Carbonyl Chemistry Part 1: Additions and Carboxylic Acids
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 16-18 - Jones
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
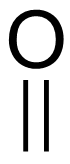
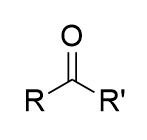
carbonyl
an oxygen double-bonded to a carbon (C=O) in an organic compound
ketone
a carbonyl group bonded to two R groups
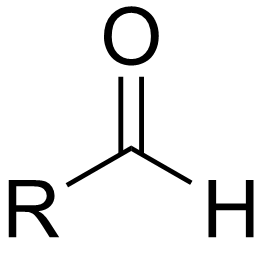
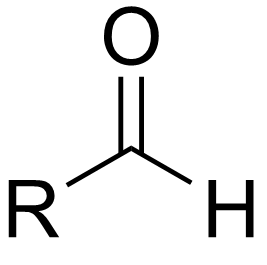
aldehyde
a carbonyl group bonded to one R group and one hydrogen; terminal group
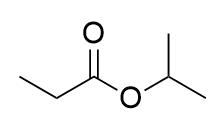
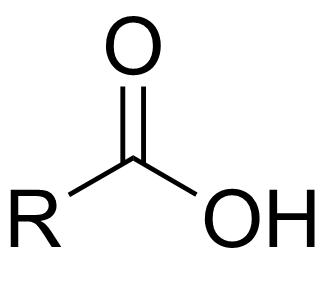
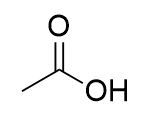
carboxylic acid
a carbonyl group bonded to one R group and one hydroxyl group (-OH); terminal group
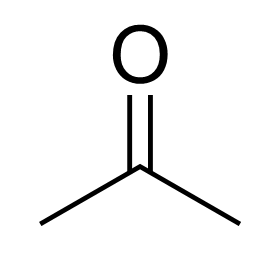
acetone
simplest ketone
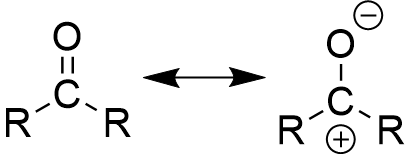
resonance forms of carbonyl compounds
allows carbonyl groups to be both nucleophiles and electrophiles
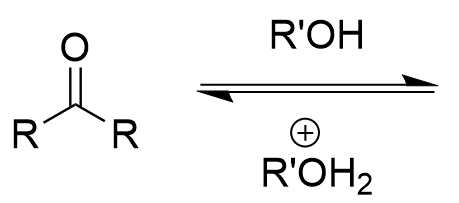
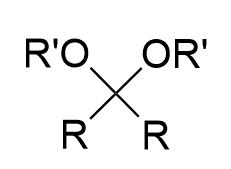
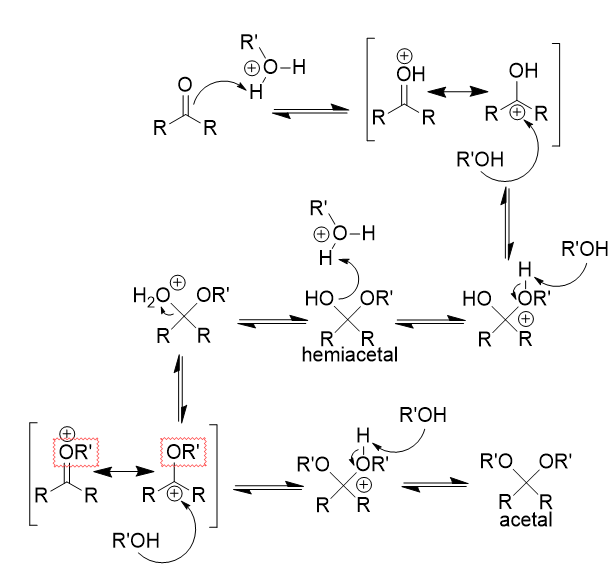
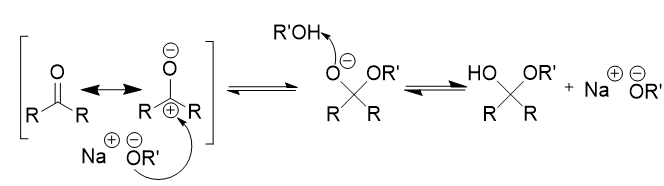
nucleophlic addition of alcohol to carbonyl (acidic)
acetal product (via hemiacetal ‘crossroads’); fully reversible with water
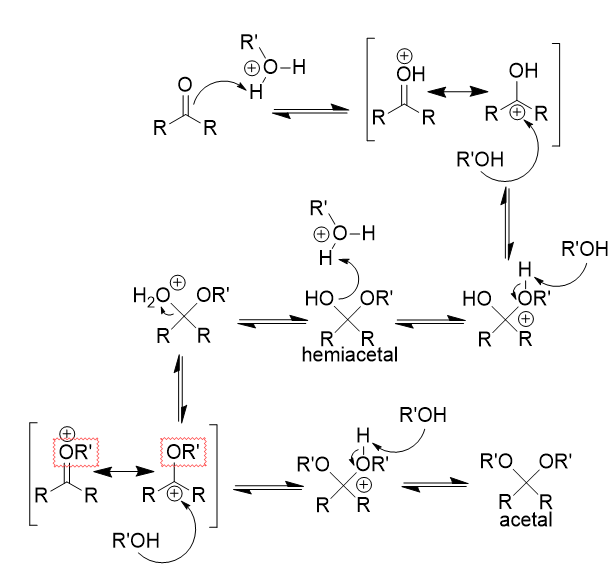
nucleophlic addition of alcohol to carbonyl (acidic) mechanism
double bond attacks proton → hydroxyl formation
resonance forms
alcohol attacks (electrophlic) carbonyl carbon
proton removal → hemiacetal formation
hydroxyl attacks proton → water leaves
alcohol attacks (electrophlic) carbonyl carbon
proton removal → acetal formation
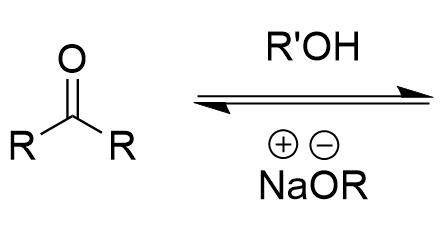
nucleophlic addition of alcohol to carbonyl (basic)
hemiacetal; no protonation, no leaving group; prefers carbonyl; equilibrium

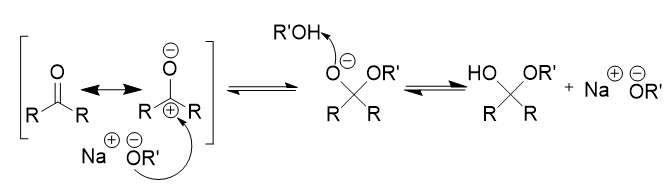
nucleophlic addition of alcohol to carbonyl (basic) mechanism
resonance forms
