Module 6- DNA replication
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Describe the general function of DNA.
to carry genetic instructions for the development, functioning growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
Name the parts of a nucleotide
a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Identify which parts of a nucleotide are involved in phosphodiester bonds and hydrogen bonds.
Nitrogenous bases are involved in hydrogen bonds, phosphate groups and the sugar component form phosphediestes bonds, creating the sugar-phosphodiestes bonds, creating the sugar-phosphate backbone.
Base pairing rule
A (adenine) pairs with
T (Thymine)
Base pairing rule
T(Thymine) pairs with
A (adenine)
C (cytosine) pairs with
G (guanine)
G (guanine) pairs with
C (cytosine)
Name the functional groups found at the 5’ and 3’ ends of a DNA strand.
The 5-end is a free phosphate group, whilst the 3-end is a free hydroxyl group.
Explain the importance of the 3-end of a DNA strand in the process of DNA replication.
The 3 is crucial because DNA polymerase can only add new nucleotides to the free hydroxyl (-OH) group at the end of a growing DNA strand.
Explain what is meant by “semiconservative replication”
after replication, each of the two new DNA double helices consists of one original (parental) strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Describe the role of origins of replication in the process of DNA replication.
It’s where the replication process starts. Proteins bind to the origin to begin the process of unwinding the DNA. In eukaryotes, multiple origins are activated simultaneously along a chromosome to speed up replication
Replication bubbles role in DNA replication
regions of unwound DNA where new strands are synthesized, serving as the fundamental structure for DNA replication to occur
Replication forks role in DNA replication
serving as the site where the DNA double helix unwinds and separates into two template strands
Could you describe the major enzyme Helicase and its involvement in DNA replication?
unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between base pairs, creating two single-stranded templates.
Could you describe the major enzyme Primase and its involvement in DNA replication?
This is the enzyme that makes small RNA primers to start DNA replication.
Could you describe the major enzyme DNA polymerase and its involvement in DNA replication?
adds new complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand in the 5 to 3 direction, using the template strand as a guide. DNA polymerase also has a proofreading function to remove incorrect nucleotides.
Could you describe the major enzyme Ligase, and its involvement in DNA replication?
joins the newly synthesized DNA fragments Cokazaki fragments on the lagging strand together by sealing the gaps in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
Could you describe the major enzyme Topoisomerase and its involvement in DNA replication?
This is the enzyme that relieves the strain caused by opening the double helix.
Could you describe the major enzyme, Single-strand binding proteins (SSBPS), and its involvement in DNA replication?
Bind to the separated single strands of DNA to prevent them from re-annealing and to protect them from degradation
Could you describe the major enzyme Exonuclease/RNase H and its involvement in DNA replication?
Removes the RNA primers that were synthesized by primase
Explain why the leading strand of DNA is made continuously while the lagging strand is not.
The leading strand is synthesized continuously towards the replication fork because DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in the 5 to 3 direction, matching the unwinding direction, matching the unwinding direction, while the lagging strand is made discontinuously in short segments, called Okazaki fragments, because it must be synthesized away from the fork.
Describe the roles of DNA polymerase 3 and nucleotide excision enzymes in ensuring the quality of copied DNA.
DNA polymerase 3. This is the enzyme that builds complementary DNA strands, while nucleotide excision enzymes repair larger, pre-existing DNA damage that occurred outside of replication.
Chromosomes consist of
____
wound around
___
proteins.
DNA
Histone
What is found at the 5’ end of a DNA strand?
A phosphate group (-PO4).
