OOP Fundamentals Pt 1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
abstraction, polymorphism, inheritance, encapsulation
4 fundamental concepts of oop (a-pie)
abstracting
when we put a piece of code in a java method, we are ______ the piece of code
implemented
the method’s name can be considered a new concept; we won’t need to know how the method was ______ when reusing it
name, arguments, return values
a method’s interface includes what?
true
T/F: abstractions can have different methods
pure methods
methods that don’t call other methods
first
pure methods belong to the ____ level of abstraction
second
a method that calls other methods belongs at least to the ____ level of abstraction
abstraction
the ability to separate the interface from the implementation
readability, usability, reusability, maintainability
abstraction benefits
higher ____, ____, ____, ____
simplifies, unnecessary
abstraction ___ complex system by hiding ____ details
method, class, package
abstraction levels
putting code in a ____
putting several methods in a ____
putting classes in a _____
true
T/F: inheritance is a two-way ability
is-a
inheritance is an ____ relationship
child, defines, capabilities
1. The ability of extending a parent class' capabilities by creating a ___ class that gets all parent's capabilities and possibly ______ more.
2. The ability of factoring out the common _____ of a group of classes (children) into a parent class.
parent-chlid
the term______ is more common in database than superclass-subclass
object
every Java class inherits from a parent class called _____
parent
more generalized and is called “superclass”
class
more specific and is called “subclass”
inherited, class member
constructors cannot be _____ because it’s not a _____
overriding
re-implementing an inherited method in the subclass
extends
Java uses the ____ keyword to denote inheritance
asymmetric
inheritance is an ____ relationship (every child is a parent but not the other way around)
inherits
ClassA _____ from ClassB
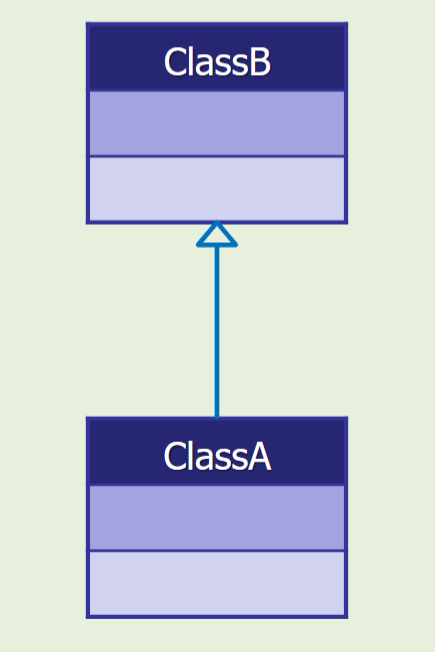
true
T/F: in a UML diagram, the child class only shows the non-inherited (new) methods
+
which sign stands for the public?
-
which sign stands for private?
#
which sign stands for protected?
~
which sign stands for package private?
visible
all ____ member of superclass are inherited by _____
true, bad
T/F: we can declare the same instance variable name of superclass in subclass. However, this is ___ practice.
super(…)
____ must be the first statement of the subclass constructor
zero-parameter constructor
if you don’t any superclass’ constructor, then by default the ____ of the superclass will be called
T/F: if you don’t have any constructor in your class, Jaa creates a zero-parameter constructor for you
aren’t, special
constructors ____class members, that’s why we need a ___ way to call it from subclass
this
inside a class, we can invoke its members by using the keyword _______
super
use the ____ keyword when we invoke a superclass method
optional
if a method is not overridden, using the super keyword is ____ (but it’s good programming practice)
multiple inheritance
to have two or more direct superclasses
isn’t, increases
multiple inheritance ____ supported by Java bc it ___ the complexity of programming
final
if a class is tagged as ____, then it cannot be extended
String
the ____ class in Java is final
overrriden
if a method is tagged as final, then it cannot be _____
attribute
if an ____ is tagged as final, then it cannot be changed
constructors
______ cannot be tagged as final
inheritance, aggregation
_____ decreases readability, avoid overusing it (use ___ instead)