nucleophile attacks (electrophlic) carbonyl carbon
proton gain → hemiacetal formation
no more protons - only nucleophile left
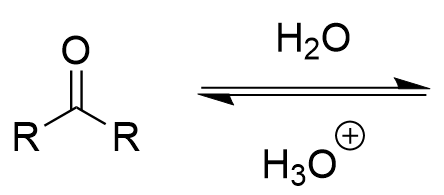
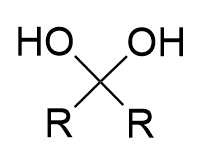
hydration of carbonyl (acidic)
hydrate/geminal alcohol; fully reversible
hydration of carbonyl (acidic) mechanism
replace R’ with H
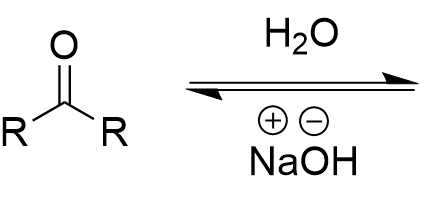
hydration of carbonyl (basic)
hydrate/geminal alcohol; fully reversible
hydration of carbonyl (basic) mechanism
replace R’ with H
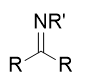
imine
compound containing carbon–nitrogen double bond (C=N)
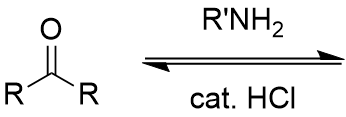
addition of primary amine (NH2R) to carbonyl
imine/Schiff base; reversible with acid and water
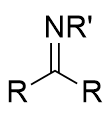
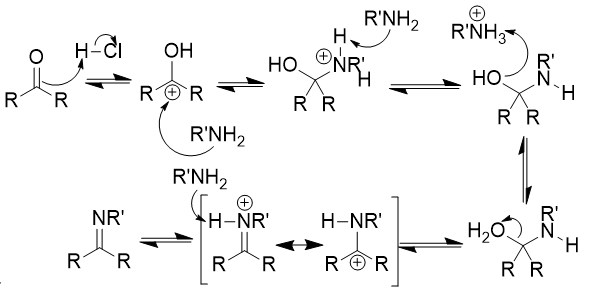
addition of primary amine (NH2R) to carbonyl mechansim
double bond attacks proton (from catalytic HCl)
amine attacks (electrophlic) carbonyl carbon
proton removal
hydroxyl attacks proton → water leaves
proton removal → imine formation
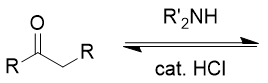
addition of secondary amine (NR2H) to carbonyl
enamine; mixture possible based on R groups; reversible with acid and water
addition of secondary amine (NR2H) to carbonyl mechanism
double bond attacks proton (from catalytic HCl)
amine attacks (electrophlic) carbonyl carbon
proton removal
hydroxyl attacks proton → water leaves
proton removal from α-carbon by base → enamine formation
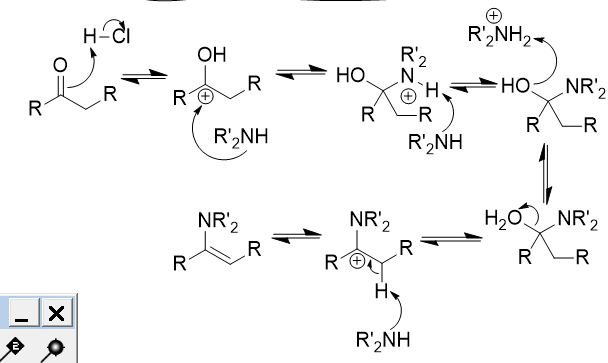
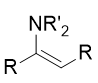
enamine
carbon-carbon couble bond (C=C) and amine
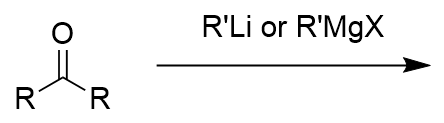
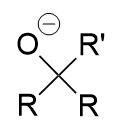
organolithium or Grignard addition to carbonyl
tertiary oxygen anion; alcohol with protonation with water/proton source; via nucleophlic attack of (electrophillic) carbonyl carbon
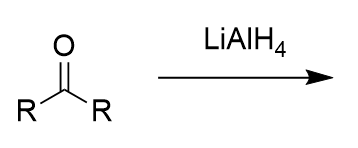
