Senses - Pain
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Pain
unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage (IASP)
Nociception
the reception of sensations carried by nociceptors (free nerve endings) in response to tissue damage
located in periphery
carry signals from noxious stimuli
A-delta Group
group of myelinated axons conduct 5-30 m/s speed
C Group
unmyelinated axons conduct less than 2 m/s speed
First Pain
sharp
carried by A-delta fibers
Second Pain
dull/burning
carried by C fibers
Pain Perception - Process
inflammation
dorsal horn
medulla
descending connections
pain signals in the brain
Pain Perception - Inflammation (1)
injury sets a release of various chemicals that alert the nerve impulses that are processed as pain
histamine released to site to cause swelling
Pain Perception - Dorsal Horn (2)
pain signal enters dorsal horn of the spinal cord and decussates to the opposite side of the spinal cord
Pain Perception - Medulla (3)
pain signals pass through the medulla which in turn activates the ANS to increase BP, HR, RR
Pain Perception - Descending Connections (4)
fibers descending from pain regions of the cortex intercept ascending pain information and modify signals
endorphins are released from the thalamus to decrease pain felt
Pain Perception - Pain Signals (5)
signals are transmitted to the various areas of the cerebral cortex which then interprets signals
Pain Pathways
nociceptor → spinal cord (decussates) → brain stem (medulla) → thalamus → cerebral cortex
Brown Sequard
pattern of disassociated sensory loss after a spinal cord hemi section
motor weakness on same side as lesion
decreased pain and temp on opposite side of lesion
Stages of Pain (4)
transduction
transmission
perception
modulation
Pain Stages - Transduction (1)
when free endings of nociceptors in the periphery become stimulated
Pain Stages - Transmission (2)
conduction of pain signals along different pathways in the periphery to the spinal cord and brain
A-delta fibers and C fibers involved
Pain Stages - Perception (3)
how the cortex attaches meaning to or interrupts pain signals
involves threshold and pain tolerance
Pain Stages - Modulation
modification of pain signals by different CNS and PNC centers along the pain pathway
pain can be modified at the level of the peripheral nociceptor, the SC, the brainstem, and the cortex
Peripheral Nociceptive
injury to musculoskeletal tissues
mediated by inflammatory response
Peripheral Neurogenic
injury within the PNS
mediated by inflammatory response
Not Mediated by Inflammatory Response (2)
central pain lesion / CNS dysfunction
presence of abnormal pain states
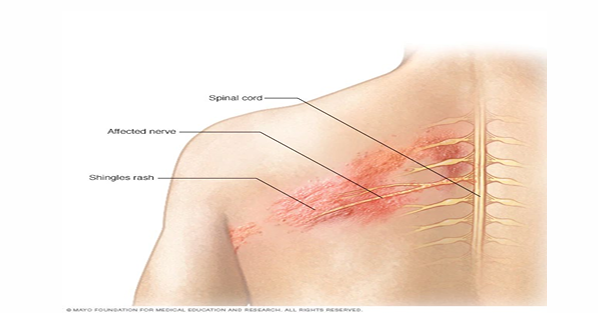
Shingles
infection of dorsal root ganglion or cranial nerve ganglion with varicella-zoster virus
affects one dermatome usually
virus irritates and inflames nerve, causing pain
skin lesions around affected area
Shingles - Treatment
antiviral drugs
NSADIS
neuropathic pain meds
alternative treatments
Pain Threshold
amount of pain stimulation required before pain is received
Pain Tolerance
the amount of pain a person can tolerate before seeking healthcare intervention
Somatic Pain
occurs from the body (skin, muscle, bones) can be divided into superficial or deep pain
Visceral Pain
pain from the viscera (internal organs, glands, smooth muscles) and is not localized
Referred Pain - Definition/Examples
pain that is perceived to originate from one body region, but truly originates from another
HA
gallbladder
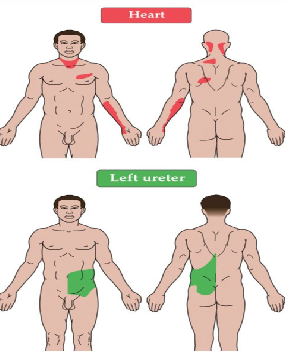
Referred Pain - Causes
dermatomal distribution could have the same level representation for dermatome
OR
dorsal root neurons have 2 peripheral axons: 1 for innervating skin and skeletal muscle, and 1 for innervating the viscera
Acute Pain
less than 30 days
resolves quickly
Chronic Pain
last longer than expected length of recovery
longer then 3-6 months
Sharp Pain
localized
short lasting
carried by A-delta fibers
Dull Pain
diffusive
longer lasting
carried by C fibers
Gate Theory of Pain
there is a “gate” that controls the transmission of pain stimuli
the brain sends inhibitory or stimulatory signals to that gate
Pronociception
biologic amplification of nociception
Descending Connections
thalamus and pituitary glands releasing natural opioids (endorphins) that are transmitted during stress and pain
Opiates
block nociceptor signals without affecting other sensations