Chapter 2 - Volcanoes
1/23
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Volcanologist - definition
Scientists that studies volcanoes

Mid ocean ridge - definition
When plates separate, lava pours out and builds up along cracks on earth’s surface forming a ridge
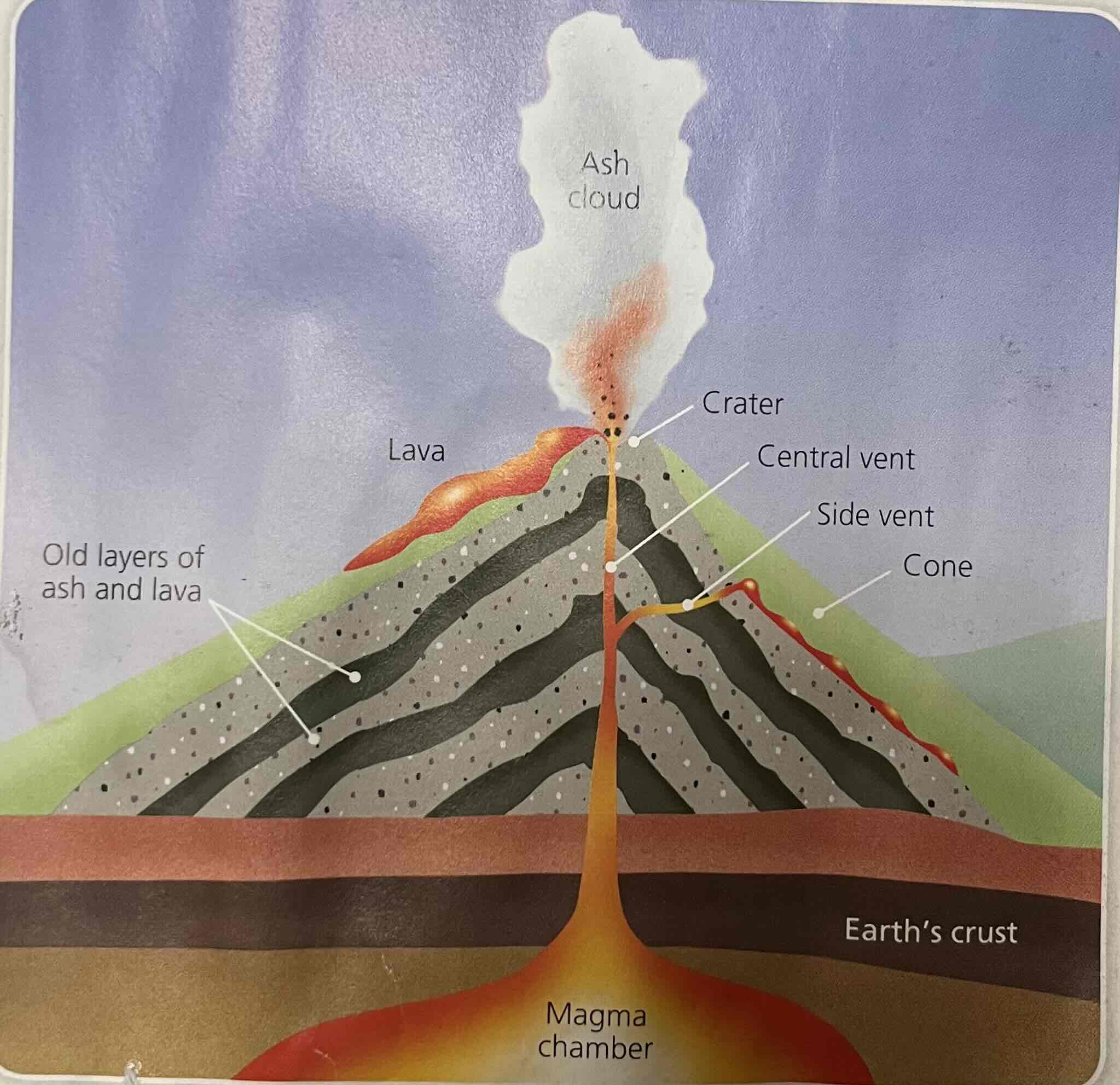
Vent - definition
Small hole lava violently forces through, forming volcanic mountain
Lava - definition
Magma reaching the surface and cools and hardens
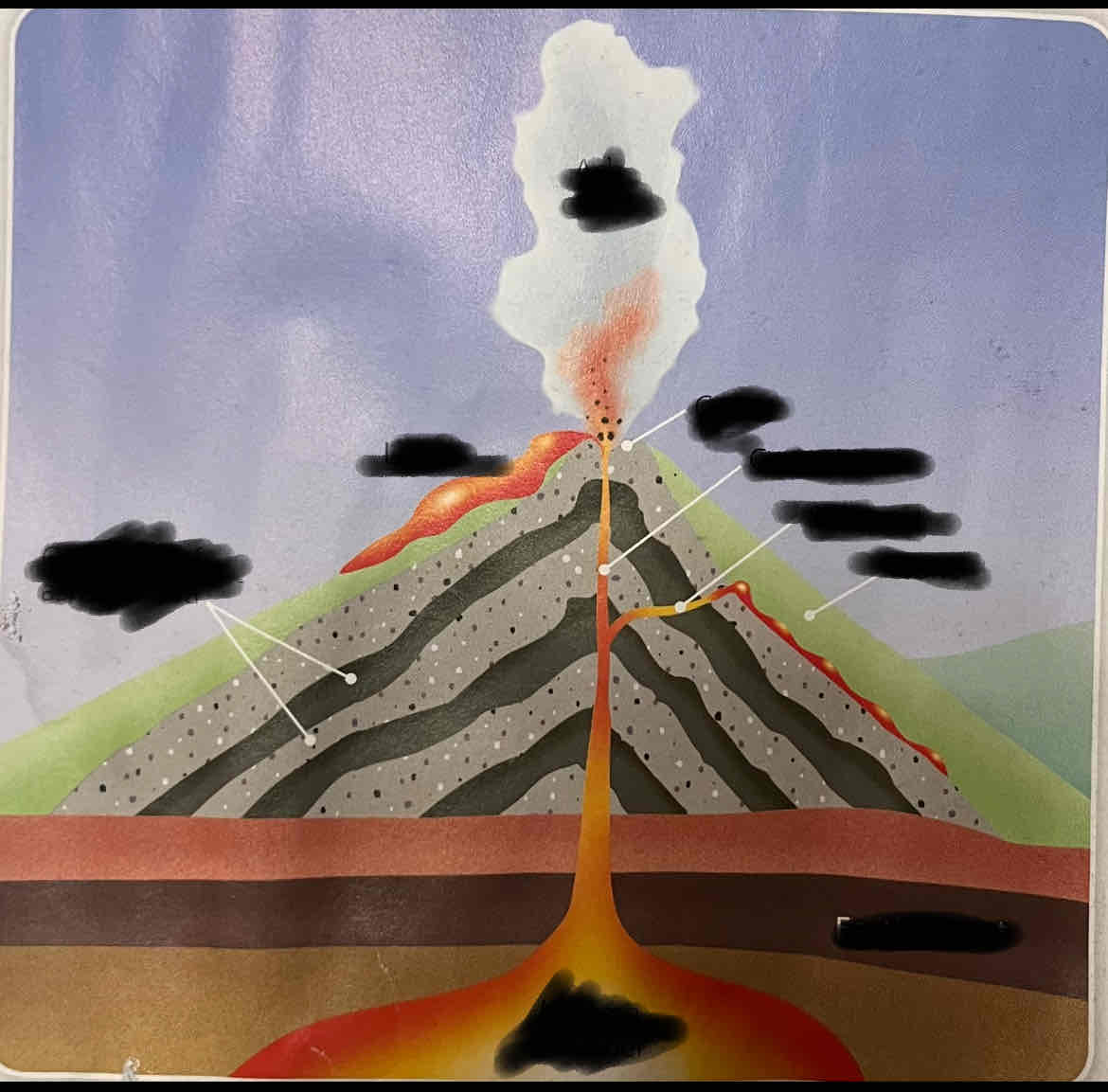
How are volcanic mountains formed
2 plates separate or collide, magma rises from mantle to fill space that opens up in crust (vent). Causes eruption that can be violent due to great pressure of magma in mantle
Magma wells up from magma chamber and reaches surface. Cools and hardens to form lava
After many eruptions, layers of ash and lava build up and forms vent. Cone shaped mountain forms with crater on top where lava flows
Active volcano - time period
Eruption within last 10000 years
Active volcano - example
Mount St Helens, North America
Dormant volcano - time period
Not erupted within 10000 but expected to erupt again
Dormant volcano - example
Kilimanjaro - Tanzania
Extinct - time period
Never expected to erupt again
Extinct volcano - example
Mount Kenya, Kenya
Mid ocean ridge- example
Mid Atlantic ridge - Eurasian and North American plates separating
How are volcanic island formed
Submarine volcanoes and mountains build up and rise above sea level
Volcanic island - example
