Chapter 2 - The Chemistry of Life (Professor’s Study Guide)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
CHOPKINS CaFe Mg Na Cl
What are the symbols for the 13 major elements found in the body?
CHON
What are the 4 major elements found in the body?
Elements needed in very small amounts
Ex: Iron, Iodine, Zinc
What are trace elements? What are some examples?
Protons and Neutrons
What subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom?
Electrons
What subatomic particles orbit the nucleus?
Number of protons
What is the atomic number of an atom?
Number of protons + neutrons
What is the mass number of an atom?
Isotope
What does an atom become if you change the number of neutrons it has?
You change the element that it is
What happens if you change the number of protons an atom has?
It becomes a negatively charged ion, called an anion
What happens if an atom gains electrons?
It becomes a positively charged ion, called a cation
What happens if an atom loses electrons?
Up to 2
How many electrons can the first electron shell hold?
Up to 8
How many electrons can all the other electron shells hold?
Share electrons with another atom (Covalent Bonding)
Donate electrons / accept electrons from another atom (Ionic Bonding)
What 2 things can atoms do to fill their outer electron shells?
Valence shell is full of electrons, so the atom will not interact with other atoms.
What does it mean if an atom is inert?
Valence shell is not full of electrons, so the atom will interact with other atoms to try to fill the valence shell.
What does it mean if an atom is reactive?
Physically mixed together
In mixtures, are atoms chemically bonded or physically mixed together?
Mixture that contains large particles that stay suspended
What is a colloid?
Mixture where particles will fall out of the mixture; Suspensions must be shaken to resuspend particles.
What is a suspension?
Solute is dissolved in solvent
What is a solution?
Solvent dissolves the solute so that there are no particles to stay suspended.
How do a solute and solvent make a solution?
An atom that has become charged by either gaining or losing an electron
What is an ion?
Cations have lost an electron(s) and become positively charged
Anions have gained an electron(s) and become negatively charged
How are cations and anions different?
Na+ , K+ , Ca2+
What is an example of a cation?
Cl- , I-
What is an example of an anion?
Positive charge on cation is attracted to negative charge on anion
How do ionic bonds form?
1 and 2 create cations; 7 creates anions
What columns of the periodic table contain the atoms that are most likely to participate in ionic bonds?
Salts (NaCl, Kcl, etc.)
When 2 ions interact to form an ionic bond, what do they form?
Ability of an atom’s protons to attract electrons
What is electronegativity?
Lower
Do metals have a lower or higher electronegativity?
Higher
Do non-metals have a lower or higher electronegativity?
Oxygen is more electronegative, so will have a stronger pull on shared electrons than Carbon will have
Based on electronegativity, what will happen when an Oxygen interact with a Carbon?
Electrons are shared between atoms by overlapping their valence shells
What happens to electrons in covalent bonds?
Single - one electron is shared
Double - two electrons are shared
Triple - three electrons are shared
Triple is strongest
How are single, double, and triple covalent bonds different? Which is the strongest?
Equal sharing between atoms
How are electrons shared in nonpolar covalent bonds?
Unequal sharing between atoms
How are electrons shared in polar covalent bonds?
One atom will be more electronegative and will pull more electrons to it than the less electronegative atom. The more electronegative will have a partial negative charge and the less electronegative atom will have a partial positive charge.
Explain why a dipole is formed in polar covalent bonds.
Similar electronegativities = Nonpolar covalent bond
*occurs between atoms of same element and atoms arranged so electronegativities cancel out
Different electronegativities = Polar covalent bond
*occurs because the more electronegative atom will have a stronger pull on shared electrons
How does an atom’s electronegativity determine if a polar or nonpolar covalent bond will form between two atoms?
Polar molecules have dipoles, with opposite charges. Nonpolar molecules are not charged. Dipoles allow attraction between partial charges w/ polar molecules.
Explain why polar molecules can form hydrogen bonds but nonpolar molecules cannot.
Since e- are shared equally, there is no charge. Therefore they cannot interact with polar water molecules that have dipoles. So hydrophobic means that nonpolar molecules stay separate from water due to their lack of charge.
What does it mean that nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic?
Polar molecules are charged, so they can interact with partial charges on water molecules. Hydrophilic means attraction to water. Since polar molecules can interact with water through their charge, they are hydrophilic.
What does it mean that polar molecules are hydrophilic?
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom donates electrons to another atom.
Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons by overlapping their valence shells.
How are ionic and covalent bonds different?
Polar - share electrons unequally due to different electronegativities
Nonpolar - share electrons equally due to similar electronegativities
How are polar and nonpolar bonds different?
