2.4.1 - VSEPR Theory
Introduction
- ^^VSEPR^^ - Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion.
- VSEPR is only for covalent bonds
- Refers to the distribution of electrons so that they have the least amount of repulsion.
- This means that bonding regions will be as far away from each other as possible (repulsion)
- VSEPR results in the creation of five different shapes, depending on the number of bonding regions and lone pairs.
- Linear
- V-Shaped
- Trigonal planar
- Trigonal pyramidal
- Tetrahedral
- ^^Bonding regions^^ - electrons shared between two atoms
- ^^Lone pairs^^ - electrons that are not bonded to any other atom
- Central atoms have the lowest electronegativity of the entire molecule.
- Molecular shape (VSEPR) can be determined from number of electron regions and lone pairs.
- Structure affects polarity.
VSEPR Shapes
Linear Molecules

Have either one or two bonding regions that are around a central atom.
e.g - Cl2, CO2, HCl
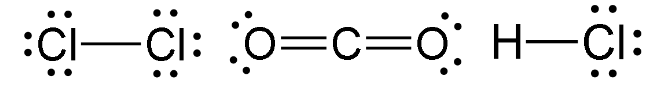
Note that it refers to bonding regions, specifically - double and triple bonds (see above: CO2) can still be linear molecules.
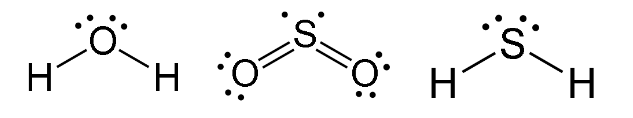
V-Shaped Molecules
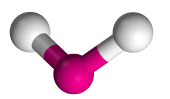
Have two bonding regions and one/two lone pairs around a central atom.
Will always be polar.
e.g H2O, SO2, H2S
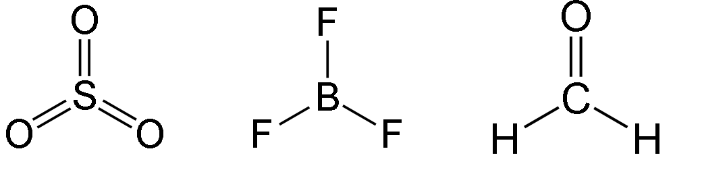
Trigonal Planar
Have three bonding regions around the central atom.
Molecule itself is flat.
Can be polar or nonpolar - if molecule is symmetrical, it is nonpolar. Else, polar.
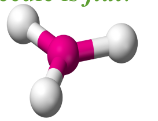
e.g SO3, BF3, H2CO
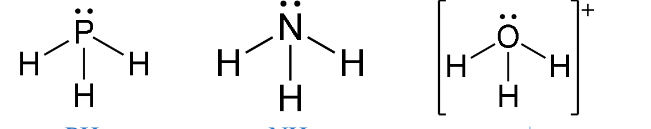
Trigonal Pyramidal
Have three bonding regions and one lone pair of electrons.
Will always be polar.
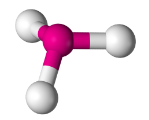
e.g PH3, NH3, H3O+
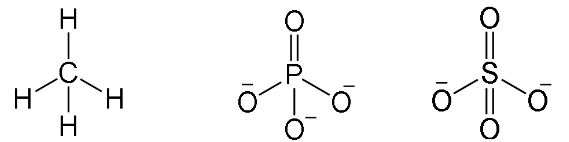
Tetrahedral
Have four bonding regions.
Can be polar or nonpolar - if molecule is symmetrical, it is nonpolar. Else, polar.
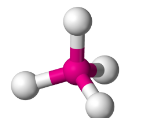
e.g CH4, PO4(3-), SO4(2-)