Module 4&5 - Maternal Testing & Screening
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
11-14w
When does the 1st trimester screen occur
19-20w
When does the 2nd trimester detailed anatomy scan occur
Fetal assessment scan
What does FAS stand for
Non-invasive prenatal testing
What does NIPT stand for
After 10weeks
When does the NIPT occur
Cell-fee DNA in maternal plasma
What does NIPT test
>99%
What is the detection rate of NIPT
Increased BMI
What may decrease the accuracy of the NIPT
78%
What is the detection rate of the NIPT when the mother is 300lbs
Trisomy 21, 18, 13
What does NIPT stand for
Low-risk and high-risk
What are the two results that can come back from NIPT
False
T/F: NIPT is converse by Alberta health
First trimester screen
What does FTS stand for
11-14 weeks
When does a FTS occur
NT, B-hCG, PAPP-A, and maternal age
What does the FTS combine in its testing
Trisomy 13, 18, 21
What does the FTS screen for
Subcutaneous fluid collection under the skin behind the fetal neck
What is the nuchal translucency and where is it located
Increases
NT ______________ with CRL
Chromosomal abnormalities cardiac defects, genetic disorders
What is increases NT thickness associated with
Noonan syndrome
What is the most common genetic disorder associated with an increased NT
Nuchal fluid begins to increase, can appreciate other anatomy, the abdominal hernia see at 8-10 weeks should start to resolve
Explain why we look at the NT at 11 weeks
Increase in false negatives after this point
Why do we stop looking at the NT after 14 weeks
80%
What is the detection rate of trisomy 21 with the NT alone
82%-87%
What is the detection rate of trisomy 21 with all tests included in the FTS
11-14 weeks
What must the gestational age be for the nuchal translucency scan
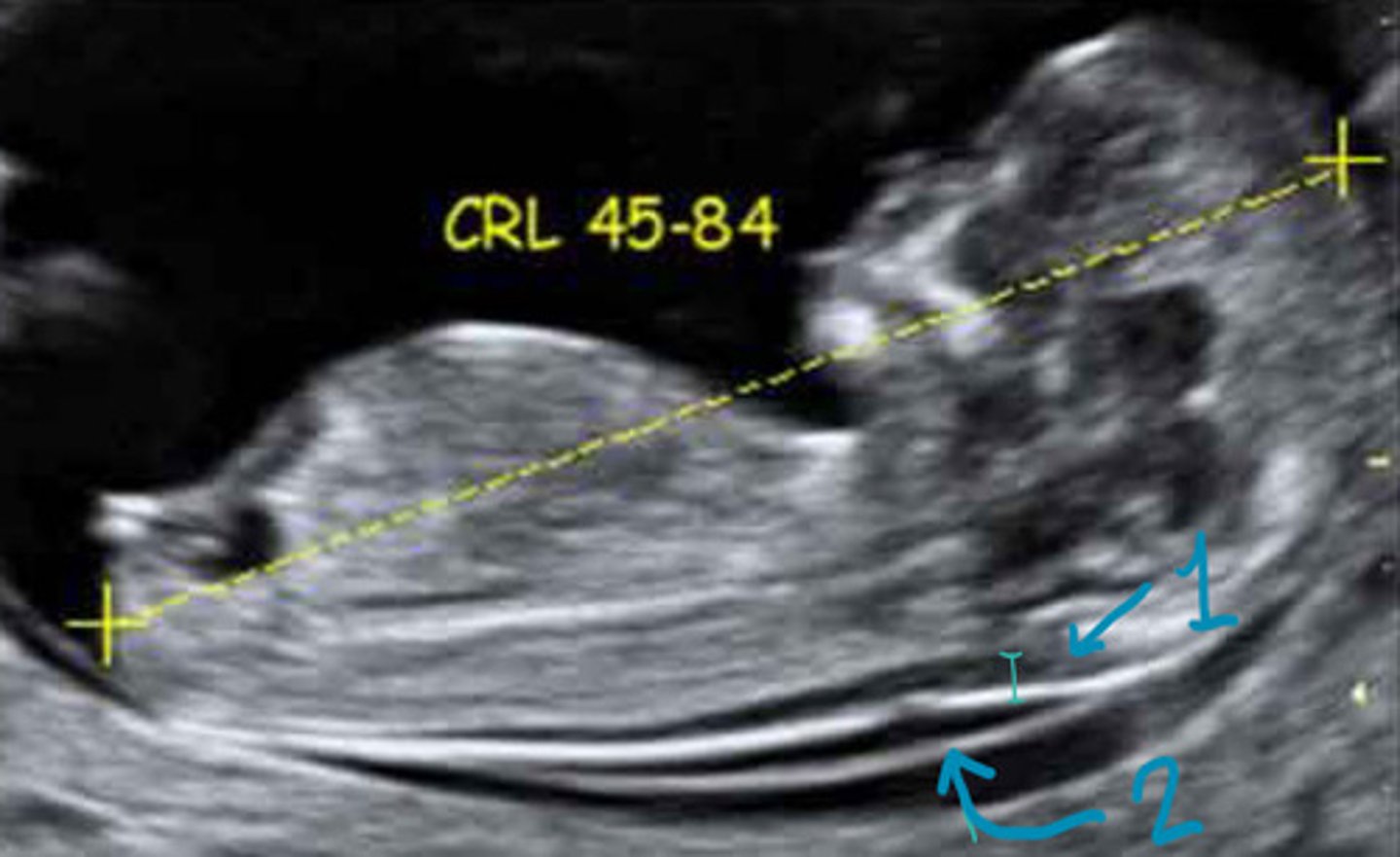
45-84mm
What must the CRL be for the NT scan
