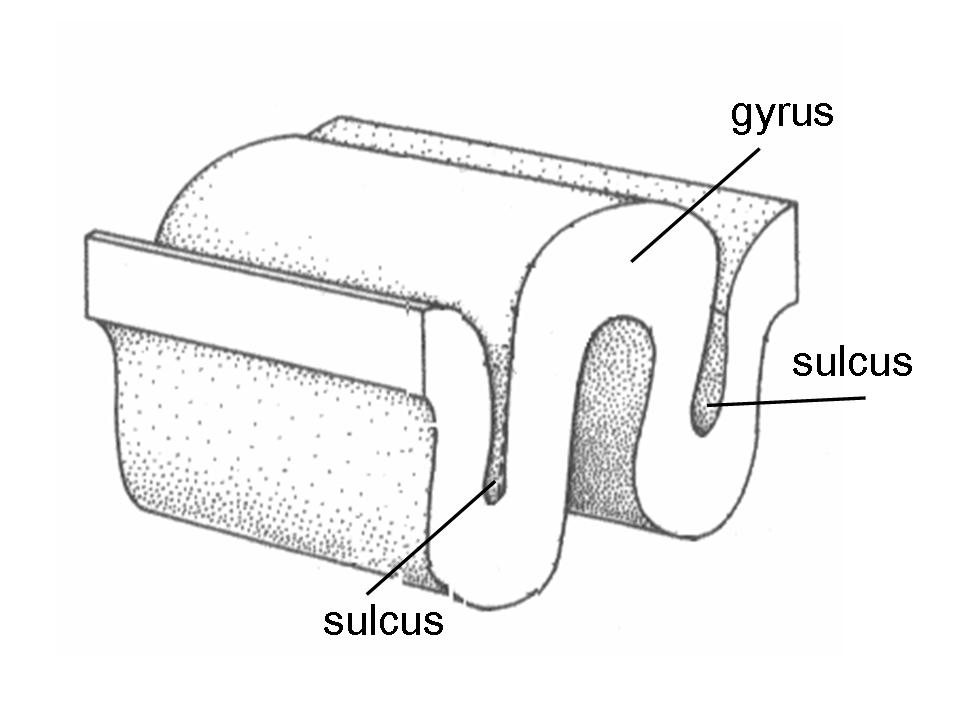
Sulci
Valleys of the Brain between Gyri
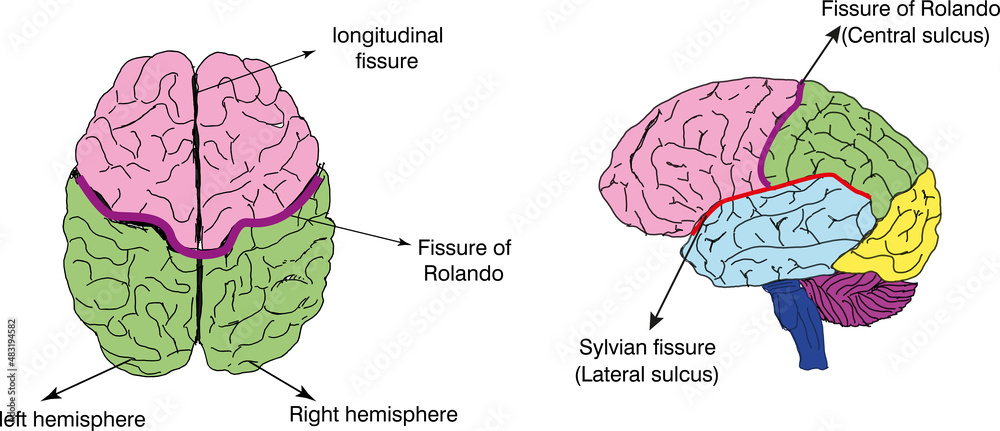
Fissures
Deeper Valleys of the Brain Separating Lobes
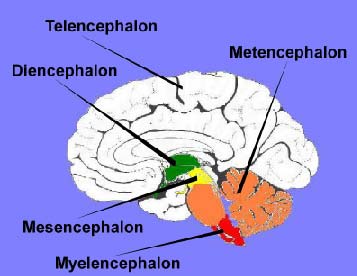
Telencephalon
The Cerebrum of the Brain
Tel, Di, Mes, Met, My
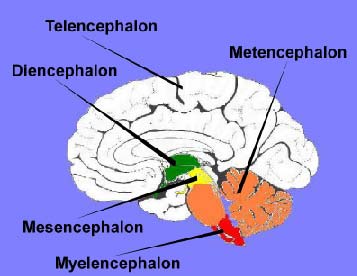
Diencephalon
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus
Middle Most Vesicle of the Brain
Tel, Di, Mes, Met, My
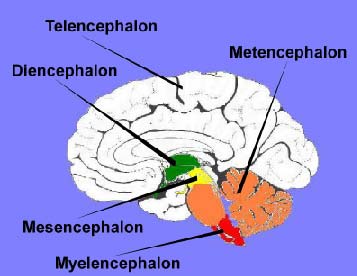
Mesencephalon
Midbrain
Directly Below the Diencephalon
Tel, Di, Mes, Met, My
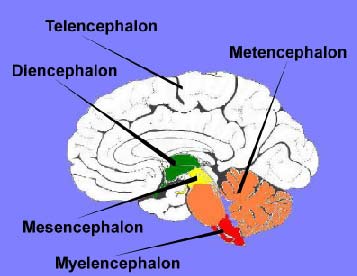
Metencephalon
Pons and Cerebellum
Below Mesencephalon, Above Myelencephalon
Tel, Di, Mes, Met, My
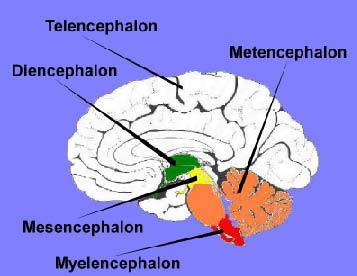
Myelencephalon
Medulla Oblongata - CARDIAC, VASOMOTOR, RESPIRATORY, and REFLEXES
Bottom Most Vesicle of the Brain, Above Brain Stem
Tel, Di, Mes, Met, My
Gray Matter
Neuron Cell Bodies, Dendrites and UNMYELINATED Axons
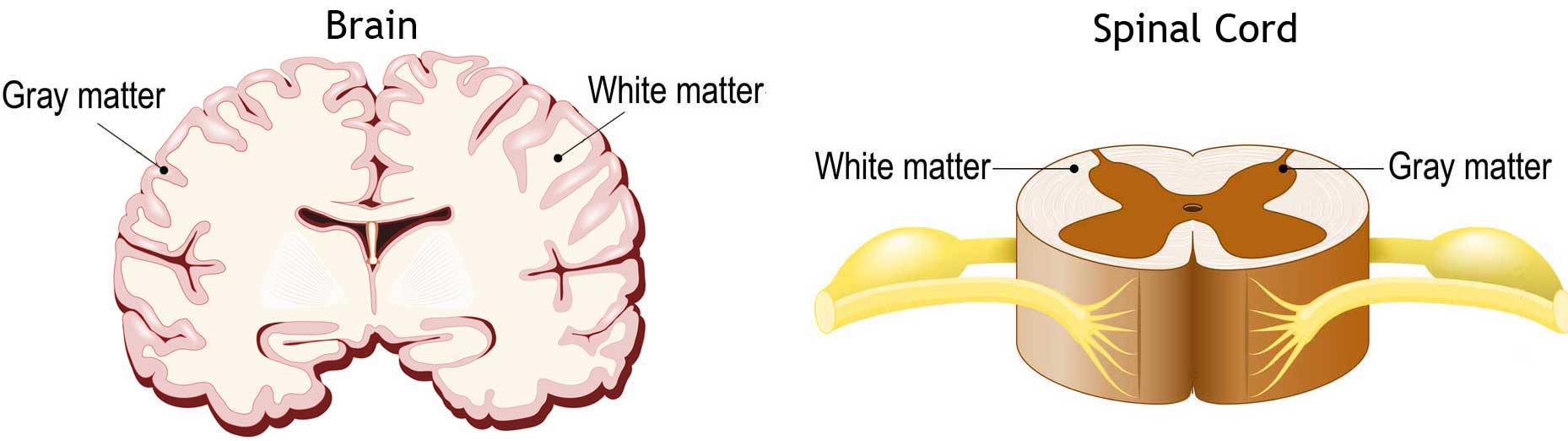
White Matter
MYELINATED AXONS
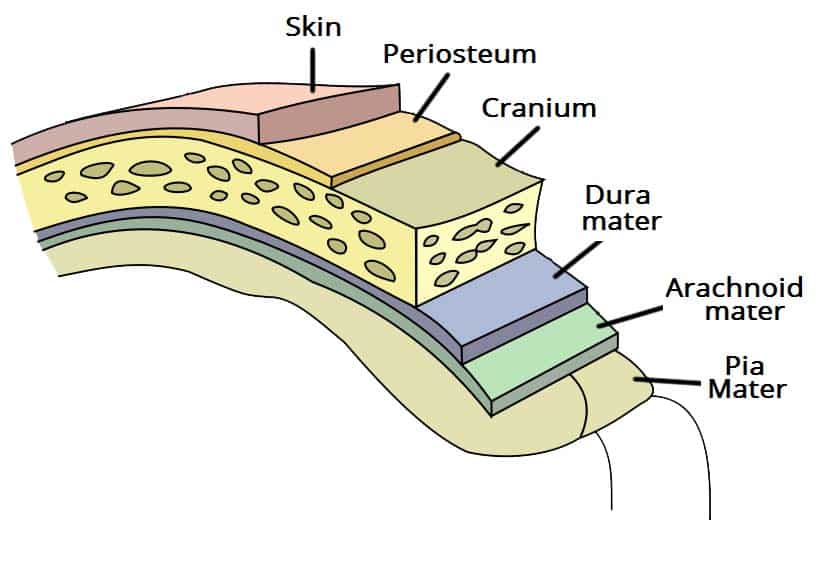
Cranial Meninges
3 Connective Tissue Layers Covering Skull
Composed of the Dura, Arachnoid and Dura Mater
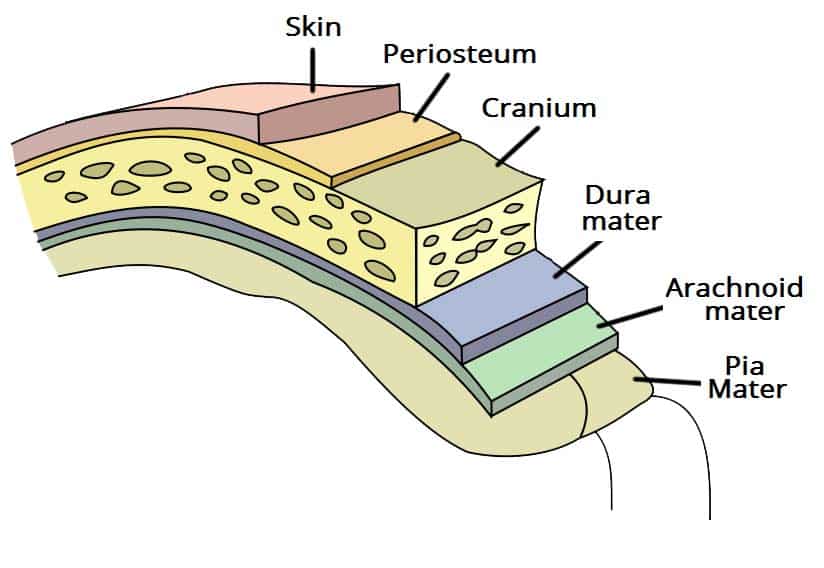
Dura Mater
Tough, Outer Membrane (Superficial C. Meninges)
Composed of the Meningeal and Periosteal Layers
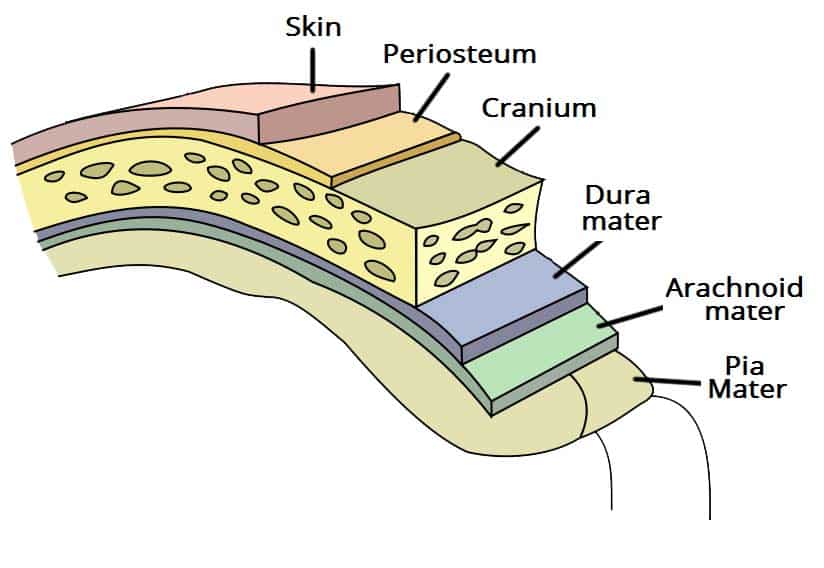
Arachnoid Mater
Middle Web-like Fibers (Middle C. Meninges)
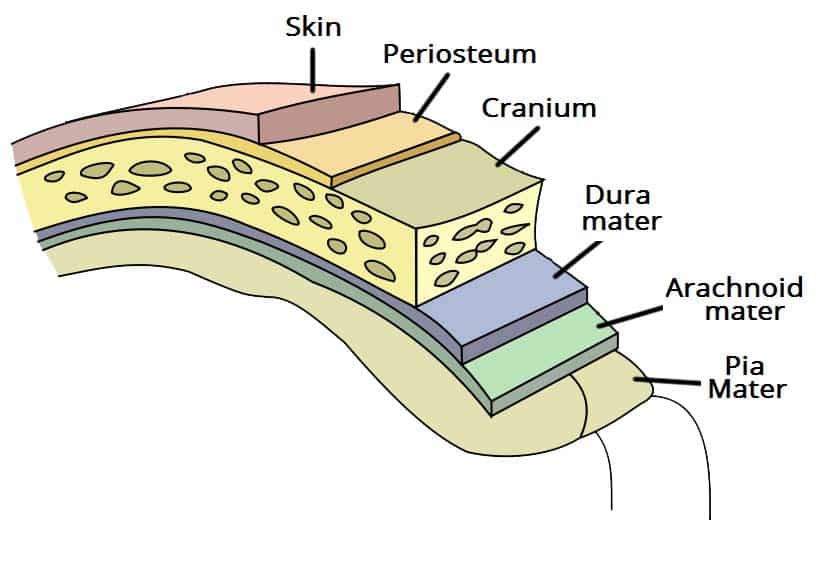
Pia Mater
Layer Clinging to Brain (Deep C. Meninges)
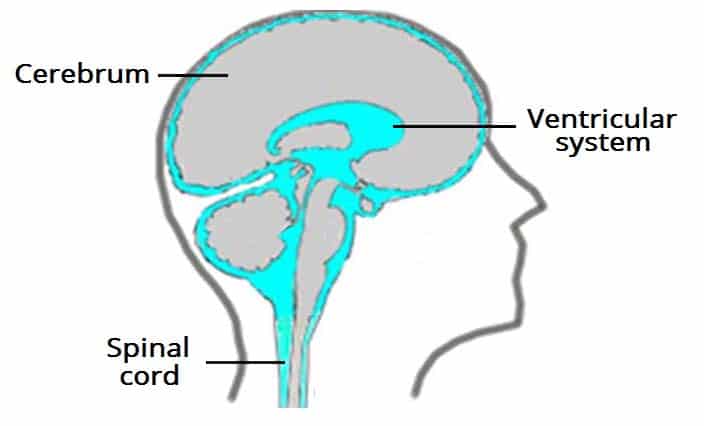
Lateral Ventricles
Sheep-Horn Ventricles
Connected to 3rd via Interventricular Foramen
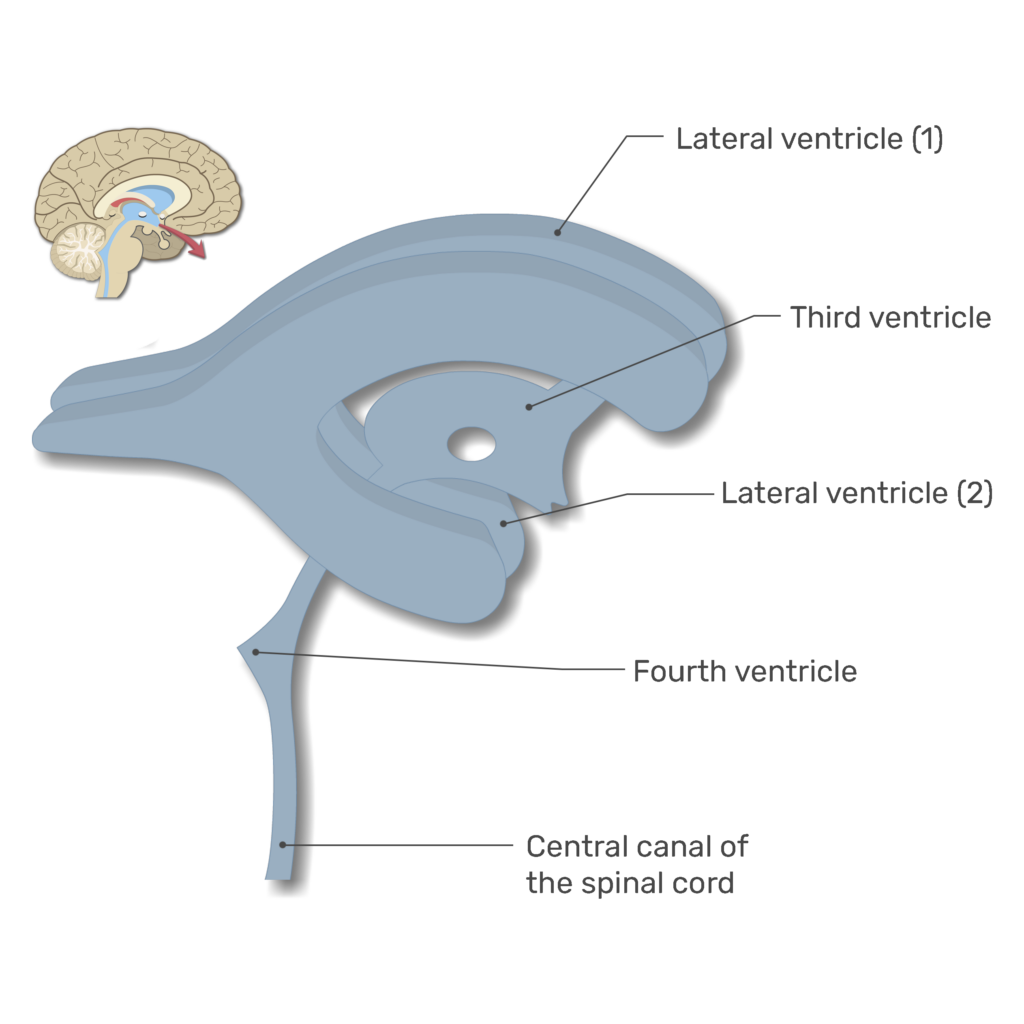
3rd Ventricle
