4 Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
prokaryotes
-DON'T have membrane (lack nucleus)
-are simple structures; small about 1.0um in diameter
-includes bacteria & archaea
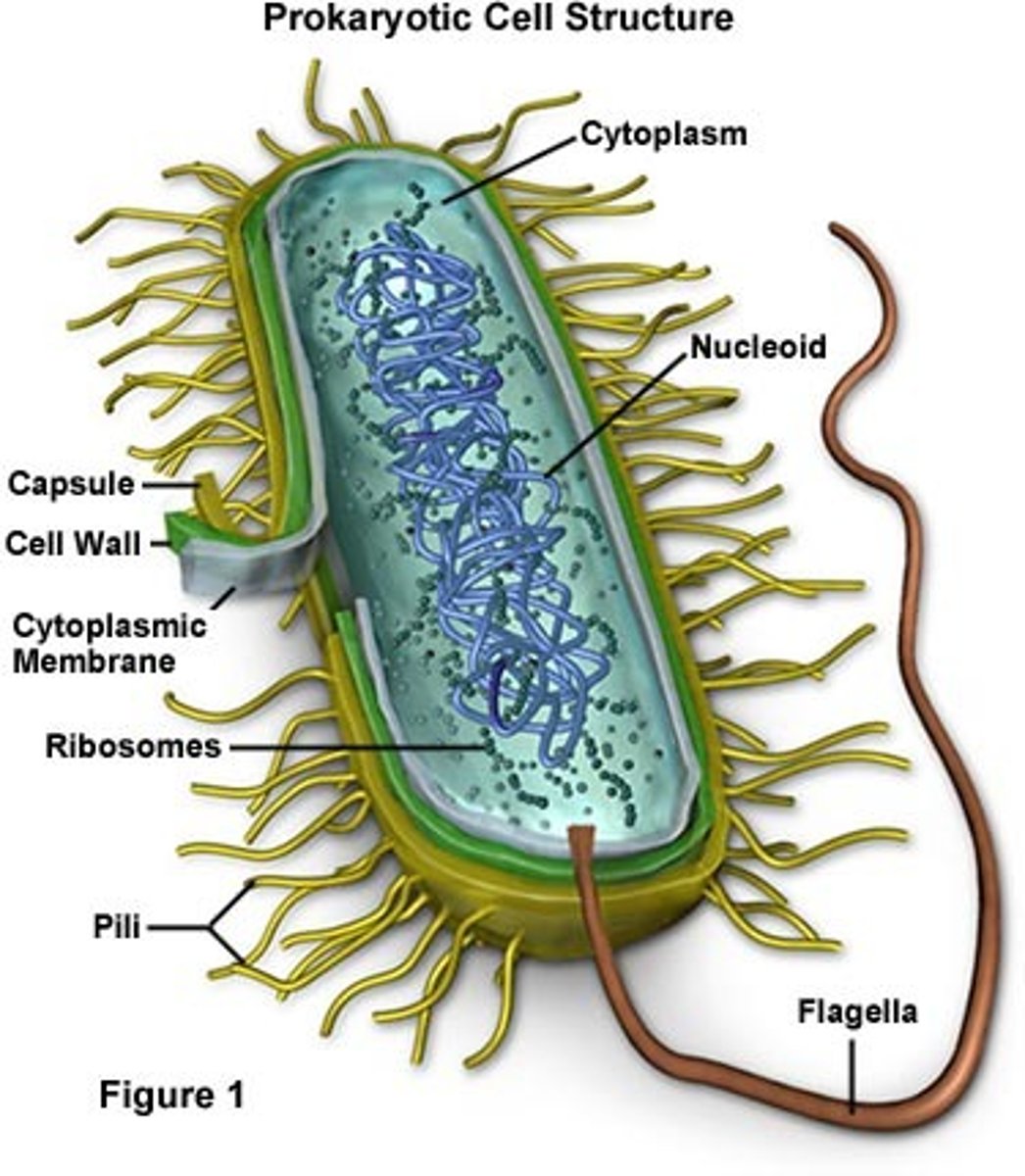
structure of prokaryotic cells
ribosome, cytoplasm, nucleoid, glycocalyx, cell wall, cell membrane, flagellum, inclusions
prokaryotic cell shapes (morphologies)
bacilli, cocci, vibrios, spirilla
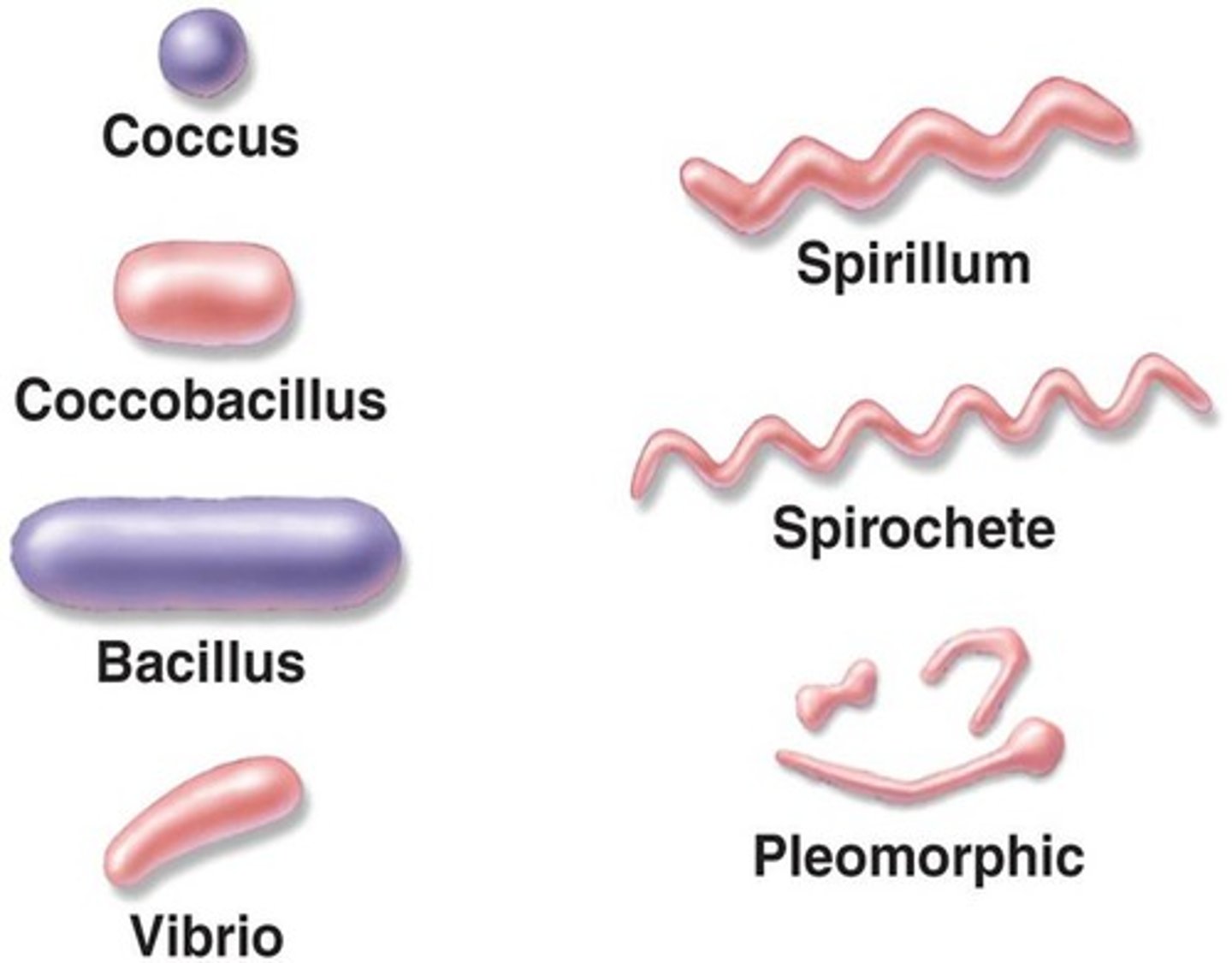
bacillus
rod shaped
coccus
spherical shaped
spirillum (spirochete)
spiral shaped (more than three bends)
vibrio
curved rod shape (one bend)
monomorphic
single shape for the genus(bacteria)
pleomorphic
microorganisms can alter their shape into multiple varies