Gains turned down, widest translucency measured, neutral position
Describe the scanning technique for the NT
1
Which is the NT
NT
What is 1
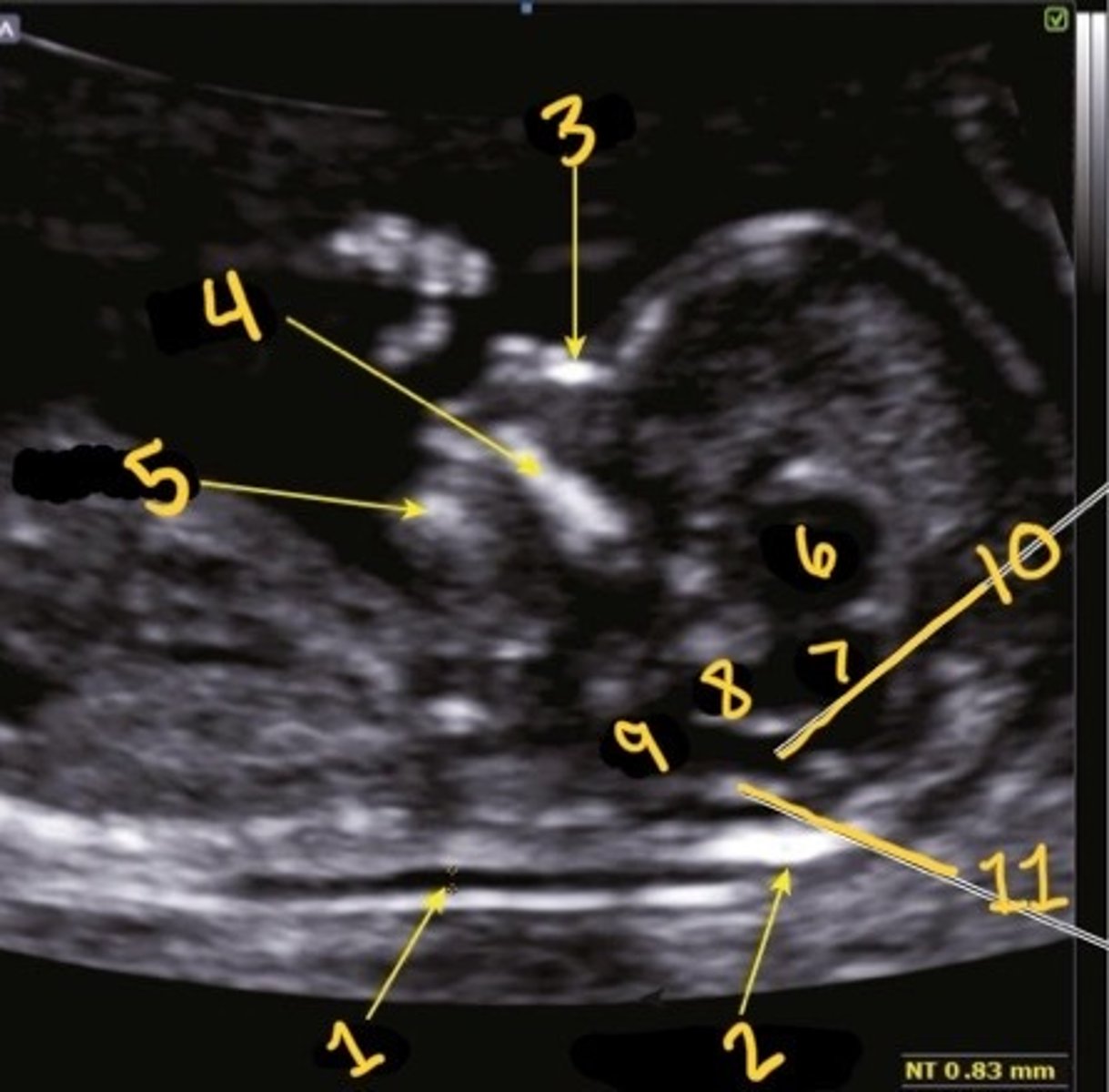
Occipital bone
What is 2
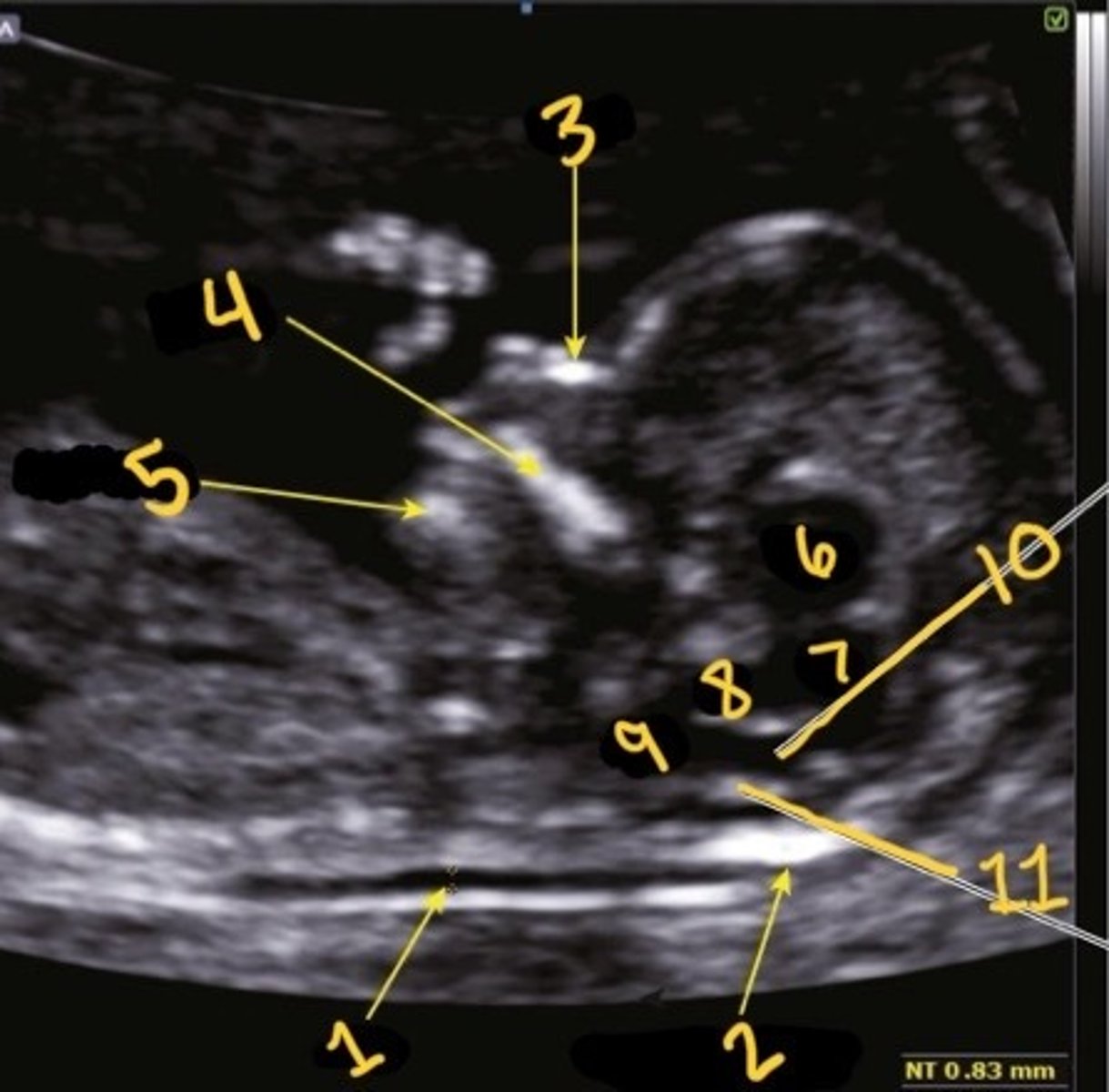
Nasal bone
What is 3
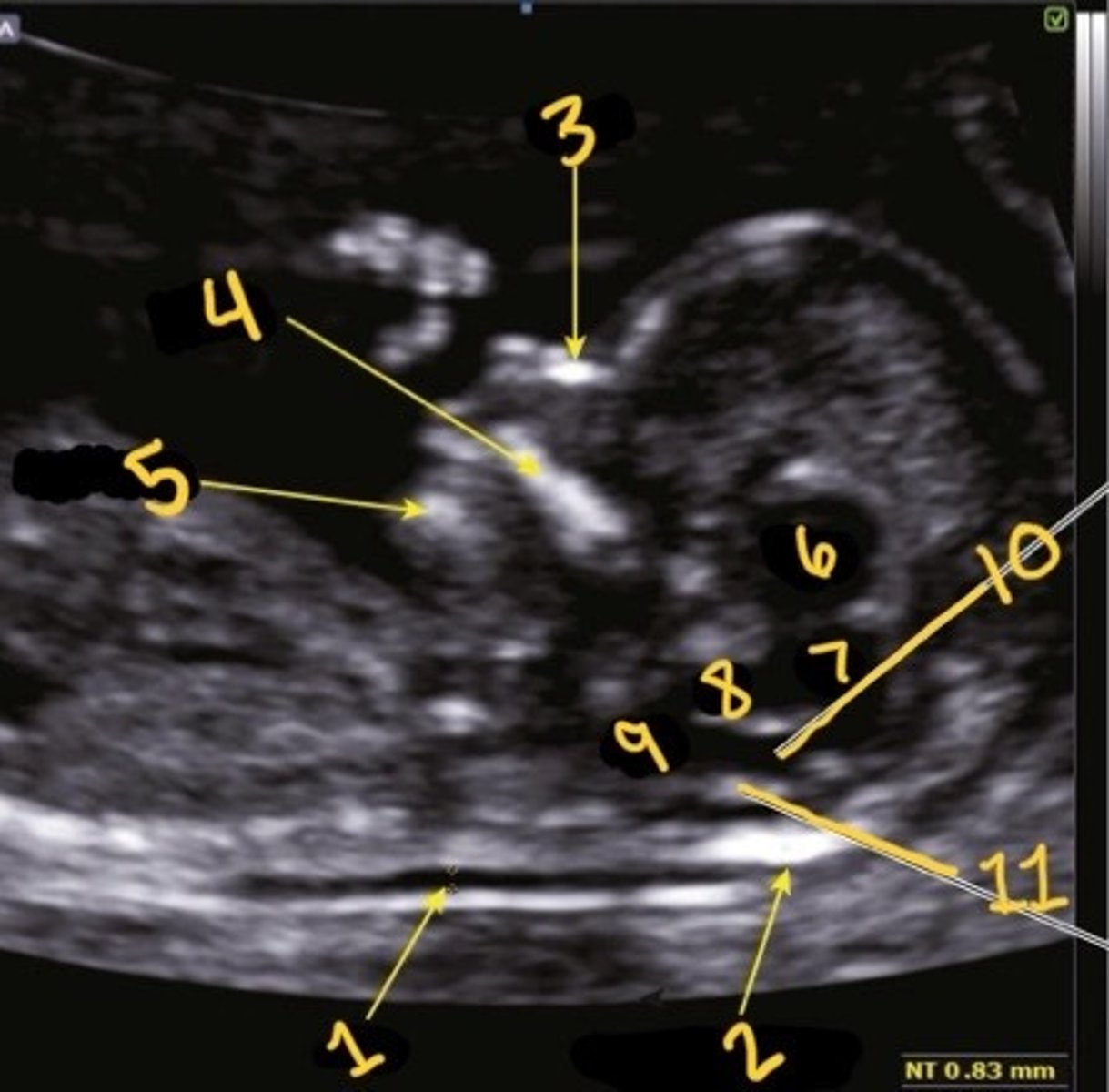
Palate
What is 4
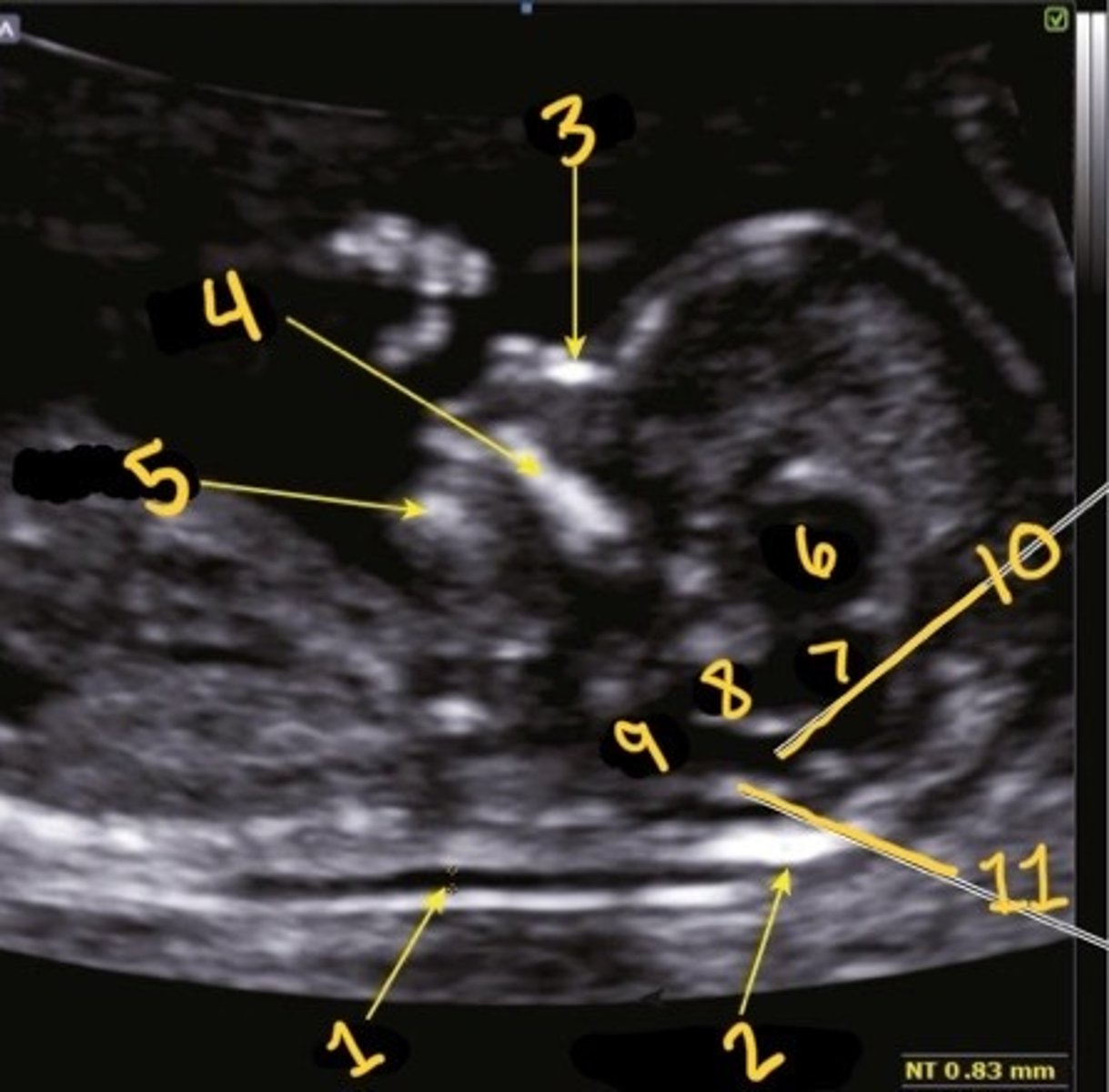
Mandible
What is 5
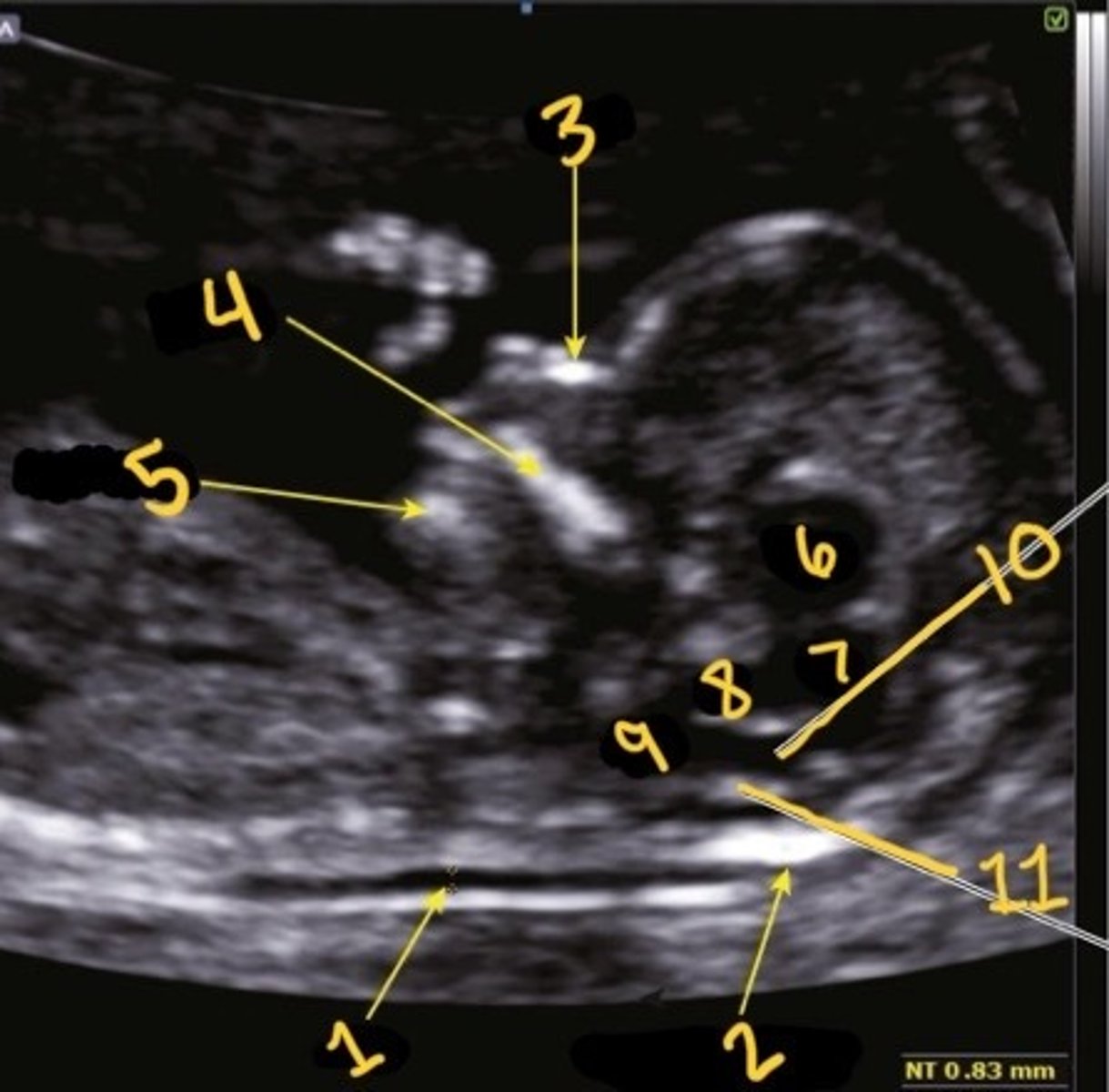
Thalami
What is 6
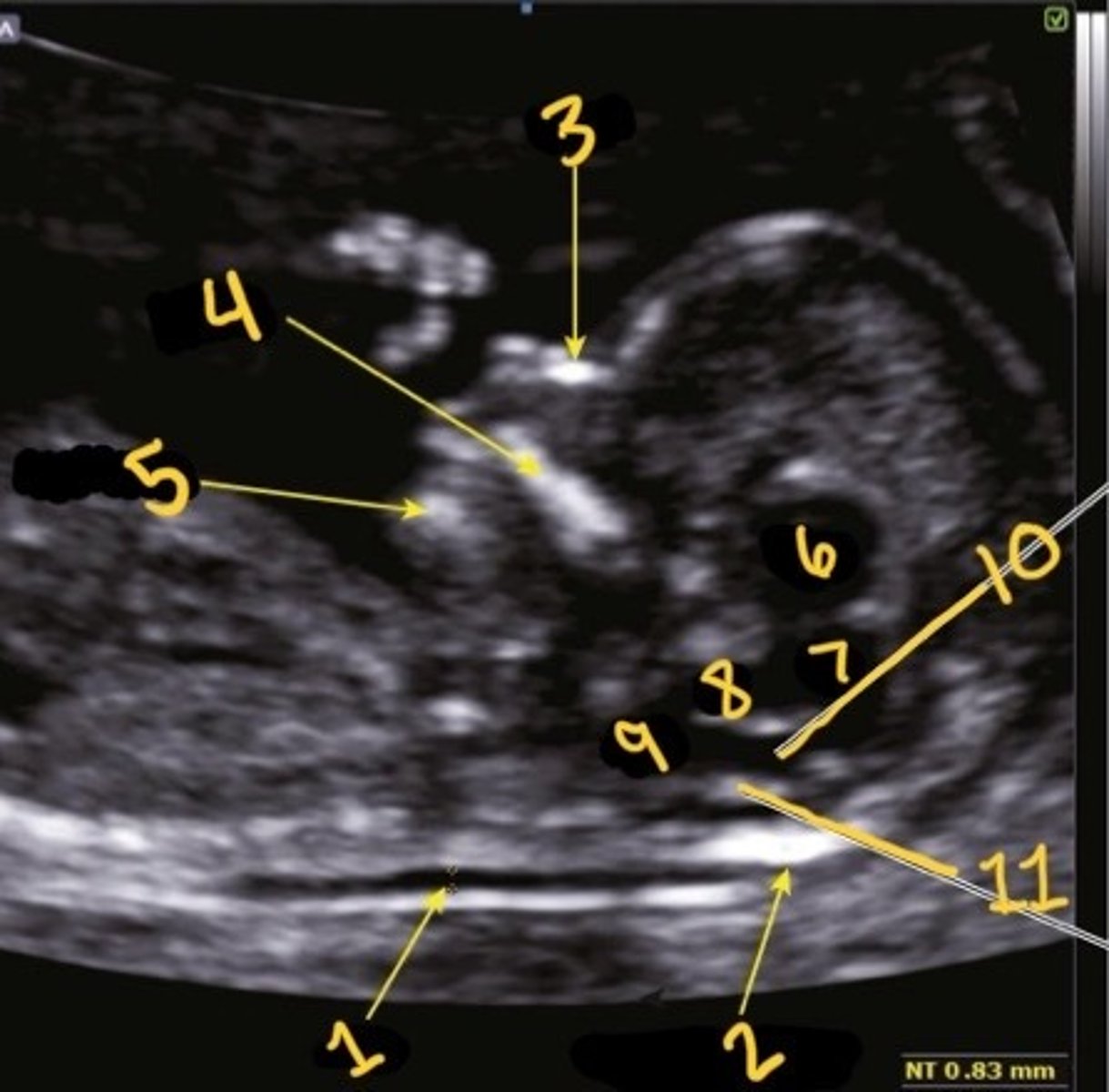
Midbrain
What is 7
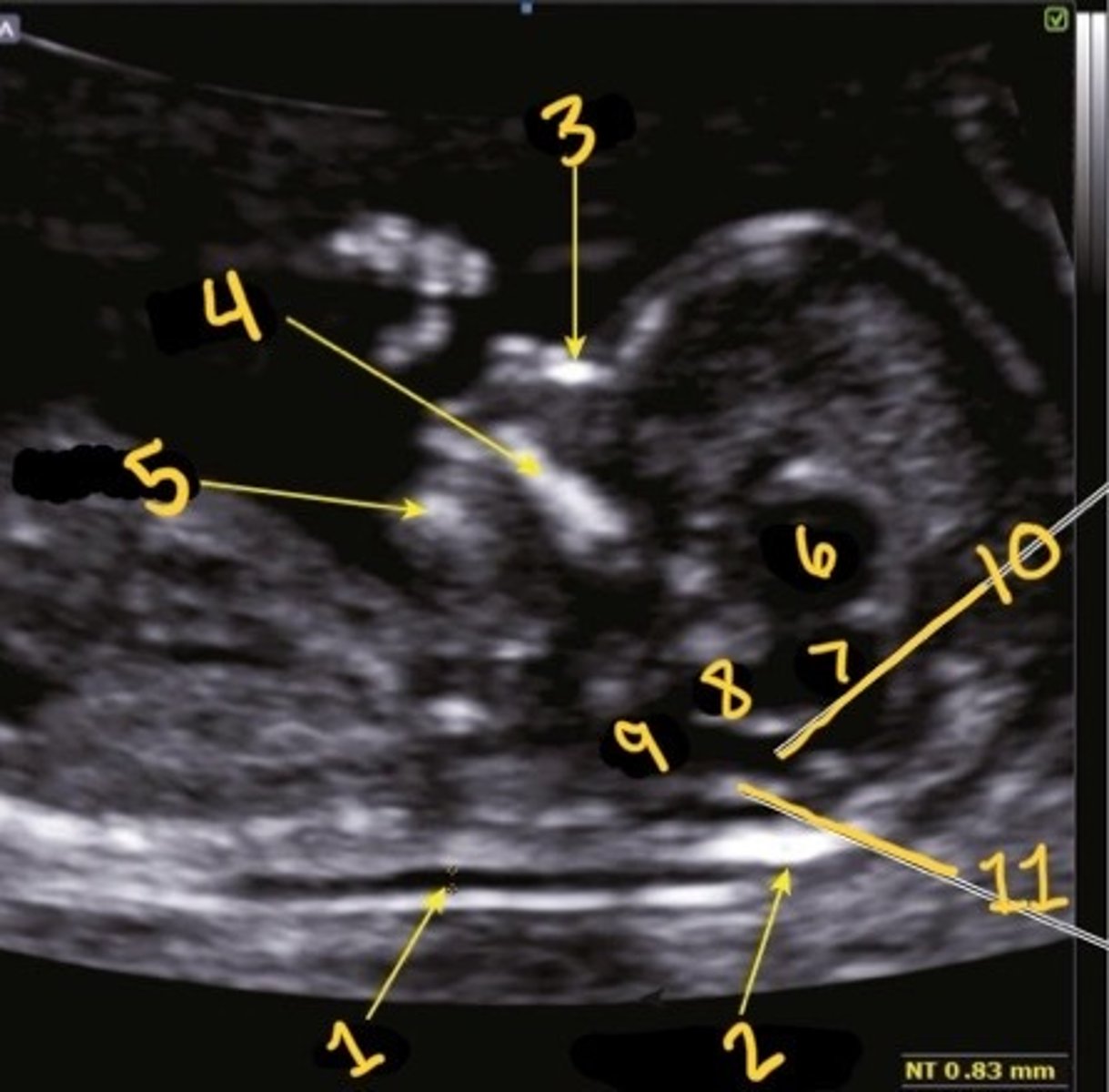
Inner to inner
What is the correct calliper placement for the NT mmt
False
T/F: you can still measure the NT even is you can't see the amnion under it
Brain stem
What is 8
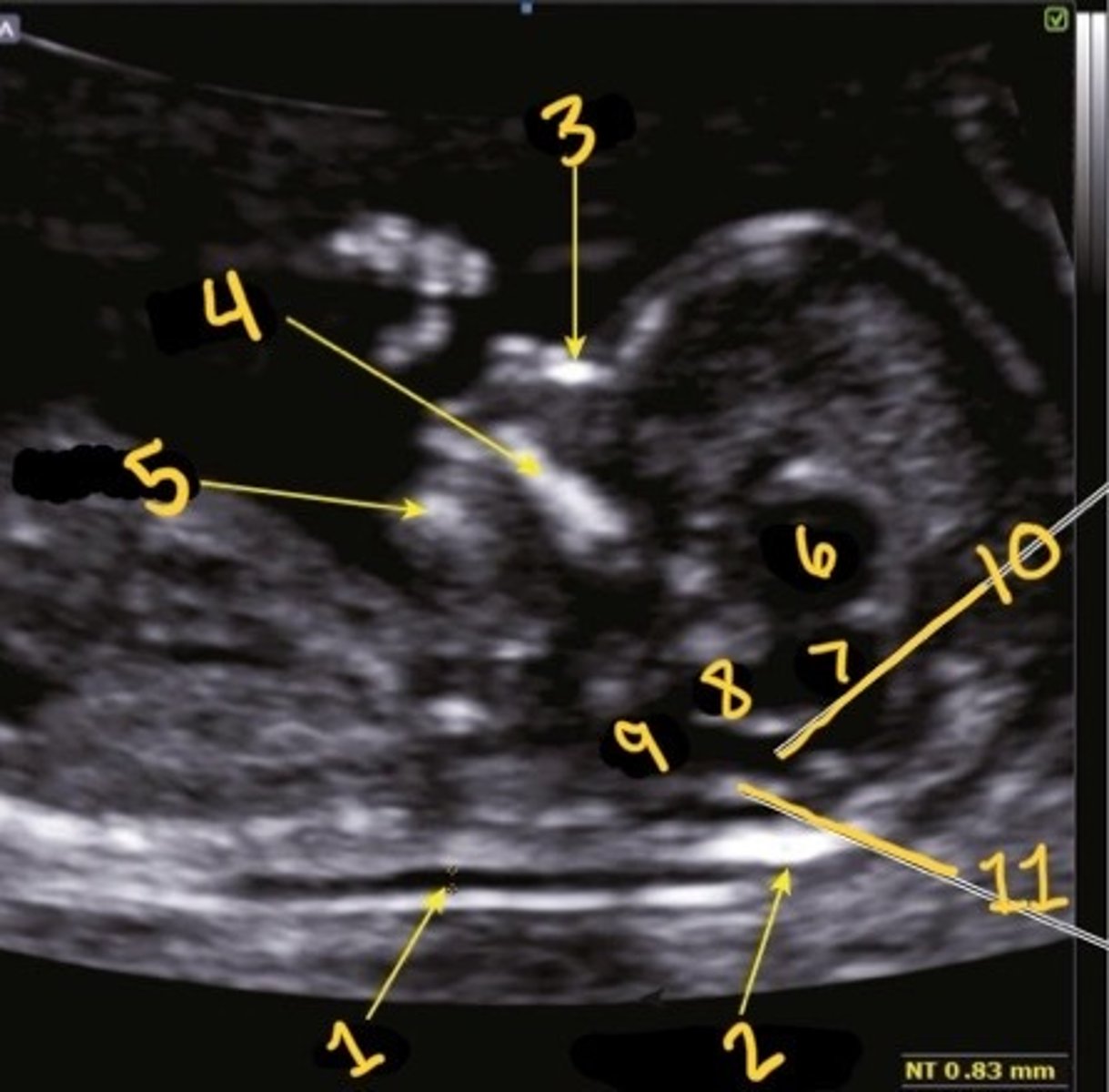
Medulla oblongata
What is 9
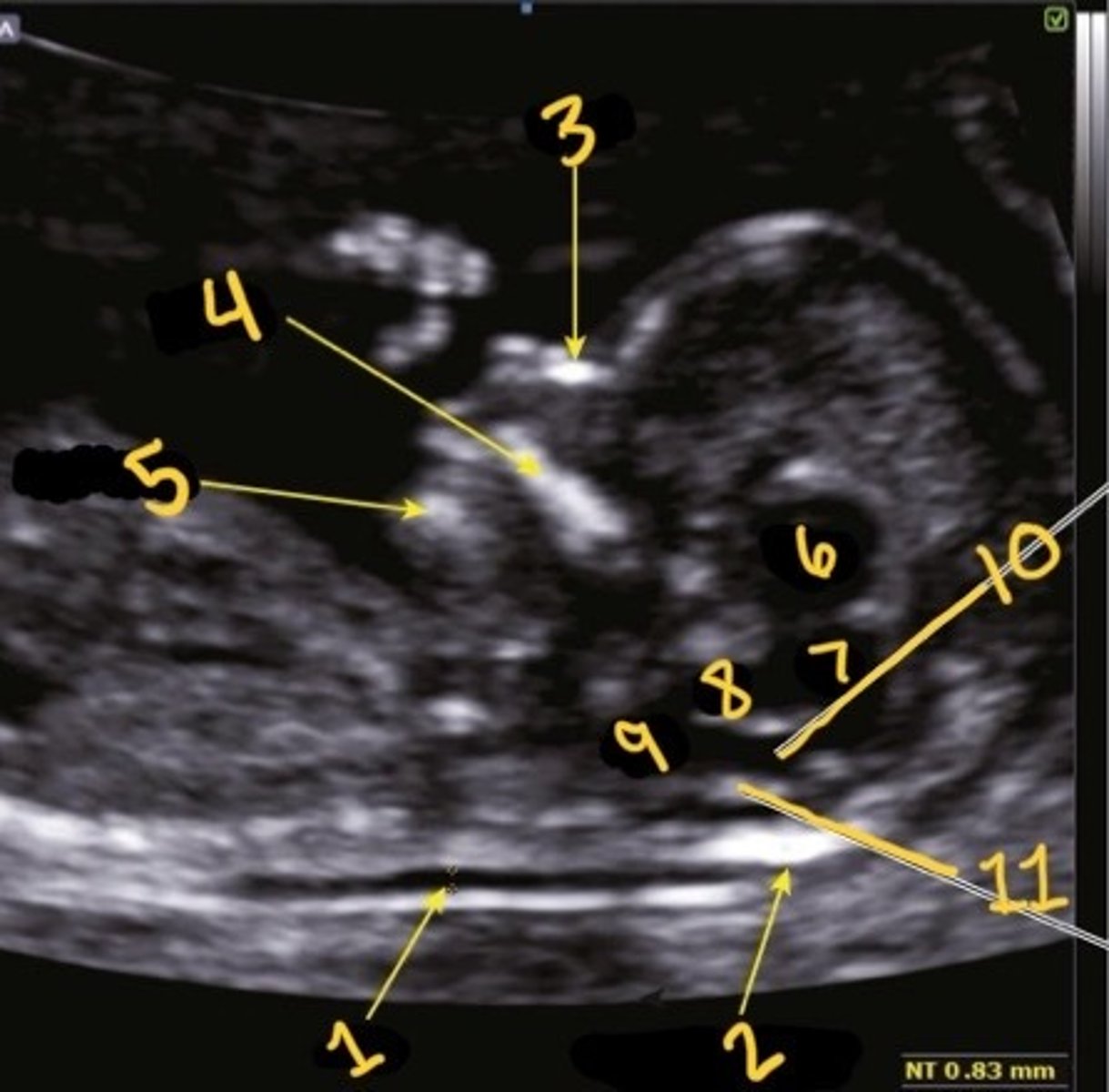
4th ventricle
What is 10
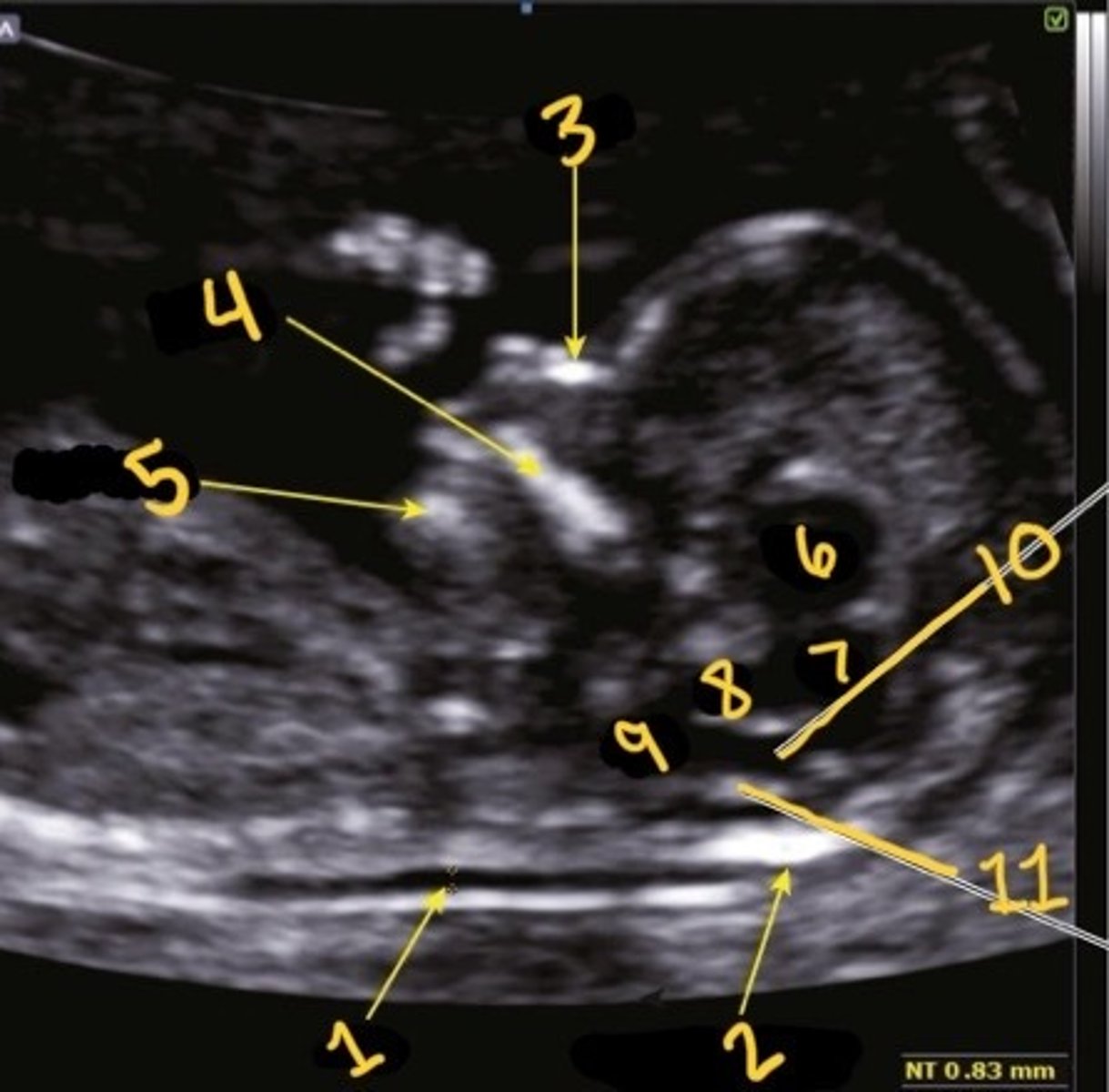
Choroid plexus of 4th ventricle