Connect to 4th Ventricle via Cerebral Aqueduct
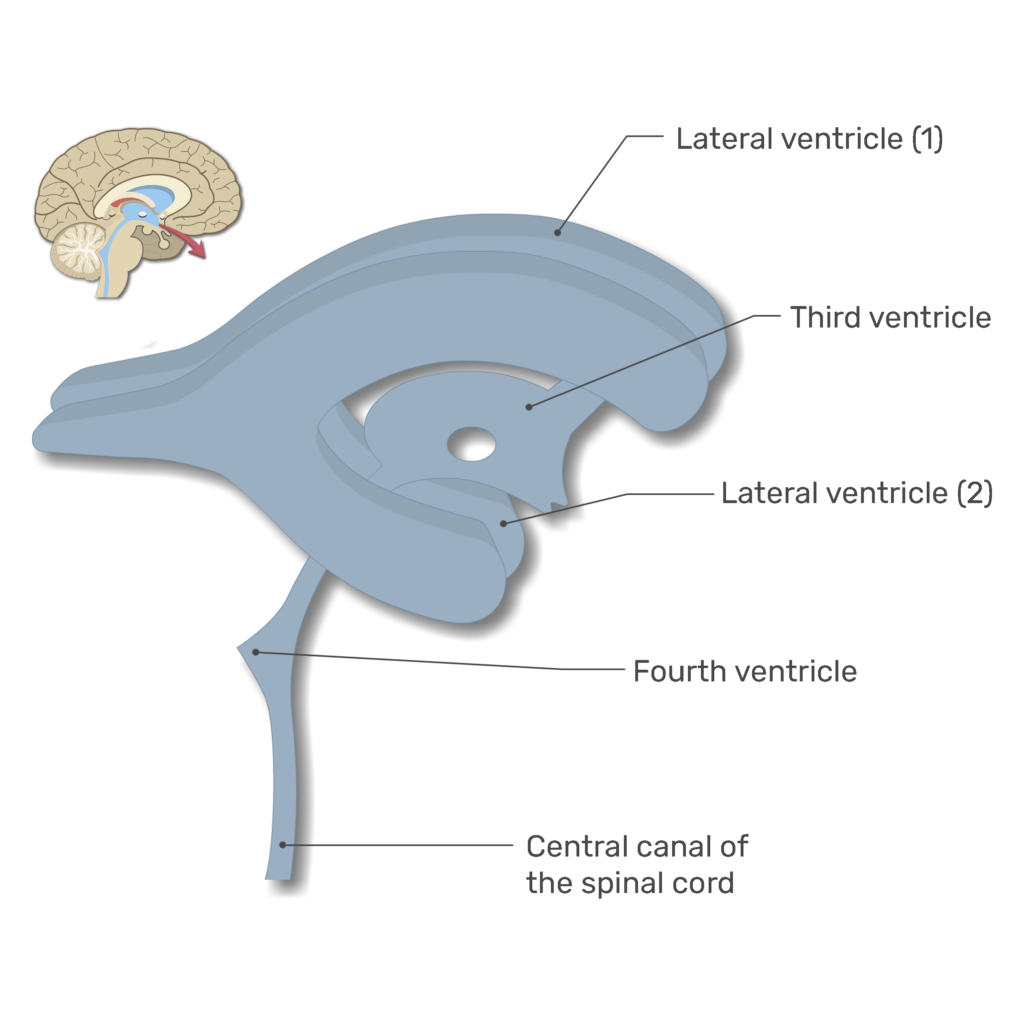
4th Ventricle
Connected to Central Canal + Subarachnoid Space
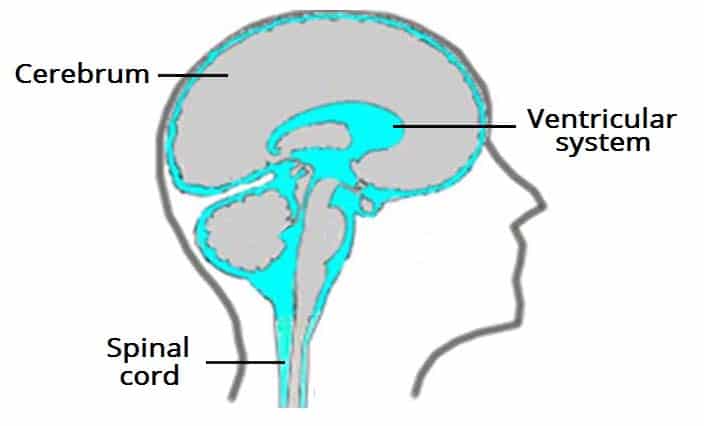
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Fills Ventricles in Brain
‘Reduces’ Brain’s Weight, Liquid Cushion
Transport Nutrients, Shield from Chemical Fluctuations
Choroid Plexus
Creates CSF, Made by Ependymal Cells Located in Pia Mater
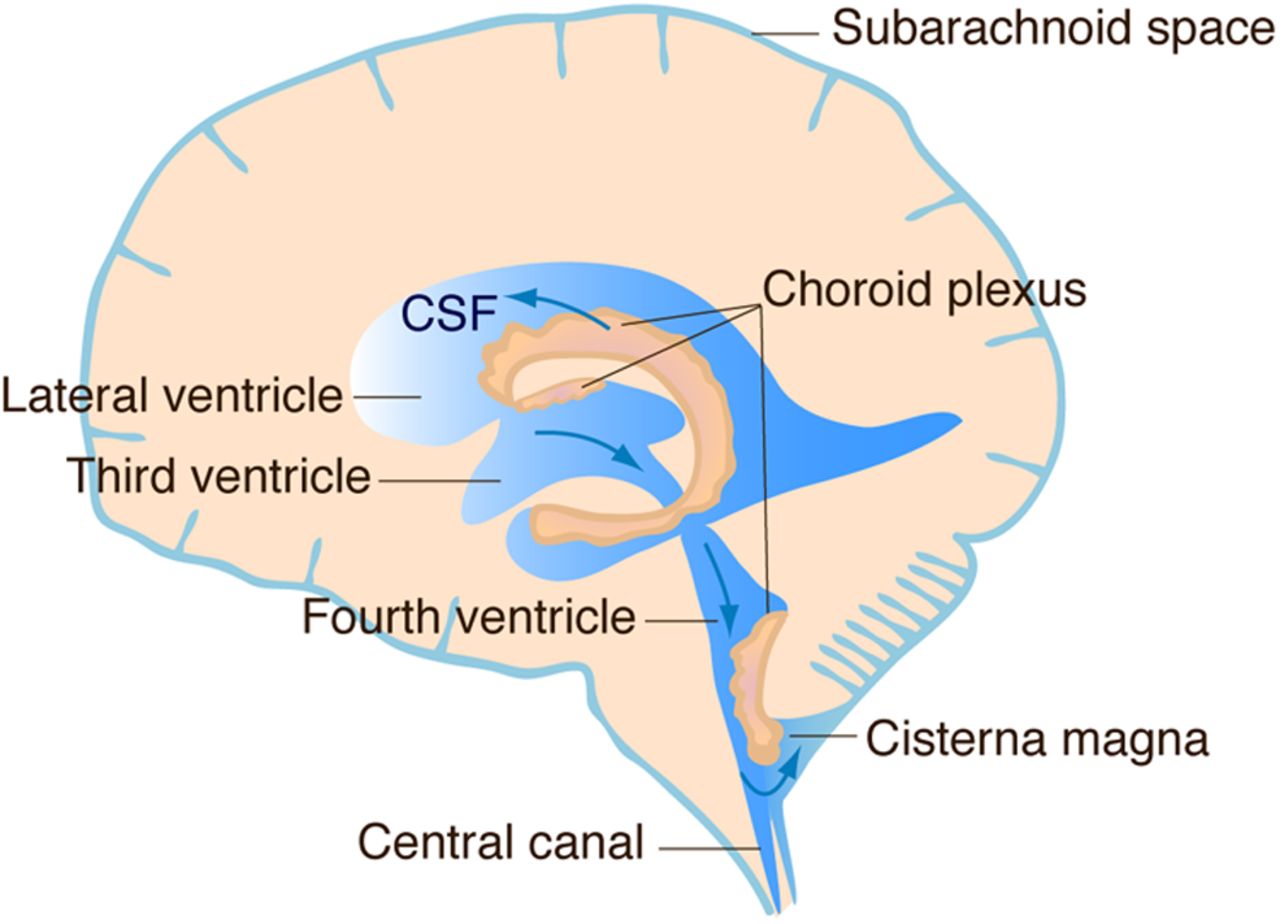
CSF Circulation
Continuously Formed and Reabsorbed
(Flows from Arachnoid Villi into Dural Venous Sinuses)
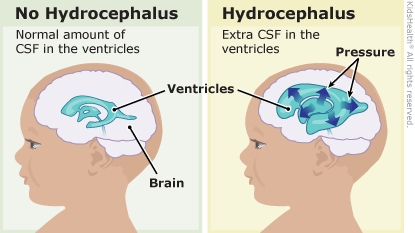
Hydrocephalus
Excessive CSF Condition, Megamind
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Regulates what Substances Enter the Brain’s Interstitial Fluid
Helps Prevent Neurons to Toxic Substances
Cerebrum
Origin of all Complex Intellectual Function
Intelligence / Reasoning
Thought, Memory, Judgement
VOLUNTARY Motor, Visual and Auditory
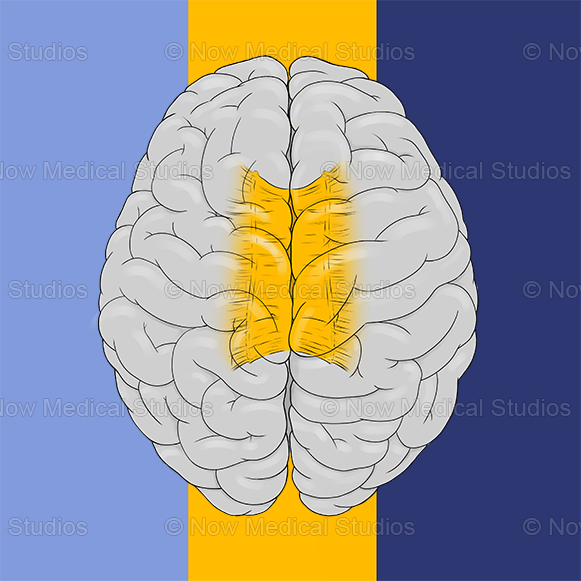
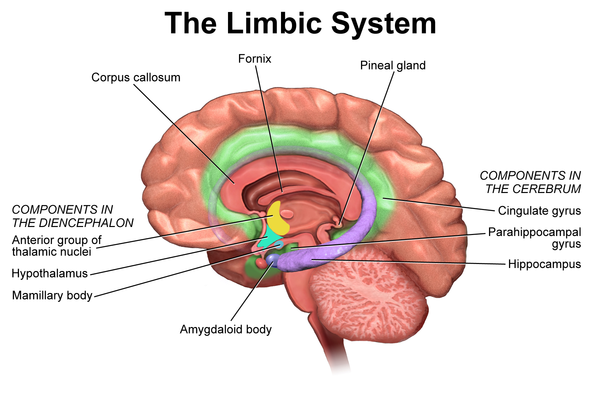
Corpus Callosum
White Matter Tract Connecting Left + Right Hemispheres
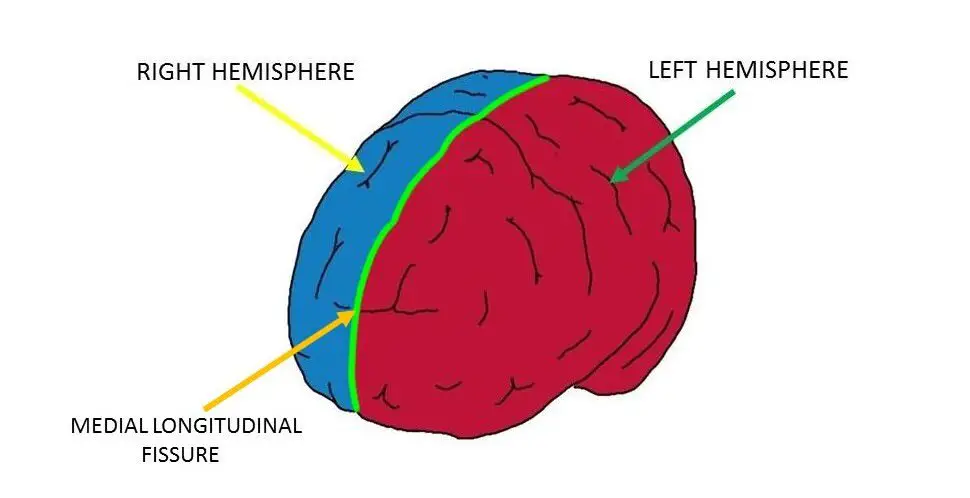
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep Sulcus Separating Left and Right Hemispheres
Frontal Lobe
PRECENTRAL GYRUS - VOLUNTARY MOVEMENT
Concentration, Communication, Personality etc…
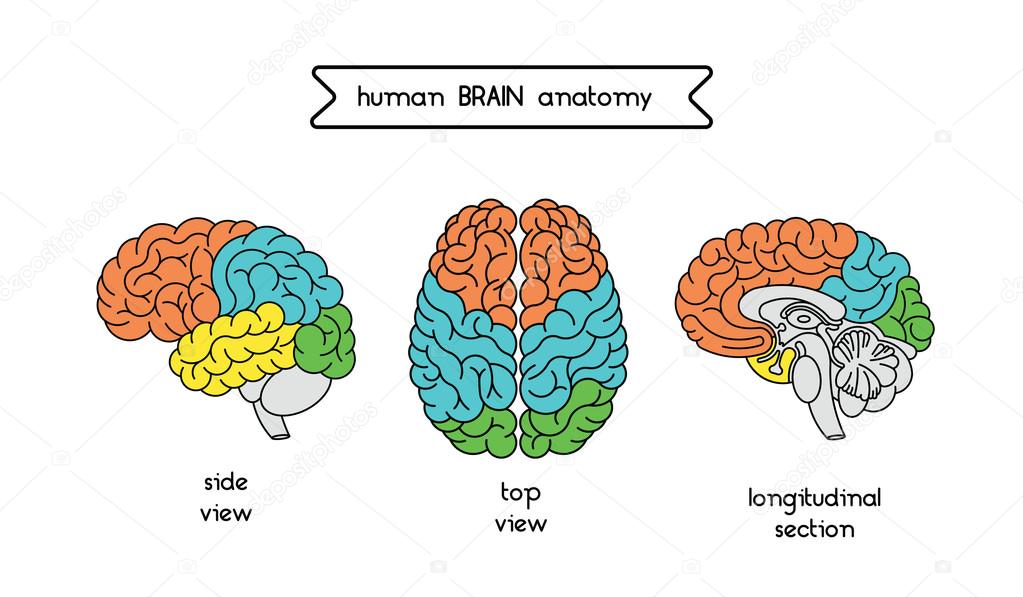
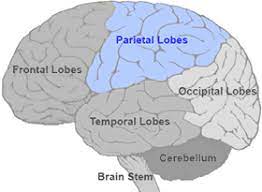
Parietal Lobe
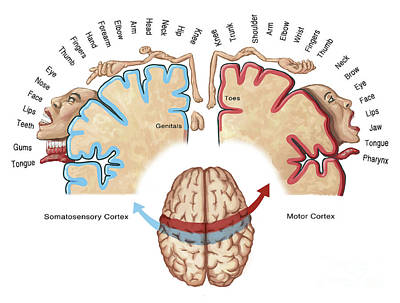
POSTCENTRAL GYRUS - SENSORY FUNCTIONS
Temporal Lobe
Hearing and Smell
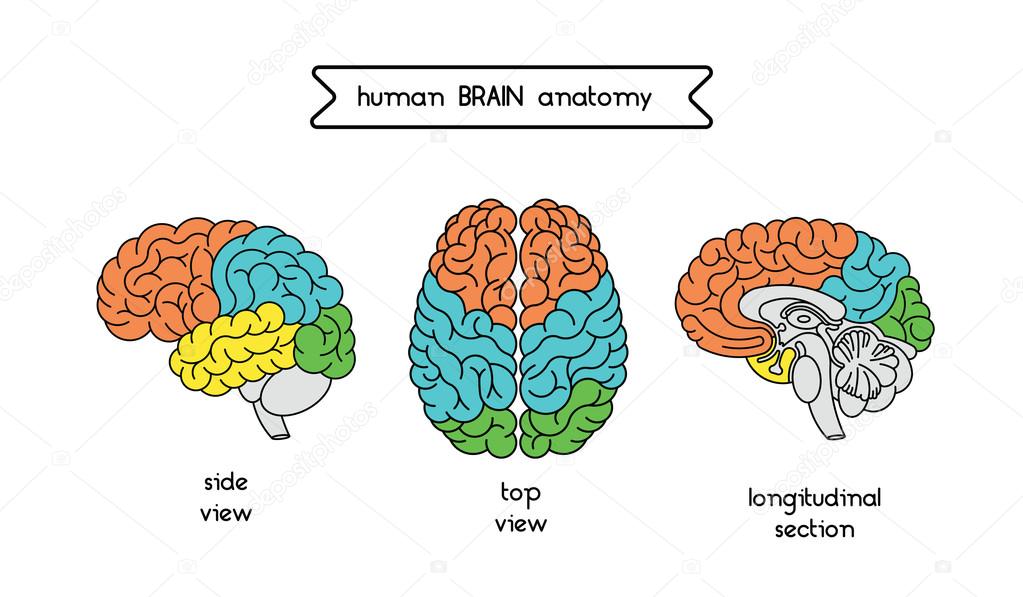
Occipital Lobe
Vision / Visual Memory
Insular Lobe
Memory and Taste
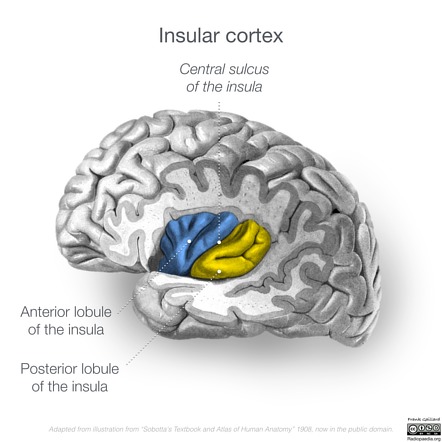
