Animal Kingdom - Chordata
Phylum Chordata:
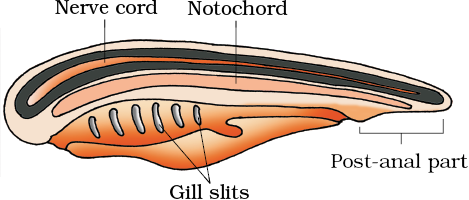
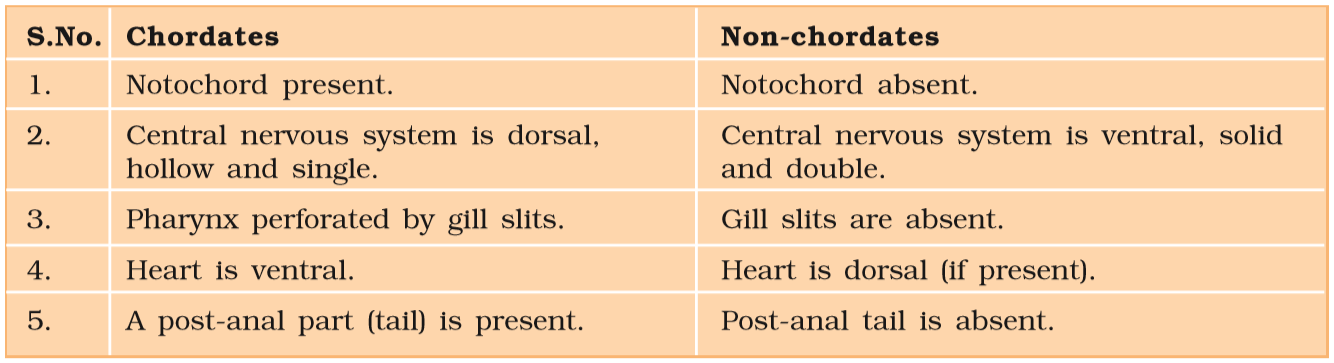
Animals belonging to phylum Chordata are fundamentally characterized by the presence of a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, and paired pharyngeal gill slits.
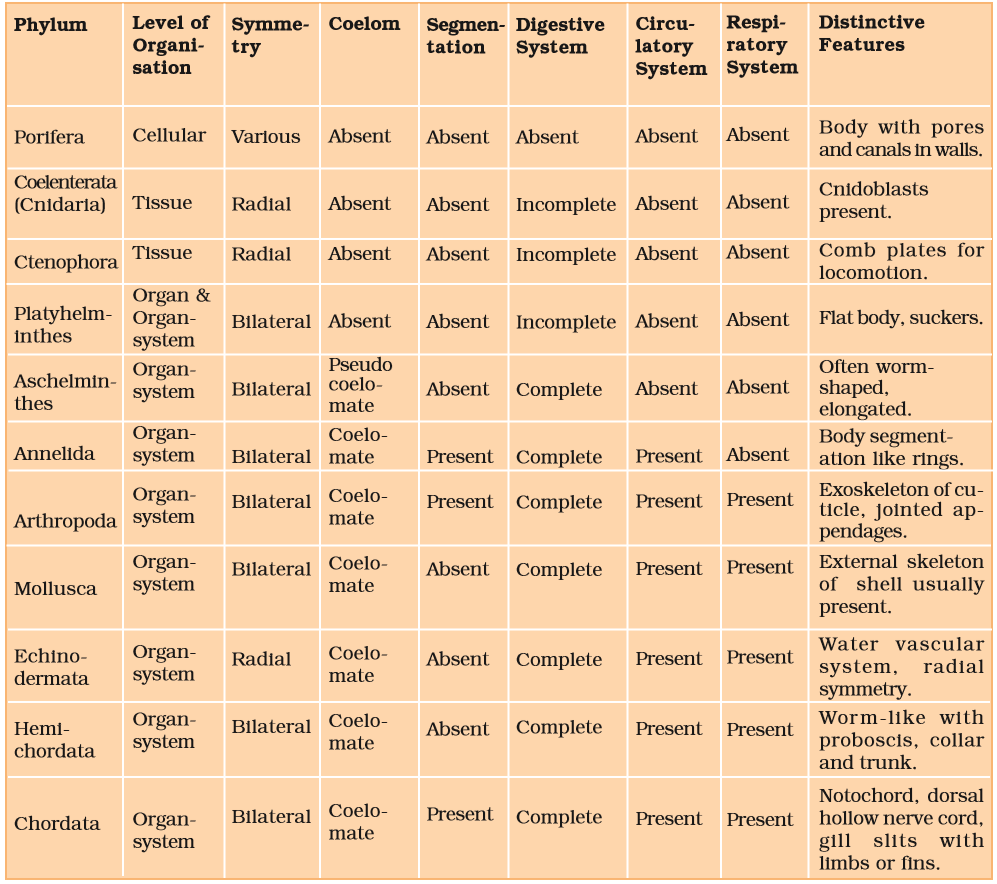
These are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate with the organ-system level of organization.
