Lab Test #2 Physiology
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exercise 4 - The Cardiovascular System ~ Blood; Exercise 5 - The Digestive System; Exercise 6: The Respiratory System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
What are the functions of the blood?
-Transport= transports nutrients and oxygen and removes waste products (carbon dioxide and urea)
-Protection= white blood cells and antibodies help
destroy and eradicate infectious microbes from the
body; platelets help in the production of blood
clots to prevent the loss of blood through broken
vessels
-Regulation= distributing heat as needed around
the body
What is the normal blood pH range?
7.35—7.45.
Whole blood makes up how much of body weight?
8%
Whole blood can be separated into what 2 major components?
Plasma and formed elements
Plasma makes up how much of the total blood
volume?
55%
Formed elements makes up how much of the
total blood volume?
45%
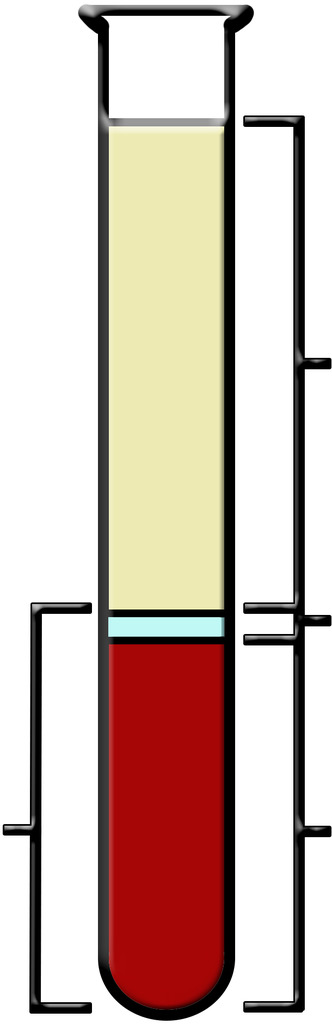
Plasma
the straw colored liquid in the upper part of the tube
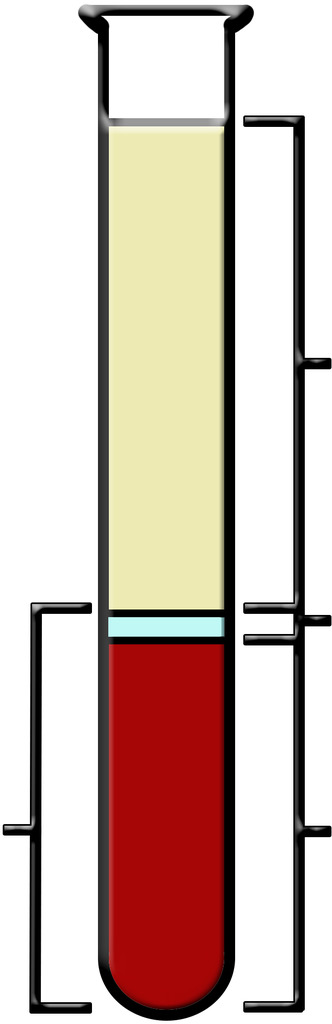
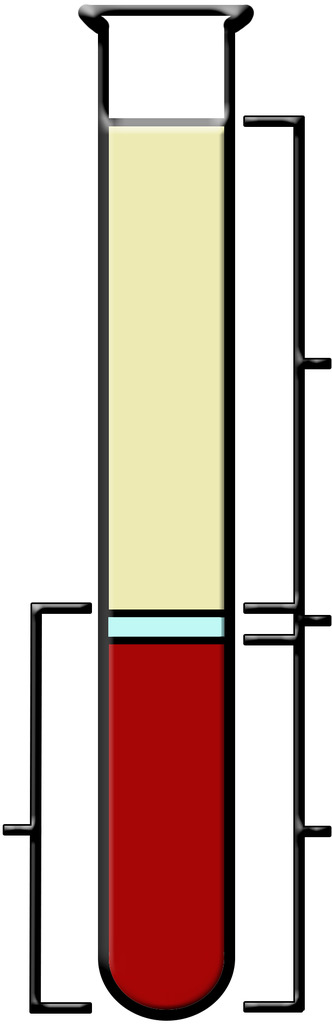
The Buffy Coat
small clear section which contains the white blood cells and platelets
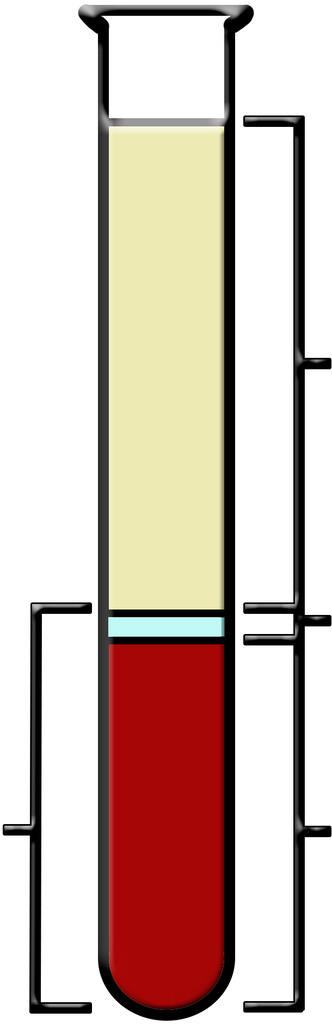
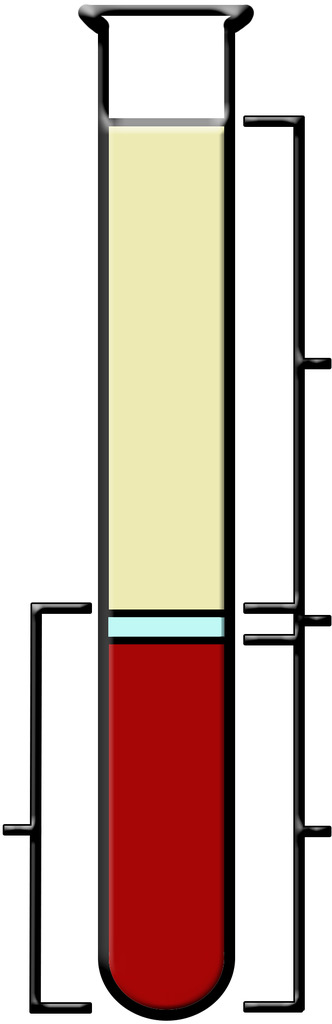
The Packed Cell Volume (PCV) or Hematocrit
red portion at the bottom of the tube which contains only red blood cells
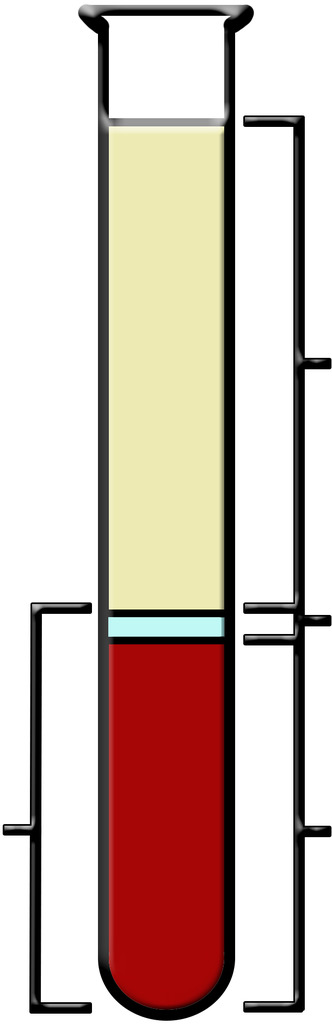