Covalent
Which type of bond is the strongest?
Hydrogen
Which type of bond is the weakest?
Attraction of charges of nearby molecules
*There is no electron sharing/donating
*The interaction is between molecules, not atoms
What is a hydrogen bond? Why is it not a true bond?
Reactant/Substrate
In a chem rxn, what is the starting material called?
Product
In a chem rxn, what is the ending material called?
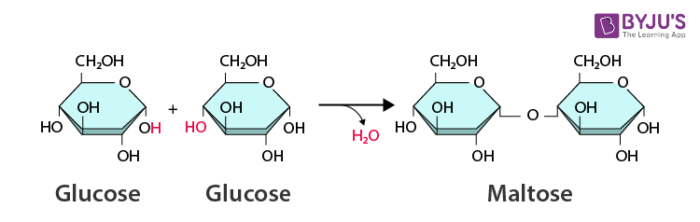
Dehydration: Water is created by removing -H & -OH from ends of monomers that are connected to form a larger product
What is a Synthesis/Dehydration reaction?
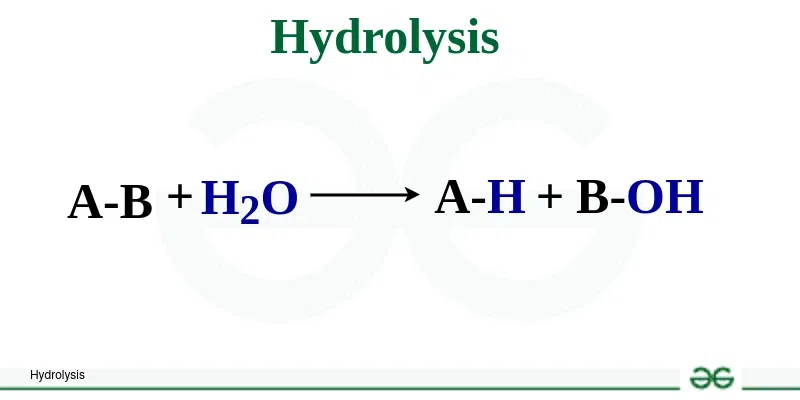
Hydrolysis: Water is broken apart to provide the -H and -OH to put on the
ends of the monomers that are broken apart
What is a Decomposition/Hydrolysis reaction?
Reaction can run forward or backwards
What is a reversible reaction?
Electron is transferred from one molecule to another
Molecule receiving the electron is reduced
Molecule donating the electron is oxidized
What happens in a RedOx/Oxidation-Reduction reaction?
Chemical: energy stored in the bonds of food
Potential: stored energy
Kinetic: energy of movement
How are kinetic, chemical, and potential energy different? Give an example of each.
Amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
What is activation energy?
Exergonic - produces more energy than it needs
Endergonic - needs more energy than it produces
How are exergonic and endergonic reactions different?
Lower the activation energy to jumpstart chemical reactions
How do enzymes/catalysts speed up chemical reactions?
Organic contains Carbon and contains covalent bonds
Inorganic usually lacks Carbon and are usually simpler (water, salts, acids, bases)
How are organic and inorganic compounds different?
Universal solvent, lubricant, high heat vaporization, high heat capacity, involved in many chemical reactions
Explain some of the important properties of water
Ions
What are electrolytes?
0-7-14
zero: most acidic (most H+)
seven: neutral
fourteen: most basic (most OH-)
pH scale range
Acidic! More acidic = more H+ !
Will an acidic, neutral, or basic pH have more H+?
Weak acid and weak base
What are buffers?
Prevent large changes in pH
What is the purpose of buffers?
Weak acid can donate H+ to lower pH is too basic
Weak base can bind H+ to raise pH if its too acidic
How do buffers work?
Major source of energy
Source of dietary fiber to maintain regularity of bowel movements
What are some functions of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides: 1 sugar
Disaccharides: 2 sugars; 2 monosaccharides connected by a covalent bond
Polysaccharides: multiple sugars connected by covalent bonds
How are the following types of carbohydrates different: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides?
Glycogen
What carbohydrate is used for energy storage in humans?
Cellulose
What storage carbohydrate of plants cannot be digested by humans and is called fiber?
Nonpolar (think of how oil and water don’t mix!)
Are lipids (fats and oils) polar or non polar?

Hydrophobic! (think of how oil and water don’t mix!)
Are lipids (fats and oils) hydrophilic 💙💧 or hydrophobic💧❌?

Long chains of Carbons with Hydrogens attached
What is a fatty acid?
Saturated: Carbons are connected with single bonds and are completely saturated with Hydrogens
Unsaturated: At least one double bond between Carbons, so Carbons are not saturated with Hydrogens
How are saturated and unsaturated fatty acids different?