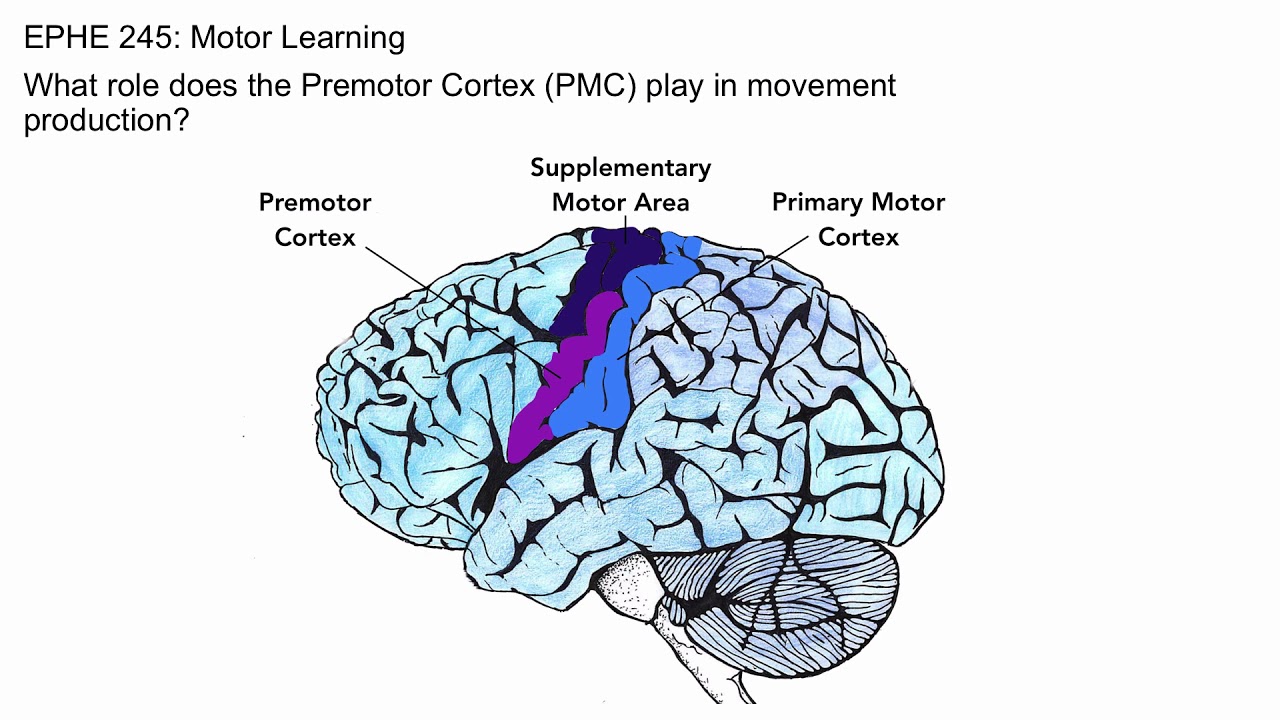
Primary (Somatic / Voluntary) Motor Cortex
Motor Homunculus, Controls Skeletal Muscle Activity on Opposite Side of Body
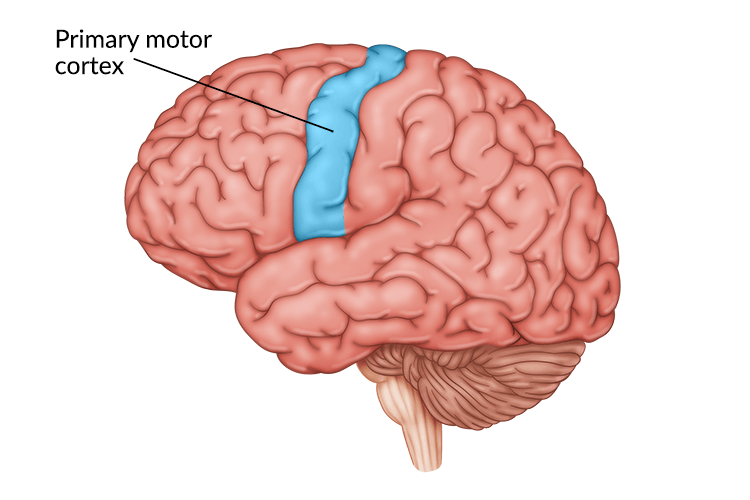
Broca and Wernicke Area
Controls Speech and Language Comprehension Respectively
Premotor Cortex (Somatic / Voluntary Motor Association)
Coordinated Learned Activities (Muscle Memory)
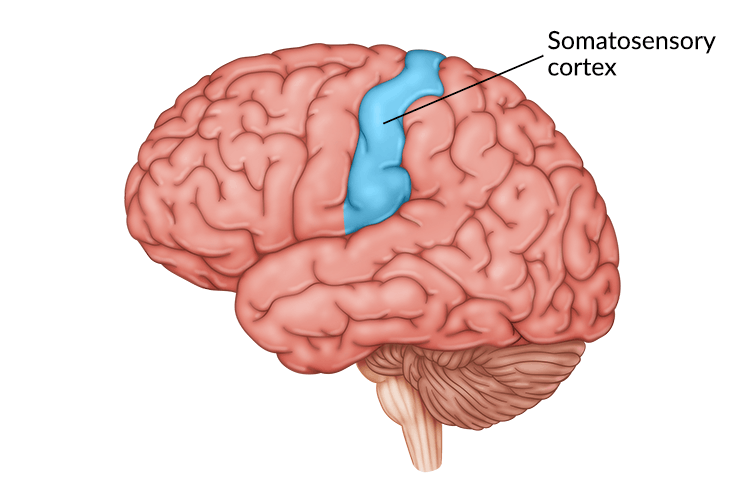
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Receives Somatic Sensory Information (Touch / Feel)
Sensory Homunculus, Posterior to Motor Cortex
Homunculus
Larger Gyri Provide for More Detailed Movement
Association Tracts
Relay Impulses to Same Hemisphere
Commissural Tracts
Relay Impulses to Opposite Hemisphere
BLUE
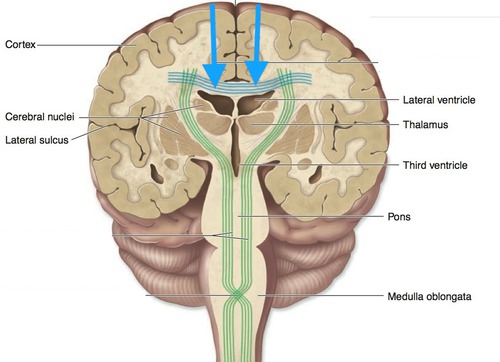
Projection Tracts
Link Cerebral Cortex to Inferior Brain + Spinal Cord
GREEN
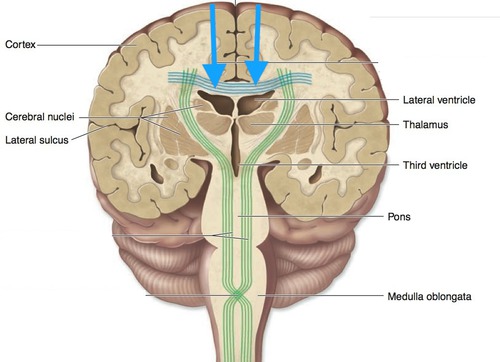
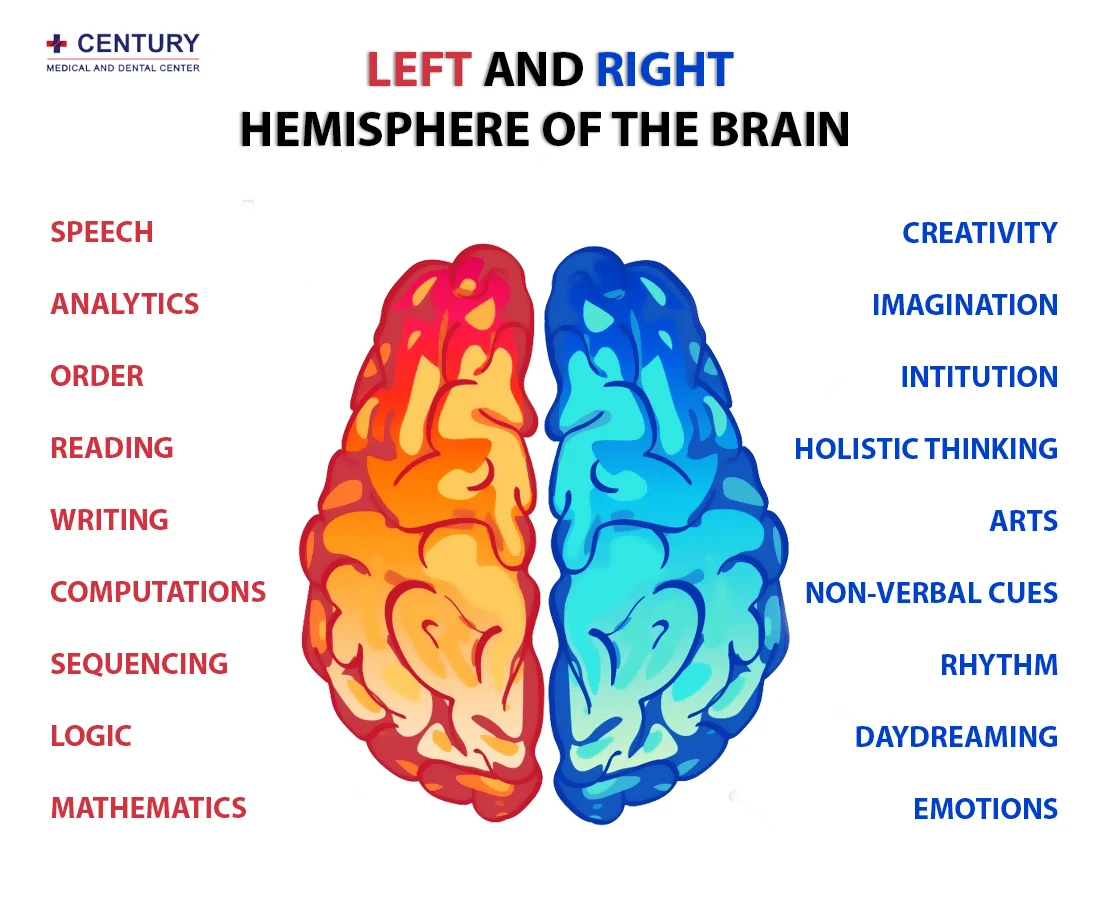
Right Hemisphere
The Emotional and Creative Brain
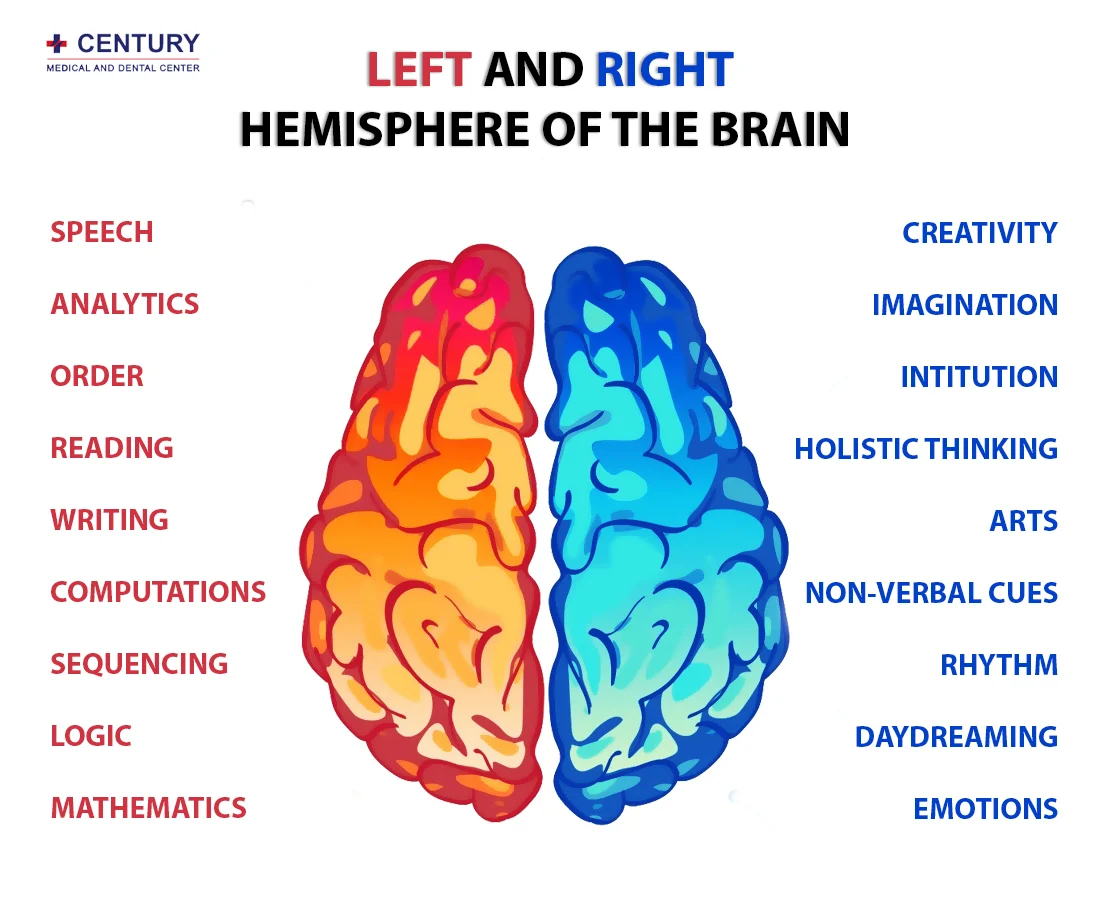
Left Hemisphere
The Logistical and Analytical Brain
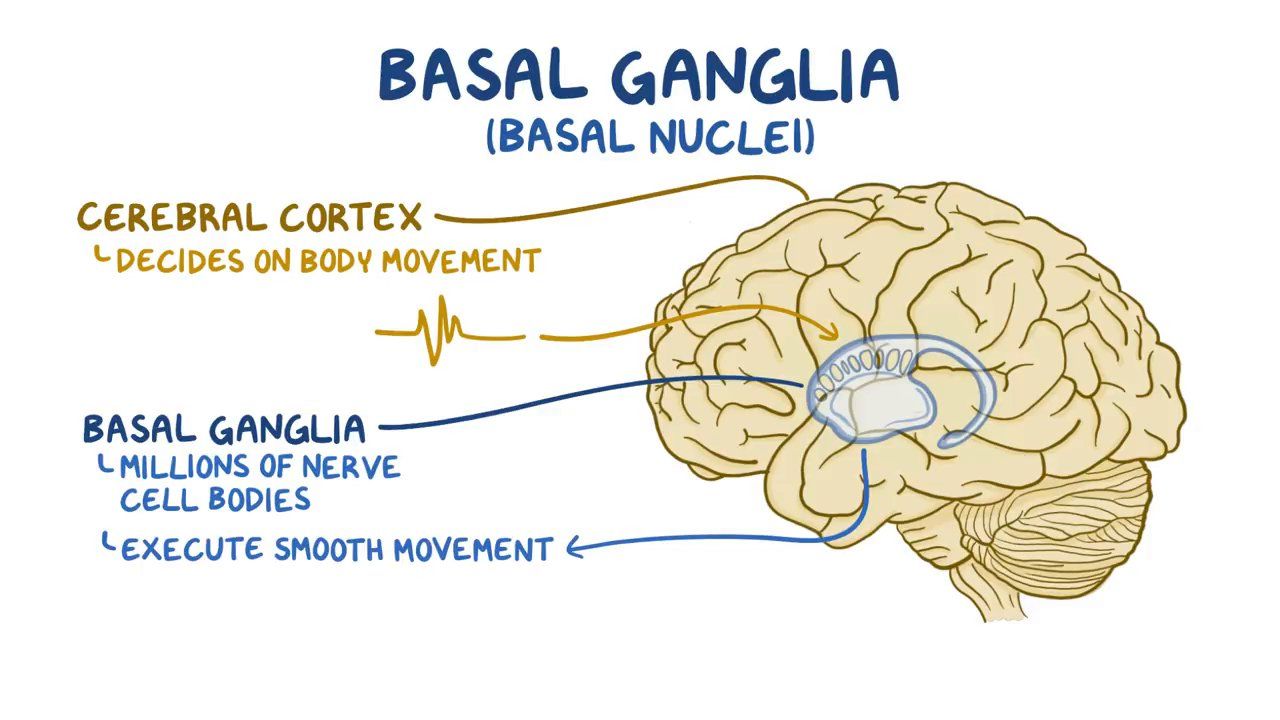
Cerebral (Basal) Nuclei
Deep Gray Matter in Cerebrum that Regulate Motor Output
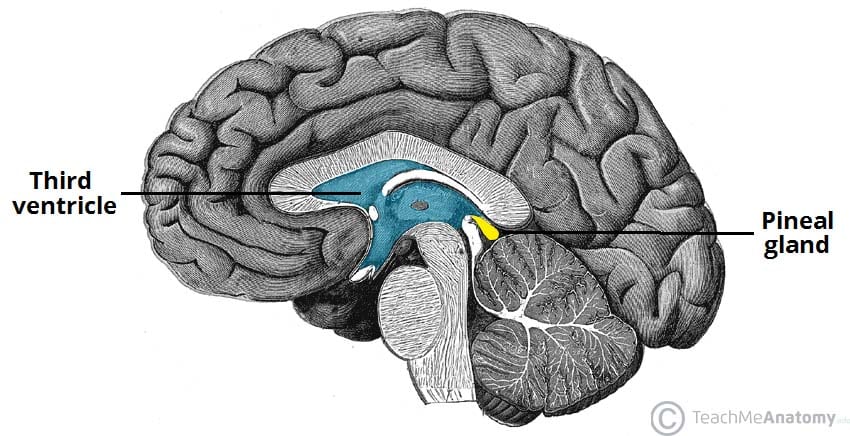
Pineal Gland
Secretes Melatonin
Regulates Day-Night Cycles
Helps Circadian Rhythm
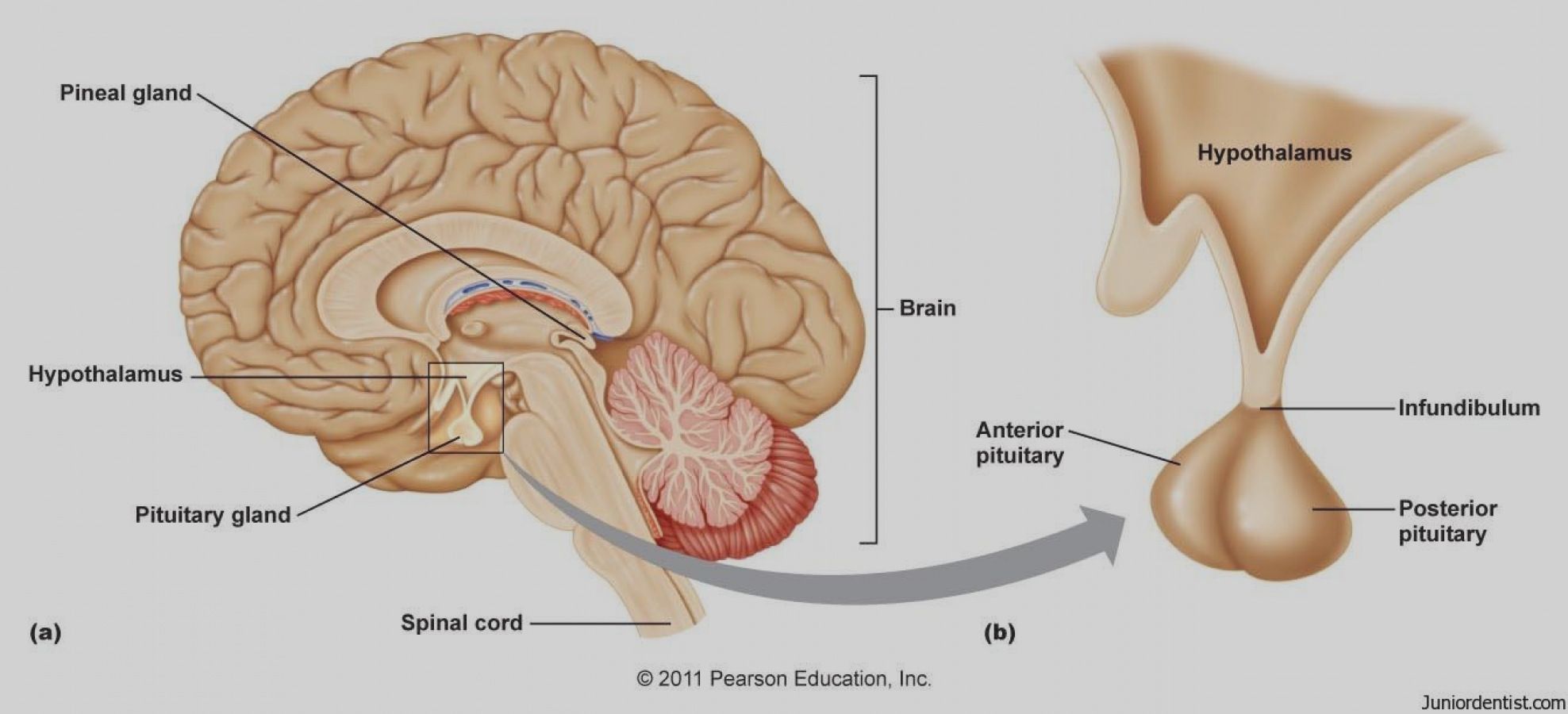
Infundibulum
Stalk of the Pituitary Gland
The Midbrain
Holds…
CN III (Oculomotor)
CN IV (Trochlear)
Cerebral Peduncles
Cerebral Aqueduct
Tectum
Superior Colliculi
Inferior Colliculi
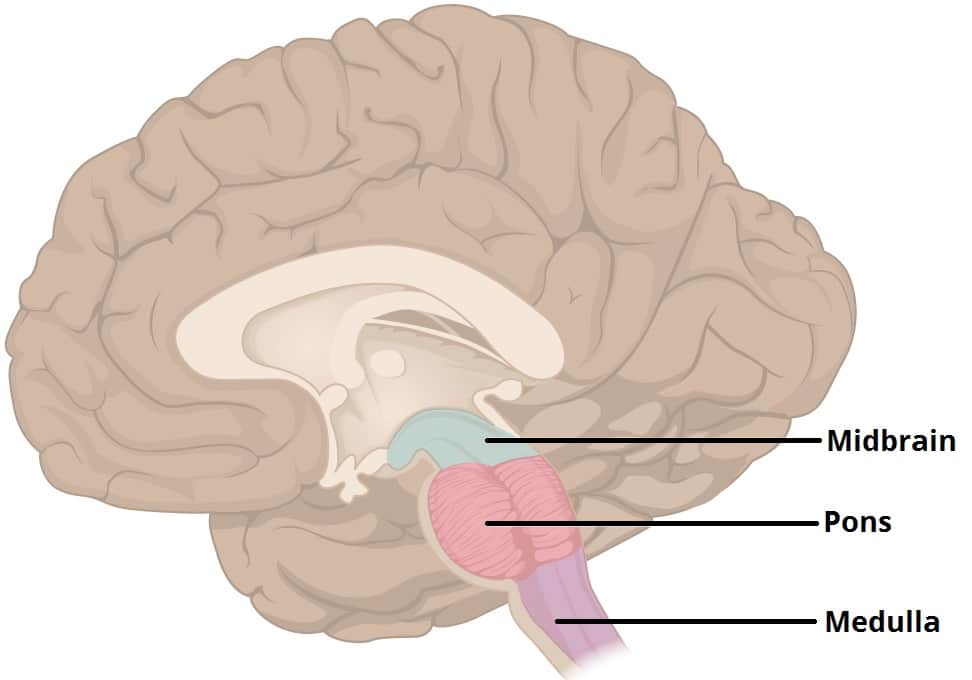
The Brainstem
Holds…
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
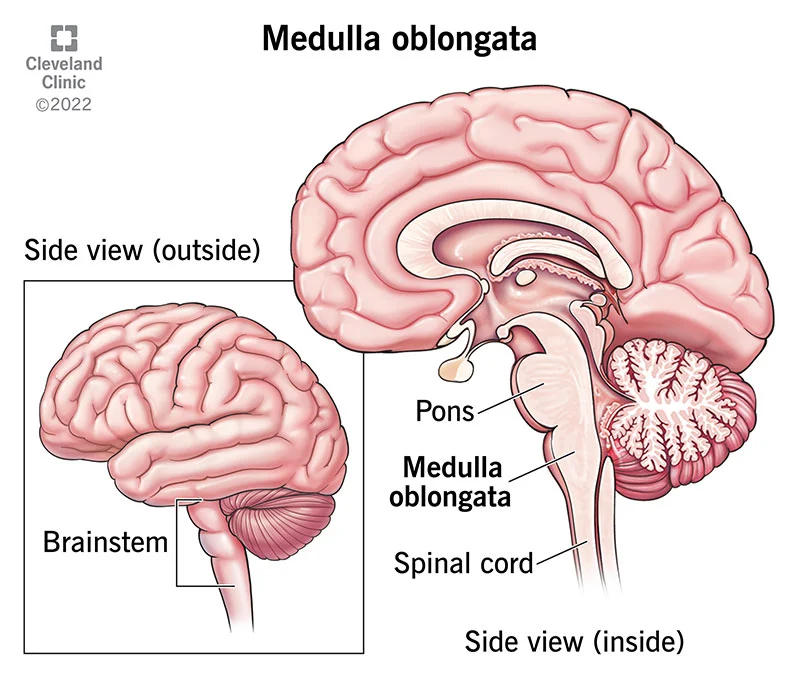