Plasma is composed mostly of ______ with
dissolved solutes including ________ and other
_______ like ______
-water (91%)
-proteins (7%)
-solutes (2%)= ions, hormones, nutrients, waste prod-
ucts, and gases)
The Formed Elements include
-Erythrocytes– Red Blood Cells (RBC)
-Leukocytes– White Blood Cells (WBC)
-Platelets
____________ are biconcave disc shaped cells containing the protein hemoglobin involved in the transport of respiratory gases (Oxygen and Carbon dioxide)
Mature RBC’s
Mature RBC’s are biconcave disc shaped cells containing the protein _________ involved in the transport of ________________.
hemoglobin; respiratory gases (Oxygen and Carbon dioxide)
Do RBC’s contain a nucleus or any other cellular organelle
No
RBC’s live for an average of ________ before they are removed from circulation by phagocytic cells in the spleen, liver, and red bone marrow
120 days
The body normally makes as many RBC’s as are removed from circulation each minute (____________) so as to ____________
1-2 million RBC’s per minute; maintain a constant hematocrit
Lower than normal Hematocrit which decreases oxygen delivery to tissues
anemia
What various conditions cause anemia?
nutritional deficits of iron which decreases
hemoglobin production, sickle cell anemia
a disease caused by the faulty production of hemoglobin and
hemolytic disease
sickle cell anemia
hemolytic disease
diseases that destroy RBC’s and decrease their numbers.