ex) Streptomyces -soil bacteria
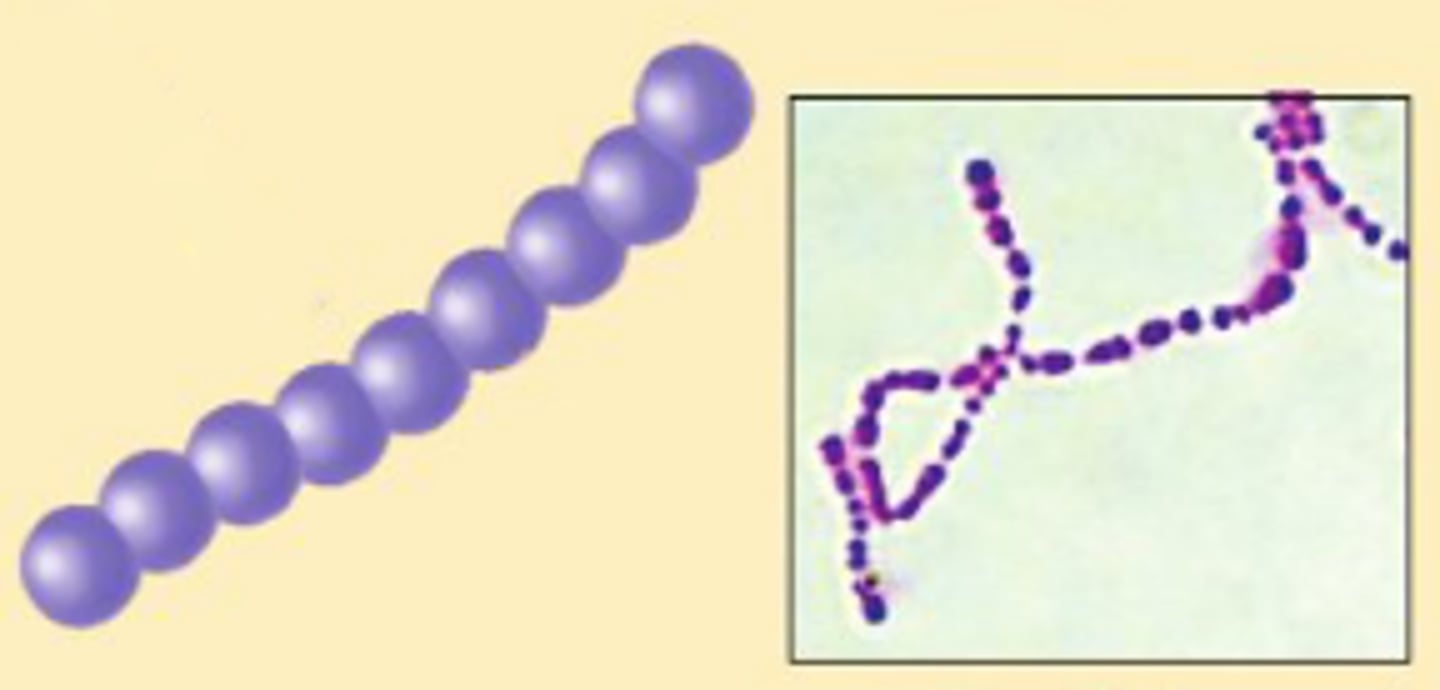
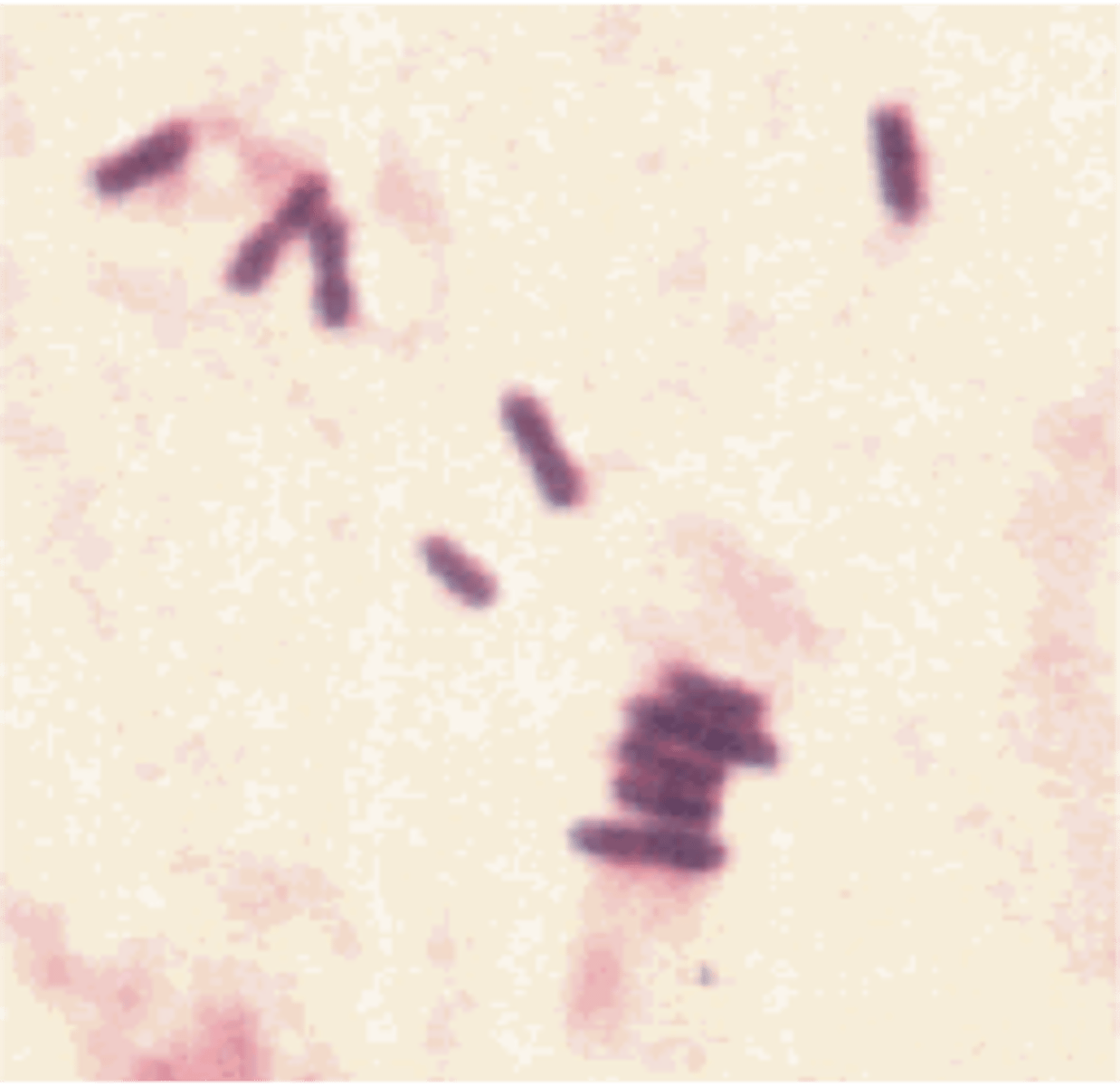
strepto arrangement
chains and pairs
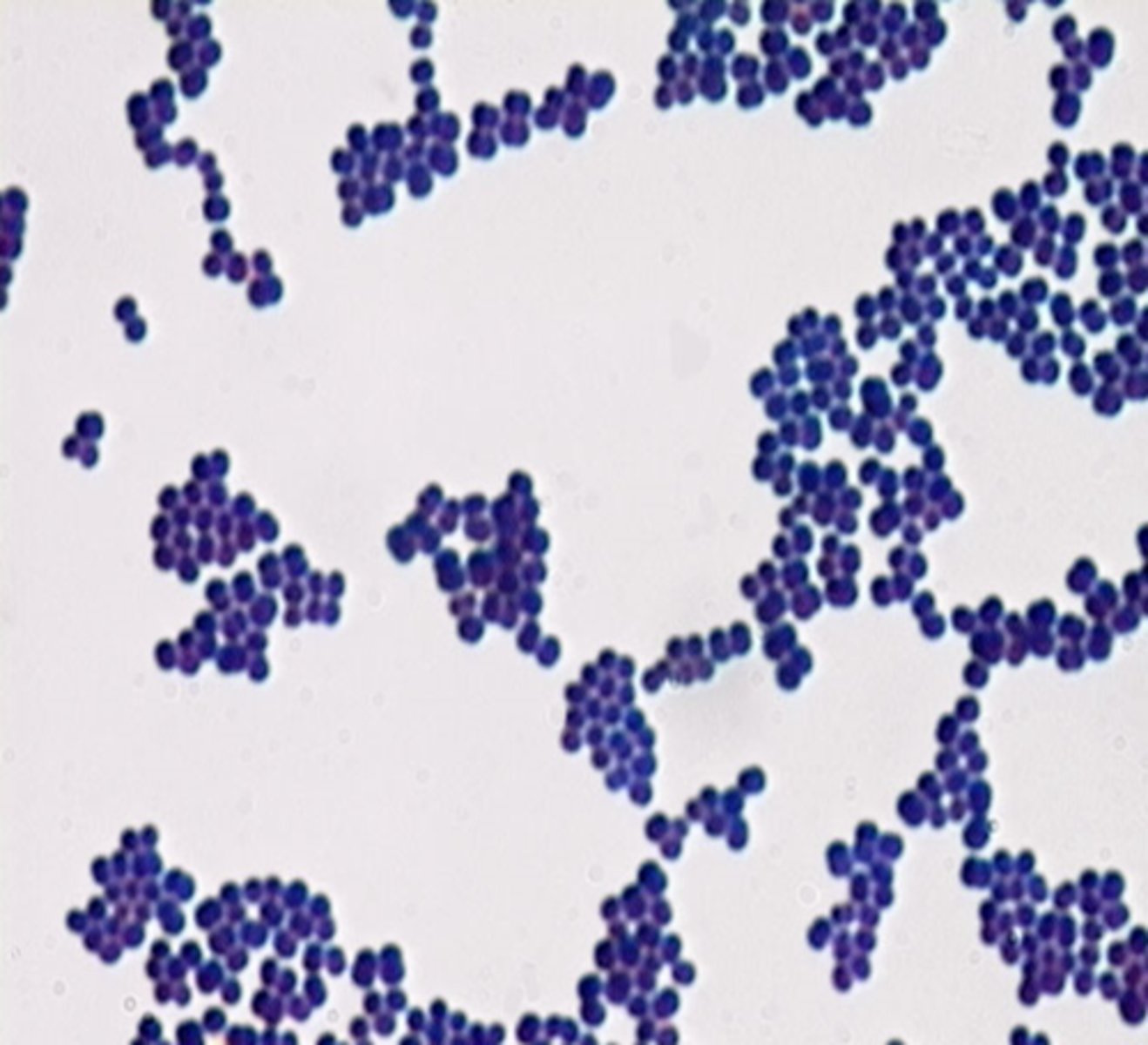
staph arrangement
clusters
-all the rods are chained together by their short ends
palisades arrangement
a wall
glycocalyces
-gelatinous, sticky substance surrounding the outside of cell
-composed of polysaccharides, polypeptides, or both
types of glycocalyces
capsule and slime layer
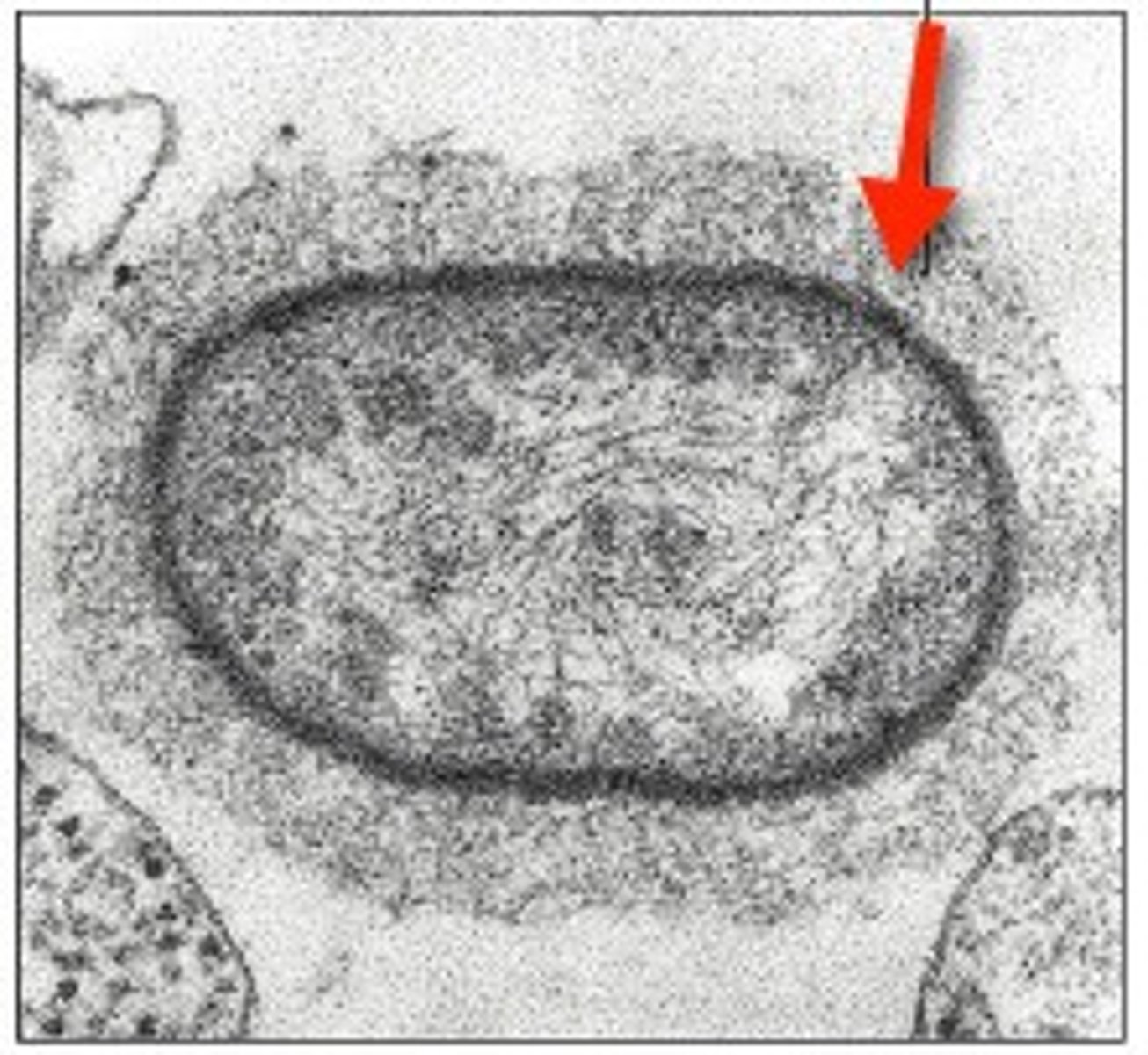
capsule (dark ring)
-composed of organized repeating units of organic chemicals
-firmly attached to cell surface
-protects cells from drying out