The Pons
Does…
Sensory + Motor Tracts
Respiratory Center (RR)
Cranial Nerve Nuclei
CN V (Trigeminal)
CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear)
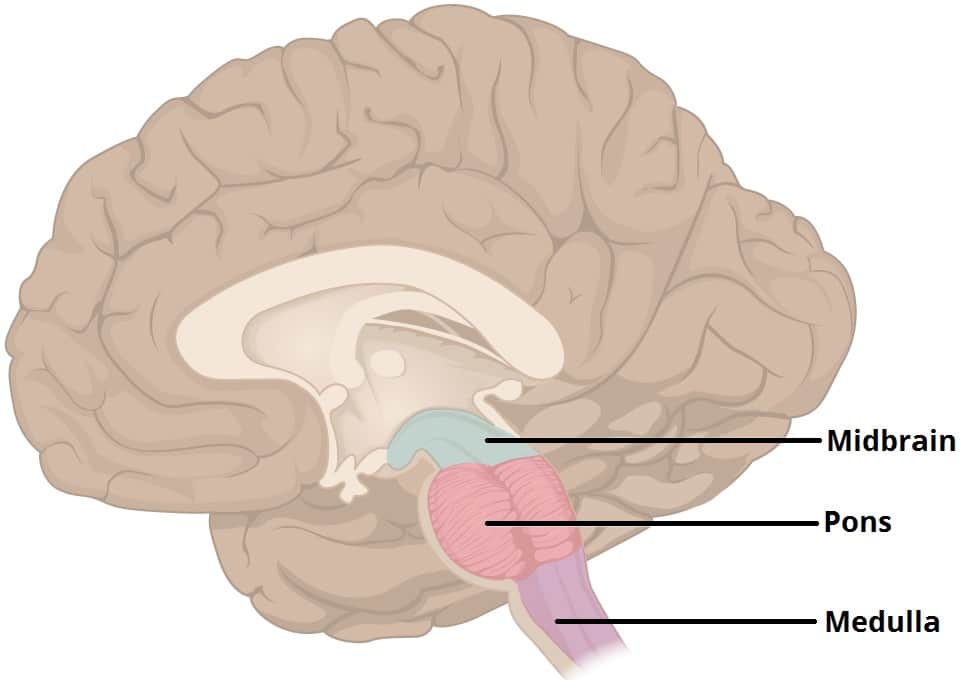
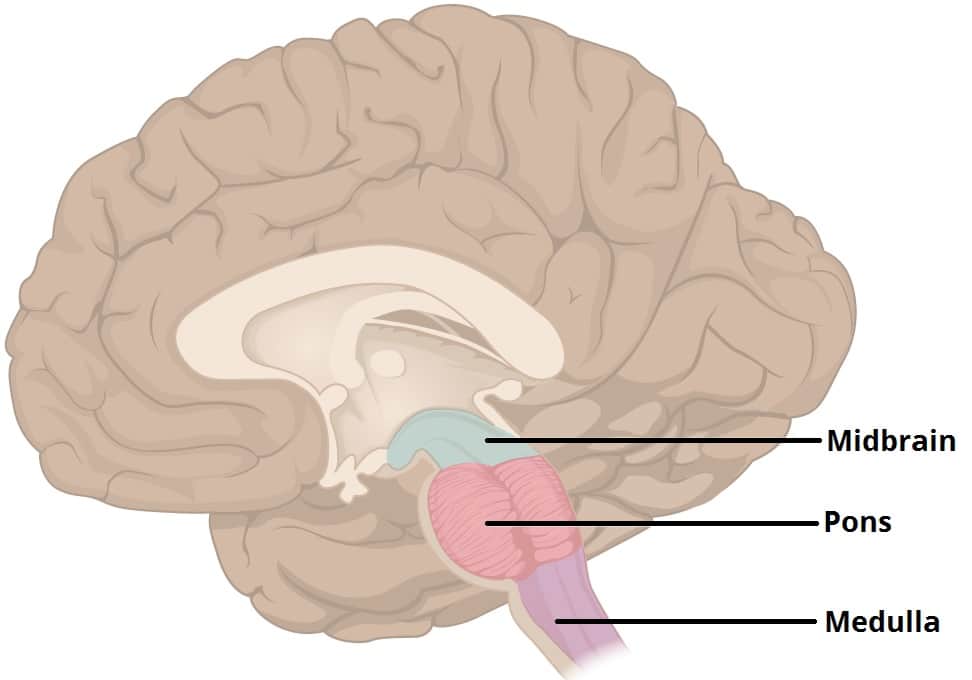
Medulla Oblongata
Does…
Cardiac Center (HR)
Vasomotor Center
Medullary Respiratory Center
Nuclei for CNs IX - XII
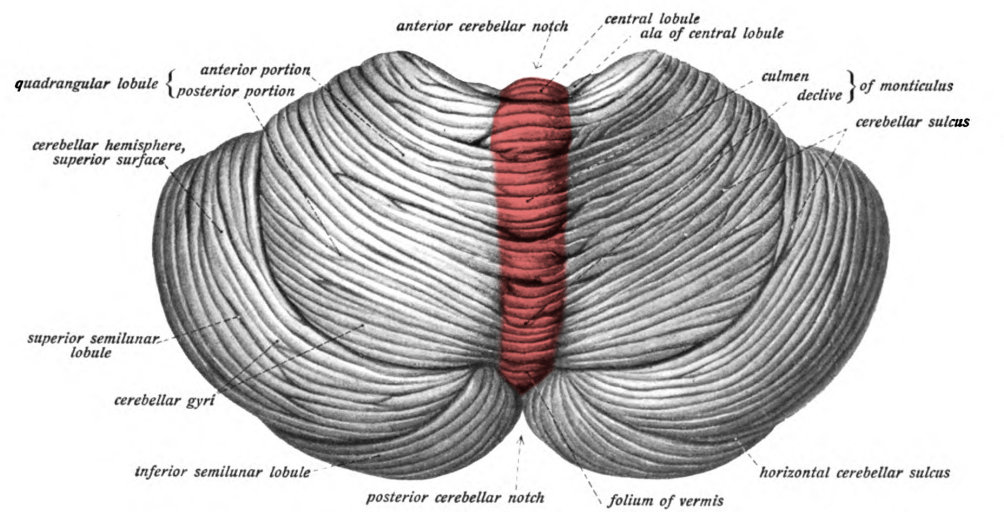
Cerebellum
Continuously Receives Motor Plans + Sensory Feedback
Left and Right Hemispheres
Middle Separation - Vermis
Cerebellar Cortex - Outer Gray Matter
Arbor Vitae - Internal White Matter
The Limbic System
Controls Emotions (Just Know This)
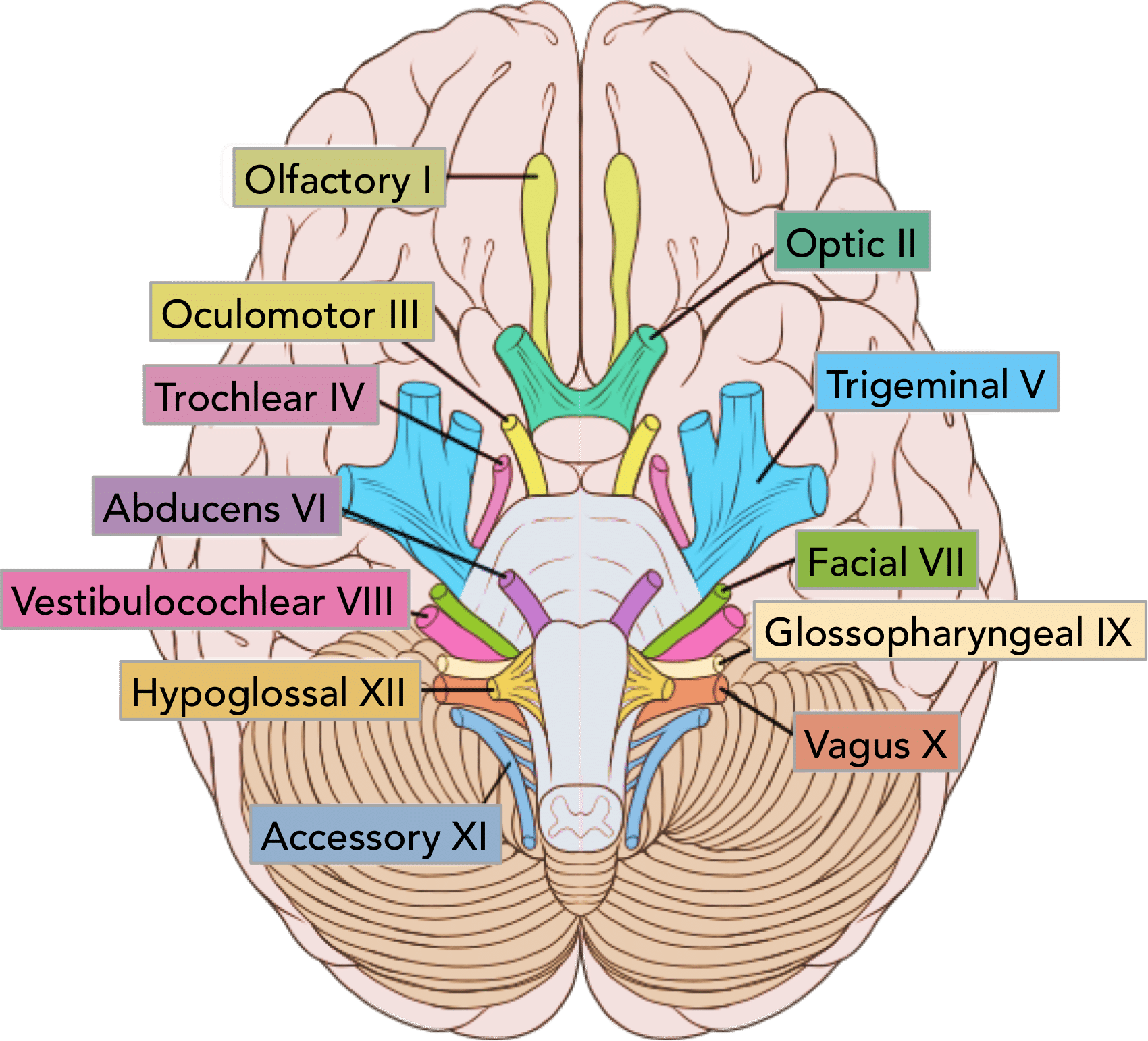
Olfactory Nerve
CN I - Sense of Smell
1/3 Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
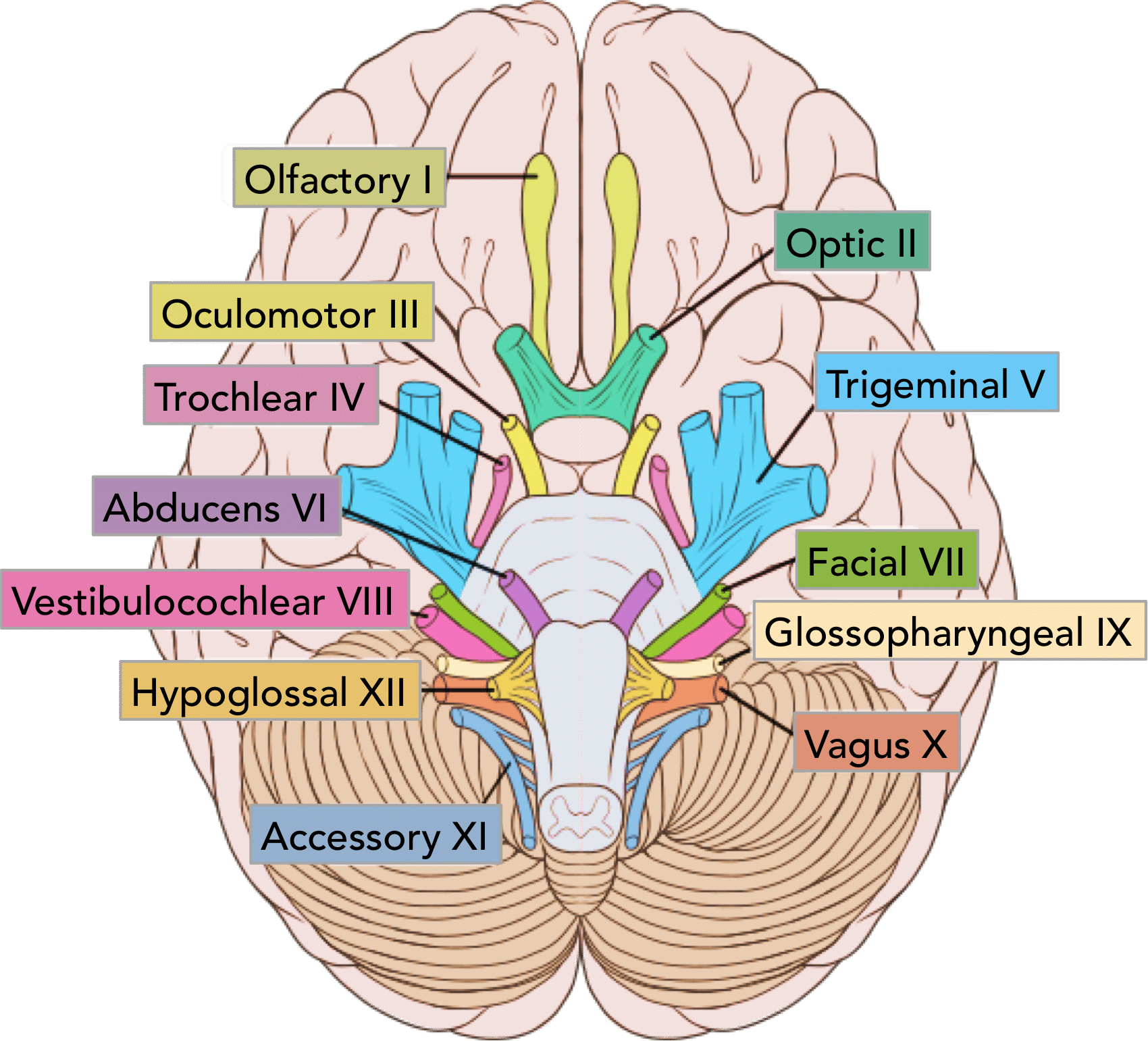
Optic Nerve
CN II - Sense of Vision
1/3 Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
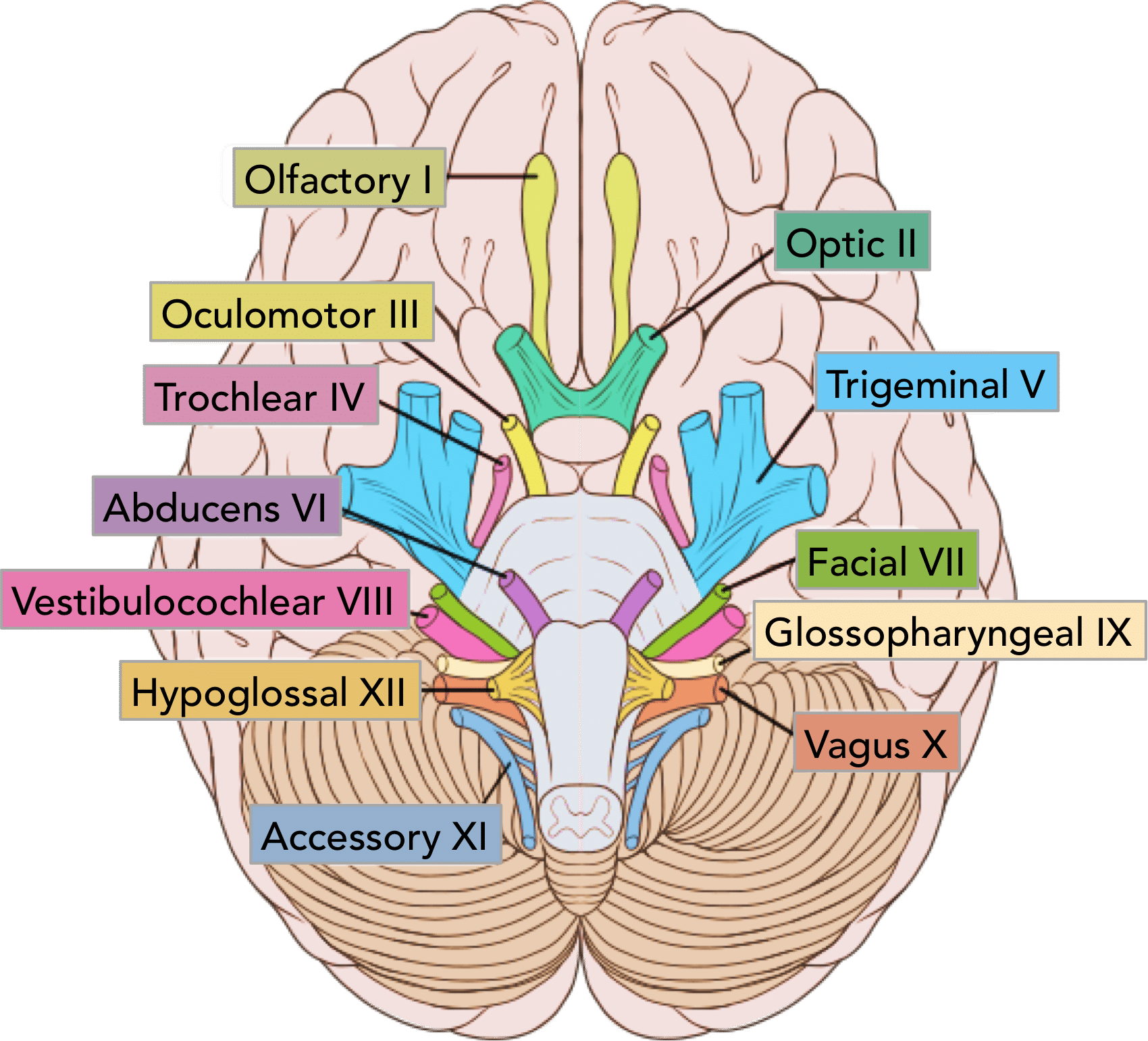
Oculomotor Nerve
CN III - Controls Most Eye Movement, Eyelids, and Pupil Diameter (Light Sensors)
1/5 Motor Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
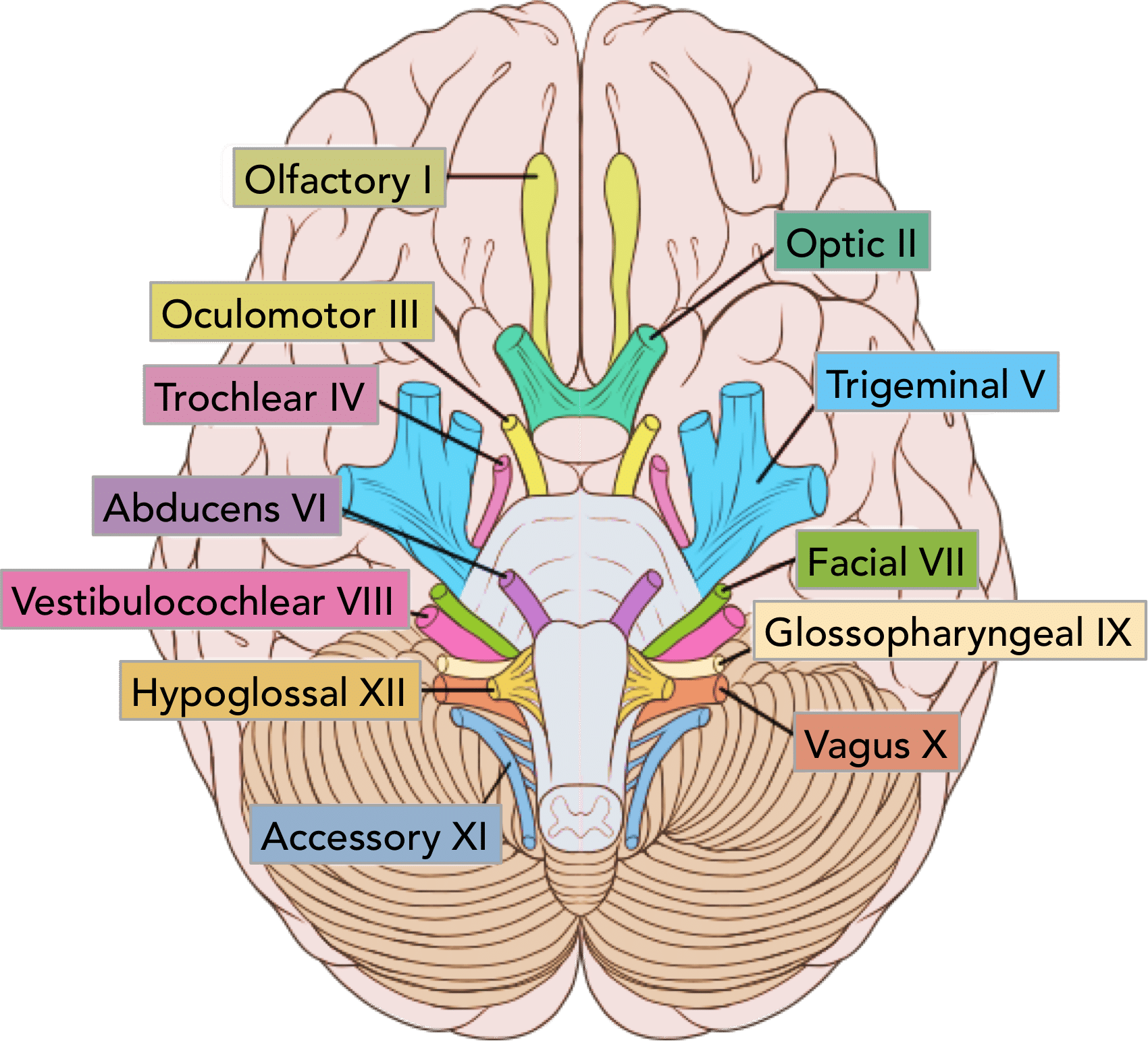
Trochlear Nerve
CN IV - Controls Superior Oblique Eye Muscles
1/5 Motor Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
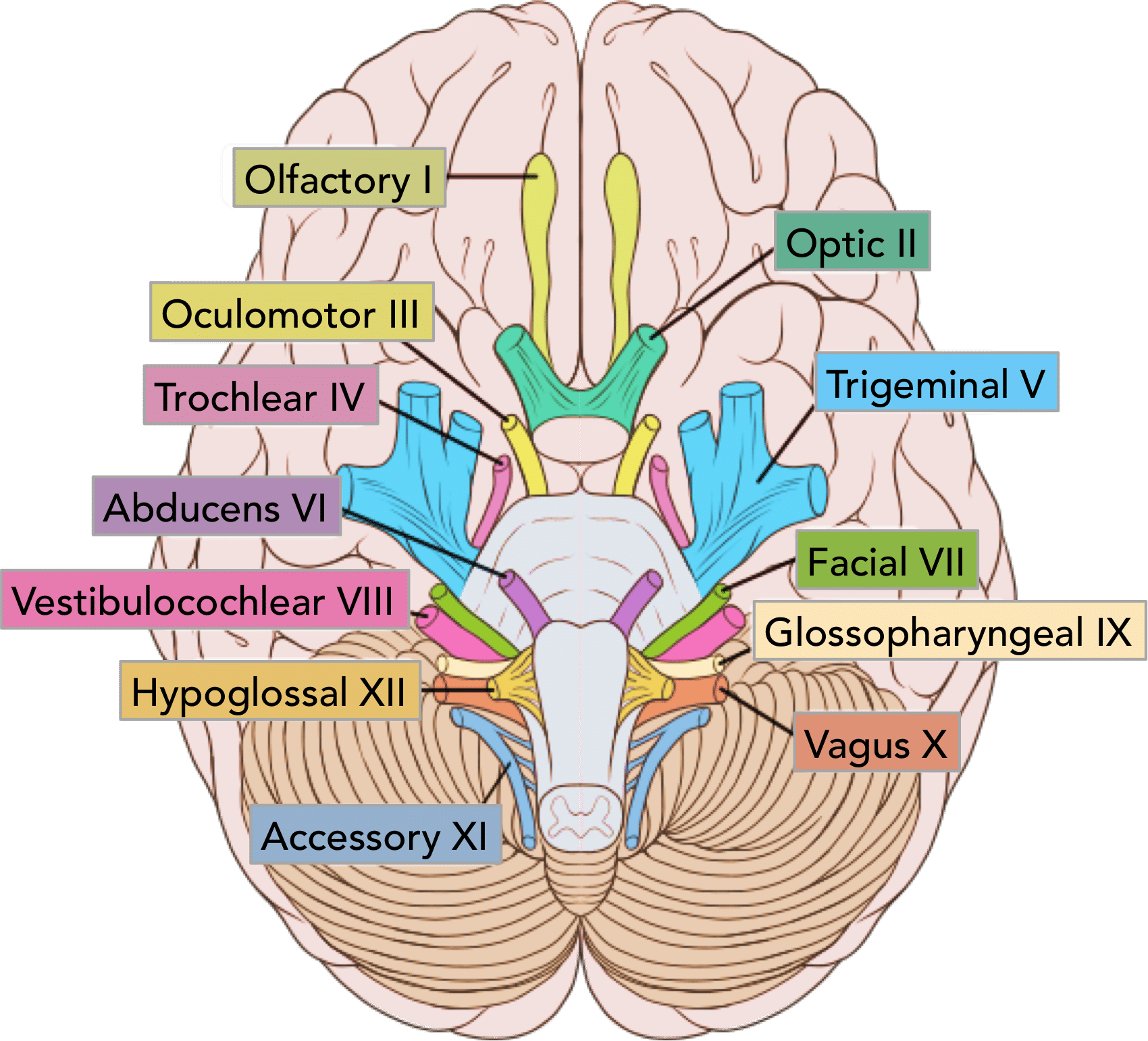
Trigeminal Nerve
CN V - Somatic Sensation from Face + Chewing
1/4 Motor + Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
Abducens Nerve
CN VI - Controls Lateral Eye Movement Only
1/5 Motor Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
Facial Nerve
CN VII - Controls Face Muscles, Provides Signals for Taste
1/4 Motor + Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