What is 11
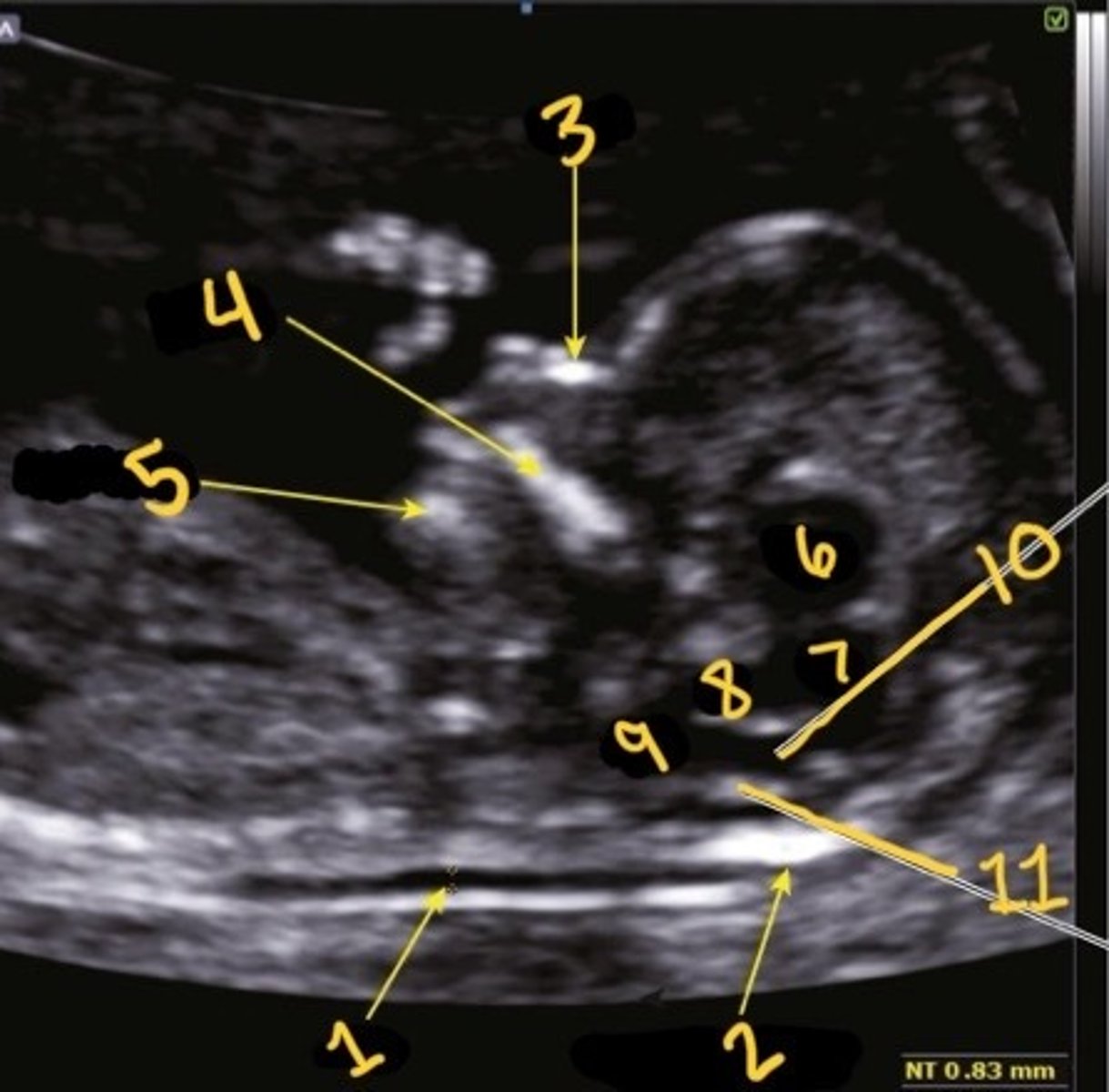
1st one
Which is the correct calliper placement for the NT
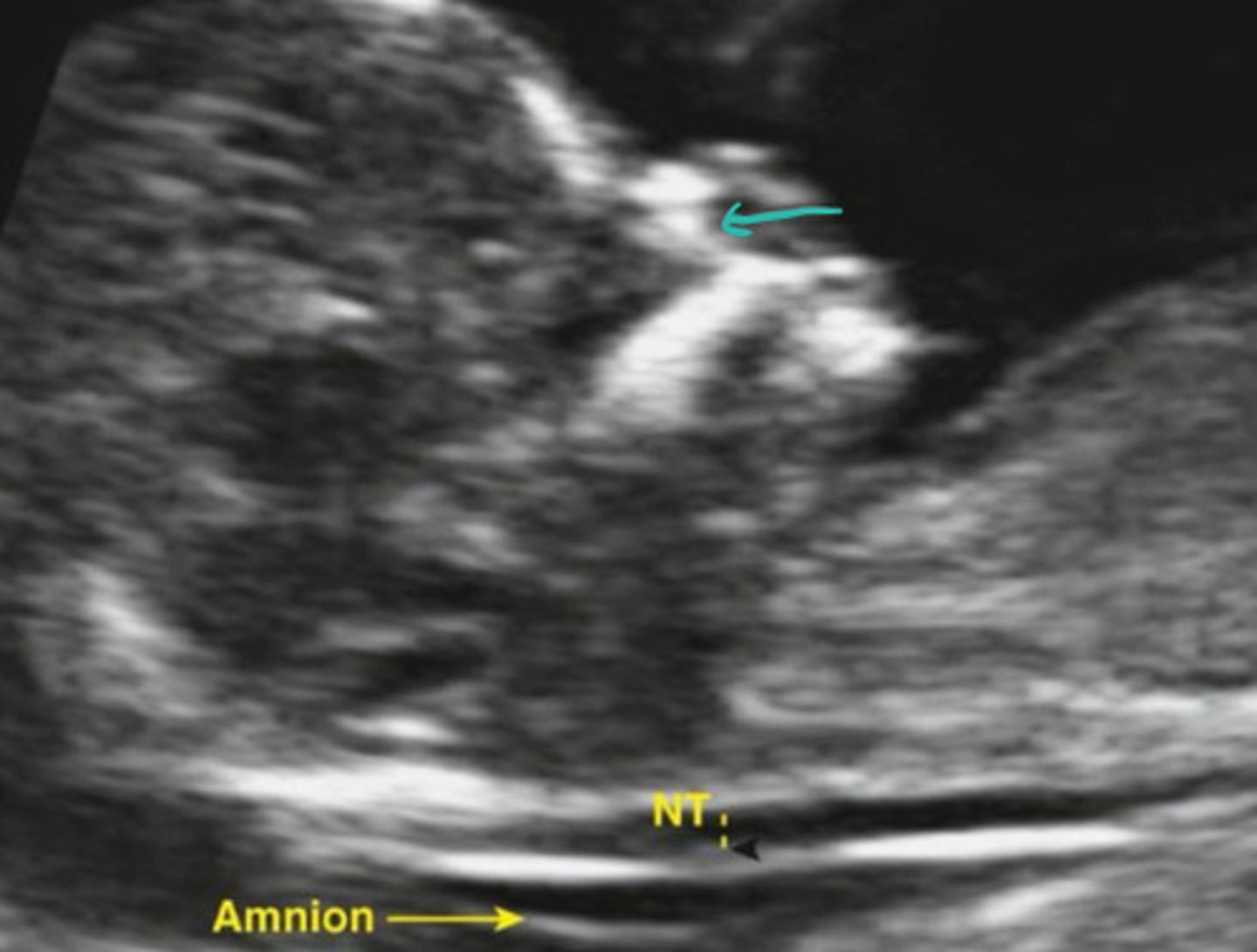
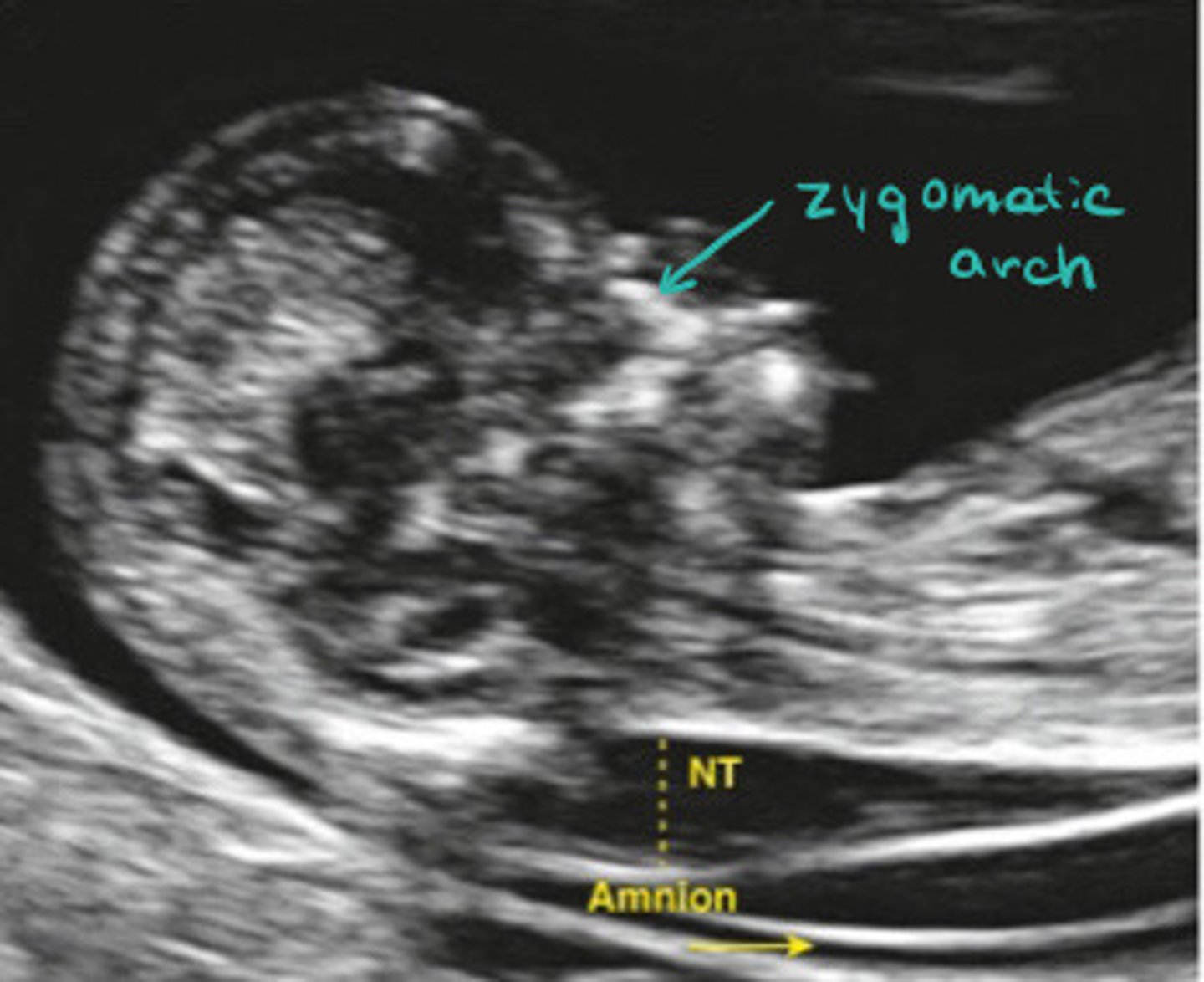
Zygotmatic arch
What is the teal arrow pointing to
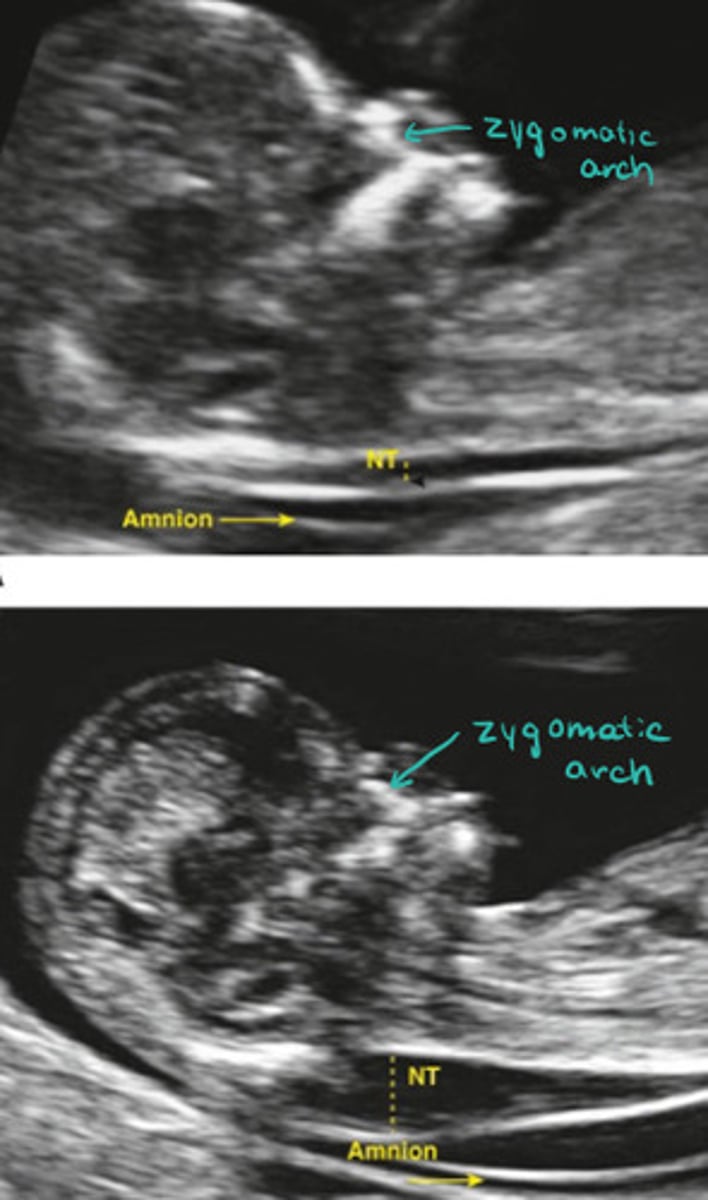
Mean you aren't mid sagittal and need to adjust your angle
What does it mean if you see the zygomatic arch in the image
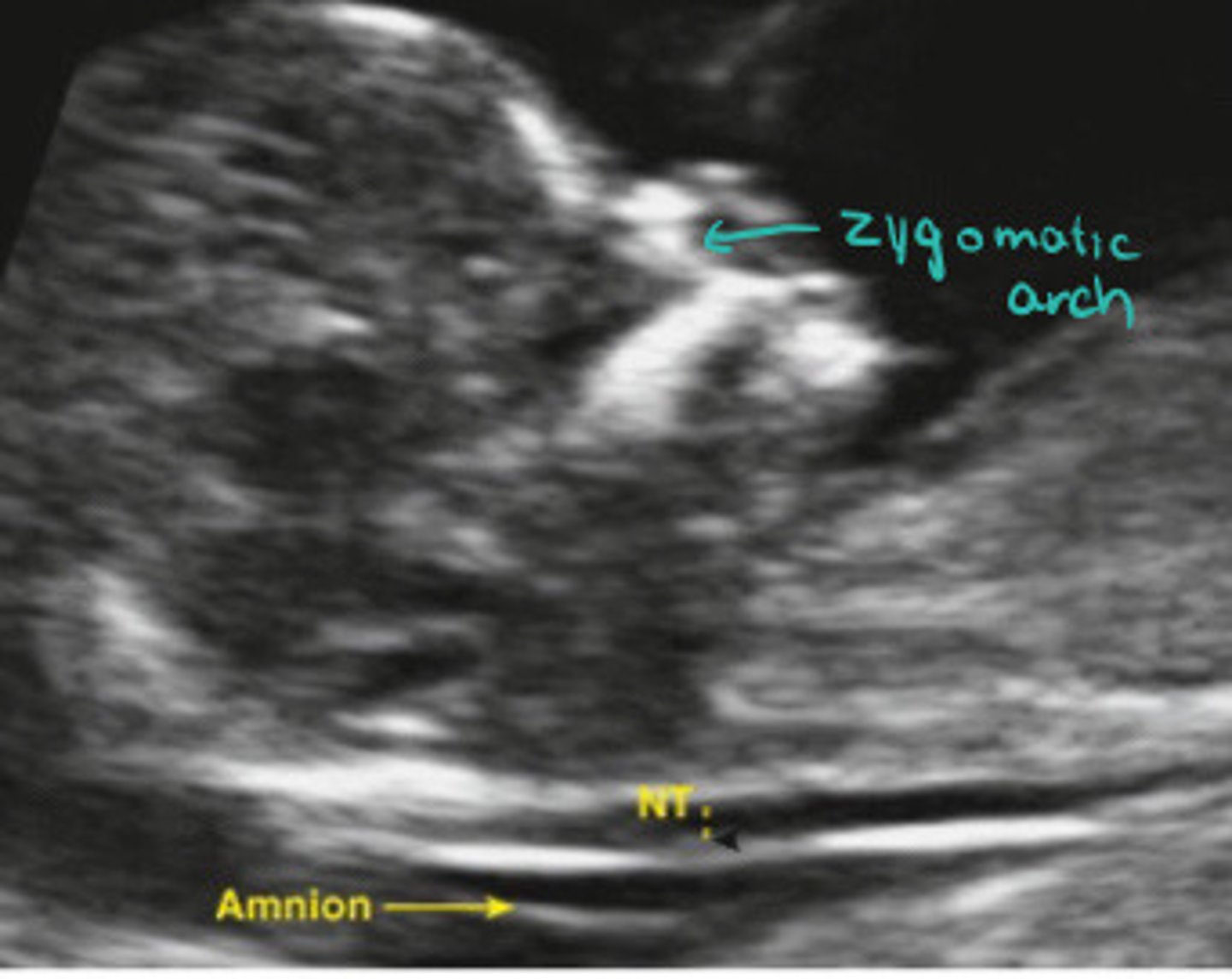
Normal
Visually estimating, does this NT look normal or thick
Thick
Visually estimating, does this NT look normal or thick
95%
What is the detection rate of trisomy 18 and 13 with FTS
Increased maternal age, increased fetal NT, decreased PAPP-A
What are all three trisomy's associated with
Increased
In trisomy 21, B-hCG is ______________
Decreased
In trisomy 13 & 18, B-hCG is ____________
B-hCG decreases and PAPP-A increases with gestation