-may prevent bacteria from being recognized & destroyed by host
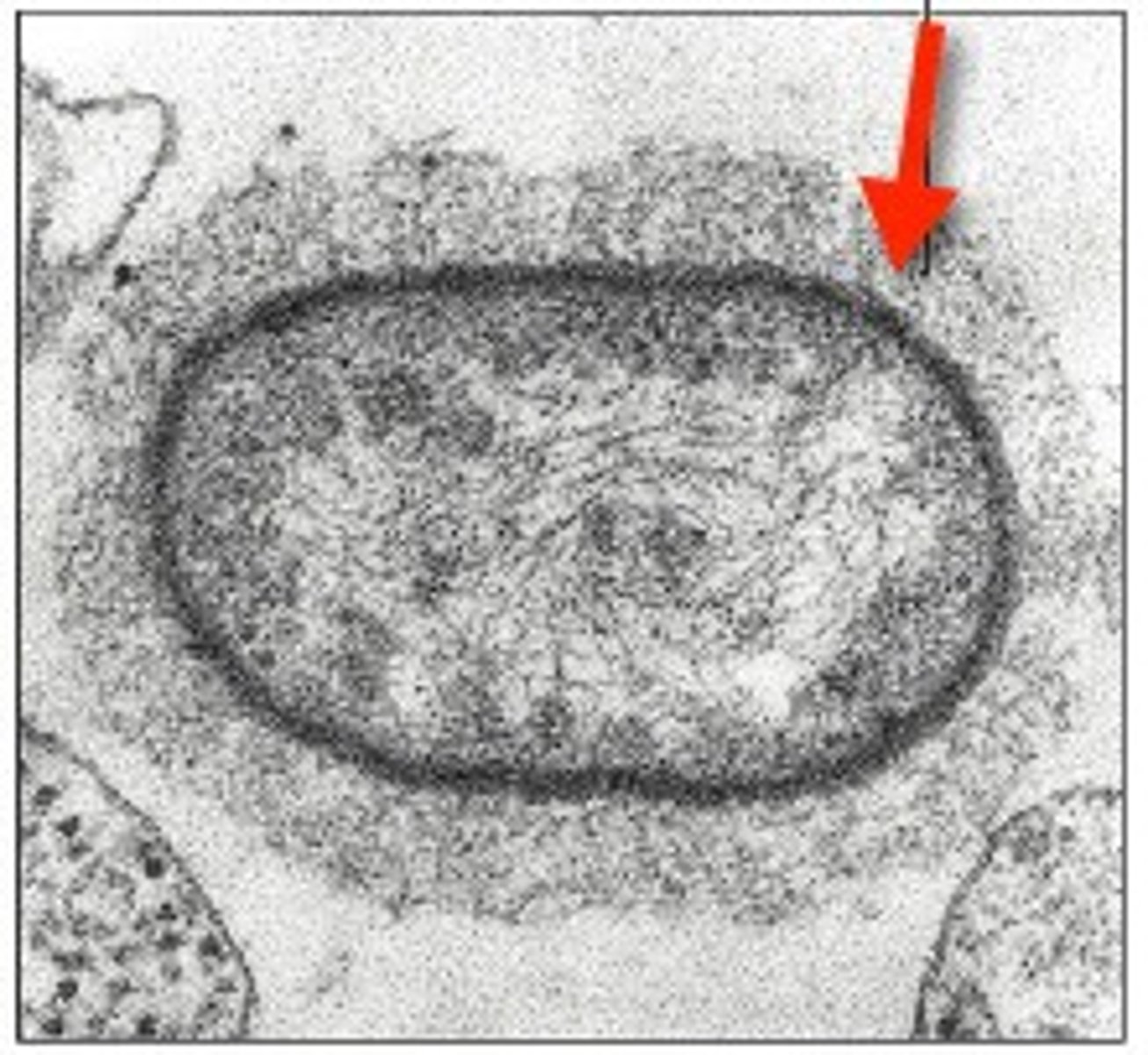
slime layer (lighter outer ring)
-loosely attached to cell surface
-water soluble
-protects cells from drying out
-sticky layer that allows prokaryotes to attach to surfaces
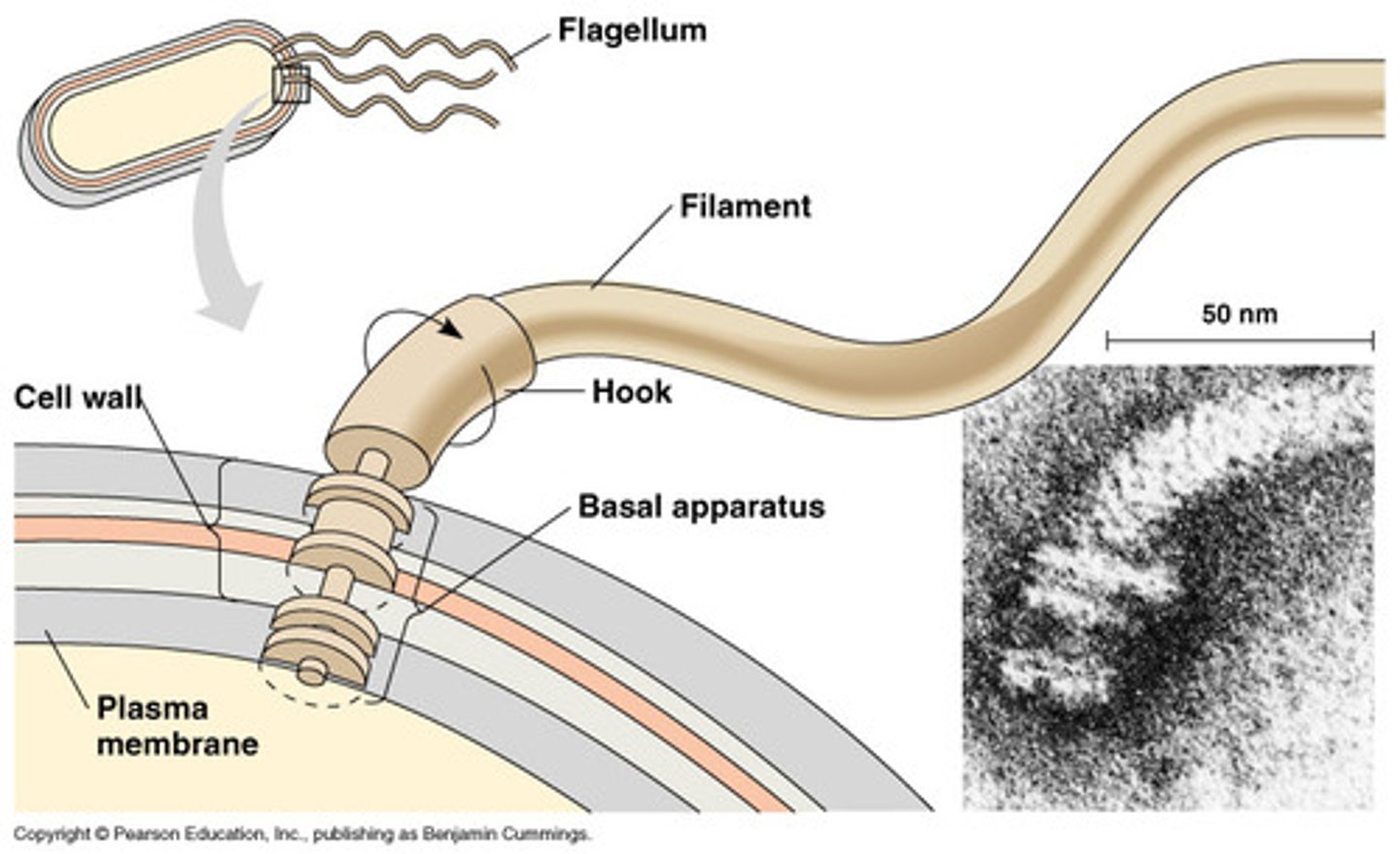
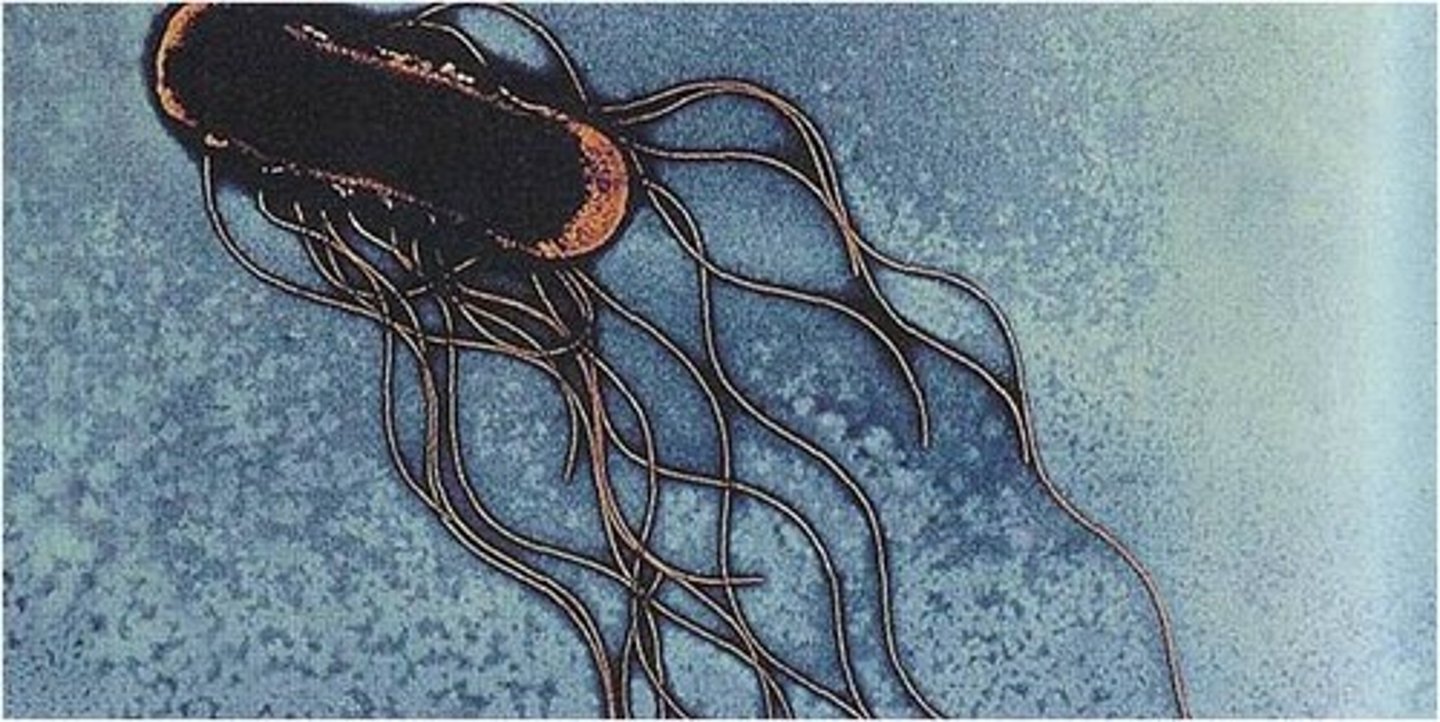
flagella
-responsible for movement
-have long structures that extend beyond cell surface
-not present in all prokaryotes
structure of flagella
-filament, hook, basal body
-filament capable of rotating 360'
-sperm =only human flagellated cell
types of flagellar arrangements
monotrichous, lophotrichous, amphitrichous, peritrichous