CN VIII - Senses Hearing, Balance and Equilibrium
1/3 Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
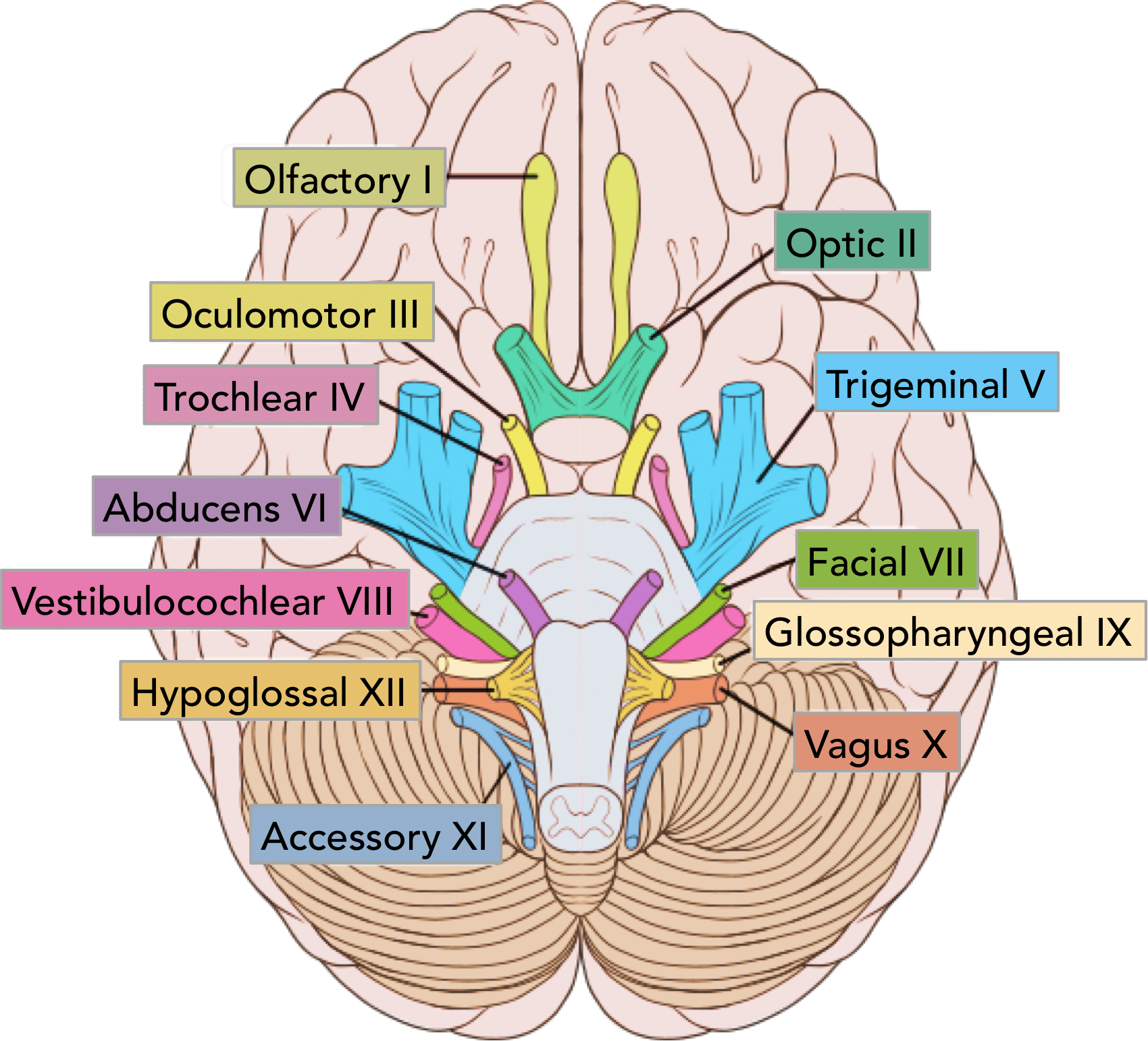
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Cn IX - Taste and Touch from Tongue, Controls Swallowing, Controls Big Salivary Gland
1/4 Motor + Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
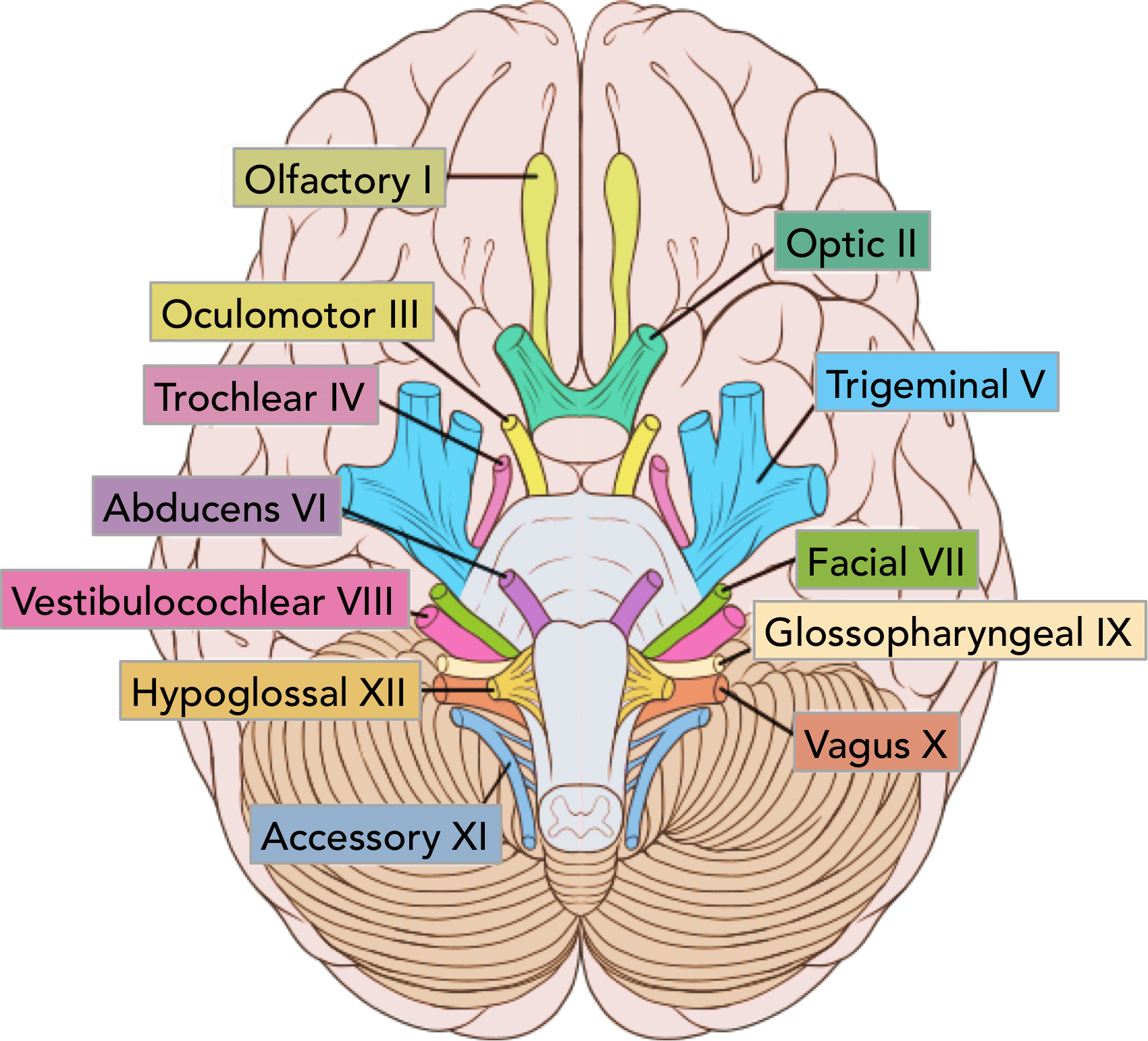
Vagus Nerve
CN X - Visceral (Autonomic) Sensation, Parasympathetic Nerve to Many Body Organs
1/4 Motor + Sensory Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
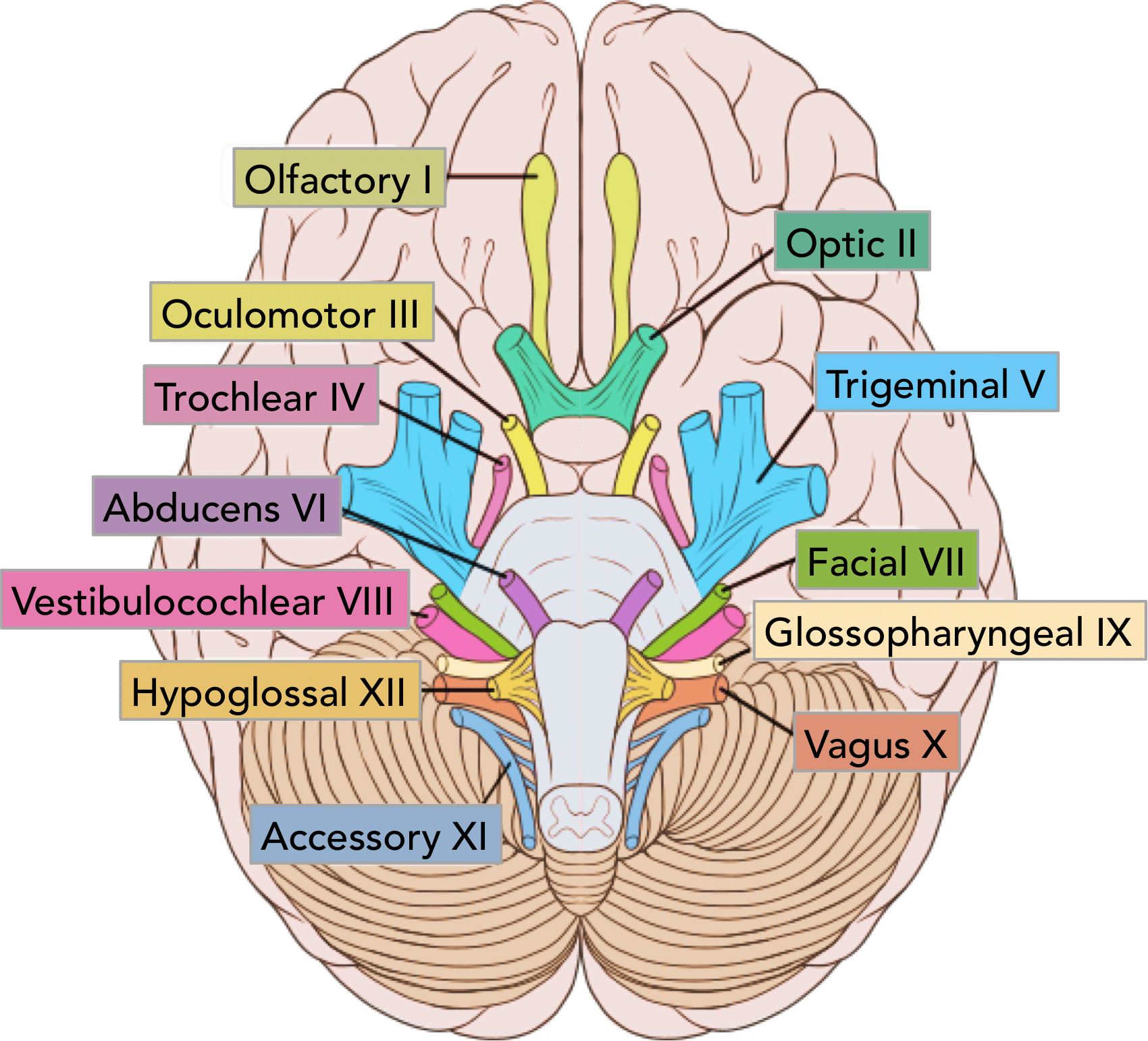
Accessory Nerve
CN XI - Controls Neck Muscles, Pharynx
1/5 Motor Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
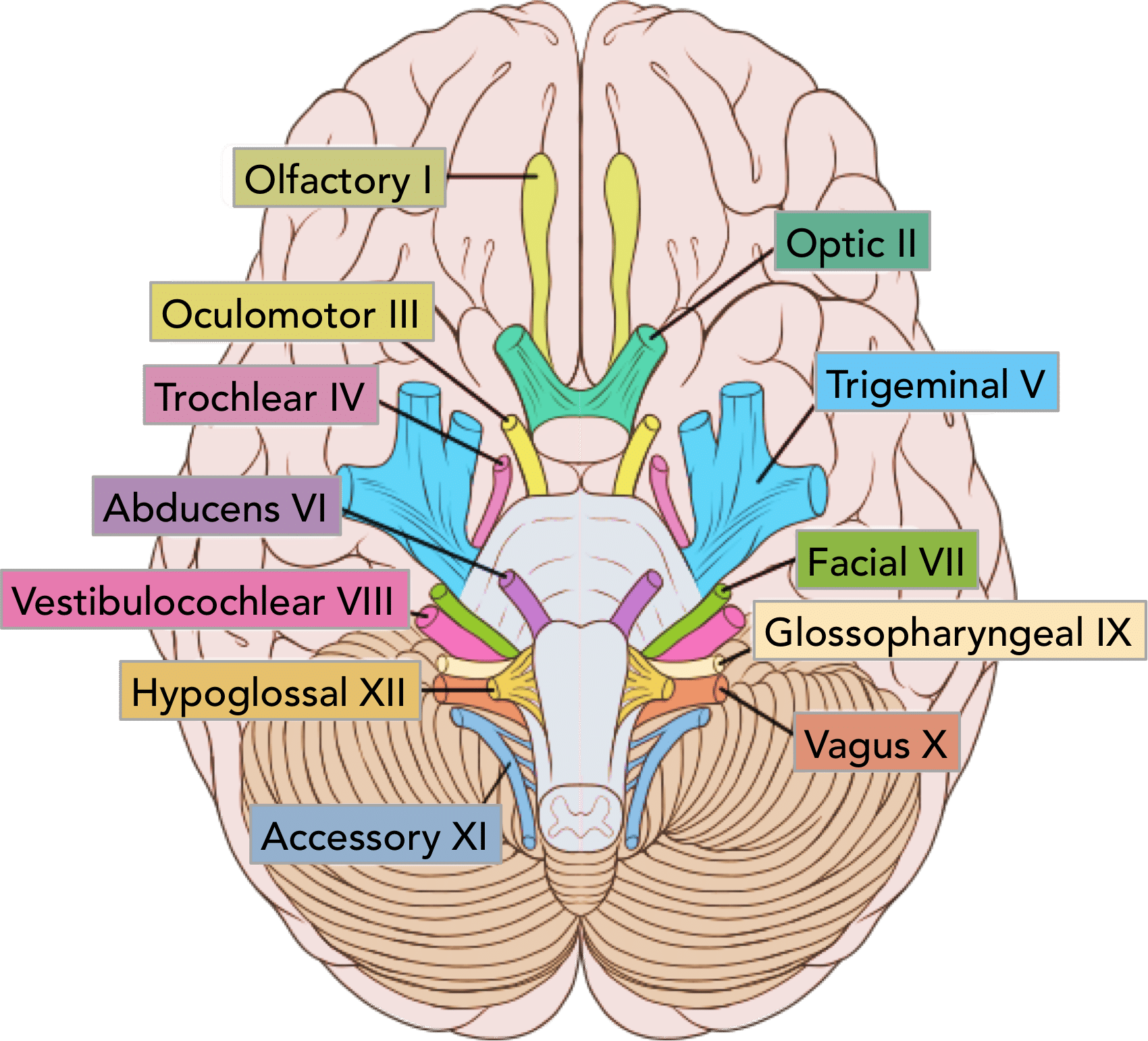
Hypoglossal Nerve
CN XII - Controls Tongue Muscles
1/5 Motor Nerves
On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Finn Vs German Viewed A Hat
Cervical Enlargement
Controls Nerves to Upper Limbs
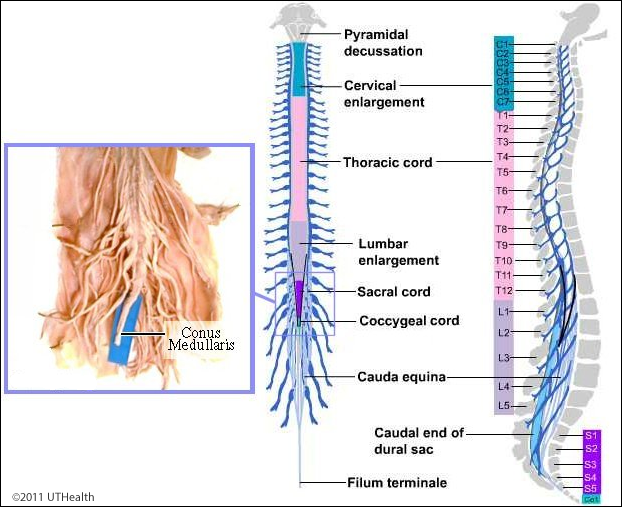
Lumbar Enlargement
Contains Nerves to Lower Limbs
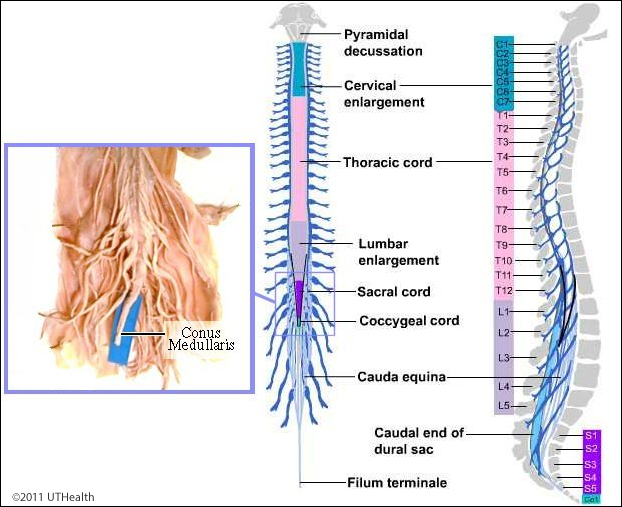
Spinal Nerves
31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves
8 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral
1 Coccygeal (Coccyx / Tailbone)
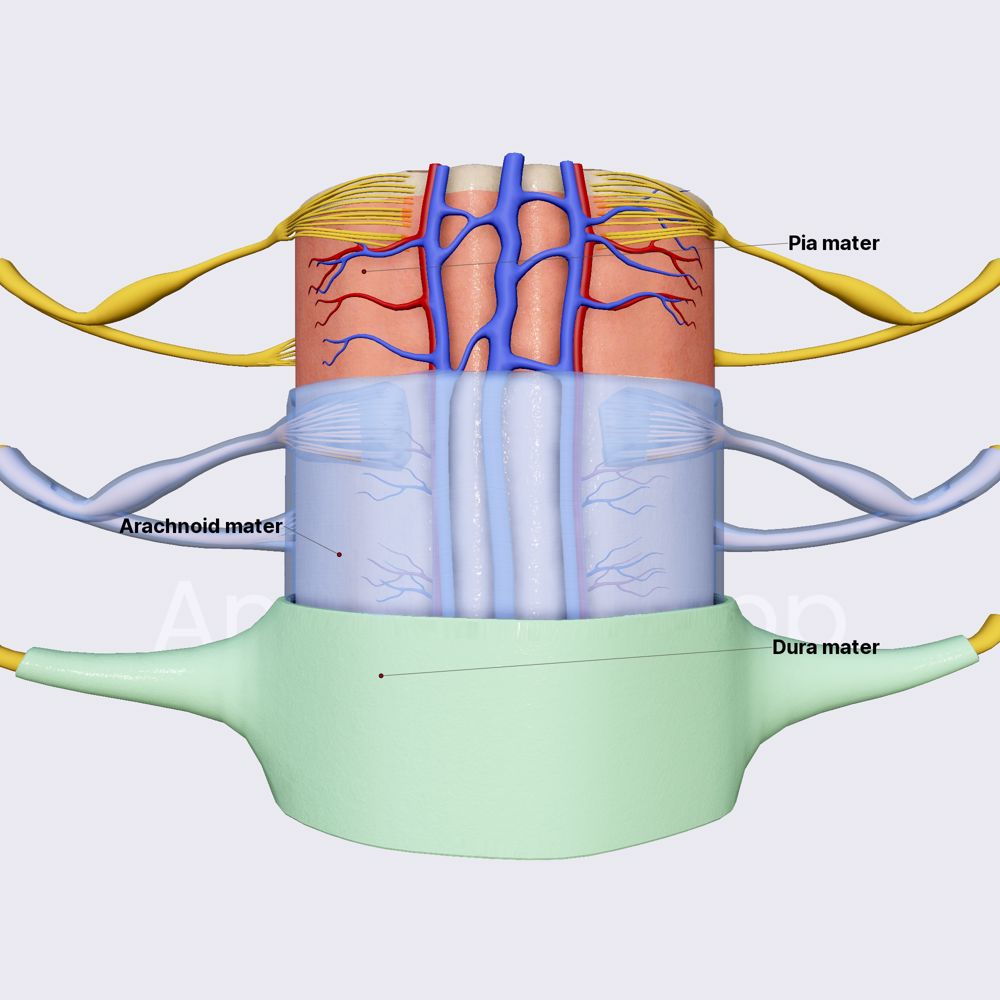
Spinal Cord Meninges
Pia Mater - Inner Most, Sticks to Spinal Cord
Arachnoid Mater - Middle, Web-Like Layer
Dura Mater - Outer Most, Tough Layer
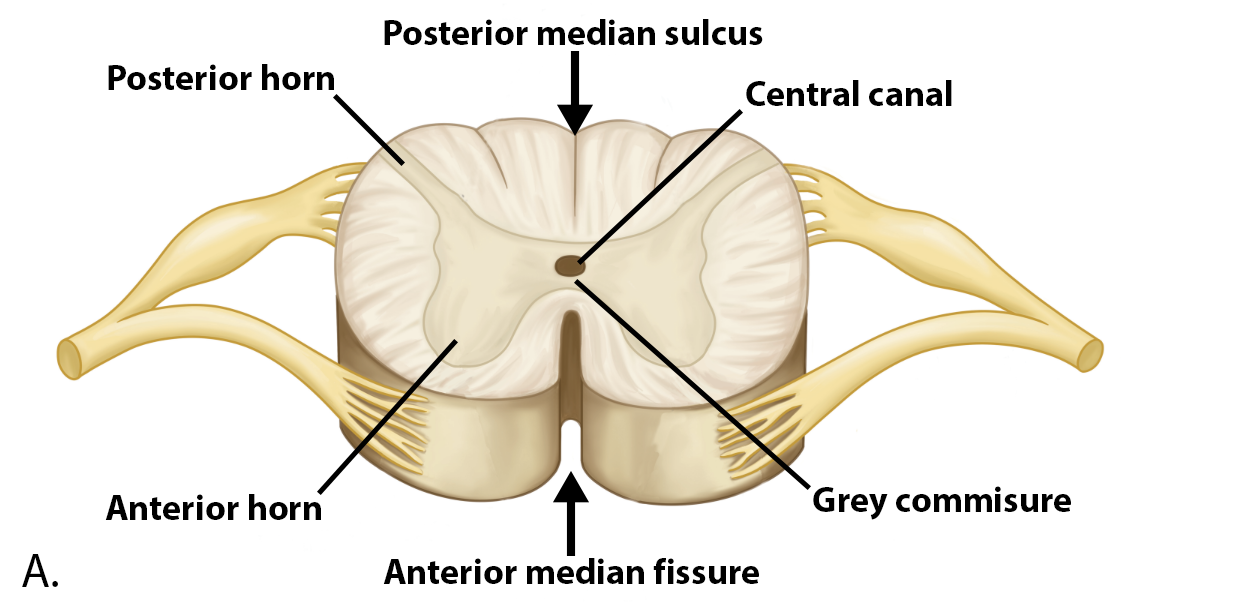
Gray Matter in Spinal Cord
Anterior Horns - Bottom Bump
Lateral Horns - Side Bump
Posterior Horns - Top Bump
Sensory Nuclei
Located in the Posterior Horn
Somatic Sensory - Receive Signals from Skin, Muscles, Joints