lithium aluminium hydride addition to carbonyl (reduction)
secondary oxygen anion; alcohol with protonation with water/proton source; via hydride attack of (electrophillic) carbonyl carbon; irreversible
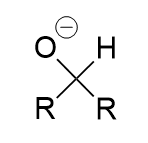
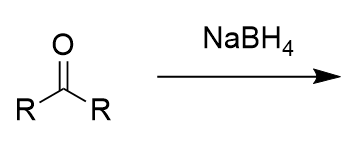
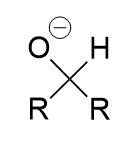
sodium borohydrate addition to carbonyl (reduction)
secondary oxygen anion; alcohol with protonation with water/proton source; via hydride attack of (electrophillic) carbonyl carbon; irreversible
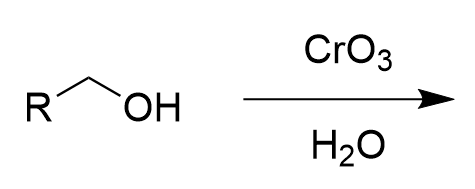
chromate salt addition to 1° alcohol in water (oxidation)
carboxylic acid; irreversible
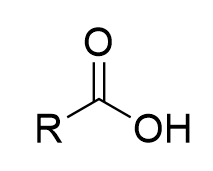
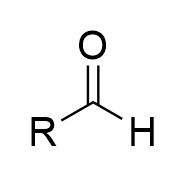
chromate salt addition to 1° alcohol in dry pyridine (oxidation)
aldehyde; irreversible
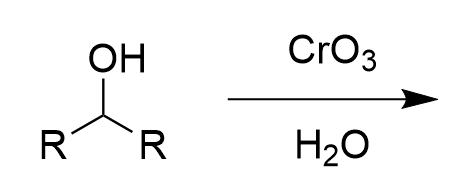
chromate salt addition to 2° alcohol (oxidation)
ketone; irreversible
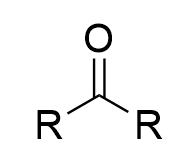
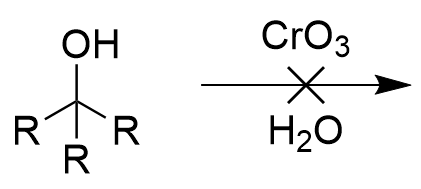
chromate salt addition to 3° alcohol (oxidation)
no reaction; sterics
chromate salt addition to 2° alcohol (oxidation) mechanism
hydroxyl oxygen attacks chromium
water takes hydrogen
chromate ester formation
hydronium donates proton
proton transfer from carbonyl carbon → separation
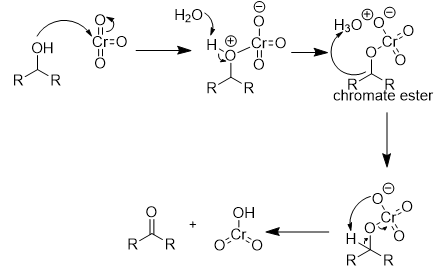
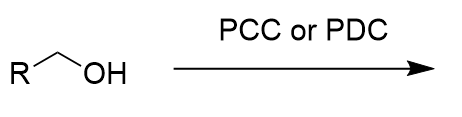
addition of weak oxidant (PCC/PDC) to alcohol (oxidation)
aldehyde; cannot go to carboxylic acid; irreversible
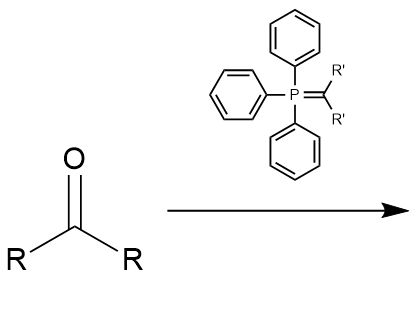
Witting Reaction: addition of phosphorus ylide to ketone
alkene; carbon-carbon bond; reverse ozonolysis; irreversible
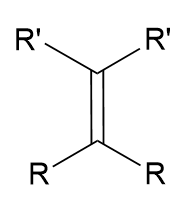
Witting Reaction: addition of phosphorus ylide to ketone mechanism
form and break a square
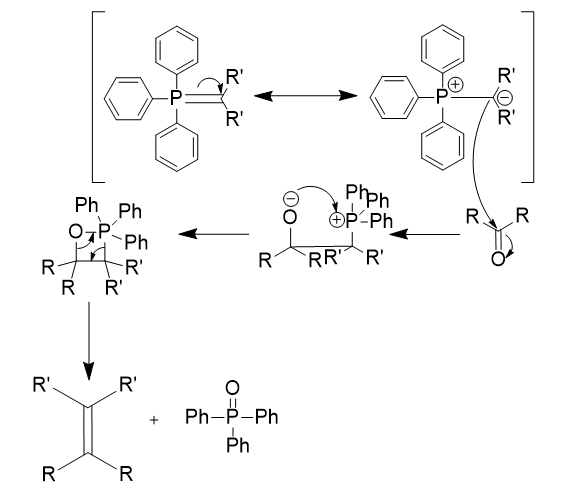
ylide
neutral dipolar molecule containing a negative charge adjacent to a positive charge