Higher than normal Hematocrit which increases the viscosity and resistance to blood flow
Polycythemia
What causes polycythemia?
Severe dehydration, increased production or abuse of erythropoietin (EPO)- the hormone that stimulates RBC production, and the introduction of more blood into the body than normal as in blood doping
hormone secreted by the kidney to stimulate the production of red blood cells in red bone marrow
Erythropoietin
___________ are produced from the development and differentiation of pluripotent stem cells in red bone marrow
The formed elements, including WBC’s
Do WBC’s contain a nucleus?
Yes
With the exception of the Lymphocytes, ______ do not divide once they enter blood circulation from red bone marrow.
WBC’s
The 5 classes of leukocytes are subdivided into 2 major subdivisions based on the presence or absence of cytoplasmic granules:
-Granulocytic Cells (Granulocytes)
-Agranulocytic Cells (Agranulocytes)
Granulocytic Cells (Granulocytes)
Neutrophils, Basophils, and Eosinophils
Agranulocytic Cells (Agranulocytes)
Monocytes and Lymphocytes
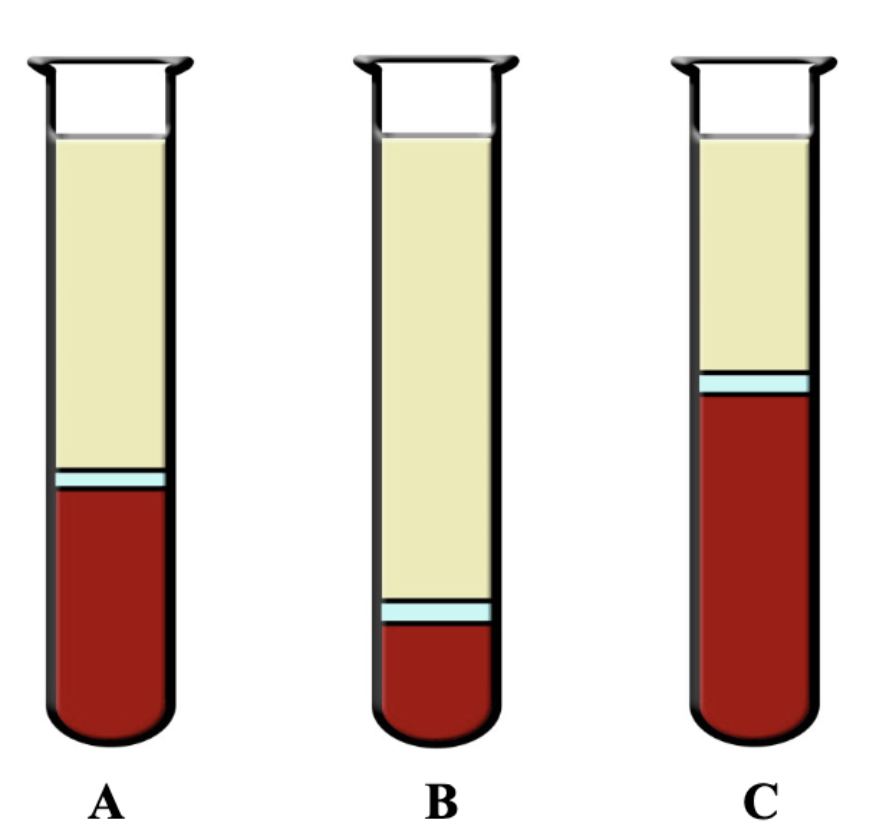

What is A? What is the average in males and females?