Describe the increase/decrease of B-hCG and PAPP-A with normal pregnancy
11weeks
When do you start to see the nasal bone
Yes
Can you see the nasal bone in this picture
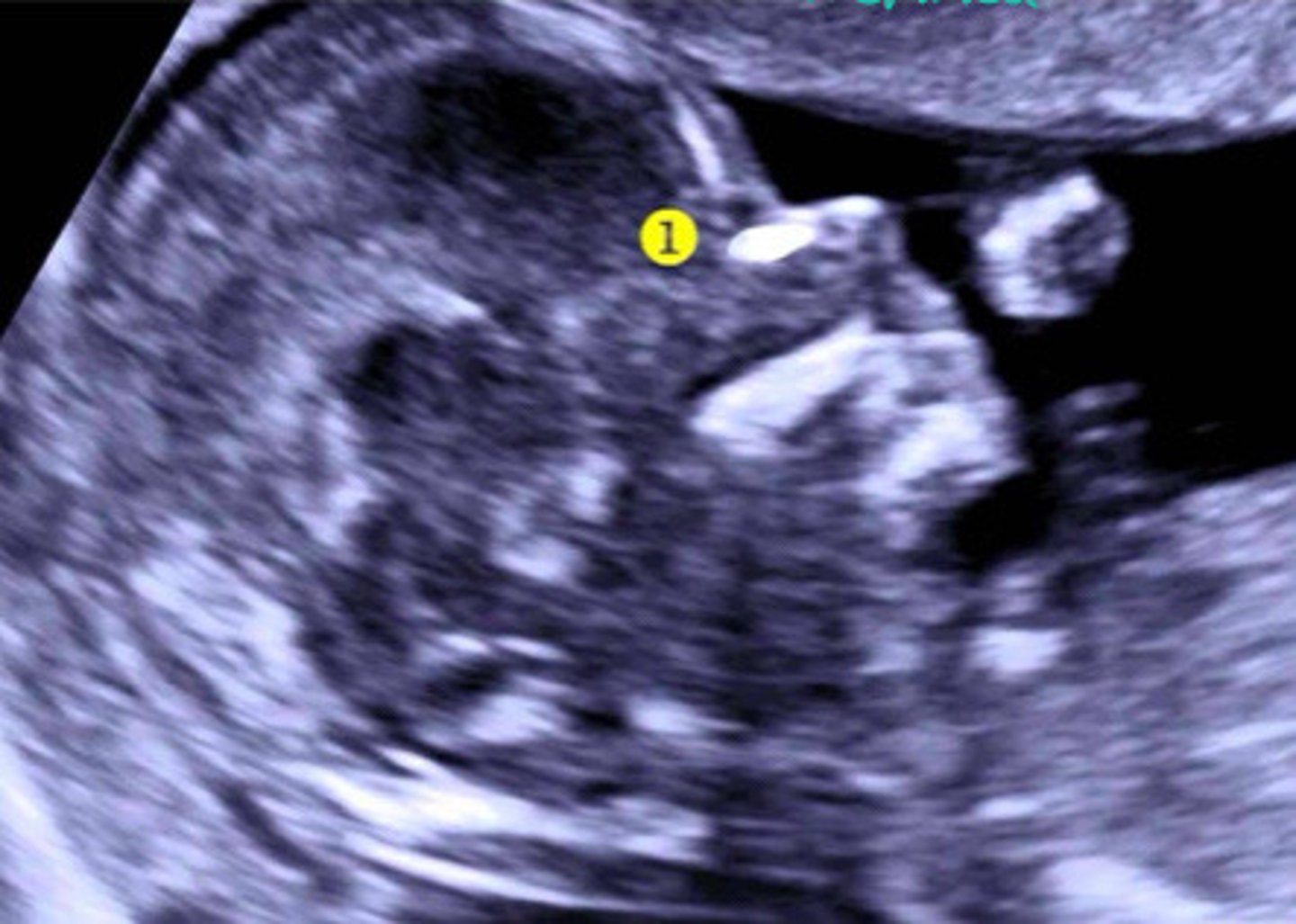
No, just a skin line
Can you see the nasal bone in this picture

60-70%
What percentage of fetuses with trisomy 21 have a hypoplastic nasal bone
50%
What percentage of fetuses with trisomy 18 have a hypoplastic nasal bone
30%
What percentage of fetuses with trisomy 13 have a hypoplastic nasal bone
Turner's syndrome
What does cystic hygroma indicate
Persistence of mid-gut herniation
What is omphalocle
Omphalocle, anechphaly, alobar holoprosencephaly, cystic hygroma, megacystis
What other abnormalities can be seen at the 11-14 week scan
Trisomy 13 and 18
What may megacystis indicate
Trisomy 13
What does alobar holoprosencephaly indicate
Alobar holoprosencephaly, facial defects, microcephaly, micronathia, VSD
What findings may indicate trisomy 13