formation of phosphorus ylide
SN2
deprotonation
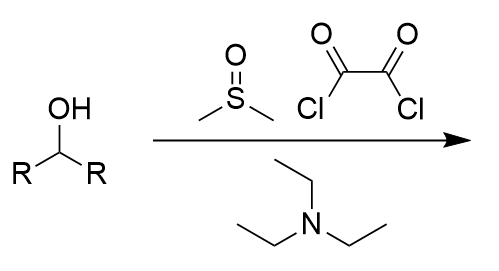
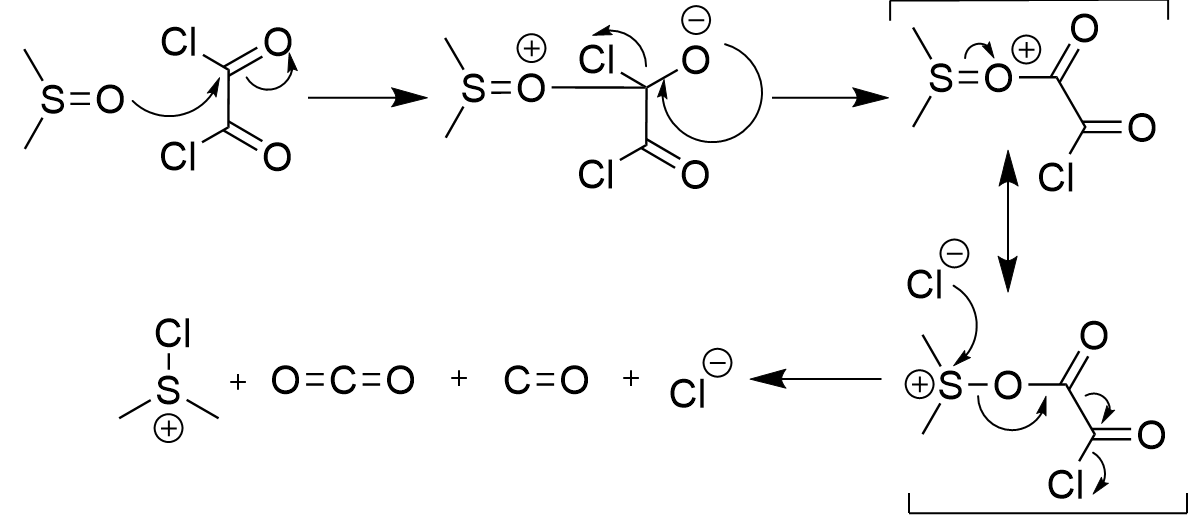
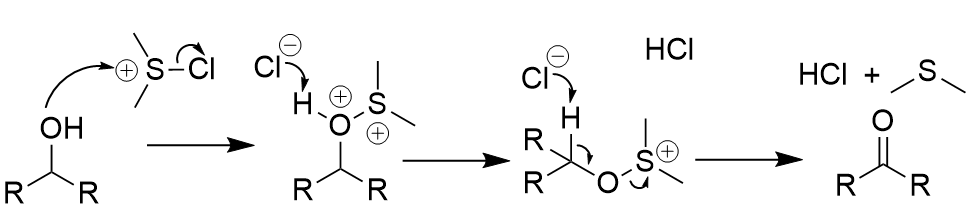
Swern Oxidation - DMSO, oxalyl dichloride, triethyl amine on alcohol
carbonyl; does not work on tertiary alcohols; irreversible; also makes CO, CO2, dimethyl sulfoxide and 2 x HCL
Preparation of Swern catalyst mechanism
Swern oxidation mechanism
oxygen attacks (electrophlic) sulfur
deprotonation x 2
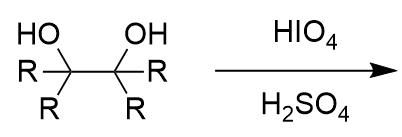
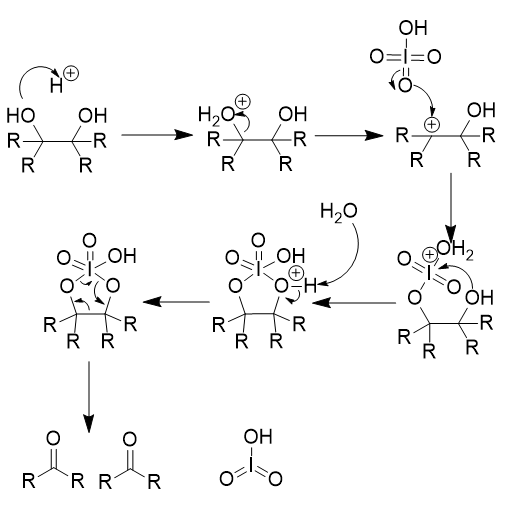
Oxidative Cleavage of vicinal diols - HIO4/H2SO4
two carbonyl-containing groups; irreversible
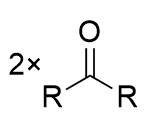
Oxidative Cleavage of vicinal diols - HIO4/H2SO4
note cyclic intermediate/transition state
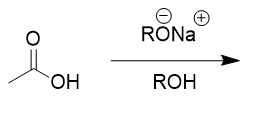
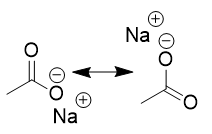
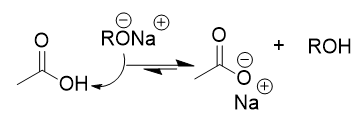
carboxylic acids in basic organic environment
deprotonates; resonance; spectator ion
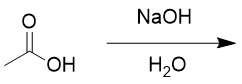
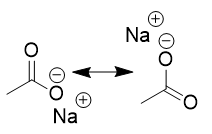
carboxylic acids in basic aqueous environment
deprotonates; resonance; spectator ion
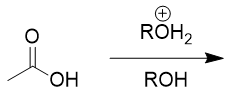
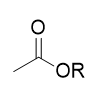
carboxylic acids in acidic organic environment
Fischer’s esterification; reversible; equilibrium
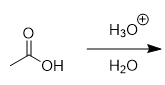
carboxylic acids in acidic aqueous environment
no change; exchangable protons
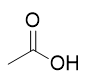
carboxylic acids in base mechanism
deprotonation
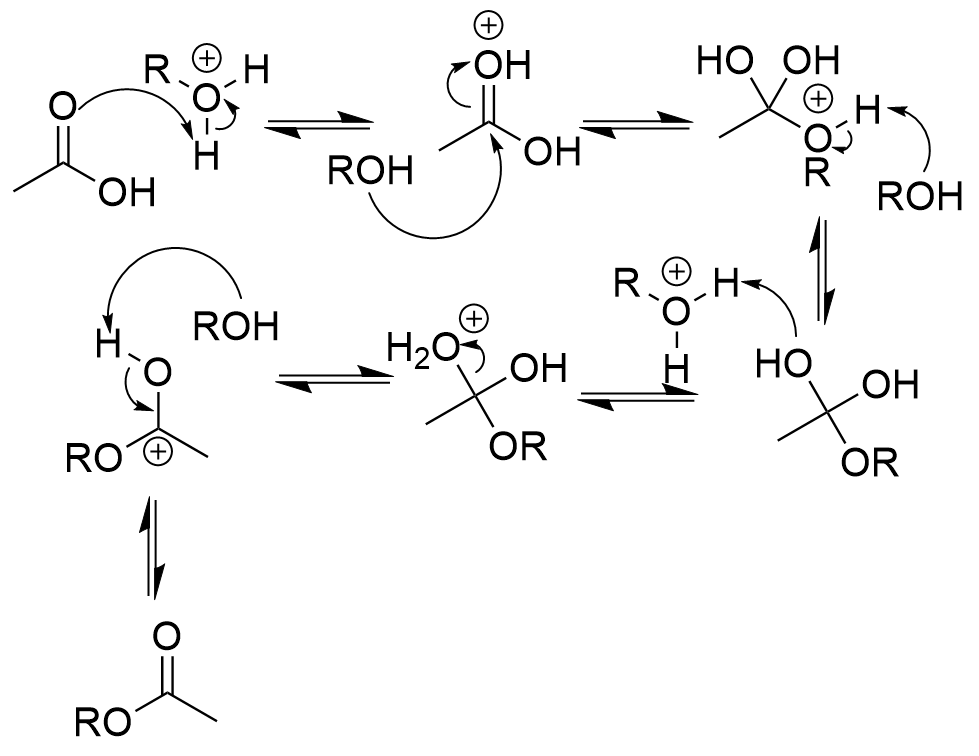
Fischer’s esterification mechanism
carbonyl oxygen attacks acid → protonation
forms hemiacetal
protonation and dehydration
reform carbonyl via deprotonation
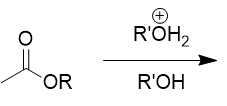
transesterifcation
switch R group on ester; essentially Fischer’s esterification mechanism
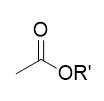
ester