Normal Hematocrit
Males= average 45%
Females=average of 42%
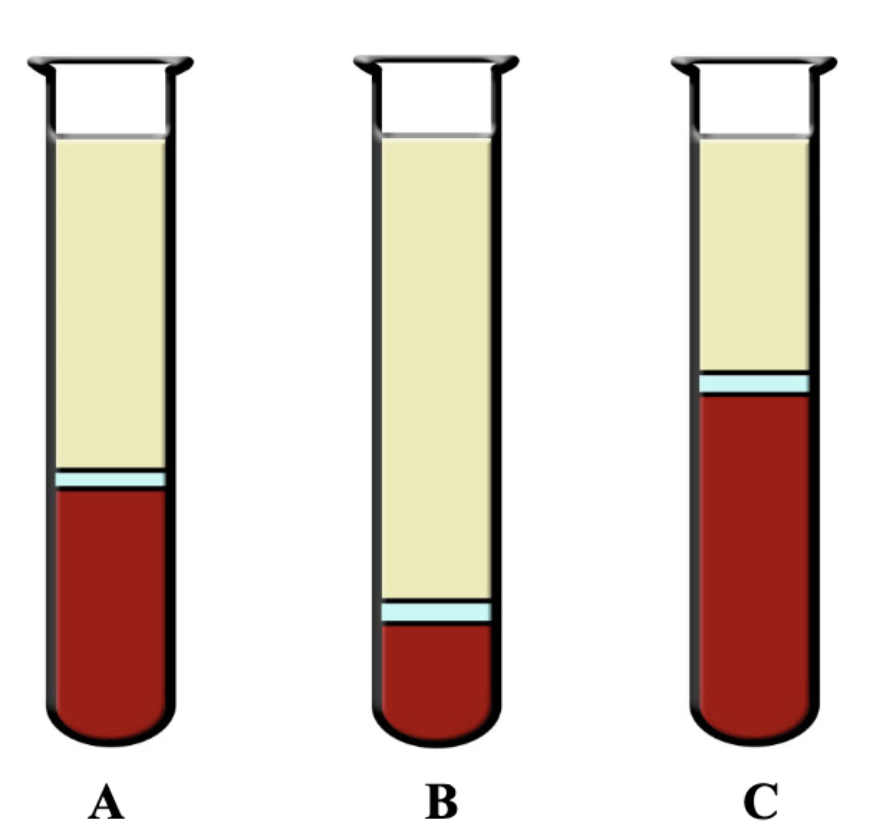

What is B?
Anemia (Lower than normal hematocrit)
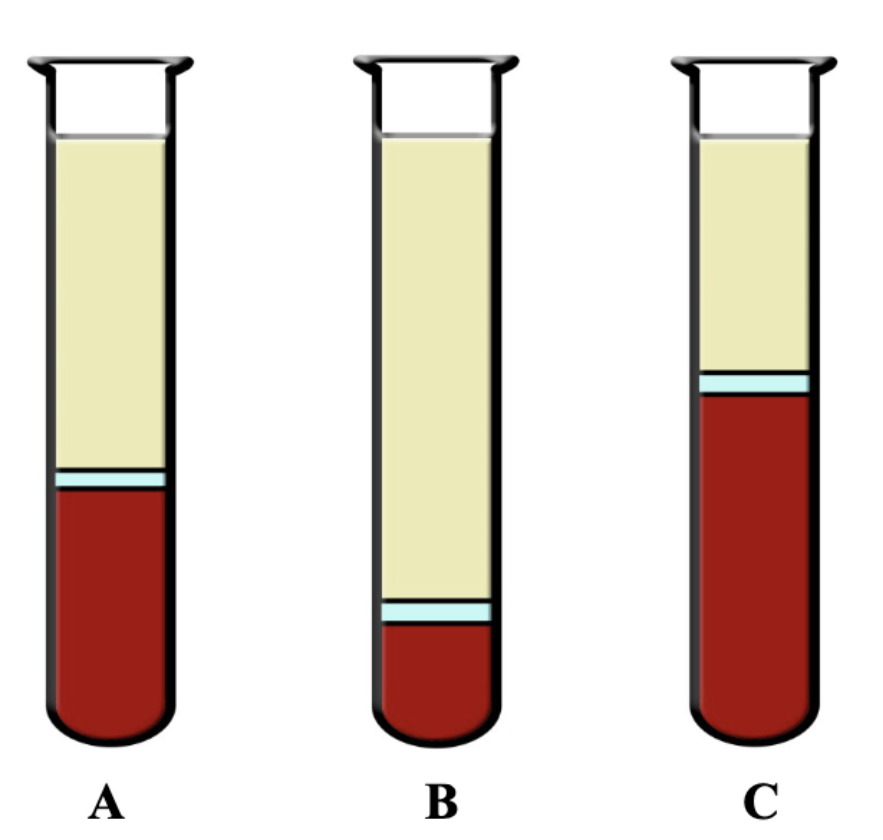

What is C?