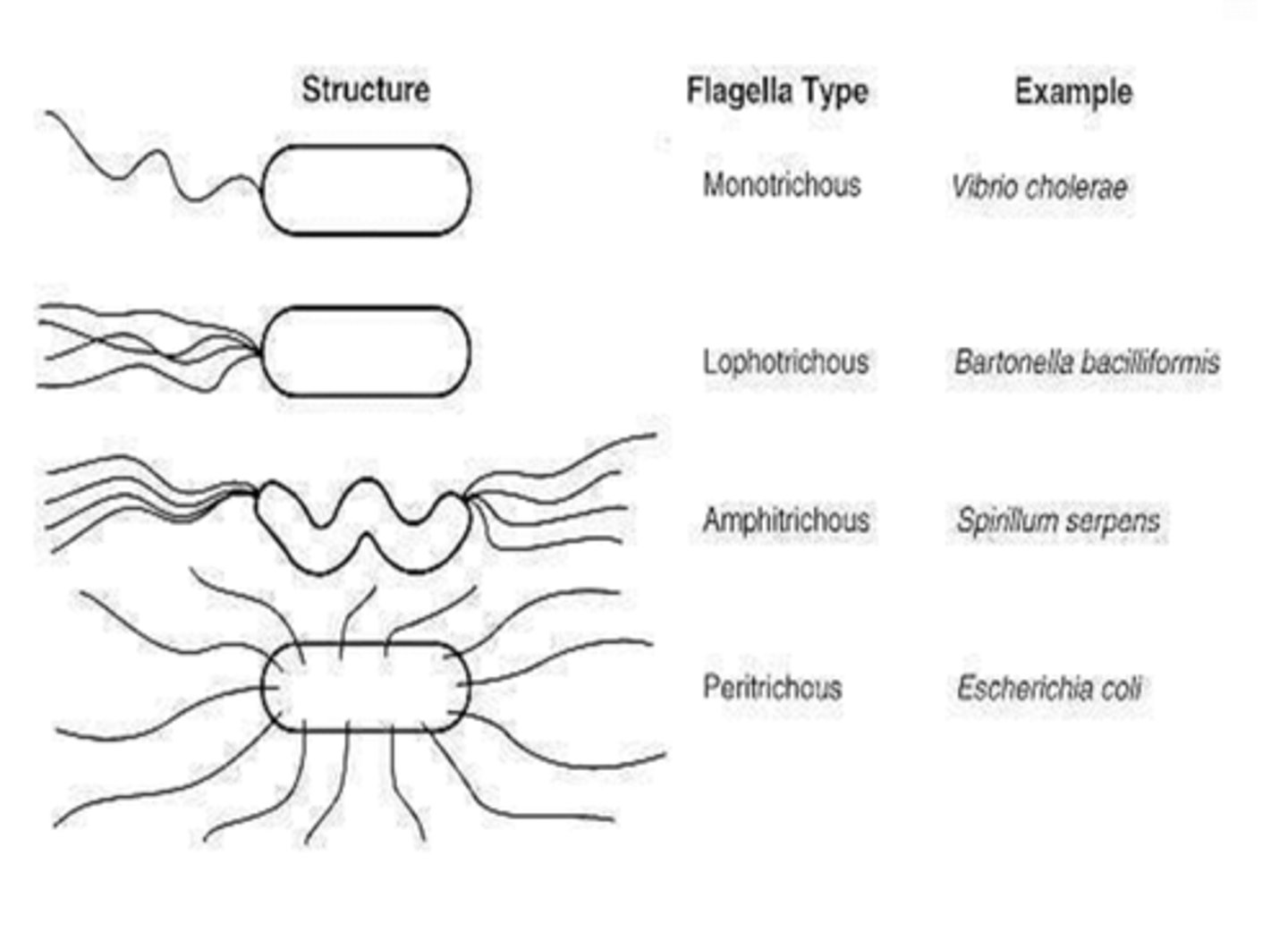
monotrichous
one flagellum
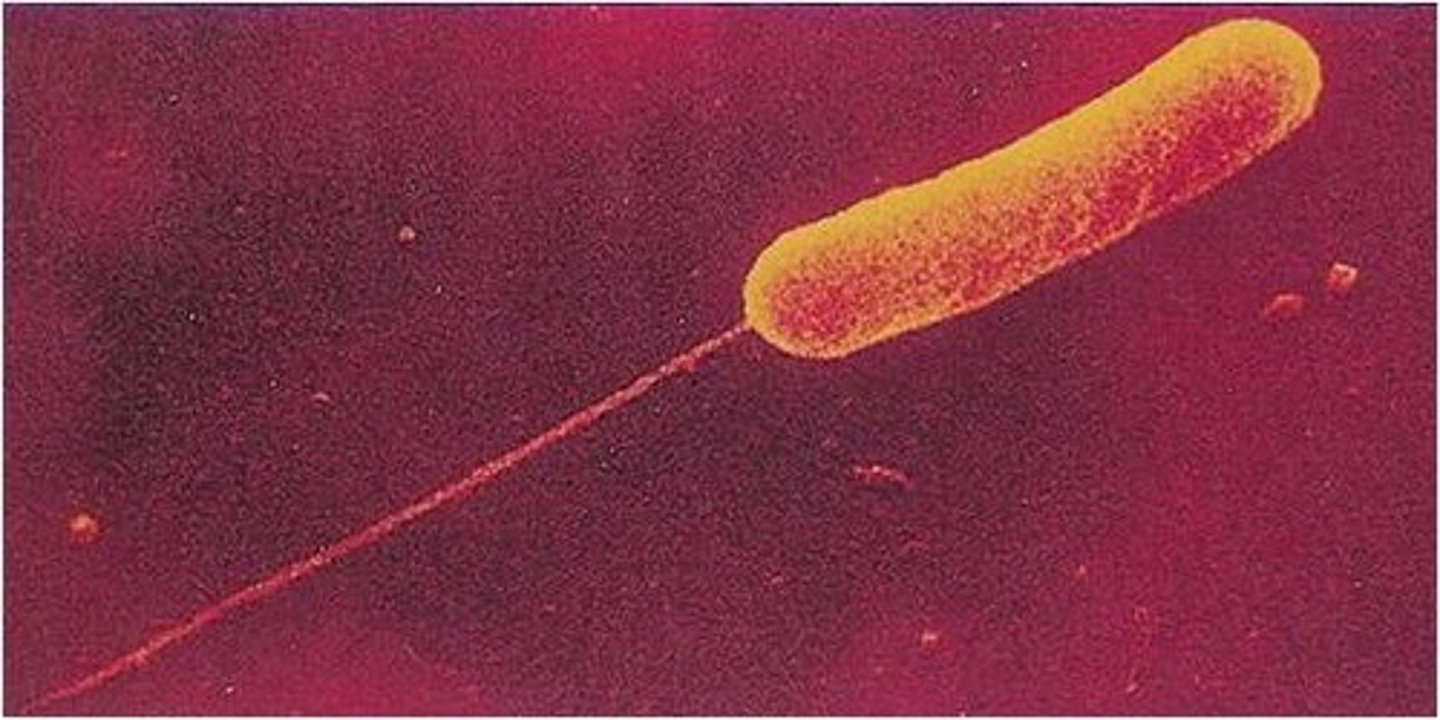
amphitrichous
flagella at both ends of cell
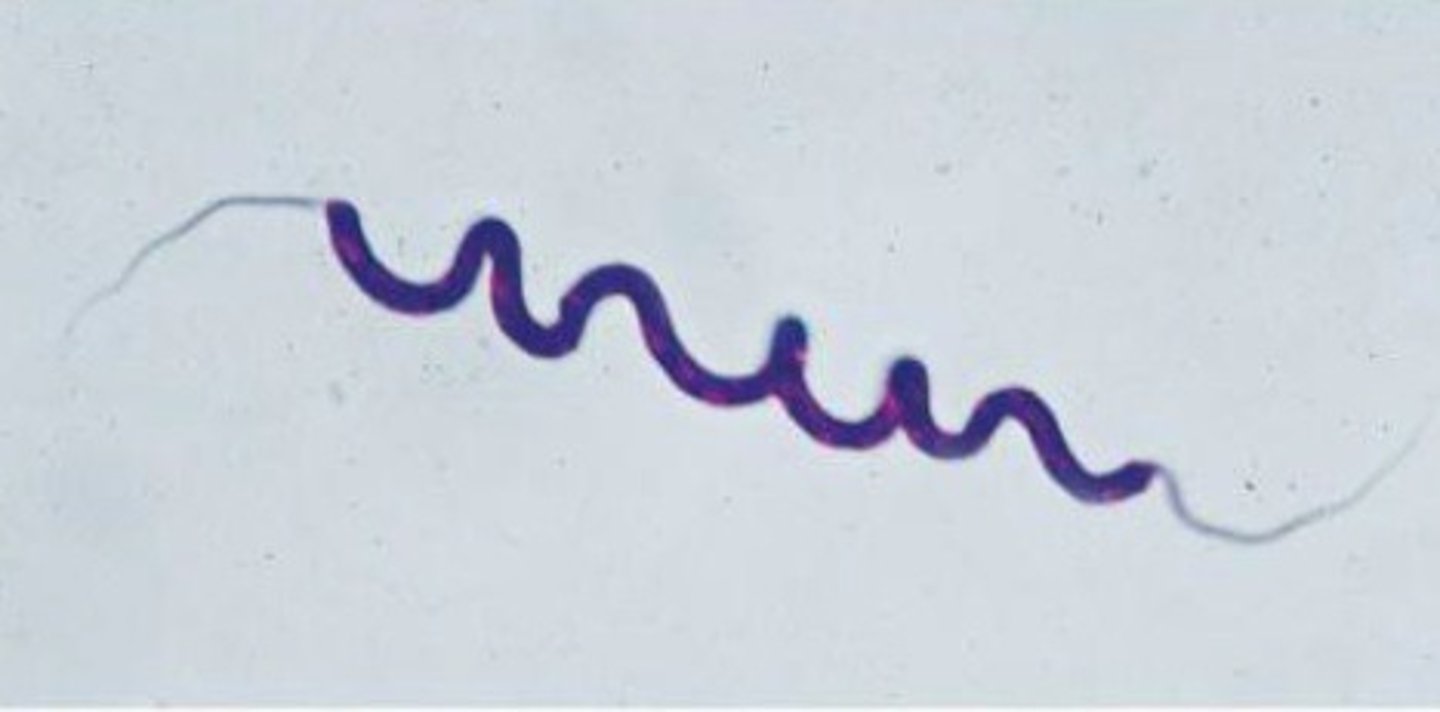
Lophotrichous
clusters of flagella
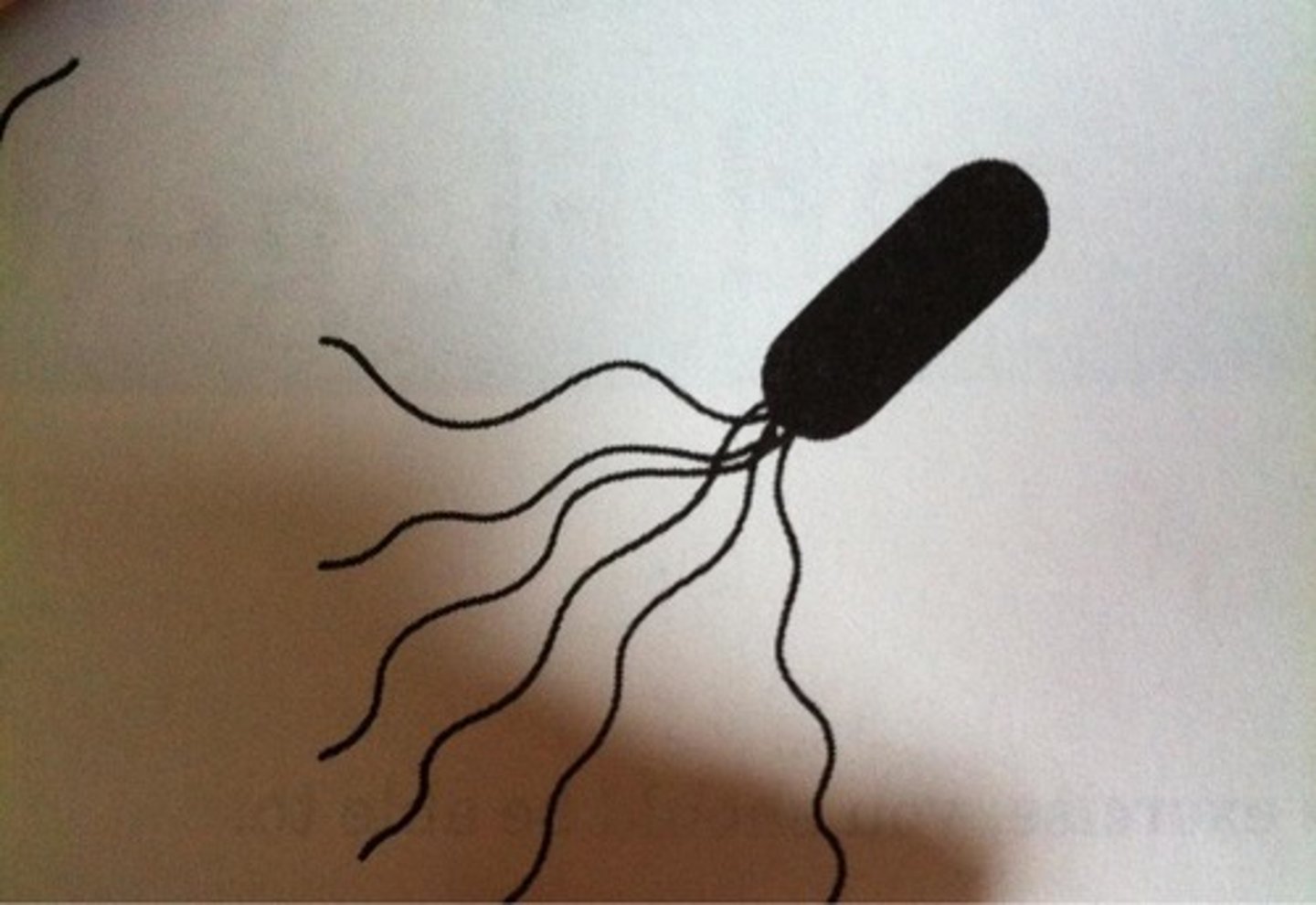
peritrichous
flagella surrounding the entire outside of bacteria
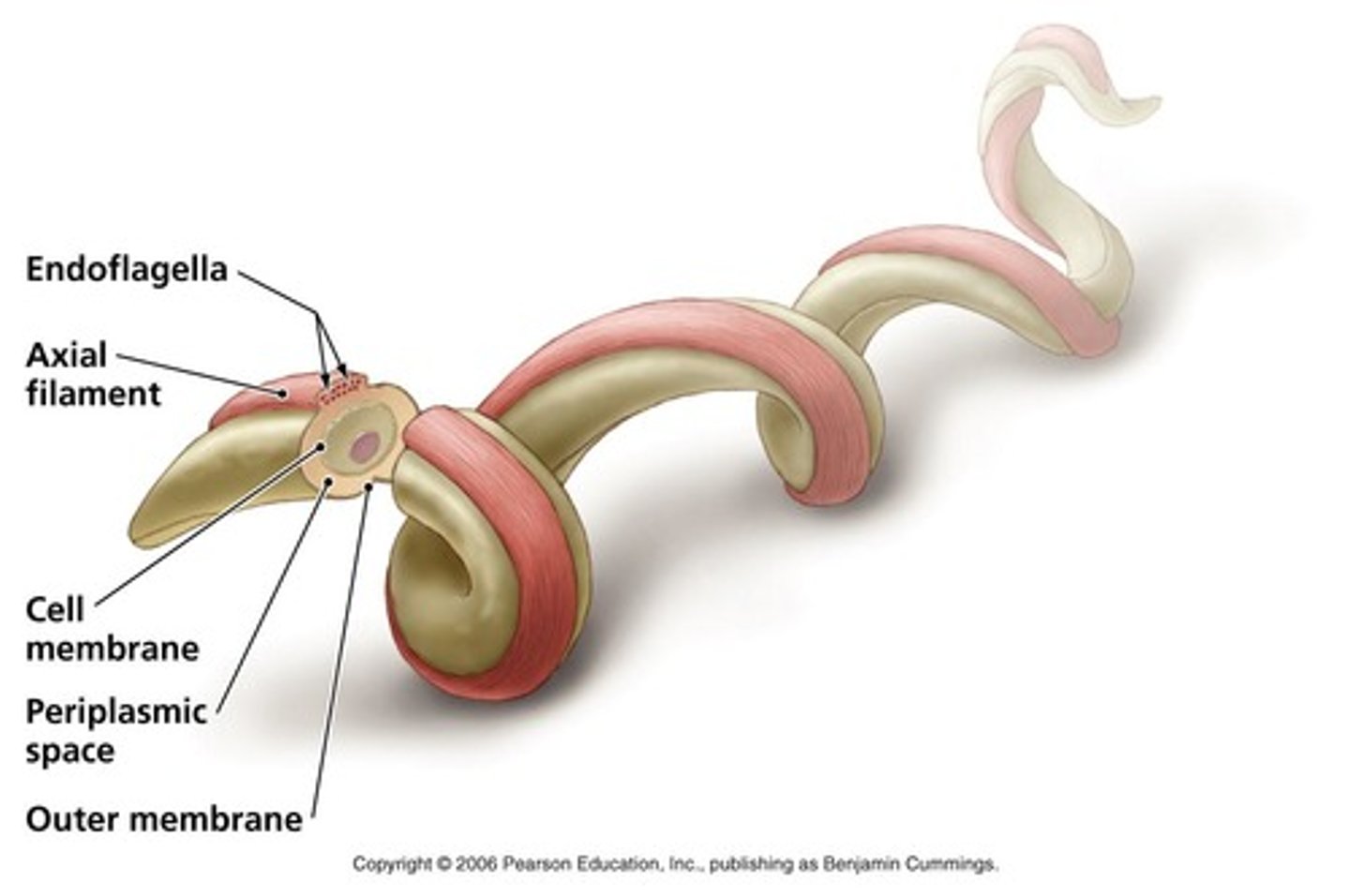
axial filament
-very long soft thin bodied bacteria
-wraps around the inside of the bacteria and helps it move in a twisting or corkscrew motion. (making it more flexible)
external structures of prokaryotic cells
glycocalyces, flagella, fimbriae, pili
function of flagella
-helps bacteria move and find better environments to survive.