carbonyl + ester; formed from carboxylic acids
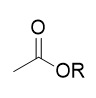
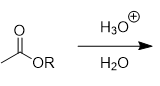
ester hydrolysis
reverse of Fischer esterification; reversible
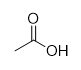
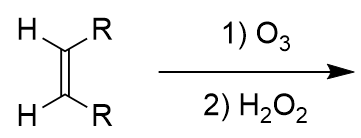
ozonolysis and oxidation of an alkene
2x carboxylic acid
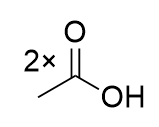
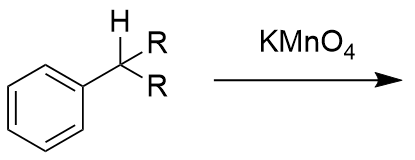
addition of KMnO4 to substituted benzene
benzoic acid
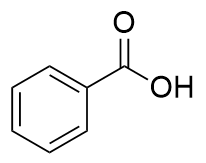
strong oxidants
HNO3, KMnO4, CrO3, K2Cr2O7, RuO4
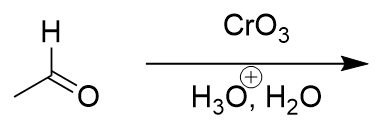
addition of chromate salt to aldehyde
carboxylic acid
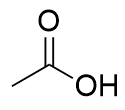
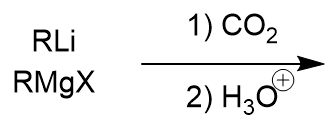
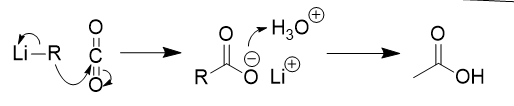
Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Carbon Dioxide
carboxylic acid
Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Carbon Dioxide
attack on carbon of CO2
protonation
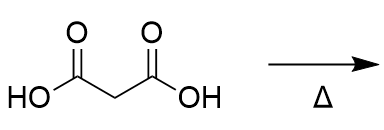
decarboxylation
removes one acid; needs one carboxylic acid at the beta position of another
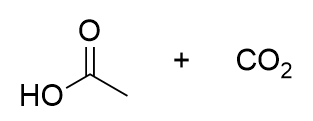
decarboxylation mechanism
proton transfer
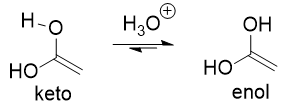
enol → keto
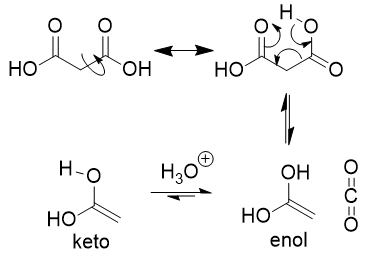
keto-enol tautomerization
many aldehydes and ketones are in equilibrium with a structural isomer known as the enol form; not resonance forms but structural isomers that can interconvert
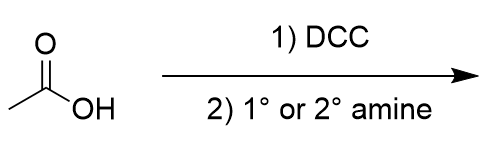
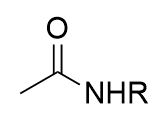
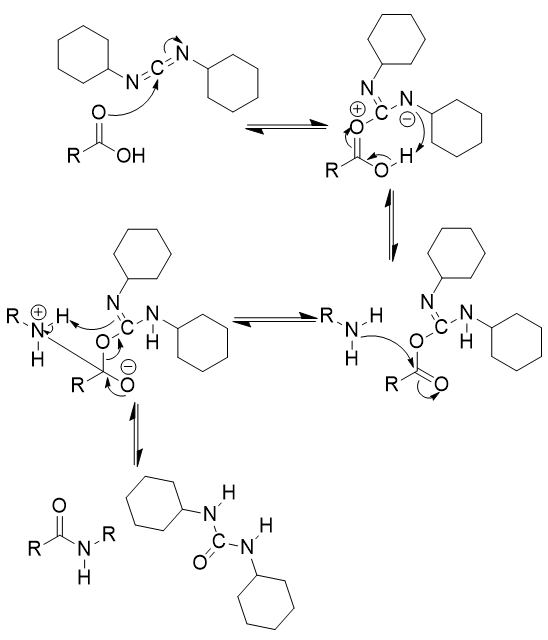
addition of DCC and amine to carboxylic acid
amide synthesis; reversible; urea side product
addition of DCC and amine to carboxylic acid mechanism
carbonyl oxygen attack on carbon
nitrogen deprotonates
amine addition
nitrogen deprotonates
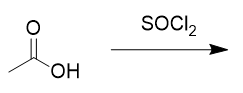
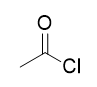
addition of sulfurous dichloride to carboxylic acid
