IB Computer Science HL Paper 1 Topic 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
Recursion
* A method that calls itself
* Involves the use of stacks to store data that will be returned at end
* Can be memory intensive if many recursive calls are made
* Involves the use of stacks to store data that will be returned at end
* Can be memory intensive if many recursive calls are made
2
New cards
Characteristics of a stack
* A data structure
* LIFO
* dynamic
* LIFO
* dynamic
3
New cards
Stack access methods
* push()
* pop()
* isEmpty()
* pop()
* isEmpty()
4
New cards
Characteristics of a queue
* FIFO
* dynamic
* dynamic
5
New cards
Queue access methods
* enqueue()
* dequeue()
* isEmpty()
* dequeue()
* isEmpty()
6
New cards
Real world examples of queues
* Printer queues
* Computer modelling of real-life queues (like in supermarkets)
* Computer modelling of real-life queues (like in supermarkets)
7
New cards
Linked lists
* Linear collection of nodes, which are self-referential
* Nodes connected by pointer links
* Nodes connected by pointer links
8
New cards
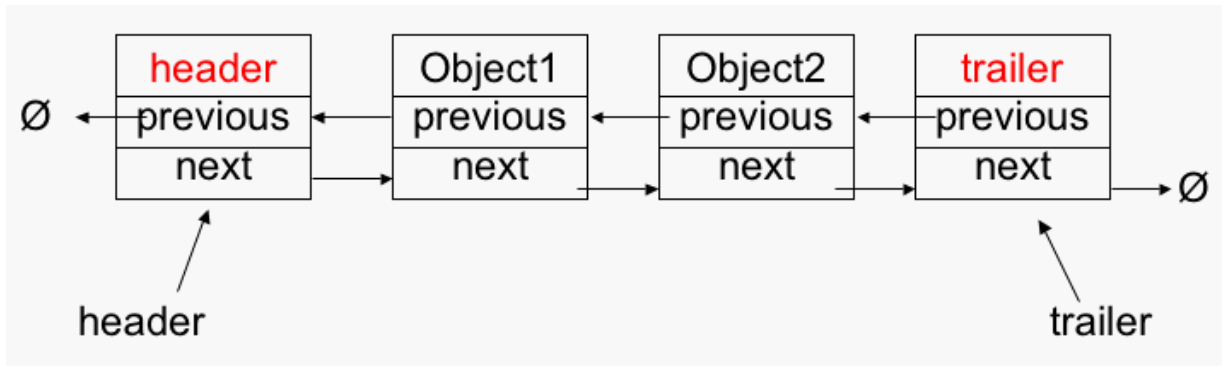
Features of a doubly linked list
* Single head, single tail
* Each node has two pointers - one to next, one to previous
* Each node has two pointers - one to next, one to previous
9
New cards
Features of a circular linked list
* Single head
* One pointer for each element
* Last element’s pointer points to head
* One pointer for each element
* Last element’s pointer points to head
10
New cards
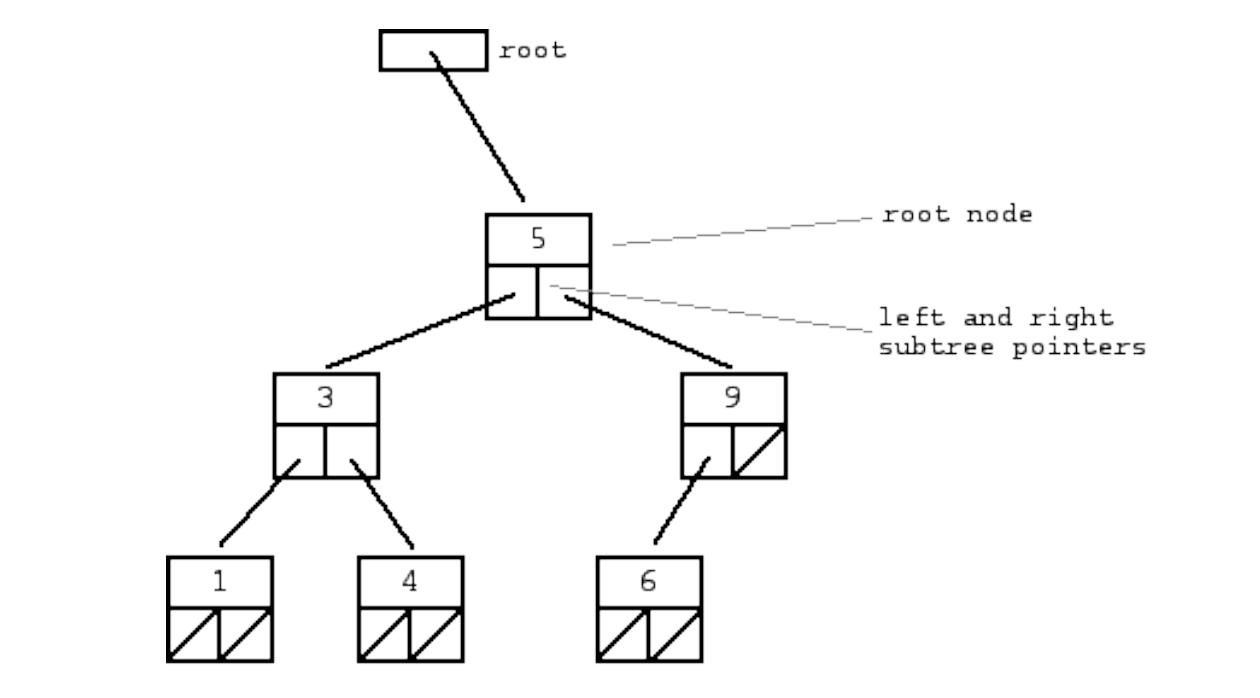
**Binary trees**
11
New cards
Parent
* A node in a tree that has children (left, right or both)
12
New cards
Root
* The top node in a tree
13
New cards
Subtree
* A parent with children within another parent-child relationship
14
New cards
Dynamic data structures pros and cons
Pros
* Can change size while program is running
* Makes efficient use of memory
* Storage no longer required can be returned to the system for other use
Cons
* Difficult to program
* Can be slow / complex to implement
* A linked list only allows serial (in order) search
* Can change size while program is running
* Makes efficient use of memory
* Storage no longer required can be returned to the system for other use
Cons
* Difficult to program
* Can be slow / complex to implement
* A linked list only allows serial (in order) search
15
New cards
Static data structures pros and cons
Pros
* Easy to program
* Easy to check for overflow
* An array allows random access
* Does not change in size while program is running
\
Cons
* Can waste space
* Programmer has to estimate space needed, could be wrong
* Easy to program
* Easy to check for overflow
* An array allows random access
* Does not change in size while program is running
\
Cons
* Can waste space
* Programmer has to estimate space needed, could be wrong