Visceral Sensory - Receive Signals from Blood Vessels / Visceral Organs
Motor Nuclei
Located in Anterior and Lateral Horns
Somatic Motor - ANTERIOR HORNS - Skeletal Muscle
Autonomic Motor - LATERAL HORNS - Smooth / Cardiac Muscle
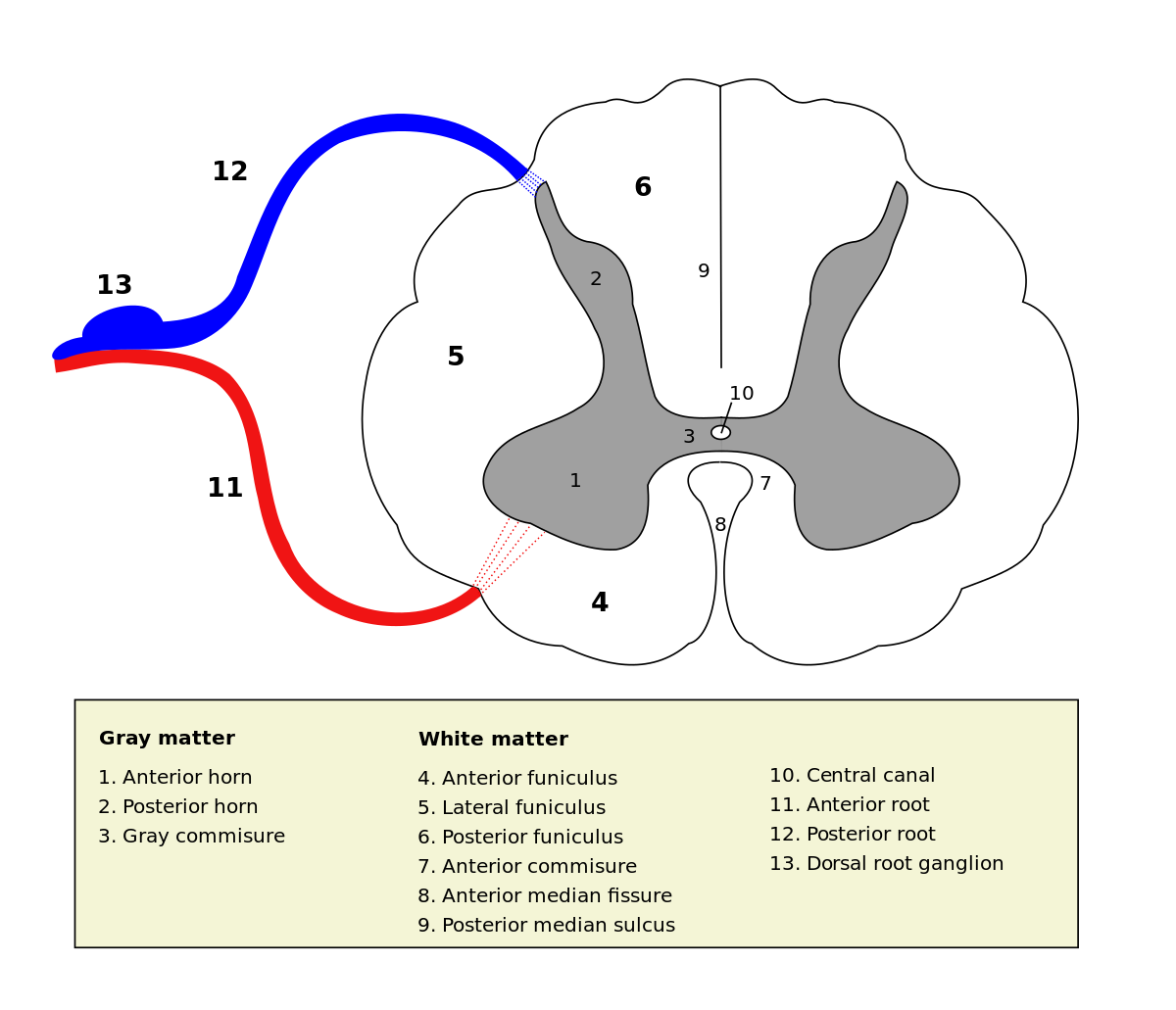
Spinal Cord White Matter
Funiculus = WHITE MATTER
(4) Anterior Funiculus - Sensory + Motor Tracts
(5) Lateral Funiculus - Sensory + Motor Tracts
(6) Posterior Funiculus - Sensory Tracts called Fasciculi
Sensory Pathways
Ascend to the Brain
Motor Pathways
Descend from the Brain
Controls Skeletal Muscles
Includes 2 Neurons
Upper Motor - Contacts Lower Motor Neuron
Lower Motor - Located in Cranial Nerve Nucleus or Anterior Horn of Spinal Cord
Sensory Pathway to Brain
PRIMARY - Cell Body in Posterior Root
SECONDARY - Is an Interneuron to Thalamus
TERTIARY - 3rd Order - Is an Interneuron to 1st Degree Sensory Cortex
Nerve Plexus
Network of Interweaving Anterior Rami
4 Main Plexuses Occurring Bilaterally
Cervical, Brachial, Lumbar, Sacral
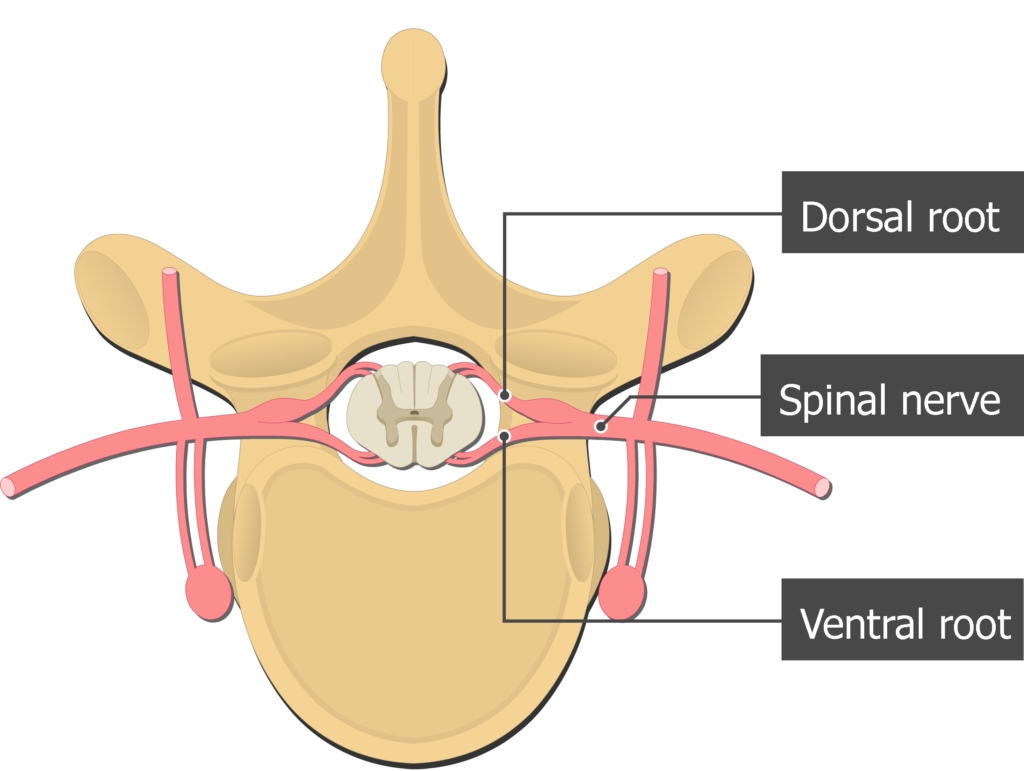
Spinal Nerves Split
(DORSAL ROOT) Posterior Ramus - Controls Muscles and Skin of Back - BACK ROOT
(VENTRAL ROOT) Anterior Ramus - Forms Nerve Plexuses - FRONT ROOT
Rami Communicants - Small Branches of Autonomic Fibers
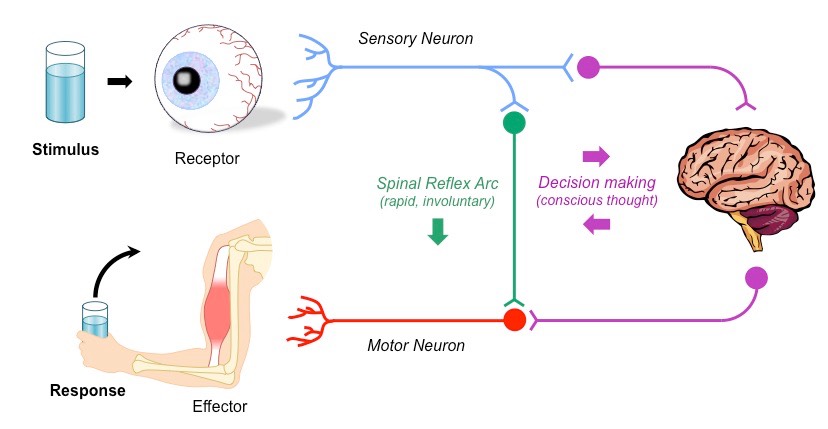
Reflex Arc
Stimulus
Afferent Pathway
Control Center
Efferent Pathway
Response
Classification of Spinal Reflexes
Is the Spinal Cord / Cranial the Control Center…
Somatic - Skeletal Muscle is the Effector
Visceral - Cardiac / Smooth Muscle is the Effector
honestly i really dont fucking know
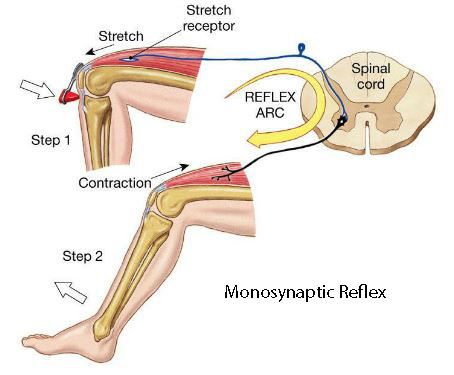
Monosynaptic Reflex - Stretch Reflex
Reflexive Contraction of a Muscle After it is Stretched