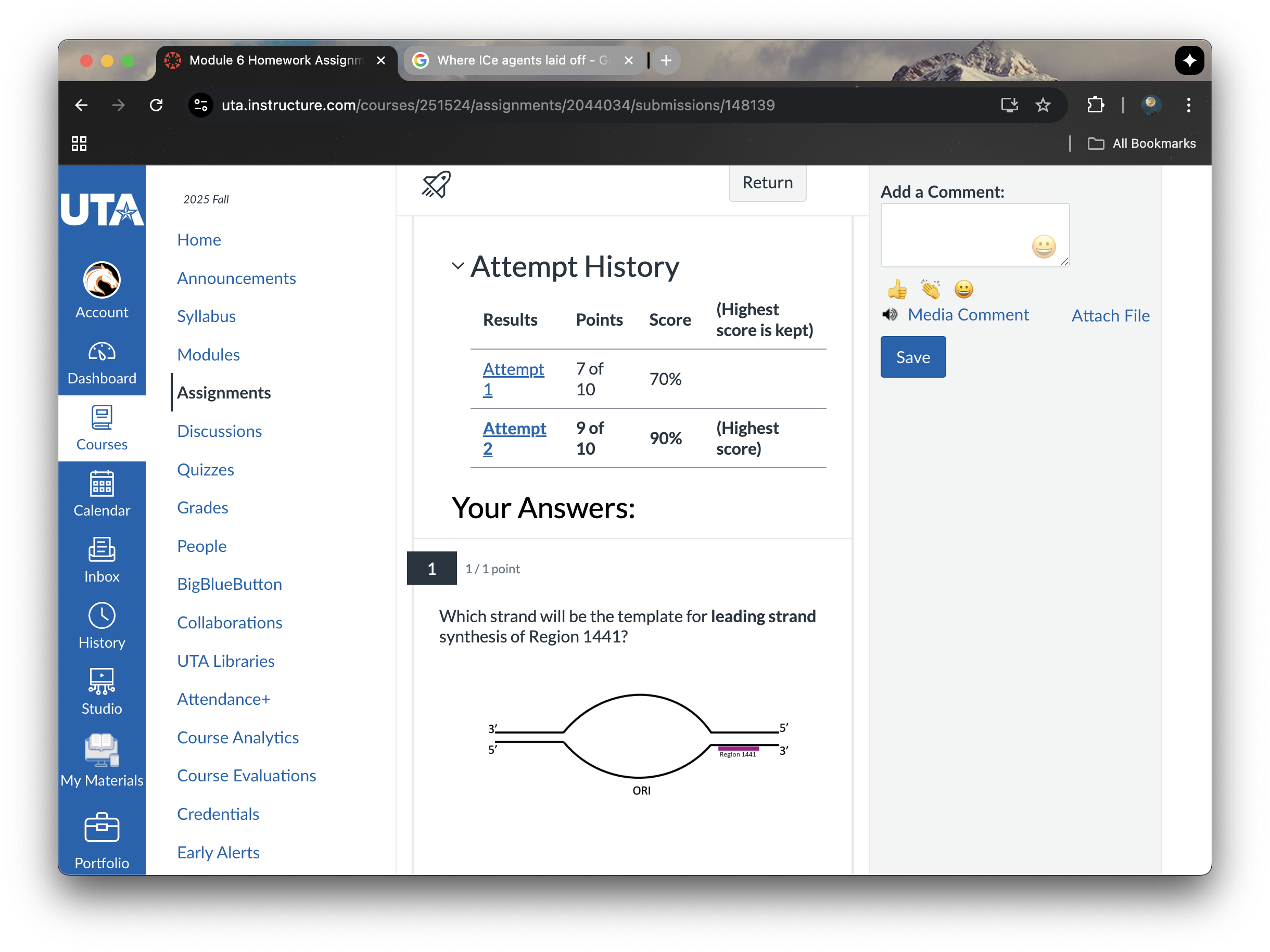
The top strand
Which of the following are purines?