-have sensor proteins that can sense chemicals in environment to detect movement
-bacteria move in response to stimuli (taxis)
Bacteria motility
run & tumble
run (bacteria motility)
counterclockwise flagella, progressive (towards/straight line)
tumble (bacteria motility)
clockwise flagella (spinning but doesn't move -picks a random direction and starts going forward again)
fimbriae & pili
rod like proteinaceous extensions
fimbriae
-sticky, bristlelike projections
-used by bacteria to adhere to one another, to hosts, and to substances in environment
-may be hundreds per cell
-shorter than flagella
pili
-longer than fimbriae but shorter than flagella
-mediate the transfer of DNA from one cell to another (conjugation)
-bacteria typically only have one or two per cell
-hollow
Conjugation pilus
an external structure used to connect two bacteria (bridge allows for sharing of genetic information
ex) spreading of genetic resistance like antibiotics
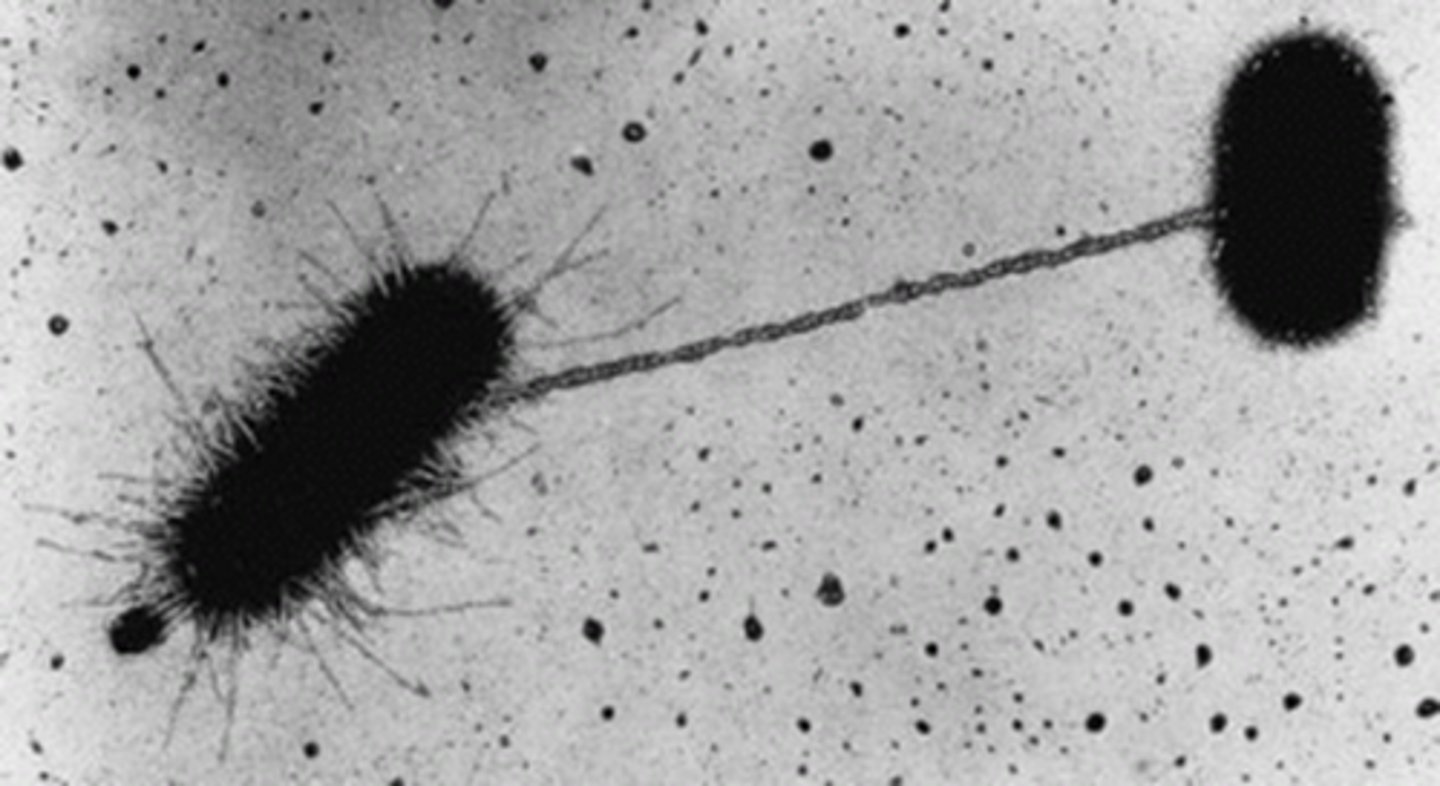
Horizontal gene transfer
when bacteria share genetic material with each other — not from parent to offspring, but between individuals (vertical =PartoChild)
osmosis
the diffusion of water across the semipermeable membrane (tendency of water crossing into the cell, too much water =bursts)
Diffusion
movement down from a high to low level of concentration gradient
prokaryotic cell walls
-protect the cell from osmotic forces
-provide structure and shape
-assist some cells in attaching to other cells or in avoiding antimicrobial drugs
-not present in animal cells (bacteria & archaea have different cell wall chemistry)
bacterial cell walls
-mostly composed of peptidoglycan (sugars, NAG, NAM)
-chains of NAG and NAM attached to other chains by tetrapeptide crossbridges (may be covalently bonded or held together by short connecting chains of amino acids)
types of bacterial cell walls
gram postive/negative
peptido
refers to peptides =amino acids
Glycan
"sugars" -a chain of sugar molecules (also called polysaccharides or carbohydrates) that are linked together.
Hydroxyl group
OH -participates in dehydration synthesis
NAG
(N-acetylglucosamine) a modified sugar that's a key building block of bacterial cell walls and other important biological structures.
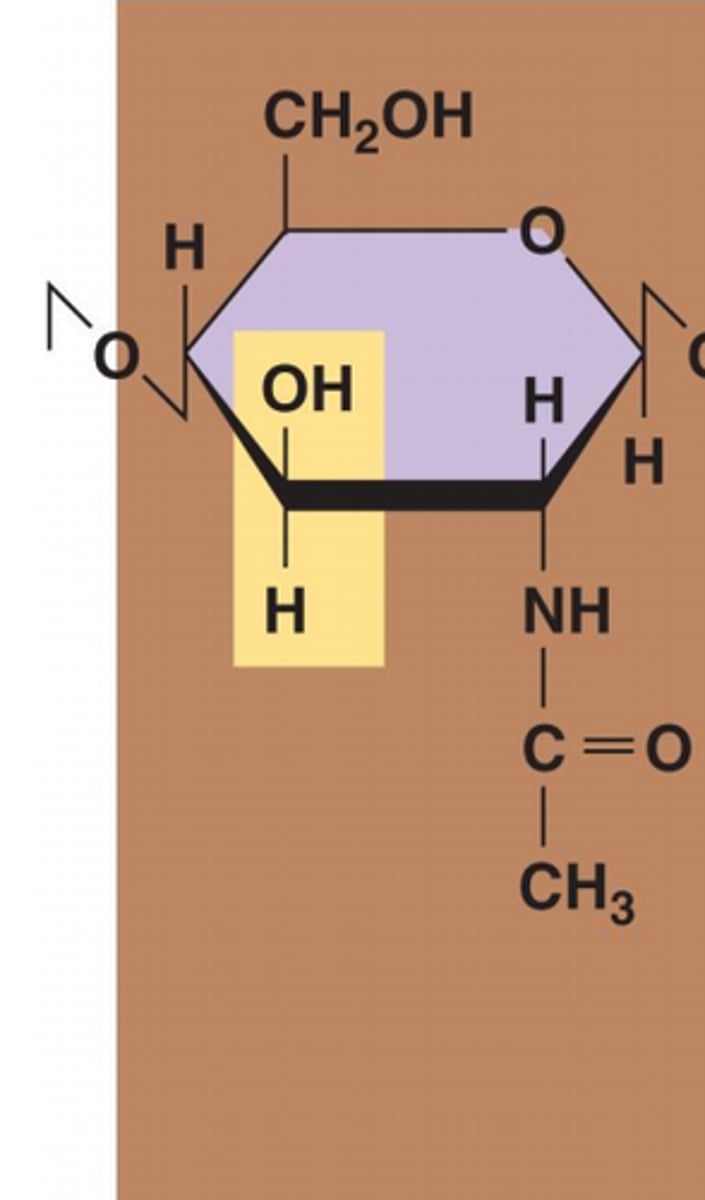
NAM
(N-acetylmuramic acid) a sugar with a special side chain that helps link peptide chains in the bacterial cell wall, making it strong and tough.
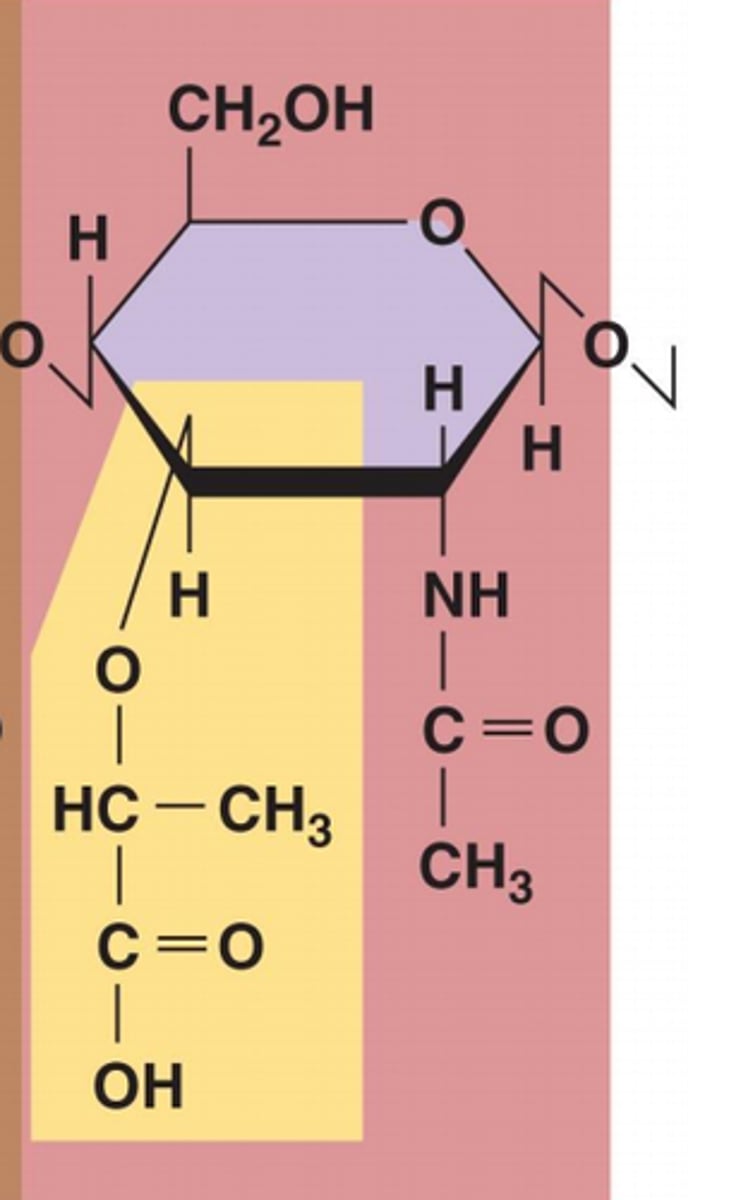
structure of Peptidoglycan
like a trapeze net made of sugar chains and peptide links, giving bacteria strength and protection.
