BIO 101: Midterm Lab Practical (Labs 1 - 8)
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
observation
Information obtained through the senses.
inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning
hypothesis
a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect
qualitative data
descriptive data using words
quantitative data
numerical data
results
data and observations gathered from the experiment
conclusion
A summary based on evidence or facts
experimental/independent variable
part of the experiment that the scientist changes or manipulates
responding/dependent variable
the part of the experiment that is measured as data
constants (aka controlled variables)
factors that do not change in the experiment
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
negative control
Control group where conditions produce a negative outcome
positive control
Group expected to have a positive result
repeated measures
Experiments in which a subject is exposed to more than one level of an experimental treatment.
length
distance between two points; measured in meters (m)
mass
the amount of matter in an object; measured in grams (g)
volume
The amount of space an object takes up; measured in liters (L)
temperature
A measure of how hot or cold something is; measured in Celcius (C) or Kelvin (K)
kilo
10^3
hecta
10^2
deca
10^1
deci
10^-1
centi
10^-2
milli
10^-3
meniscus
The curved upper surface of a liquid in a tube
beaker

dropper pipette
volumetric pipette
pipette pump

micropipette
Erlenmeyer flask

safety goggles

graduated cylinder

test tube

test tube rack

test tube holder
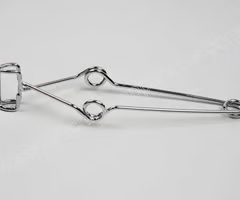
forceps

triple beam balance

thermometer

metric ruler

stage
platform which supports the specimen being viewed

arm
curve or slanted part which is held while carrying the microscope
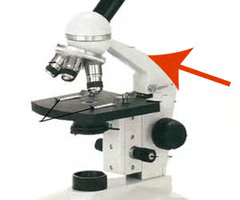
ocular lens (eyepiece)
the lens that you look through

objective lenses
the lenses that are used to magnify the object

coarse adjustment knob
big knob moving the stage up and down

fine adjustment knob
small knob moving the stage up and down

base (foot)
the bottom of the microscope, used for support

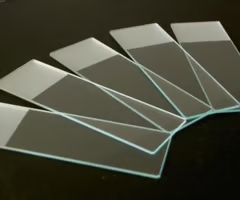
slide
rectangular glass plate on which the specimen is mounted
total magnification
The power of a microscope, found by multiplying the power of the (eyepiece) by the power of the objective lens.

specimen
sample that is prepared to be viewed

Compound microscope
A microscope with two or more lenses.

field-of-view
When you look down a microscope, the circle that you see is called ''
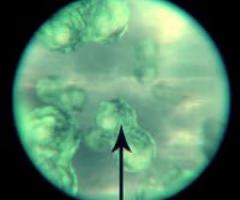
400X
The total magnification of a 10X eyepiece lens coupled with the high power 40X objective lens
condenser
focuses light through the specimen
iris diaphragm
controls the amount of light passing through the specimen

nosepiece
Holds the objectives and can be rotated to change the magnification
light source
provides light

mechanical stage
holds the slide in position for viewing and has two adjustable knobs that control the precise movement of the slide
how to carry a microscope
one hand on the arm and one hand on the base
field of view
The area visible through the microscope eyepiece
how to clean and store a microscope
use a lens wipe (not a tissue/towel/sleeve etc); unplug it, rotate to the scanning objective lens, put the stage in its lowest position, cover it with a dust cover, place it in the cabinet
wet mount
a glass slide holding a specimen suspended in a drop of liquid (as water) for microscopic examination
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14
pH
measure of hydrogen ion concentration
solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution; pH below 7
base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution; pH above 7
neutral
hydrogen ion concentration equals hydroxide ion concentration; pH of 7
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
buffer
weak acid or base that can react with strong acids or bases to help prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH
antacid
a weak base that neutralizes stomach acid
litmus paper
an indicator paper that turns red in an acid and blue in a base
protein
a macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; it folds into a 3D shape that allows it to perform its function; most diverse macromolecule in terms of function
carbohydrates
a macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; provides substrates for cellular respiration and therefore provides energy to the cell; also has some structural function;
lipids
a macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; these are insoluble in water and are used for energy and building cell structures like the plasma membrane
nucleic acids
macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus; includes DNA, RNA, and ATP
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules like glucose and fructose
disaccharide
two monosaccharides linked together, like sucrose which is made of a glucose and a fructose
polysaccharide
multiple monosaccharides linked together, such as cellulose, starch, and glycogen
amino acid
Building blocks of protein
polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
triglyceride
a lipid building block made of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule
dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction
a chemical reaction in which two or more monomers combine resulting in the loss of a water molecule
hydrolysis reaction
A chemical reaction that breaks apart a larger polymer by adding a molecule of water
benedict's reagent
detects presence of reducing sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides); postive results = green (low amount of sugar) and yellow/orange/red (higher amounts of sugar); negative results = blue
iodine test
detects the presence of starch (a polysaccharide); postive result = blue/black; negative result = yellowish brown
biuret test
detects the presence of proteins; positive result = violet; negative result = blue
emulsification test
detects the presence of lipids; positive result = droplets suspended in water; negative result = substance dissolves in water
emulsifer
molecules that contain a polar and non-polar end, like Tween, bile salts, and soaps
paper test
detects the presence of lipids; postive result = paper turns a different color; negative result = substance evaporates and paper stays the same color
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
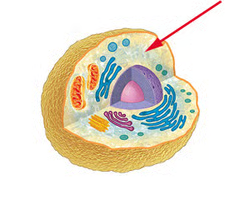
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
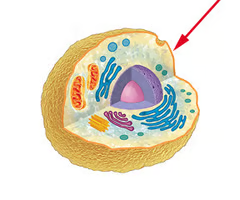
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
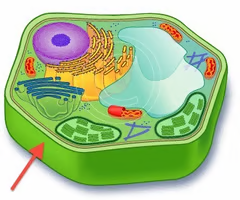
glycocalyx
The external surface of a plasma membrane that is important for cell-to-cell communication and identification
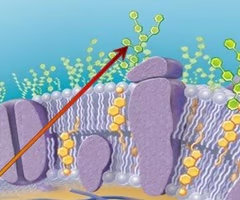
capsule
when the glycocalyx is bound more tightly to the cell and is denser and thicker