They possess a post-anal tail and a closed circulatory system.
Phylum Chordata is divided into three subphyla:
- Urochordata or Tunicata
- Cephalochordata
- Vertebrata
- Subphyla Urochordata and Cephalochordata are often referred to as protochordate and are exclusively marine.
- In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
- Examples: Urochordata – Ascidia, Salpa, Doliolum; Cephalochordata – Branchiostoma (Amphioxus or Lancelet).
- The members of subphylum Vertebrata possess notochord during the embryonic period.
- The notochord is replaced by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult.
- Thus all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
- Besides the basic chordate characteristics, vertebrates have a ventral muscular heart with two, three, or four chambers, kidneys for excretion and osmoregulation, and paired appendages which may be fins or limbs.
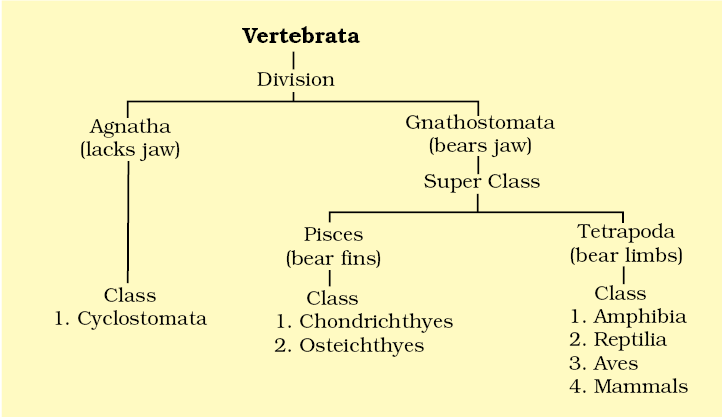
Class – Cyclostomata:
All living members of the class Cyclostomata are ectoparasites on some fishes.
- They have an elongated body bearing 6-15 pairs of gill slits for respiration. Cyclostomes have a sucking and circular mouth without jaws.
- Their body is devoid of scales and paired fins.
- The cranium and vertebral column are cartilaginous.
- Circulation is of a closed type.
- Cyclostomes are marine but migrate for spawning in fresh water.
- After spawning, within a few days, they die.
- Their larvae, after metamorphosis, return to the ocean.
Examples: Petromyzon (Lamprey) and Myxine (Hagfish).
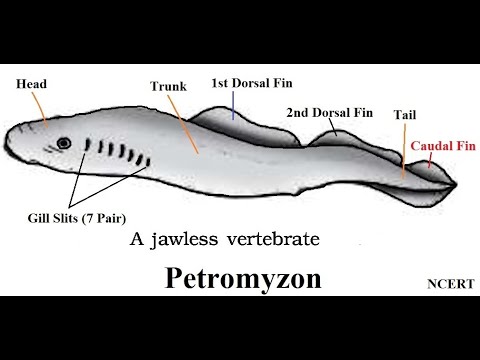
Class – Chondrichthyes:
They are marine animals with streamlined bodies and have cartilaginous endoskeletons.
- The mouth is located ventrally.
- The notochord is persistent throughout life.
- Gill slits are separate and without operculum (gill cover).
- The skin is tough, containing minute placoid scales.
- Teeth are modified placoid scales which are backwardly directed.
- Their jaws are very powerful.
- These animals are predaceous.
- Due to the absence of an air bladder, they have to swim constantly to avoid sinking.
The heart is two-chambered (one auricle and one ventricle).
- Some of them have electric organs (e.g., Torpedo) and some possess poison sting (e.g., Trygon).
- They are cold-blooded (poikilothermous) animals, i.e., they lack the capacity to regulate their body temperature.
- Sexes are separate.
- In males pelvic fins bear claspers.
- They have internal fertilization and many of them are viviparous.
Examples: Scoliodon (Dog fish), Pristis (Saw fish), Carcharodon (Great white shark), and Trygon (Sting ray).
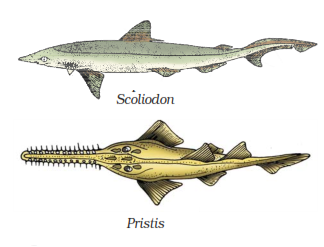
Class – Osteichthyes:
It includes both marine and freshwater fishes with a bony endoskeleton.