Guanine and Adenine
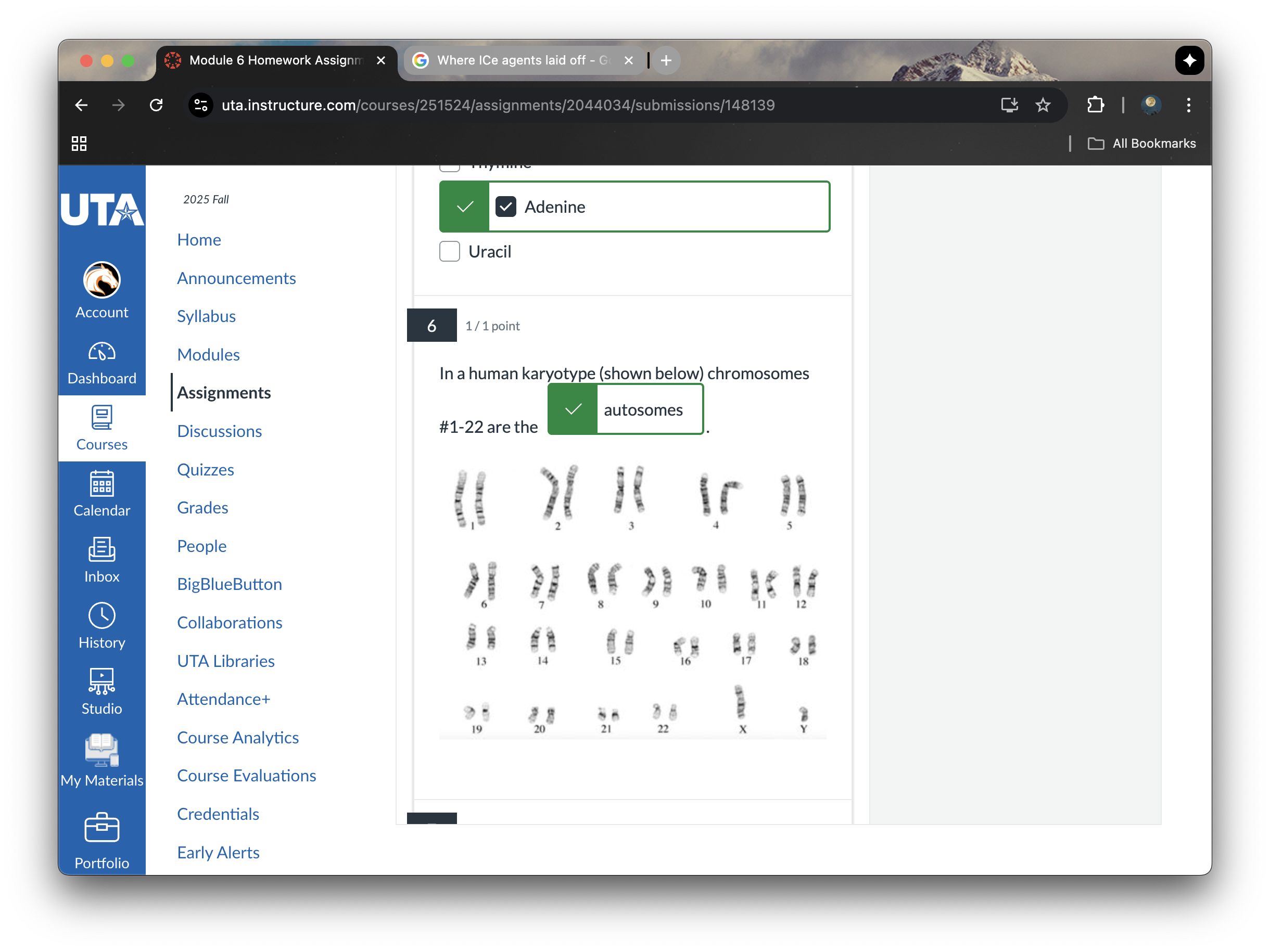
autosomes
What is the name of the locations where helicase separates the DNA double helix?
The replication forks
What is found at the 3 end of a DNA strand?
A hydroxyl group (-OH)