Polycythemia (Higher than normal hematocrit)
The granular leukocytes are so named due to the presence of ___________ located in their _____
large numbers of membrane bound vesicles (Granules); cytoplasm
What happens to granulocytes when they are activated?
They perform a mass exocytosis of their granules (called degranulation)
The increase in WBC count is referred to as ________
Leukocytosis
Leukocytes
white blood cells
Erythrocytes
red blood cells
Thrombocytes
platelets
Granulocyte with 3 - 5 lobed nucleus that eradicates microbes via phagocytosis and through the production of strong oxidants like hydrogen peroxide
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are very aggressive bactericidal cells killing bacteria through _______ and the release of ________
phagocytosis; chemicals that produce strong oxidants
Neutrophils increase in numbers during
bacterial infections.
Granulocyte with a bi-lobed nucleus with red orange staining granules
Eosinophils
Eosinophils release __________ all effective in the destruction of ___________
-strong oxidants, toxic proteins and a neurotoxin
-parasitic worms and the eradication of allergens
Which WBC release Histaminase to diminish inflammatory responses?
eosinophils
Eosinophils increase in numbers at sites of _________.
parasitic worm infections, allergy attacks, and inflammation.
Granulocyte with deep staining blue or purple granules that release inflammatory compounds like histamine
Basophils
Basophils normally increase in numbers with _________
tissue trauma, chickenpox, sinusitis, diabetes mellitus, myxedema, and polycythemia
Agranulocytic Leukocyte including T-Cells and B-Cells involved in Specific Immune Responses. The smallest of the leukocytes found in the blood.
Lymphocytes
T-Cells
attack infected cells and cancerous cells directly
B-cells
produce antibodies against specific antigen when activated
Activated B-cells are called what?
Plasma cells
the largest of the leukocytes containing a horseshoe shaped nucleus with an abundance of light blue cytoplasm
Monocytes
These cells are highly phagocytic capable of engulfing large numbers of bacteria, dead or damaged cells, and virally infected cell
Monocytes
are called macrophages once they emigrate into tissues
Monocytes
Where are the A and B antigens found?
Plasma membrane of Erythrocytes
Which blood type contains A antigens and anti-b antibodies?
Type A Blood
Which type of blood contains B antigens and anti-a antibodies?
Type B Blood
Which type of blood contains A & B antigens and neither anti-a nor anti-b antibodies?
AB
Which type of blood does not contain the A nor the B antigen but has both anti-a and anti-b antibodies?
Type O Blood
Which blood type is considered to be the Universal Recipient?
Type AB+ Blood
Which blood type is considered to be the Universal Donor?
Type O- Blood
Which blood types can a person with type A+ blood receive?
A+, A-, O+, O-
Which blood types can a person with type A- blood receive?
A- and O-
Which blood types can a person with type B+ blood receive?
B+, B-, O+, O-
Which blood types can a person with type B- blood receive?
B- and O-
What are all of the blood types that a person with type AB+ blood can receive?
A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+ and O-
Which blood types can a person with type AB- blood receive?
A-, B-, AB-, and O-
Which blood types can a person with type O+ blood receive?
O+ and O-
Which blood types can a person with type O- blood receive?
O-
Agglutination
the clumping of RBC’s together as antibodies cross link with their antigen
When is the agglutination reaction used?
To determine the blood type of someone whose blood type is not known
If the person’s blood sample demonstrates a positive agglutination reaction for a particular antigen then what does that mean?
that antigen is present on the surface of their red blood cells.
If a person has a positive agglutination reaction for anti-A, anti-B, and anti-Rh sera then that person’s blood type is _____.
AB+
A blood sample does not clump together during a _______ agglutination. In this case, we can determine that a particular antigen is absent from the surface of a person’s RBC if the agglutination reaction for the antigen is negative.
negative
If we treat an unknown blood sample with anti-A, anti-B, and anti-Rh sera and we observe a negative agglutination reaction for all 3 then we can determine that Antigen-A, Antigen-B, and Antigen-Rh are absent from the surface of the RBC and the person’s blood type is ____.
O-
__________ potentially occurs when an Rh negative female becomes pregnant with an Rh positive baby
Hemolytic disease of a newborn (HDN)
The process of breaking down food is accomplished by two digestive mechanisms:
mechanical digestion and chemical digestion
the physical degradation of larger food materials into smaller pieces
Mechanical Digestion
the breakdown of the larger food materials at the chemical level, separating individual organic monomers from their larger polymers
Chemical digestion
Incisors are able to slice, canines can puncture, and premolars and molars are used to grind food in a process
Mastication
What are the general functions of saliva?