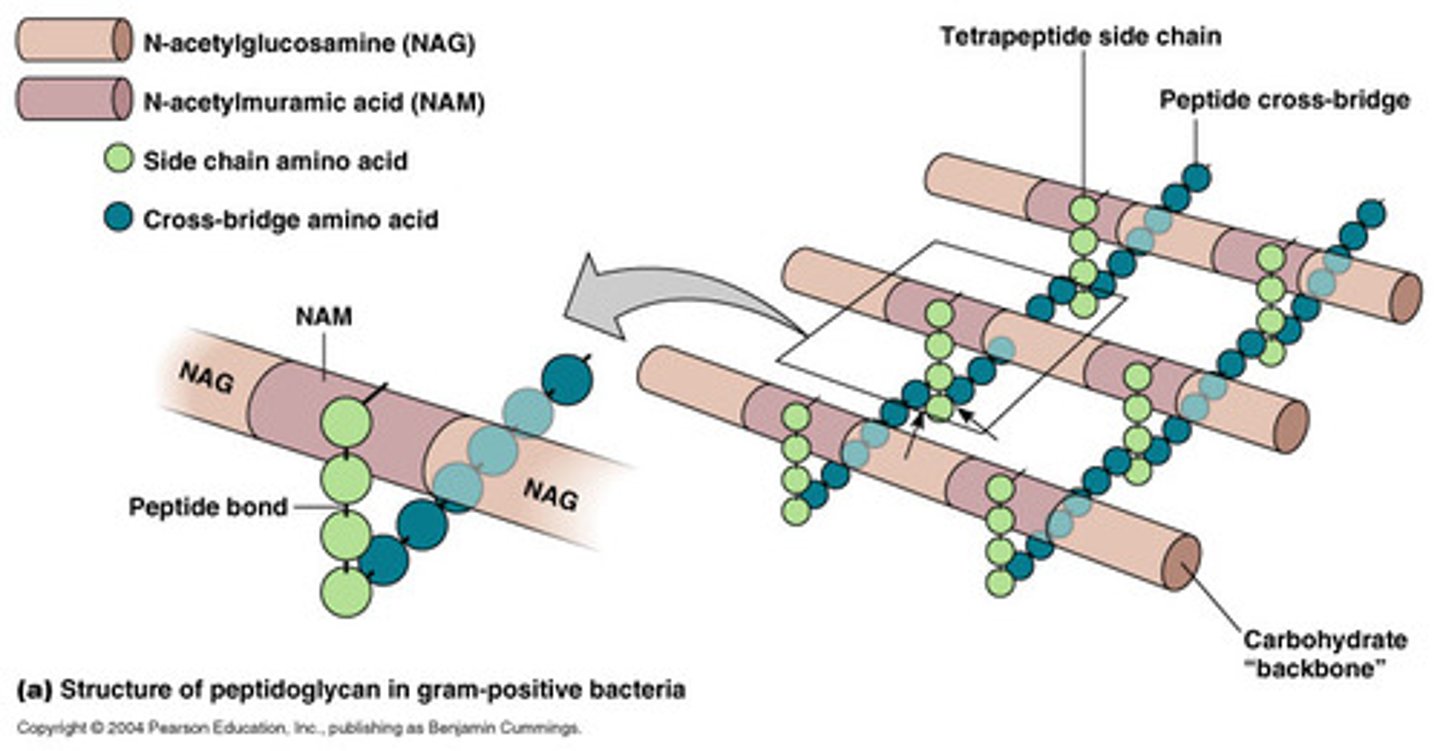
Peptidoglycan Cross-Links
connections between peptide chains attached to sugar backbones in the bacterial cell wall.
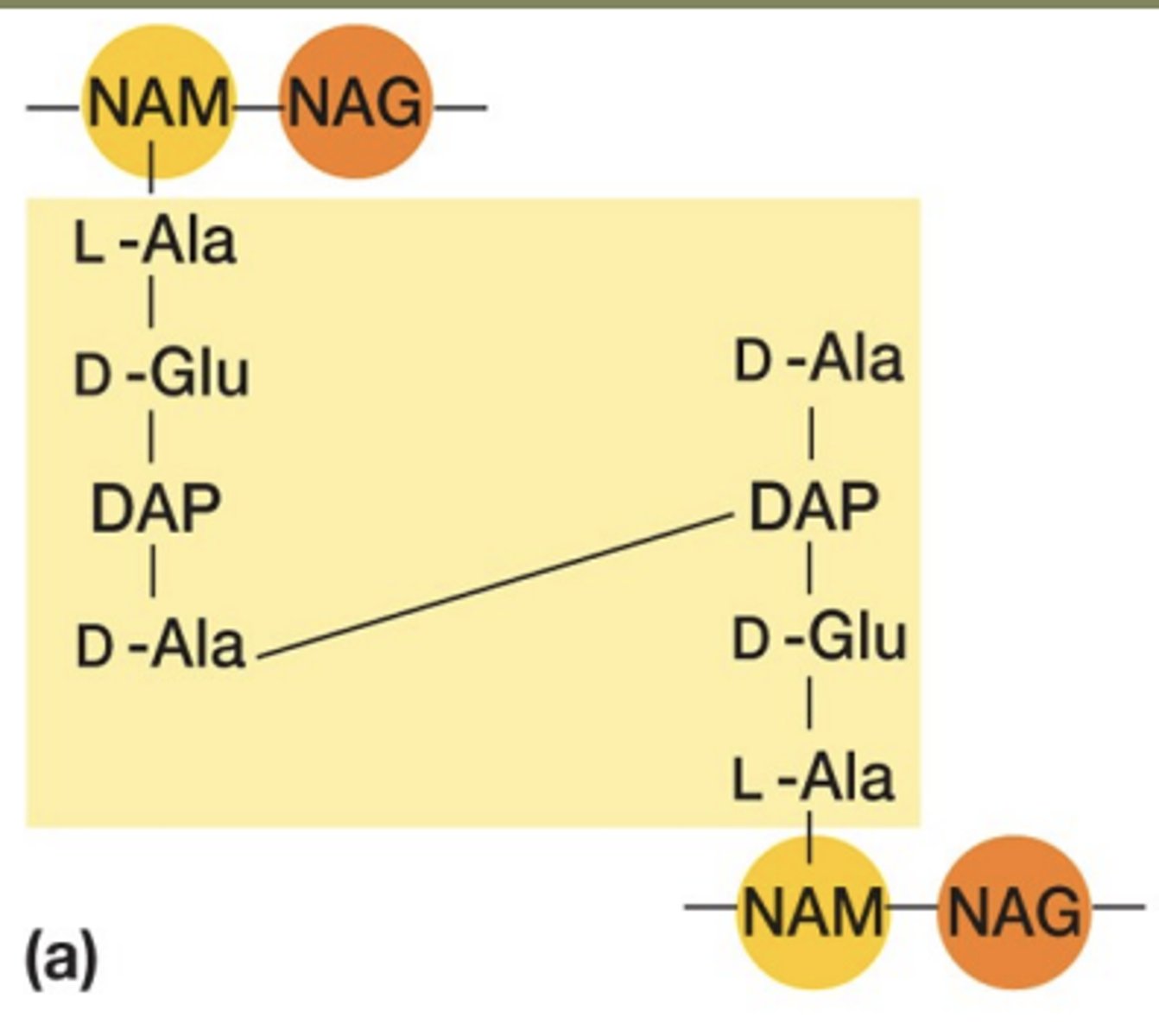
cross links in gram negative cells
direct cross-linking means peptide chains link directly to each other without extra bridging molecules, creating a strong but thinner cell wall.
-no interbridges
peptide interbridges in positive cells
the peptide chains attached to the sugar backbone are often connected by a short chain of amino acids (peptide interbridge) -acts like a connector or "spacer" between peptides on neighboring sugar chains.
gram positive cell
-thick peptidoglycan
-teichoic & lipoteichoic acid
-one membrane
-periplasm
Lipoteichoic acid
found in gram positive, anchored in phospholipids (touches the membrane) B
Teichoic acid
found in gram positive, does not reach membrane
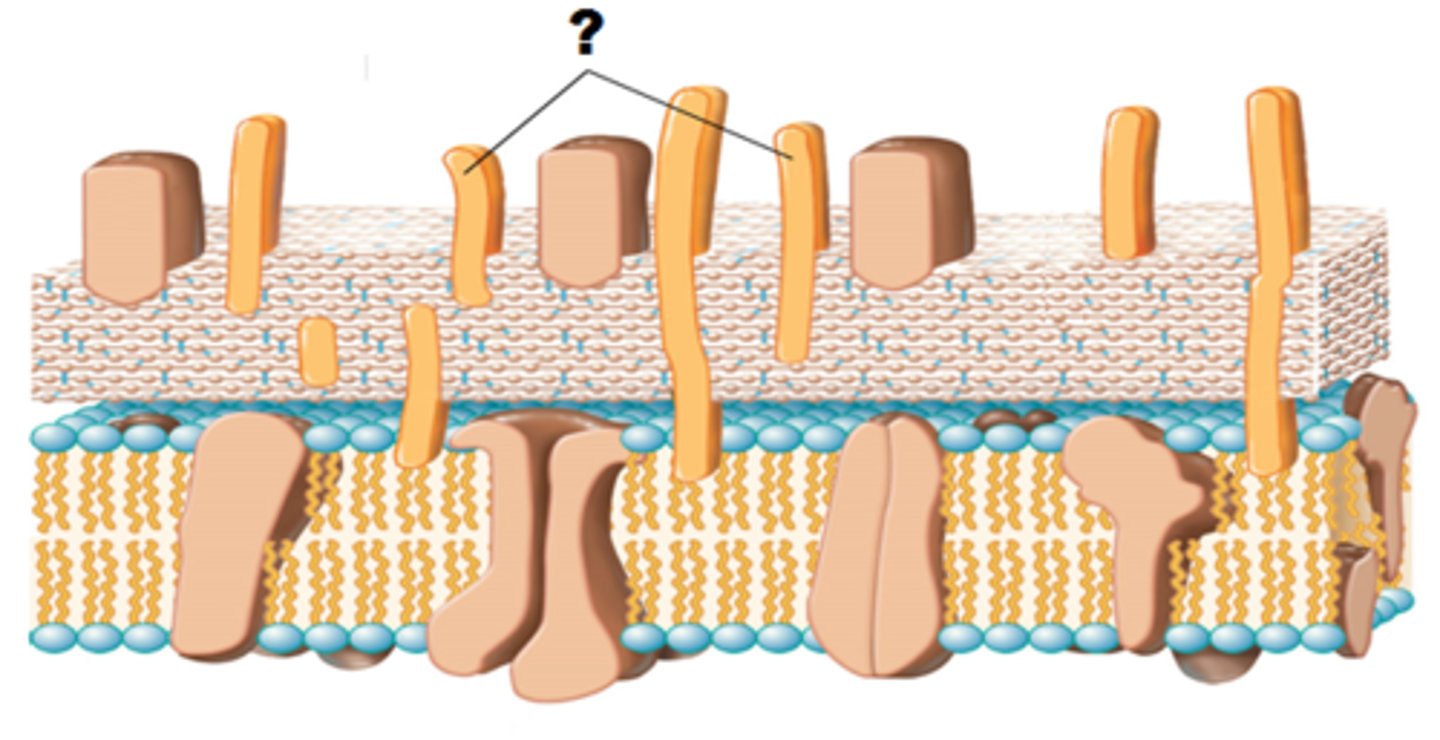
periplasm
inside the cell, storage space
ex) garage
gram pos =small, gram neg =large
gram negative cell
-two membranes
-have lipopolysaccharide
-porins
-thin peptidoglycan
-periplasm
lipopolysaccharide
-outer layer of outer membrane (only in gram neg)
-3 domains: lipid A (endotoxin), core polysaccharide, O antigen
-O is dominant antigen of gram neg cells
endo
inside (the bacteria)
structure of lipopolysaccharide