Hydrogens are on opposite side of Carbon double bond. (they would normally be on the same side)
What are trans fats and how are they different from regular unsaturated fatty acids?
Leukotrienes - cause inflammation
Prostaglandins - cause inflammation, increase pain, blood clotting, produce mucus in stomach
What are two examples of Eicosanoids?
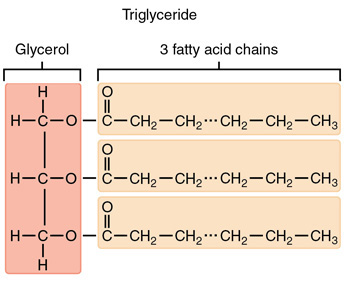
1 Glycerol, 3 Fatty Acid Chains
Diagram of a triglyceride
Energy storage
Insulation
Protection
What are the (3) functions of triglycerides?
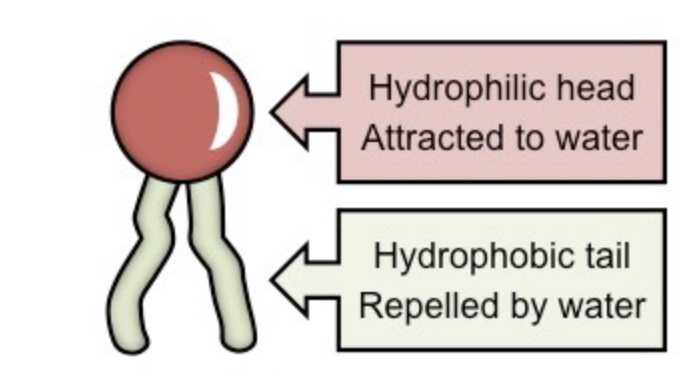
Polar head/Nonpolar tail
Diagram of a phospholipid
In cell membranes that surround all of our cells
Where are phospholipids found in the body?
Cholesterol
What lipid are steroids made from?
Testosterone, Estrogen, Cortisol
What are some examples of steroids?
Liver
Where are LDL and HDL made in the body?
Carries cholesterol from the liver out to the body
What is the function of LDL
Low - too much cholesterol carried in the blood vessels can increase BP, risk of heart attack and stroke
Is it better to have high or low LDL? Why?
Carries cholesterol from the body back to the liver
What is the function of HDL?
Sometimes: Support Cells
Mamaw: Movement of Muscles
Always: Amino Acids buffer pH
Tries: Transport
Eating: Enzymes that catalyze rxns
A: Antibodies
Hamburger: Hormones maintaining Homeostasis
What are some functions of proteins?
Amino Acids
What are the building blocks for proteins?
Primary = sequence of amino acids
Secondary = small areas of structure form from hydrogen bonding, such as alpha-helix & beta sheet
Tertiary = 3D structure of protein due to bonding between secondary structures
Quaternary = 2 more more tertiary structures form subunits of a large protein (Globular/Fibrous)
Describe the 4 levels of protein structure
The place where the substrate binds
What is the active site of an enzyme?
When a protein unfolds and structure is lost
What is protein denaturation?
Since structure is lost, the active site is also lost
What happens to the active site of an enzyme when a protein is denatured?
Since the active site is lost, there is no place to bind the substrate. So protein function will also be lost.
What happens to protein function when a protein is denatured?
High temp, extreme pH (too acidic /too basic)
What are some things that cause protein denaturation?
Each enzyme is specific for a particular substrate that it can bind to. In the Lock and Key model, the enzyme is the lock and the substrate is the key.
Briefly explain how the Lock and Key model describes what substrate an enzyme can bind to and work on
Nucleotides
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
Nitrogenous base, sugar, phosphate
What are the 3 components of a nucleotide?
In both DNA & RNA: GAC Guanine, Adenine, Cytosine
In DNA only: Thymine (T)
In RNA only: Uracil (U)
What are the 5 nitrogenous bases?
Which is found only in DNA?
Which is found only in RNA?
Adenine & Thymine or Uracil (depends on DNA/RNA)
Cytosine & Guanine
Which nucleotides base pair together?
DNA - double strand, sugar = deoxyribose, nucleotides: GACT
RNA - single strand, sugar = ribose, nucleotides: GACU
What are some differences between DNA and RNA?
Adenine, Ribose, and 3 phosphates
Major storage molecule for energy
What is ATP?
Removing the 3rd phosphate releases a large amount of energy
Sometimes the 2nd can be removed, but doesn’t release as much energy as the 3rd
How is energy released from ATP?