elsaid - M phase agents
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
M-phase specific antineoplastic agents
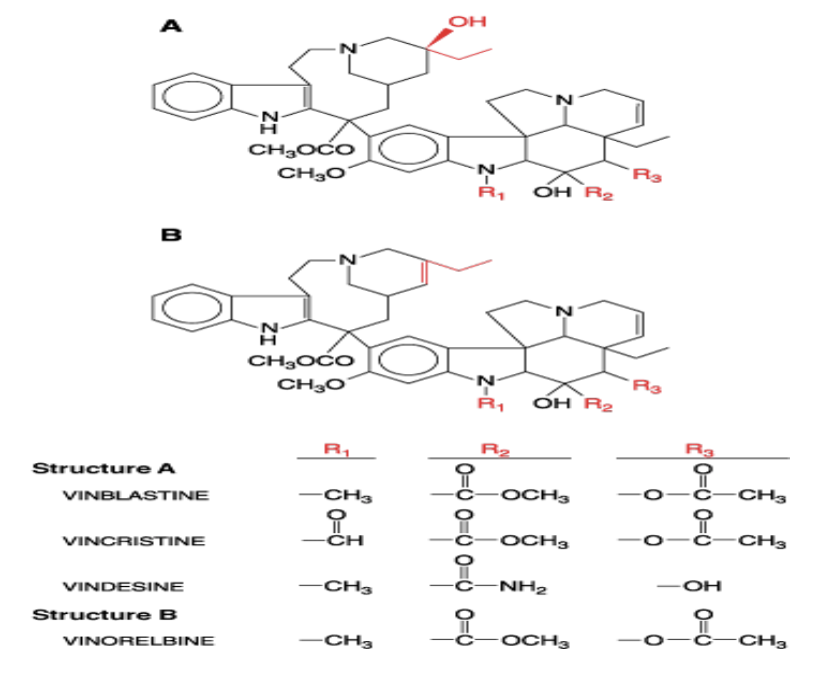
vinca alkaloids
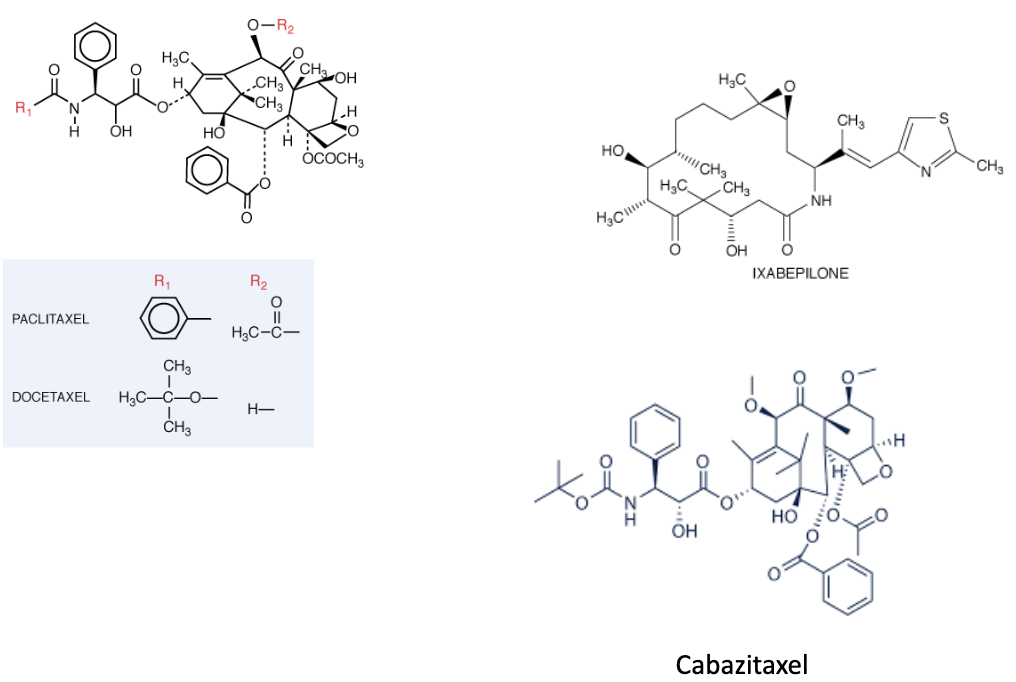
taxanes
ixabepilone
eribulin
MOA and effect of M-Phase specific agents
these drugs inhibit key processes in mitotic phase (by targeting microtubules) and this results in mitotic arrest
work synergistically with DNA-damaging and S-phase antineoplastic drugs
microtubule dynamics
hollow tubes that are composed of a heterodimer of 𝜶 and β tubulin
microtubules are unstable structures (that undergoes elongation and collapse that are important in the process of mitosis (separate the chromosomes)
microtubules have a (+) end (GTP-bound tubulin) and a negative end (-)
anti-microtubule drugs can be classified into drugs that inhibit tubulin polymerization or inhibit microtubule collapse
eribulin
binds to the (+) ends of the microtubules
prevent polymerization —> prevent growth
vinblastine (a vinca alkaloid)
binds to the β-tubulin near the (+) end
prevent polymerization —> prevent growth
paclitaxel (taxol)
binds to the β-tubulin inside the microtubule
prevents depolymerization —> prevents the collapse
ixabepilone
binds to the β-tubulin inside the microtubule
prevents depolymerization —> prevents the collapse
exchangeable GTP binding site
located on the β-tubulin
non-exchangeable GTP binding site
located on the 𝜶-tubulin
vinca alkaloids
taxanes
paclitaxel formulations
1st generation — paclitaxel (Taxol)
formulation:
Cremophor EL excipient: polyoxyethylated castor oil —> infusion related reaction due to hypersensitivity
maximum tolerated dose = 175 mg/m2
2nd generation — nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane)
formulation:
biological polymer: donor-derived human serum albumin (HSA) —> no hypersensitivty
maximum tolerated dose = 260 mg/m2
higher dose bc it has more concentration in the cancer cell —> less off-target side effects (bone marrow suppression)
nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane)
conjugation of albumin to paclitaxel leads to several favorable outcomes:
reduce Cremophor excipient concentration (responsible for hypersensitivity reactions with Paclitaxel)
enhanced receptor-mediated transcytosis via endothelial cells due to the presence of albumin receptors on endothelial cells
EPR effect improves drug accumulation in the tumor
reduction in off-target toxicity leads to an increase in maximum tolerated dose for nab-Paclitaxel compared to Paclitaxel
eribulin mesylate
eribulin inhibits tubulin polymerization and microtubule enlongation by inhibiting GTP binding
mechanisms of resistance towards antimicrotubules
up-regulation of β-tubulin expression
mutation in β-tubulin binding sites
efflux pump over-expression (cabazitaxel is NOT a substrate of the efflux pump in contrast to Paclitaxel or Docetaxel