the main body made of polysaccharides, want antigen to attack bacteria
Antigen
a compound that provokes an immune response
(want it to attack bacteria)
steps of gram stain
1. smear 2.heat fix 3. Add crystal violet (specifically binds to peptidoglycan) 4. Add iodine mordant (intensifies staining) -to stick nd intense 5. Alcohol wash (decolonization) -gram negs will lose crystal violet 6. Add safranin (counterstain) -becomes pink
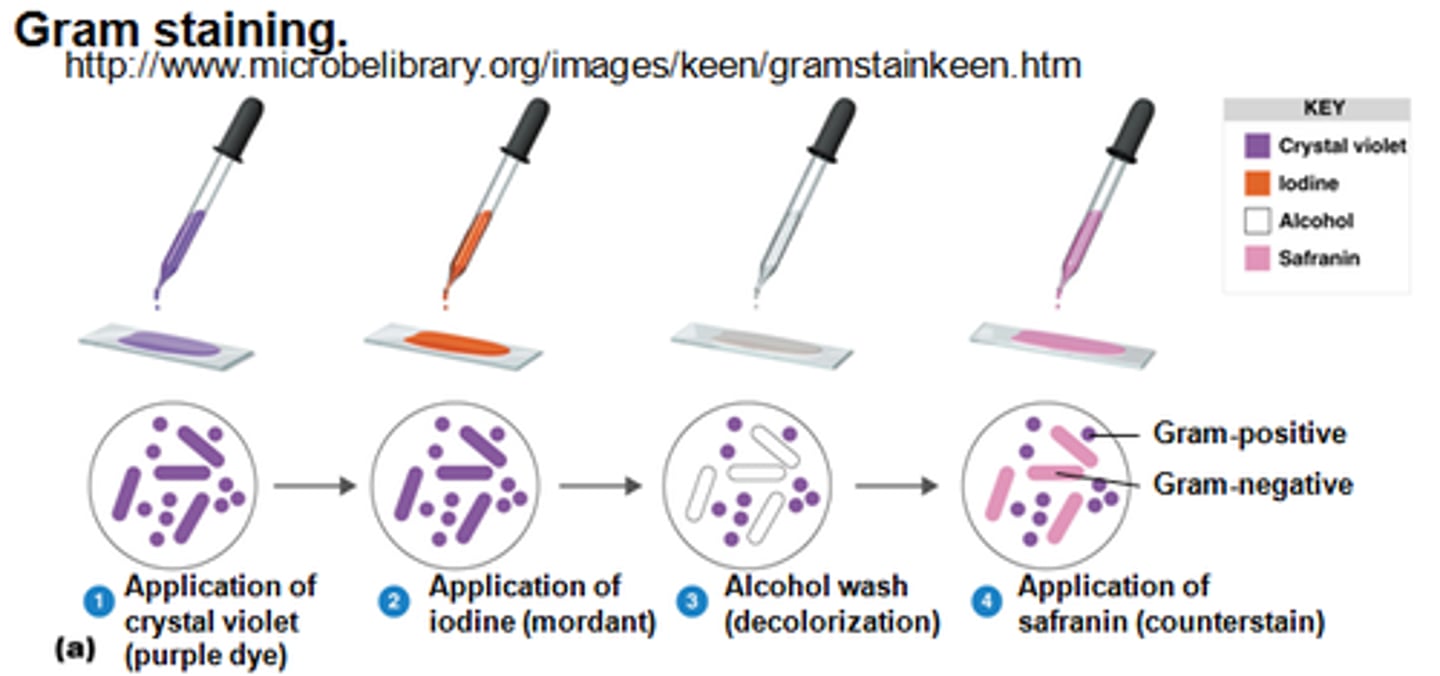
differences of gram pos/neg
-Gram reaction color: purple/ pink
-Peptidoglycan layer: thick/thin
-Gram pos small periplasm
-Gram neg large periplasm
archaeal cell walls
-don't have peptidoglycan
-contains variety of specialized polysaccharides and proteins
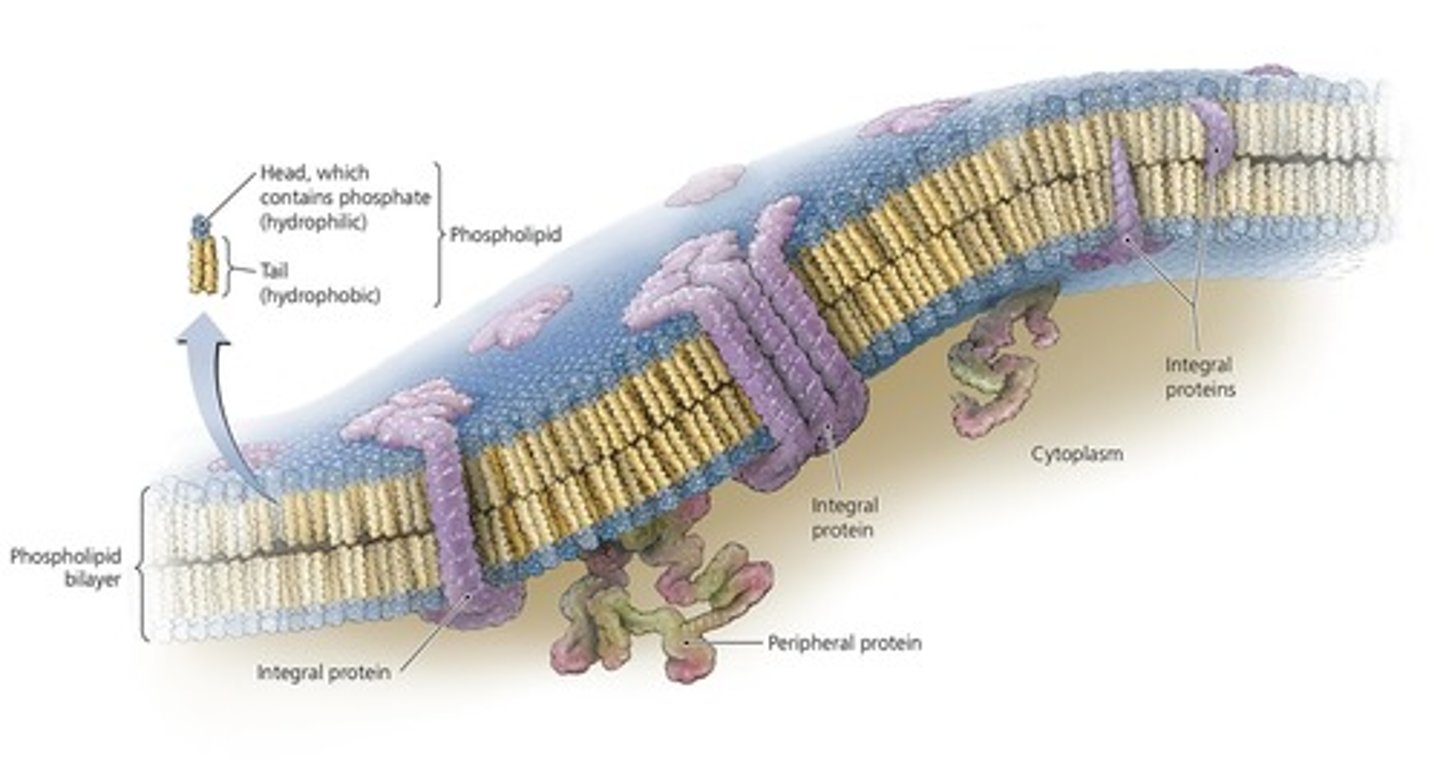
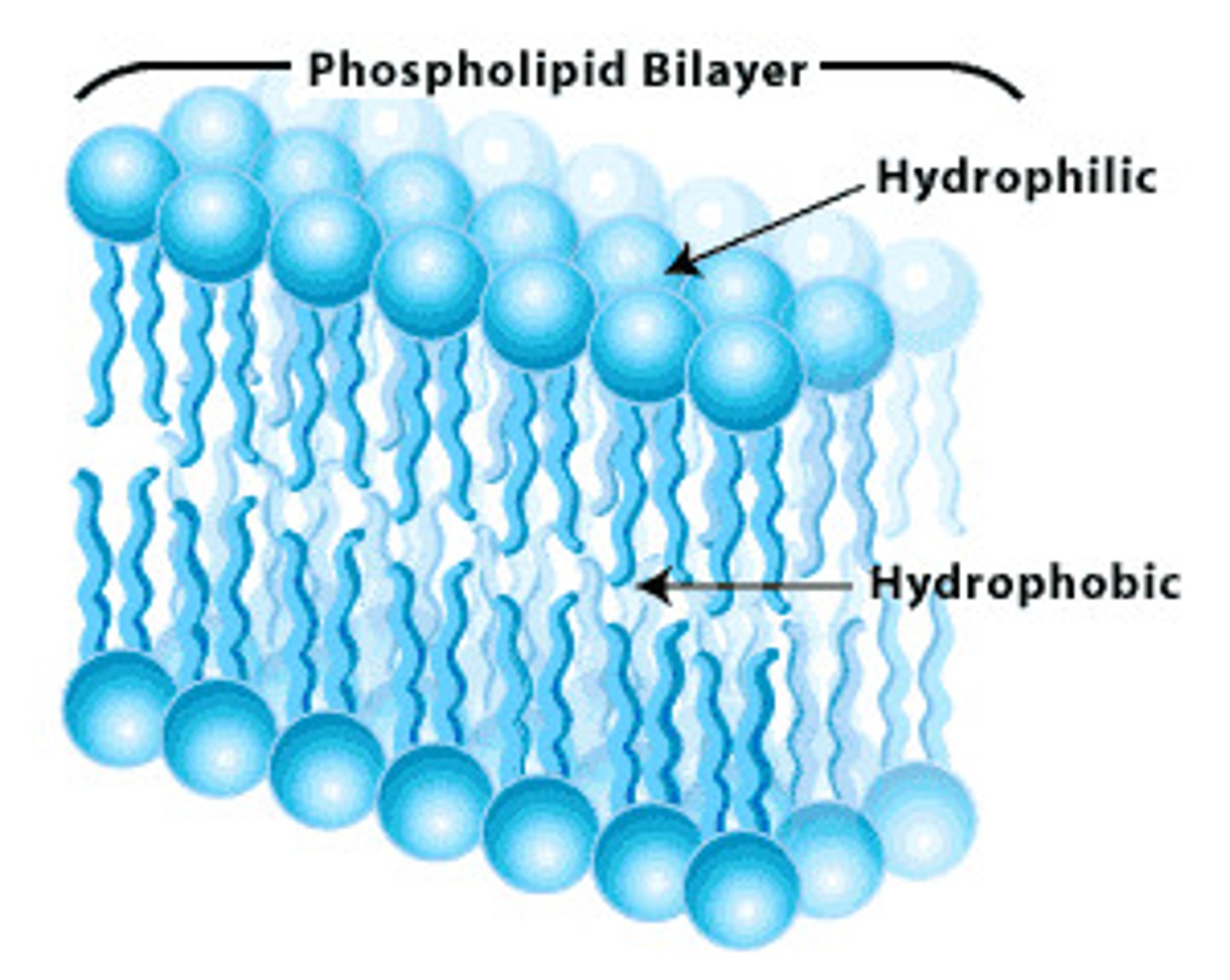
structure of cytoplasmic membranes
-referred to as phospholipid bilayer; composed of lipids & associated proteins
-Proteins important for recognition, receptors, carriers of channels
hydrophilic
polar head
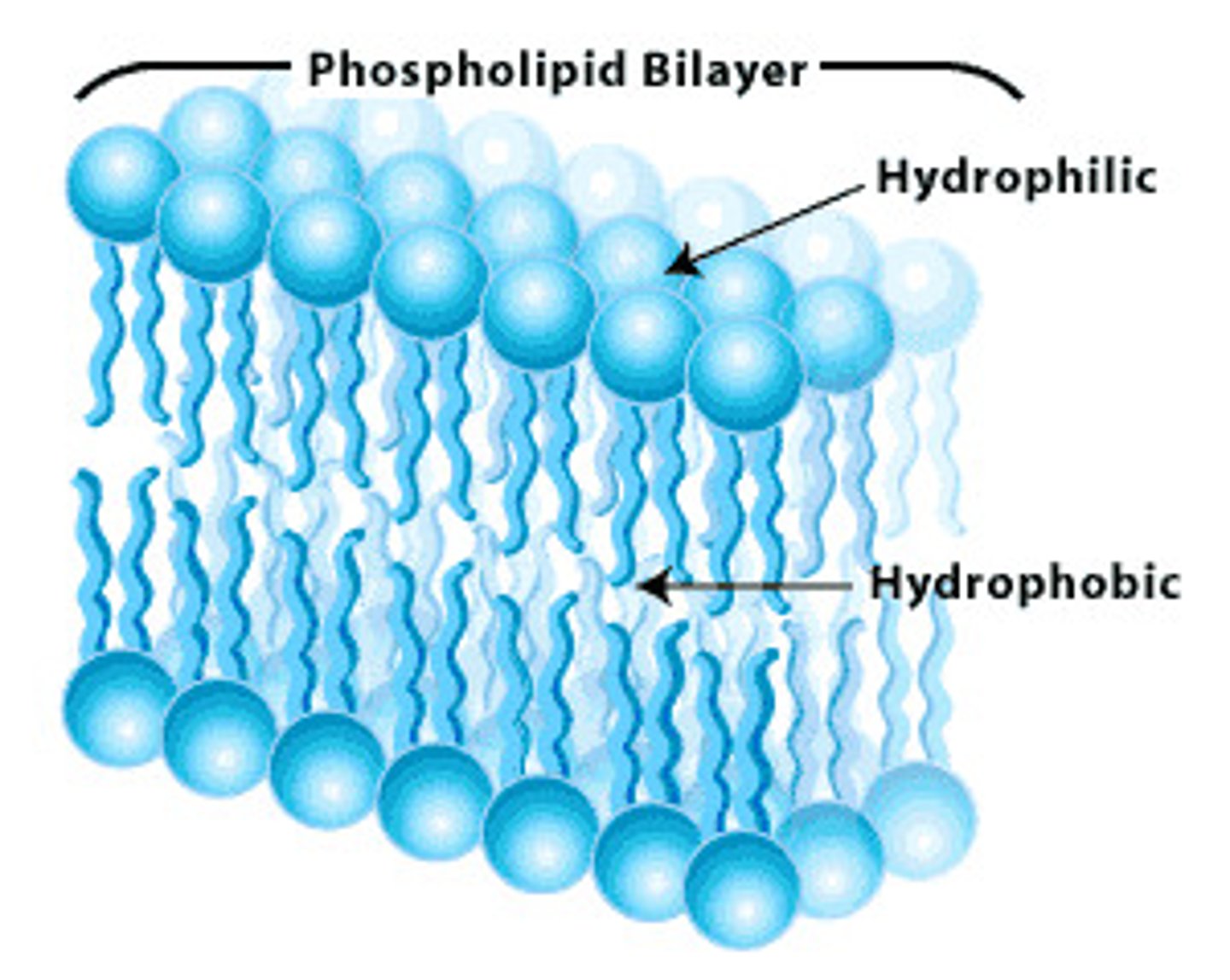
hydrophobic
nonpolar tail
Peripheral protein
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
glycoprotein
-proteins that have attached carbohydrate groups
-essential for cell communication, recognition, adhesion, immune responses,
-unique structure allows them to function in a wide variety of ways across the cell membrane and in extracellular spaces.