- Their body is streamlined.
- The mouth is mostly terminal.
- They have four pairs of gills which are covered by an operculum on each side.
- Skin is covered with cycloid/ctenoid scales.
- The air bladder is present which regulates buoyancy.
- The heart is two-chambered (one auricle and one ventricle).
- They are cold-blooded animals.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilization is usually external.
- They are mostly oviparous and development is direct.
Examples: Marine – Exocoetus (Flying fish), Hippocampus (Sea horse); Freshwater – Labeo (Rohu), Catla (Katla), Clarias (Magur); Aquarium – Betta (Fighting fish), Pterophyllum (Angelfish).
Class – Amphibia:
Amphibians can live in aquatic as well as terrestrial habitats.
- Most of them have two pairs of limbs.
- The body is divisible into the head and trunk.
- The tail may be present in some.
- The amphibian skin is moist (without scales).
- The eyes have eyelids.
- A tympanum represents the ear.
- The alimentary canal, urinary and reproductive tracts open into a common chamber called cloaca which opens to the exterior.
- Respiration is by the gills, lungs, and skin.
- The heart is three-chambered (two auricles and one ventricle).
- These are cold-blooded animals.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilisation is external.
- They are oviparous and development is indirect.
Examples: Bufo (Toad), Rana (Frog), Hyla (Tree frog), Salamandra (Salamander), Ichthyophis (Limbless amphibian).

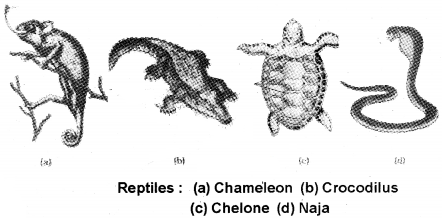
Class – Reptilia
The class name refers to their creeping or crawling mode of locomotion.
- They are mostly terrestrial animals and their body is covered by dry and cornified skin, epidermal scales, or scutes.
- They do not have external ear openings.
- Tympanum represents ear.
- Limbs, when present, are two pairs.
- The heart is usually three-chambered, but four-chambered in crocodiles.
- Reptiles are poikilotherms.
- Snakes and lizards shed their scales as skin cast.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilisation is internal.
- They are oviparous and development is direct.
Examples: Chelone (Turtle), Testudo (Tortoise), Chameleon (Tree lizard), Calotes (Garden lizard), Crocodilus (Crocodile), Alligator (Alligator). Hemidactylus (Wall lizard), Poisonous snakes – Naja (Cobra), Bangarus (Krait), Vipera (Viper).