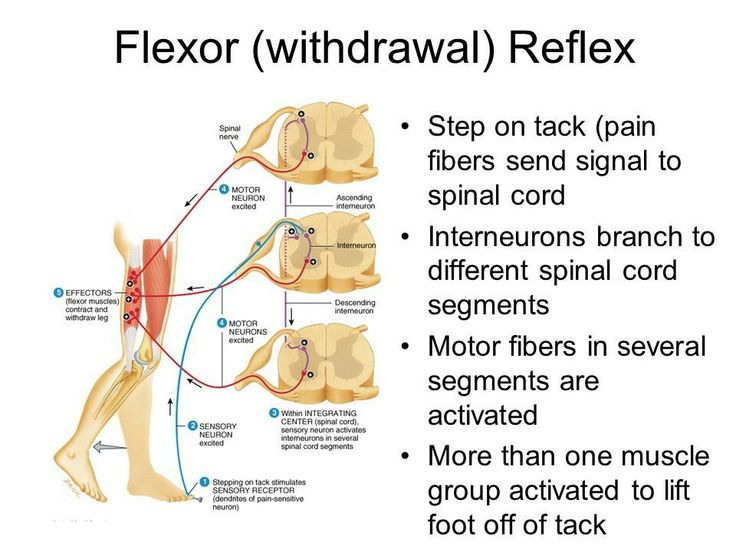
Polysynaptic Reflexes - Withdrawal Reflexes
Stimulus —> Nociceptor Sensory Neuron —> Spinal Cord —> Excites Interneurons
Interneurons —> Motor Neurons = Contraction on Muscles
Hypothalamus
Controls the ANS
Somatic Nervous System
1 Neuron Extends From CNS to Skeletal Muscles
Cell Bodies Located in Brainstem or Spinal Cord
Release ACh
Autonomic Nervous System
Visceral Motor System
Maintain Homeostasis
Preganglionic and Postganglionic Neurons
Sympathetic NS - Part of ANS
Fight-or-Flight
Preganglionic Axons are Short
Postganglionic Axons are Long
Mass Activation of Activity
Parasympathetic NS - Part of ANS
Rest-and-Digest
The 3 D’s : Digestion, Defecation and Diuresis (Digest, Shit and Piss)
Preganglionic Axons are Long
Postganglionic Axons are Short
Localized Activity
Cranial Nerves of Parasympathetic NS
CN III - Oculomotor
CN VII - Facial (Glands in Face)
CN IX - Glossopharyngeal (Big Salivary Gland in Mouth)
CN X - Vagus (All Internal Organs)
Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves
Communicating Rami
White Rami - Myelinated, PREGANGLIONIC Axons From T1 Vertebrae - L2 Vertebrae
Gray Rami - Unmyelinated, POSTGANGLIONIC Axons From Trunk to all Spinal Nerves
Preganglionic Sympathetic
Short - Myelinated
ACh
Nicotinic Receptors
Sympathetic Chain Ganglia
Preganglionic Parasympathetic
Long - Myelinated
ACh
Nicotinic Receptors
Terminal Ganglia, Intramural Ganglia
Postganglionic Sympathetic
Long
Norepinephrine
Adrenergic (Vasomotor)
Target Organs (Heart, Smooth Muscle)
Postganglionic Parasympathetic
Short
ACh
Muscarinic
Target Organs
Sympathetic Splanchnic Nerves
PREGANGLIONIC Axons do not Synapse in Sympathetic Trunk
Terminate in Prevertebral Ganglia