True
T/F: trisomy 13 is associated with a high detection rate because it has a lot of unique indications on ultrasound
Reversed A wave in the DV and TR
What Doppler findings may indicate trisomy 21
False
T/F: the risk of turners and triploidy increase with maternal age
Uterine artery Doppler, PAPP-A
What is used to screen for preeclampsia
Low
Is PAPP-A is ______ it is considered a marker for preeclampsia
Dicrotic notch and low diastolic blood flow
What abnormal signs are you looking for in the uterine artery Doppler
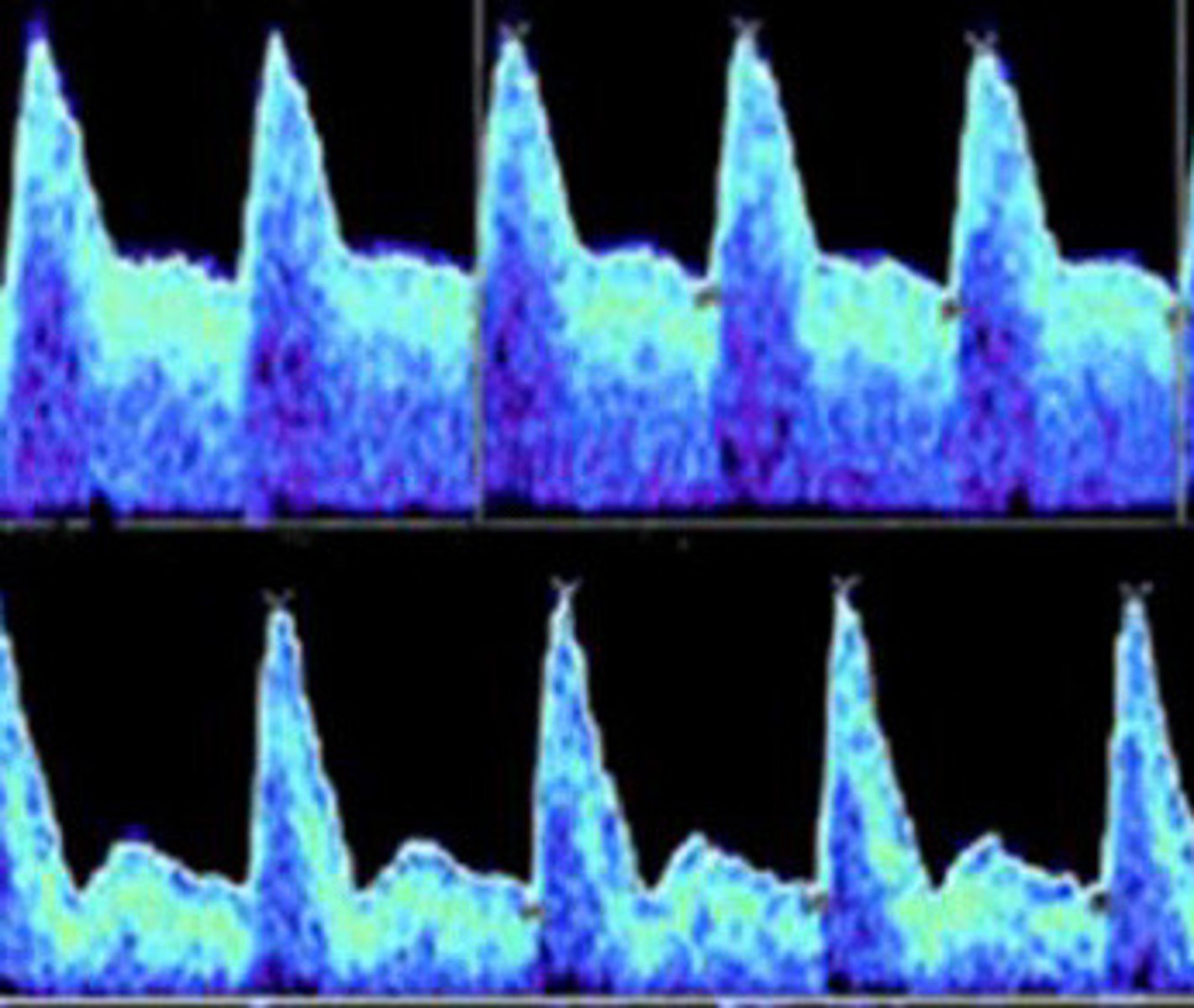
Normal
Is the spectral of the uterine artery on the top normal or abnormal
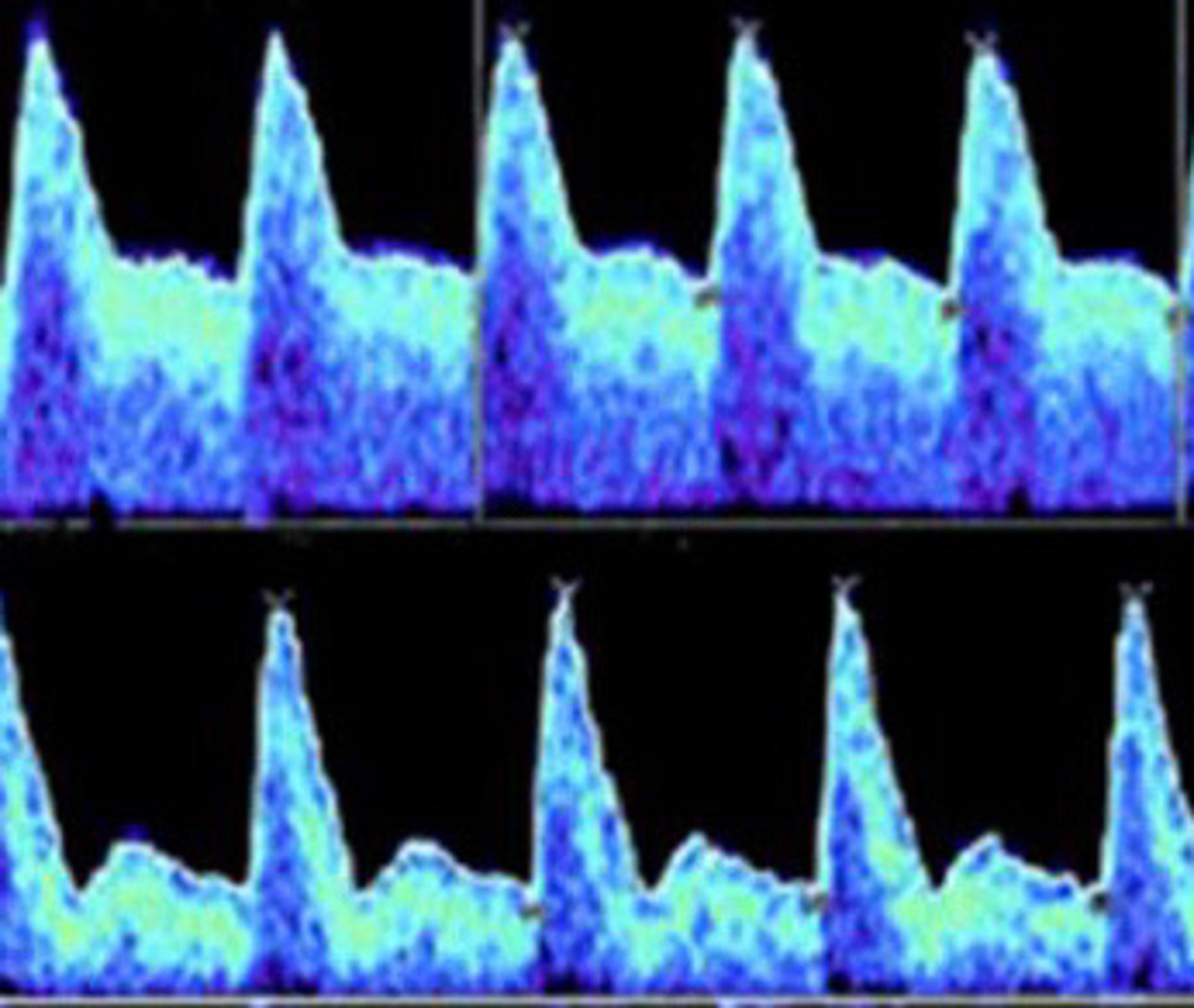
Abnormal
Is the spectral of the uterine artery on the top normal or abnormal
Prophylactic use of daily aspirin
How are those identified as high risk for preterm PE treated
False, only early or preterm PE