acid chloride; reversible with NaOH and acid
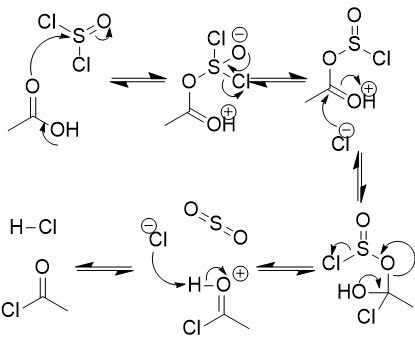
addition of sulfurous dichloride to carboxylic acid mechanism
make carbonyl a good leaving group
make alcohol a carbonyl
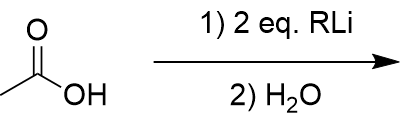
addition of organolithium to carboxylic acid
carbonyl
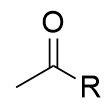
addition of organolithium to carboxylic acid mechanism
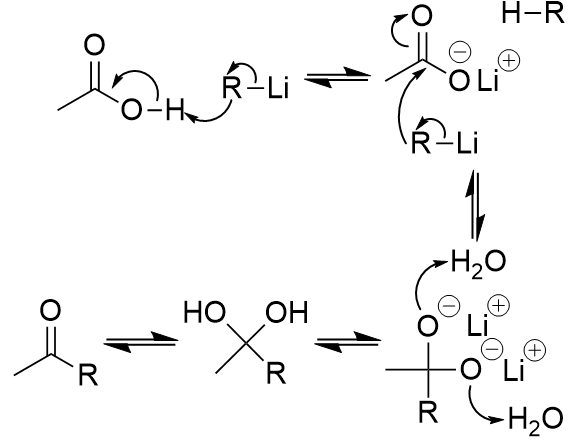
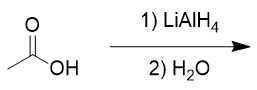
addition of lithium aluminium hydride to carboxylic acid
reduction to primary alcohol; also turns aldehyde into primary alcohol, ketone into secondary alcohol; ester into primary alcohol; amide into amine, nitrile into primary amine
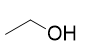
addition of lithium aluminium hydride to carboxylic acid
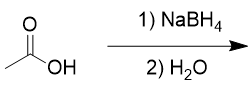
addition of sodium borohydride to carboxylic acid
doesn’t work, only reduces aldehydes and ketones
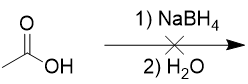
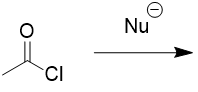
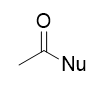
addition of nucleophile to acid chloride
SN1 type reaction
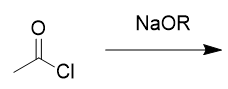
addition of base to acid chloride
ester
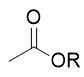
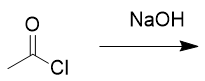
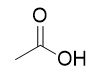
addition of hydroxide to acid chloride
carboxylic acid
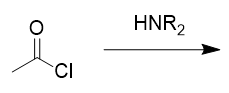
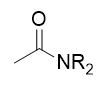
addition of secondary amine to acid chloride
amide
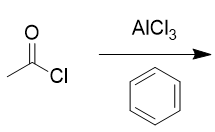
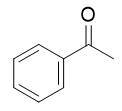
addition of benzene and aluminum chloride to acid chloride
Friedel-Crafts acylation
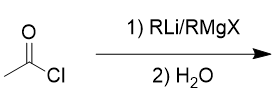
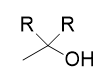
addition of organolithium/Grignard reagent to acid chloride
tertiary alcohol
addition of organolithium/Grignard reagent to acid chloride mechanism