Sympathetic Pathways (Preganglionic, Myelinated, Lateral Horn of Gray Matter)
Spinal Nerve Pathway - Sweat Glands, Smooth Muscle of Erector Pilli?
Postganglionic Sympathetic Pathway - Internal Organs, Sweat Glands of Head/Neck
Splanchnic Nerve Pathway - Abdominal Visceral Organs
Adrenal Medulla Pathway - Kidneys - Release Norepinephrine
Autonomic Nervous System Neurotransmitters (15.5a)
ANS Uses ACh and Norepinephrine
Cells Releasing ACh = Cholinergic Neurons
Target Cells have Cholinergic Receptors
All Preganglionic and Postganglionic Neurons
Sympathetic Ganglionic Neurons - Sweat Glands
Cholinergic Receptors (15.5b)
Nicotinic Receptors
Found on all Ganglionic Neurons and Adrenal Medulla Cells
When ACh Binds, N. Receptor opens Cation Channel
Muscarinic Receptors
Found in Target Organs
All Receptors use Second Messengers
Adrenergic Receptors (15.5c)
Located in Target Organs
Alpha Receptors - Stimulated by Norepinephrine
Beta Receptors - Stimulated or Inhibited by Norepinephrine
Dual Innervation (15.6b)
Organ Receives Input from both the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions
Organ may receive Same or Different Stimulus
Same Stimulus : Male Reproductive System
Different Stimulus : Pupil Size, HR and GI Tract Movement
Sympathetic Innervation (15.6c)
Opposing Effects Without Dual Innervation (15.6)
Blood Vessels Constrict with Increased Sympathetic Activity
Blood Vessels Dilate with Decreased Sympathetic Activity
Sympathetic Innervation ONLY
Sweat Glands of Trunk of Body
Arrector Pili Muscles in Skin
Adrenal Medulla Cells (Kidneys)
Vasomotor Center
Sympathetic Nervous System Only
Vasoconstriction - Increased Stimulation of SNS
Vasodilation - Decreased Stimulation of SNS