Iceland
Pacific Ring of Fire - definition
Horseshoe shaped area containing many plate boundaries. Contains 75% active volcanoes, 90% earthquakes occur
Date - E15
14 April 2010
E15 eruption description
Violent and explosive. Very little lava. Huge amounts ash sent kilometers high. Winds blew ash south eastwards towards Europe
E15 - VEI scale
3-4
VEI - meaning
Volcanic explosivity index, measures eruptions from 0-8 (weakest-strongest)
E15 - positive social impacts
Reduce unemployment: tourism because eruption created jobs
Increased tourism and unemployment: promo campaign led to big increase foreign tourists. Less than 500000 in 2008. 1.8 million in 2016
E15 - Positive economic impacts
Generated income for local community: E15 visitor centre built as tourist attraction
Fertile soil: Ash and lava rich in nutrients, soil in volcanic areas fertile and good for agriculture
E15 - negative social impacts
Contaminated water supply: Ash polluted local water. Animals couldn’t drink from streams
Evacuation of locals: 500 farmers and locals had to leave home. Wore masks to avoid choking on ash
E15 - negative economic impacts
Cancelled flights: 100000 flights to and from Europe cancelled because poor visibility and fear tiny ash would clog airplane engines. Cost airlines and businesses €145 million day
Loss of earnings: Counties, e.g. Kenya, that sell perishables affected. Flight ban meant produce transported quickly by plane not sold. Million flower stalks unsold in first 2 days