-moistening food to make it easier to swallow
-dissolving food for tasting
-buffering acidic foods with the help of bicarbonate ions
-protecting the mouth from infection with its rinsing action
Major components of saliva include:
Immunoglobulin A – important in preventing attachment of microbes, preventing penetration into the epithelium
Bacteriolytic lysozyme – kills bacteria
Salivary amylase – Carbohydrase
Lingual lipase – Lipase
Bicarbonate – buffers acidic foods
As food is masticated and mixed with saliva, it is turned into a semi-solid mass referred to as a _____. When it is time to swallow, the bolus is transferred to the ______ where the process of _______ (swallowing) is initiated
bolus; oropharynx; deglutination
Components of gastric juices include:
Water
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) – denatures proteins, making it easier for protease enzymes to target peptide bonds. Also has an antimicrobial function.
Pepsinogen – activated into pepsin (Protease) by HCl within the stomach lumen.
Gastric lipase – Lipase
Intrinsic factor – aids in vitamin B12 absorption within the ileum
____ and ______ are accessory digestive organs that secrete digestive aids into the duodenum. Bile, which is produced by the liver, then concentrated, stored and released by the gall bladder, aids lipid digestion by serving as an emulsifier. Bile also aids in lipid absorption by making fatty acid chains more water soluble. In addition, bile also contains bicarbonate to aid in the neutralization of the acidic chyme coming from the stomach
The liver and pancreas
Components of the liver
Bile – lipid emulsifier consisting of water, bile salts, cholesterol, bicarbonate, bilirubin, and ions
Components of the pancreatic juices
Bicarbonate – neutralizes acidic chyme from the stomach
Trypsinogen – activated into trypsin (Protease) by enterokinase within the duodenum.
Chymotrypsinogen – activated into chymotrypsin (Protease) by trypsin.
Procarboxypeptidase – activated into carboxypeptidase (Protease) by trypsin.
Proelastase – activated into elastase (Protease) by trypsin.
Pancreatic amylase – Carbohydrase
Pancreatic lipase – Lipase
Ribonuclease – Nuclease
Deoxyribonuclease – Nuclease
The small intestine is divided into three regions. The duodenum receives chyme from the stomach thorough the pyloric sphincter. Secretions from the liver and pancreas enter the duodenum through ducts piercing the mucosa. Following the duodenum are the jejunum and ileum. Mechanical and chemical digestion occur throughout the small intestines. In addition, the majority of absorption occurs within the ileum. Mechanical digestion within the small intestine occurs through peristalsis. This serves to mix chyme with secretions from the liver, pancreas and small intestines. It also propels chyme through the small intestine. Chemical digestion occurs both within the lumen of the small intestine through bile and pancreatic enzymes as well as along the mucosal border in a region referred to as the brush border.
Enzymes found within the brush border include:
Alpha dextrinase – Carbohydrase
Maltase – Carbohydrase
Sucrase – Carbohydrase
Lactase – Carbohydrase
Aminopeptidase – Protease
Dipeptidase – Protease
Nucleosidases – Nuclease
Phosphatases – Nuclease
Cholecystokinin (CCK) from the intestinal wall is stimulated by the presence of
protein and fat in the small intestine
stomach cell that secretes pepsinogen is the
chief cell
enzyme called salivary amylase functions to begin digestion
carbohydrates
Parts of the G.I. tube in the CORRECT order of food movement:
oropharynx, laryngopharynx, esophagus, stomach, pyloric sphincter
A structure that produces no digestive secretions of any kind is the
gallbladder
The large intestine consists of several regions ending in the
rectum and anus
Chemical digestion in the large intestine is associated with several bacterial enzymes that are responsible for producing vitamins _ and _. No human produced enzymes are found in the large intestine.
B and K
Feces are eventually eliminated when the defecation reflex is initiated when fecal matter enters into the rectum.
Regulation of digestion is accomplished by interactions of the
diencephalon, cerebrum, enteric nervous system, autonomic nervous system and endocrine system
The enteric nervous system independently regulates digestion through the activity of two plexuses:
the submucosal plexus and the myenteric plexus
The parasympathetic nervous system will further ______ the enteric nervous system as well as promote salivation, secretion of gastric fluids, and defecation
stimulate