T/F: aspirin is successful in preventing both preterm (<37 weeks) and term PE (>37 weeks)
150bpm
What is the normal FHR at 14w
Trisomy 18 or tripleuoidy
What can bradycardia indicate
Turner's syndrome or trisomy 13
What can tachycardia indicate
170bpm
What is considered tachycardic at 14 weeks
Measure again later, baby may just be active
What should you do if you find a baby with a very high heart rate to confirm the finding
15 and 20 weeks
When is the triple screen performed
MS-AFP, uE3, B-hCG
What are the 3 things testes in the triple screen test
Maternal serum alpha feta protein
What is MS-AFP
Unconjugated estriol
What is uE3
70%
What is the detection rate of the triple screen
Trisomy 21 and 18, other chromosomal abnormalities
What does the triple screen detected
No
Can the triple screen detect trisomy 13
Fetal liver
What is AFP mainly produced by
Yolk sac, GI tract, kidneys, placenta
What else is AFP produced by
True
T/F: AFP crosses the placenta into maternal circulation
True
T/F: MSAFP and amniotic fluid AFP levels change with gestational age
>2.5 times the mean
What MSAFP value is suspicious for birth defects and multiples
Wrong date
What is the most common cause of abnormla levels of MSAFP
Multiples, fetal Demi's, fetal abnormality
What else can abnormal MSAFP levels be from
Sensitive, not specific
Is MSAFP levels sensitive or specific, or both
trisomy 21 and 18
What does decreased MSAFP relate to
Neural tube defect (NTD)
What is the most common cause of increased MSAFP Q
Omphalocele, gastroschisis, congenital renal disease, esophageal atresia
What else may increases MSAFP levels be related to
Trophoblasts
What is B-hCG produced by
Trisomy 21, multiples, molar pregnancy, wrong dates
What is increased B-hCG levels related to
Trisomy 18
What is decreases B-hCG levels related to
Fetal adrenal glands and liver
What produces and synthesizes uE3