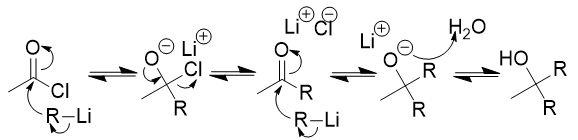
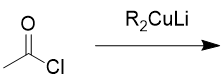
addition of organocuprate to acid chloride
ketone; like RLi but more selctive; will not react with ketone/aldehyde
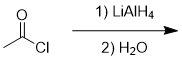
addition of lithium aluminium hydride to acid chloride
tertiary alcohol
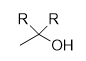
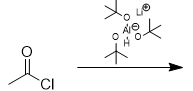
addition of lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride to acid chloride
aldehyde; doesn’t react with aldehydes/ketones
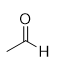
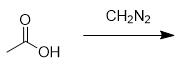
addition of diazomethane to carboxylic acid
methyl ester
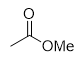
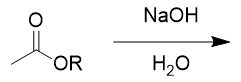
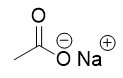
addition of aqueous sodium hydroxide to ester
saponification, deprotonated
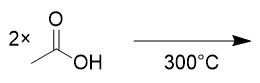
combination of two carboxylic acids @ 300°C
anhydride and water

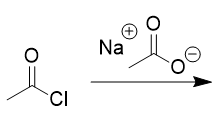
addition of deprotonated acid to acid chloride
anhydride and salt
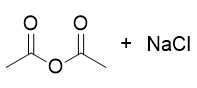
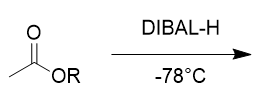
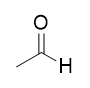
addition of DIBAL-H to ester @ -78°C
aldehyde
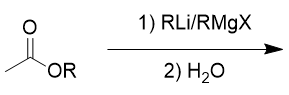
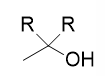
addition of organolithium/Grignard reagent to ester
tertiary alcohol
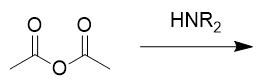
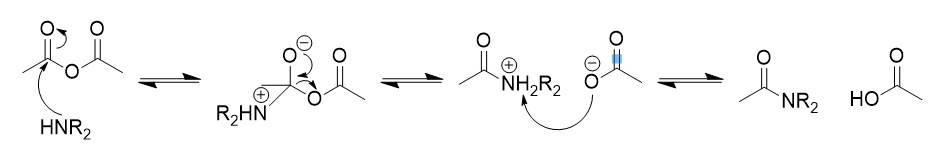
addition of amine to anhydride
amide
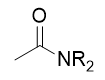
addition of amine to anhydride mechanism
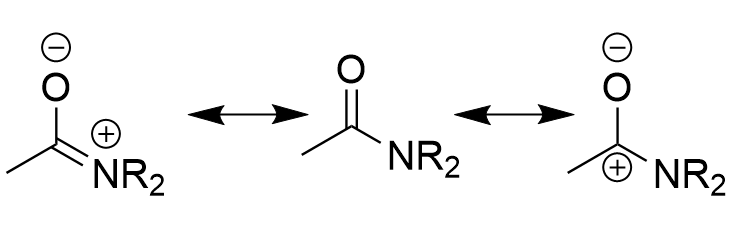
resonance of amide
stability
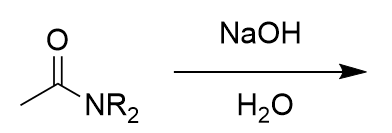
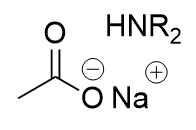
amide in basic aqueous environment
deprotonated carboxylic acid and neutral amine; electrophlic attack from carbonyl oxygen
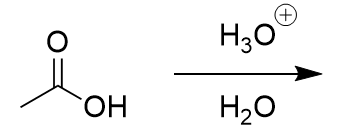