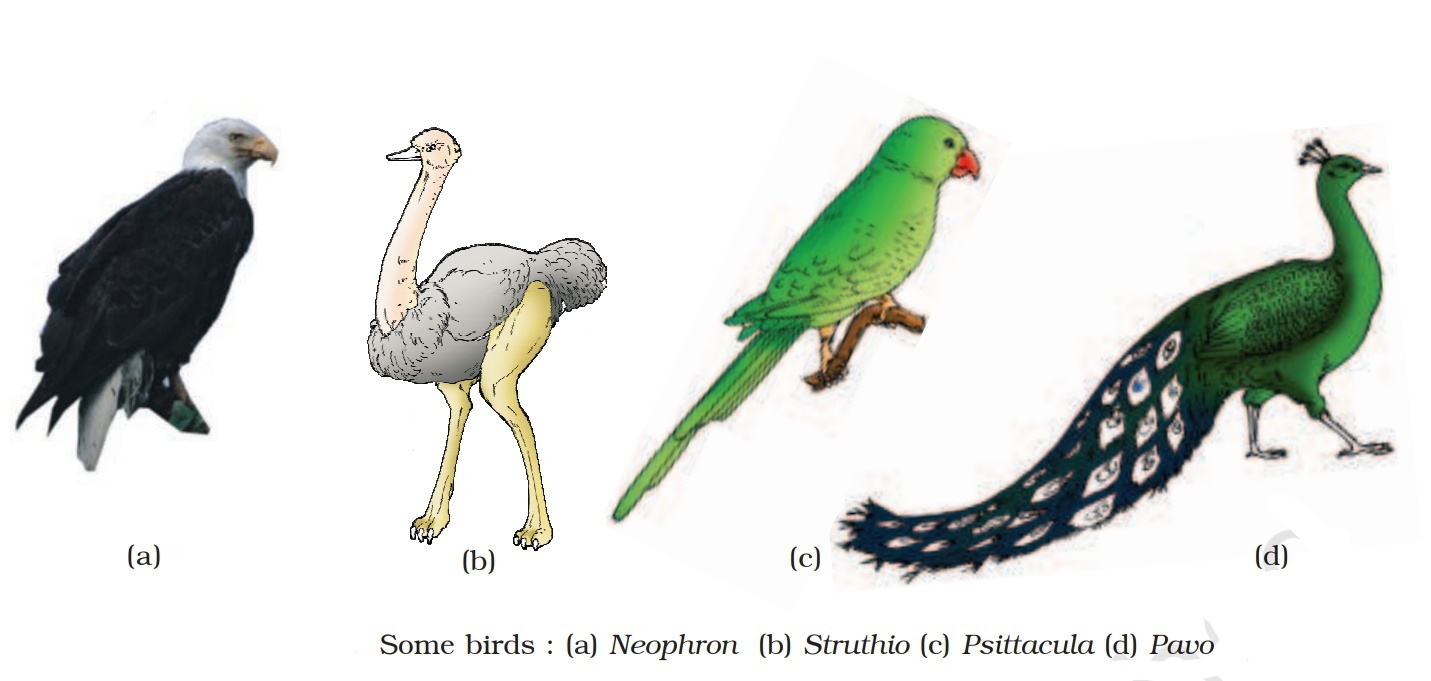
Class – Aves:
The characteristic features of Aves (birds) are the presence of feathers and most of them can fly except flightless birds (e.g., Ostrich).
- They possess beaks.
- The forelimbs are modified into wings.
- The hind limbs generally have scales and are modified for walking, swimming, or clasping the tree branches.
- Skin is dry without glands except for the oil gland at the base of the tail.
- Endoskeleton is fully ossified (bony) and the long bones are hollow with air cavities (pneumatic).
- The digestive tract of birds has additional chambers, the crop, and the gizzard.
- The heart is completely four-chambered.
- They are warm-blooded (homoiothermal) animals, i.e., they are able to maintain a constant body temperature.
- Respiration is by the lungs.
- Air sacs connected to the lungs supplement respiration.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilisation is internal.
- They are oviparous and development is direct.
Examples: Corvus (Crow), Columba (Pigeon), Psittacula (Parrot), Struthio (Ostrich), Pavo (Peacock), Aptenodytes (Penguin), Neophron (Vulture).
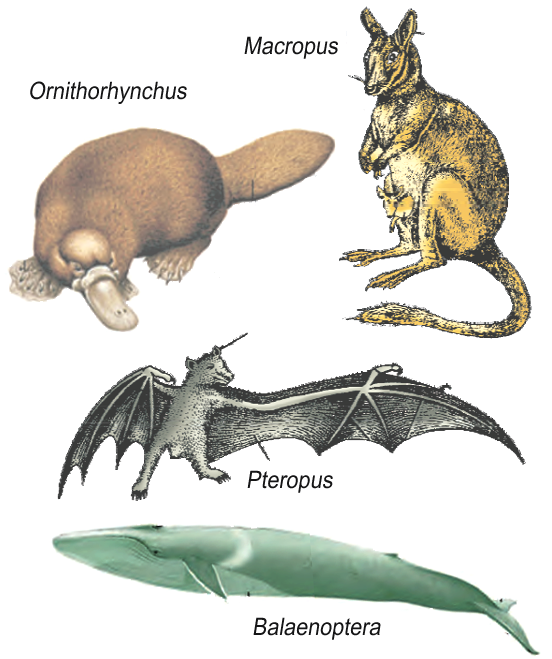
Class – Mammalia:
They are found in a variety of habitats – polar ice caps, deserts, mountains, forests, grasslands, and dark caves.
- Some of them have adapted to fly or live in water.
- The most unique mammalian characteristic is the presence of milk-producing glands (mammary glands) by which the young ones are nourished.
- They have two pairs of limbs, adapted for walking, running, climbing, burrowing, swimming, or flying.
- The skin of mammals is unique in possessing hair.
- External ears or pinnae are present.
- Different types of teeth are present in the jaw.
- The heart is four-chambered.
- They are homoiothermal.
- Respiration is by the lungs.
- Sexes are separate and fertilization is internal.
- They are viviparous with few exceptions and development is direct.
Examples: Oviparous-Ornithorhynchus (Platypus); Viviparous - Macropus (Kangaroo), Pteropus (Flying fox), Camelus (Camel), Macaca (Monkey), Rattus (Rat), Canis (Dog), Felis (Cat), Elephas (Elephant), Equus (Horse), Delphinus (Common dolphin), Balaenoptera (Blue whale), Panthera tigris (Tiger), Panthera leo (Lion).