m2 carbohydrates and derivatives
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
Common attributes of carbohydrates are that they contain:
Carbohydrates
A major source of energy for us.
Potatoes, bread, pasta and rice are rich in this
carbohydrates
chemically are polyhydric alcohols
polyhydroxy ketones ( ketoses) or
polyhydroxy aldehydes (aldoses)
glycogen
Storage form of energy in the body (carbohydrates)
Cell walls of bacteria
Exoskeleton of many insects
Fibrous cellulose of plants
carbohydrates serves as a structural component of many organisms:
carbohydrates
Cell membrane components that mediate some forms of intercellular communication
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars
Monosaccharides
Formed by only one polyhydroxy aldehydic or ketonic unit
D-glucose, also called dextrose
The most abundant monosaccharide:
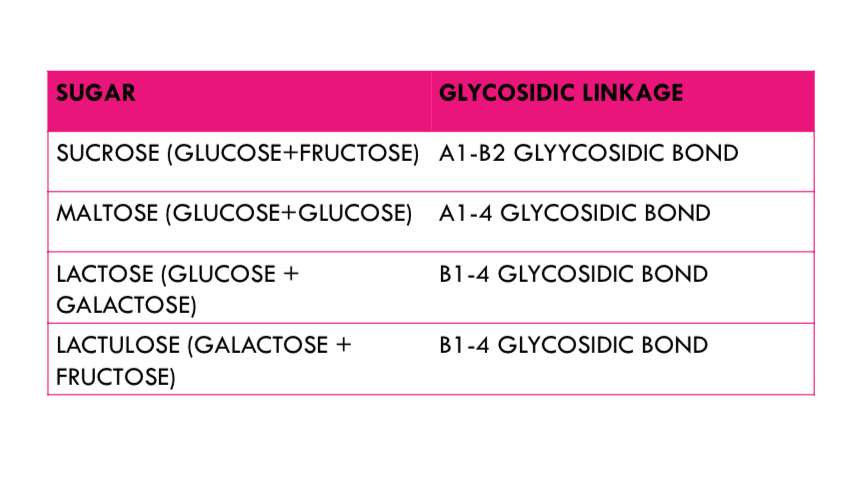
SUCROSE
GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE
MALTOSE
)GLUCOSE+GLUCOSE): a-1,4
CELLUBIOSE
(GLUCOSE+GLUCOSE): B-1,4
LACTOSE
(GLUCOSE+GALACTOSE)
Disaccharides
Meaning "two sugars“
Disaccharides
Are commonly found in nature as sucrose, lactose, and maltose
condensation
disaccharides are formed by a __ reaction where one molecule of water condenses or is released during the joining of two monosaccharides
A1-B2 GLYYCOSIDIC BOND
glycosidic linkage of sucrose (glucose+fructose)
A1-4 GLYCOSIDIC BOND
glycosidic linkage of MALTOSE (GLUCOSE+GLUCOSE)
B1-4 GLYCOSIDIC BOND
glycosidic linkage of LACTOSE (GLUCOSE + GALACTOSE)
B1-4 GLYCOSIDIC BOND
glycosidic linkage of LACTULOSE (GALACTOSE + FRUCTOSE)
Oligosaccharides
Short chains of monosaccharide units (2 to 20) linked by glycosidic bonds
disaccharides
most abundant oligosaccharide
sucrose, lactose and maltose
most important oligosaccharide in the human diet
polysaccharides
are long polymers of monosaccharides:
Homoglycans
(polysaccharide) made up of one type of sugar unit.
Heteroglycans
(polysaccharide) composed of more than one type of sugar unit; repeating disaccharide units.
Hydroxyacetaldehyde
two-carbon sugar
Hydroxyacetaldehyde
(monosaccharide) does not occur free in nature
Glyceraldehyde
(monosaccharide) intermediate product in glycolysis
Dihydroxyacetone
(monosaccharide) intermediate product in glycolysis
Glyceraldehyde
Dihydroxyacetone
3 carbon sugars
Erythrose
Erythrulose
4 carbon sugars
Ribose
Xylose
Ribulose, Xylulose
5 carbon sugars
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
6 carbon sugars
Sedoheptulose
7 carbon sugar
Neuraminic acid
9 carbon sugars
erythrose
(monosaccharide) not found free in nature
Ribose
(monosaccharide) product of gum hydrolysis; the sugar present in the RNA
Xylose
(monosaccharide) wood sugar; simplest sugar found in plants; a diagnostic aid for intestinal absorption
Glucose
(monosaccharide) dextrose, grape sugar, physiologic sugar; β-D-glucose (the most abundant type of glucose)
Fructose
(monosaccharide) levulose, fruit sugar; sweetest but with after-taste; product of inversion of aqueous solution of sucrose and hydrolysis of inulin
Galactose
(monosaccharide) found in milk and in neuronic fibers as galactosides
7 carbon sugars
(monosaccharide) ketoheptulose
Neuraminic acid
(monosaccharide) sialic acid; an aldononose
sucrose
maltose
lactose
lactulose
disaccharides
Maltotriose
Dextrin
oligosaccharides
Lactulose
Duphalac®
lactulose
a semi-synthetic sugar; product of alkaline rearrangement of lactose; used as a laxative for myocardial infarcted patients (to avoid straining)
Cellulose
structural polysaccharide in plants; long chain of β-1,4 glucose units
Chitin
structural polysaccharide in animals; long chain of N-acetylglucosamine
Starch
storage polysaccharide in plants; composed of amylose and amylopectin
Hetastarch
water soluble starch with >90% amylopectin
Glycogen
storage polysaccharide in animals; more branched than starch (every 10 glucose units);
Inulin
polyfructan of fructofuranose; β-1,2 bond; improves digestion
Dextran
homopolyglucan of α-1,6 bond; formed from sucrose by the action of transglycolase enzyme system; used as a plasma expander
Hyaluronic acid
present in vitreous humor and synovial fluid
Chondroitin sulphate
heteroglycan that is present in cartilage, tendons and ligaments
Dermatan sulphate
heteroglycan that is present in skin
Keratan sulphate
heteroglycan that is present in nails
Heparan sulphate
heteroglycan that is an anticoagulant
Agarose
heteroglycan found in sea-weeds
pectin
a heteroglycan found in the primary cell walls of the plants
pectin
rich in galacturonic acid; used as gelling agents, thickening agents and stabilizers in food
-

-