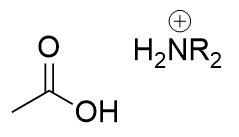
amide in acidic aqueous environment
carboxylic acid and positive amine; nucleophilic attack on carbonyl carbon
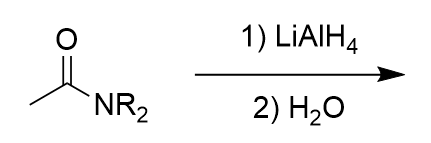
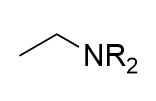
lithium aluminium hydride reduction on amide
amine; could use deuterated reagent
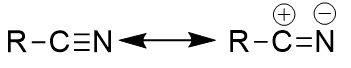
resonance for nitrile
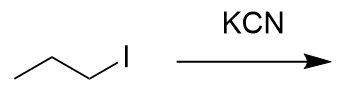
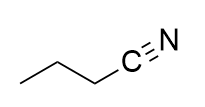
addition of potassium cynaide to alkyl halide
nitrile; SN2
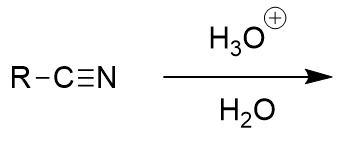
acidic workup of nitrile
carboxylic acid and ammonium; begins with protonation of nitrogen
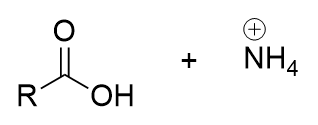
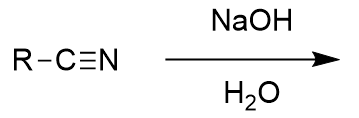
basic workup of nitrile
deprotonated carboxylic acid and ammonia
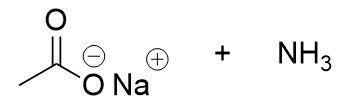
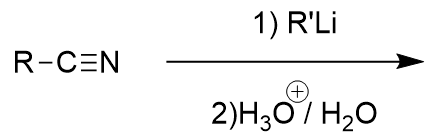
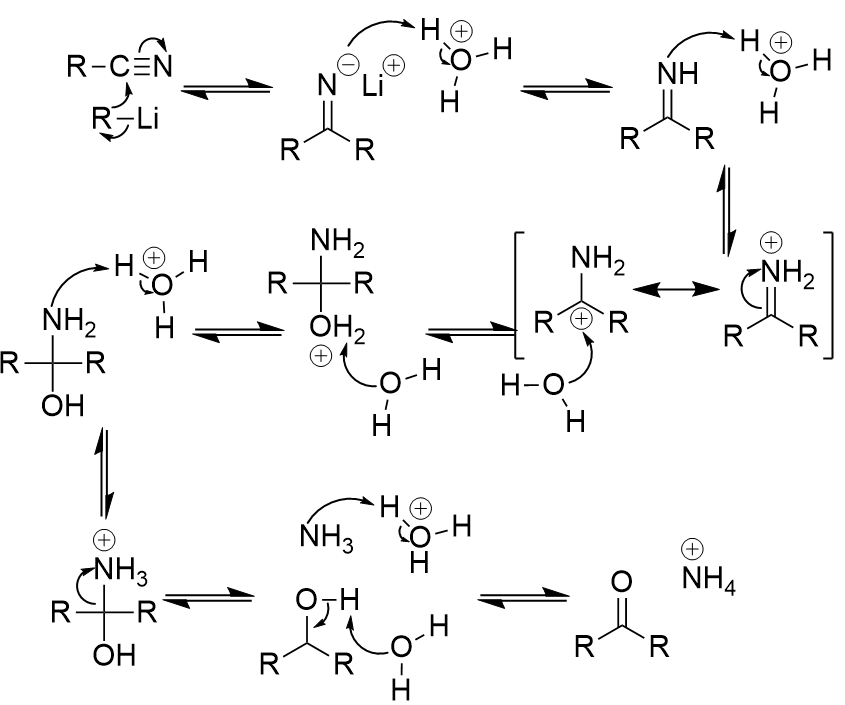
addition of organolithium to nitrile
ketone; nucleophlic attack on nitrile carbon; iminium ion
addition of organolithium to nitrile mechanism
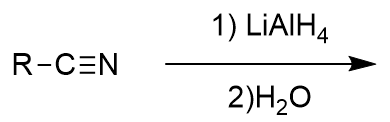
lithium aluminium hydride reduction of nitrile
amine
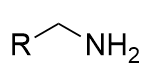
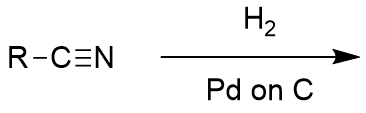
amine
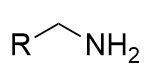
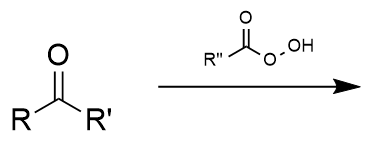
Bayer-Villager rearrangement general formula
transfers one side group of a ketone to an ester
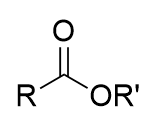
Bayer-Villager rearrangement mechanism
proton attack → more suitable R group moves to oxygen
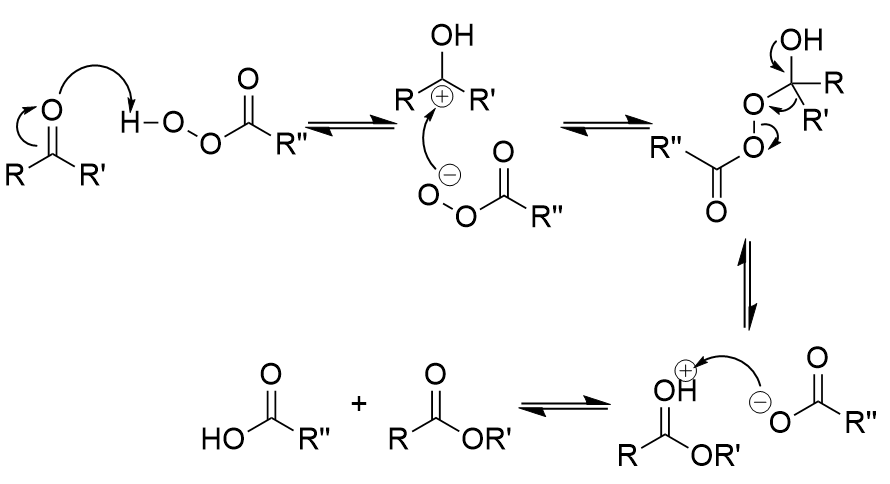
rate of migration for different side groups in rearrangement
H > 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3
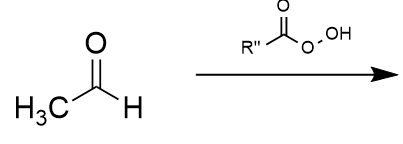
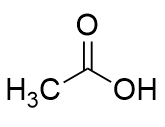
Bayer-Villager rearrangement example 1
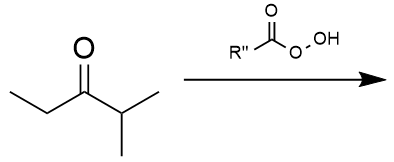
Bayer-Villager rearrangement example 2