integral proteins
-proteins embedded in the cell membrane
-essential for functions like transport, signal reception, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and structural support.
Semi fluid nature
refers to the fluid-like characteristics of the cell membrane ex) bend and flex, proteins can move around
Function prokaryotic cytoplasmic membrane
-Energy storage
-Membrane made of phospholipids
-Harvest light energy in photosynthetic prokaryotes
-Proteins allow substances to cross membrane
-Maintain concentration and electrical gradient (chemicals concentrated on one side of the membrane or the other; Voltage exists across the membrane)
voltage
measure of potential energy because of charge separation
current
the flow of charge
Endospores
some bacteria can produce that go against unfavorable conditions (Allows bacteria to survive in difficult conditions for a really long time
ex) C. Diff
what can small nonpolar molecules in prokaryotic cytoplasmic membrane do
can enter the cells, reach and potentially damage prokaryotic DNA directly, leading to mutations or cell death. (resulting in a damage of dna)
cytosol
liquid portion of cytoplasm
inclusions
-reserve deposits of chemicals
-storage granules or deposits found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells (like bacteria)
what is the function of ribosomes
are the sites of protein synthesis
cytoskeleton
plays a role in forming the cells basic shape
ribosomes structure
composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) + proteins
-prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S (small30, large50)
nucleoid
contains genetic material, a single circular chromosome, has no nuclear membrane
-DNA is in close proximity to the cytoplasm and ribosomes
-more likely to have plasmids
plasmids
a piece of extra chromosomal DNA (can be transferred between bacteria)
what is the function of plasmids
extra genetic information that may encode important features
plasmids structure
composed of DNA, are small circular "mini chromosomes"
inclusion bodies
are non membrane bound granules, usually for storage of nutrients
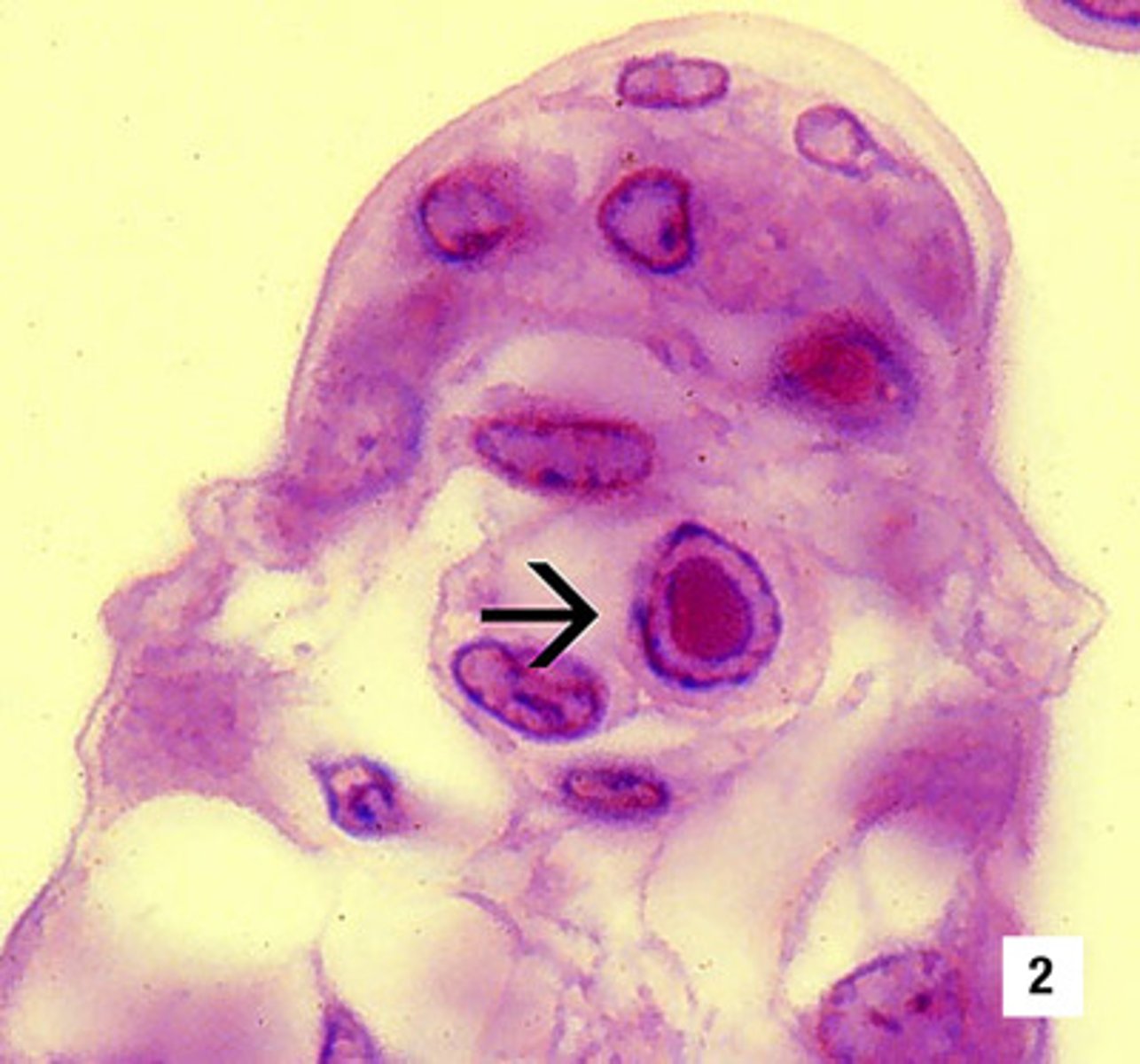
types of inclusion bodies
Polyhydroxybutyrate, volutin, magnetosomes
volutin
p storage
Polyhydroxybutyrate
carbon storage
Magnetosomes
magnetic iron crystals -using iron crystals as a compass needle (to control its motion)
eukaryotic cell
Larger in size, have a nucleus, organelles, division of labor
Animal have no cell wall
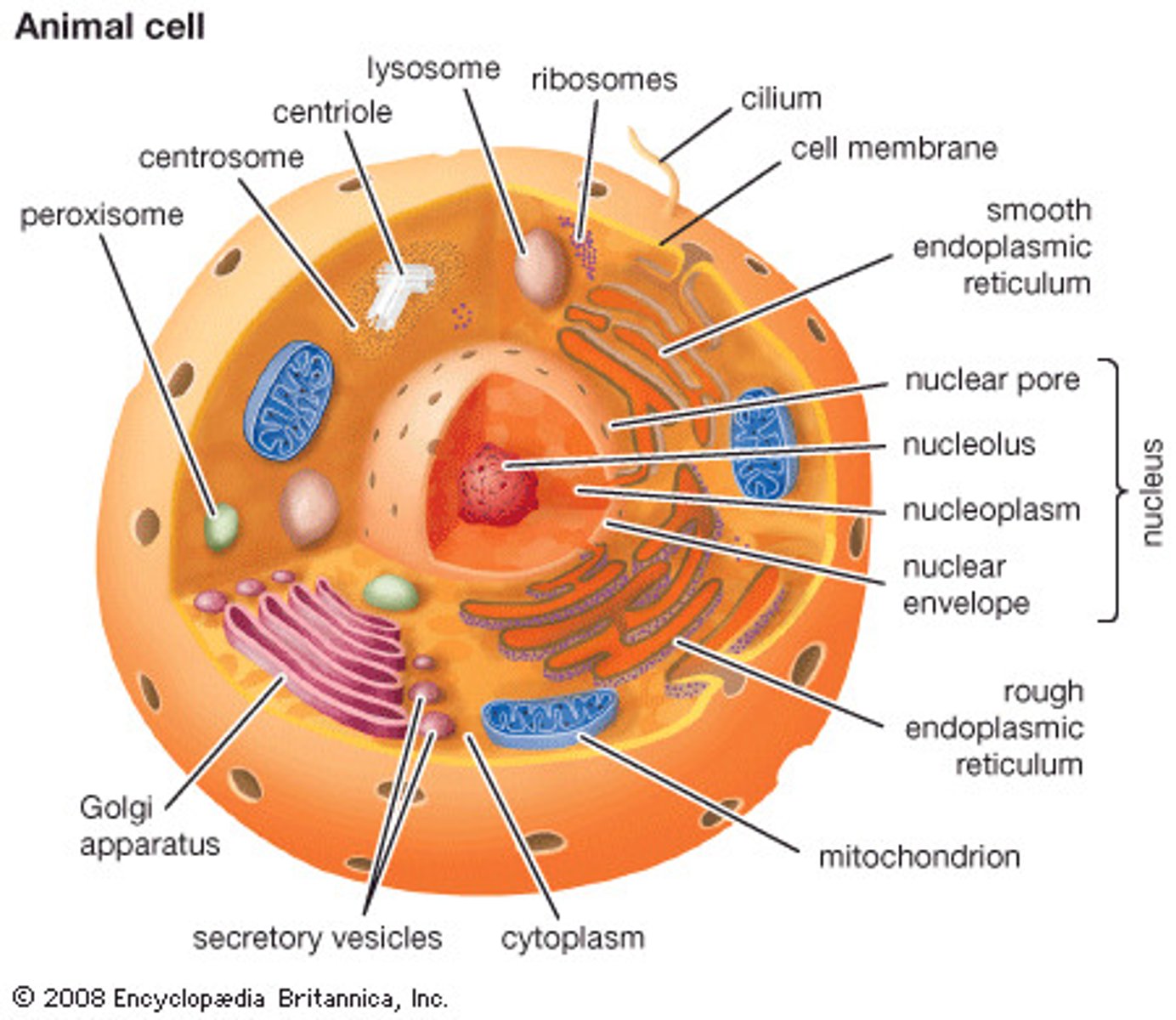
nucleus of eurkaryotic cells
-enclosed by double lipid bilayer
-Nucleolus (rRNA synthesis)
-DNA is inside the nucleus
-Nuclear pores allow traffic into and out of the nucleus
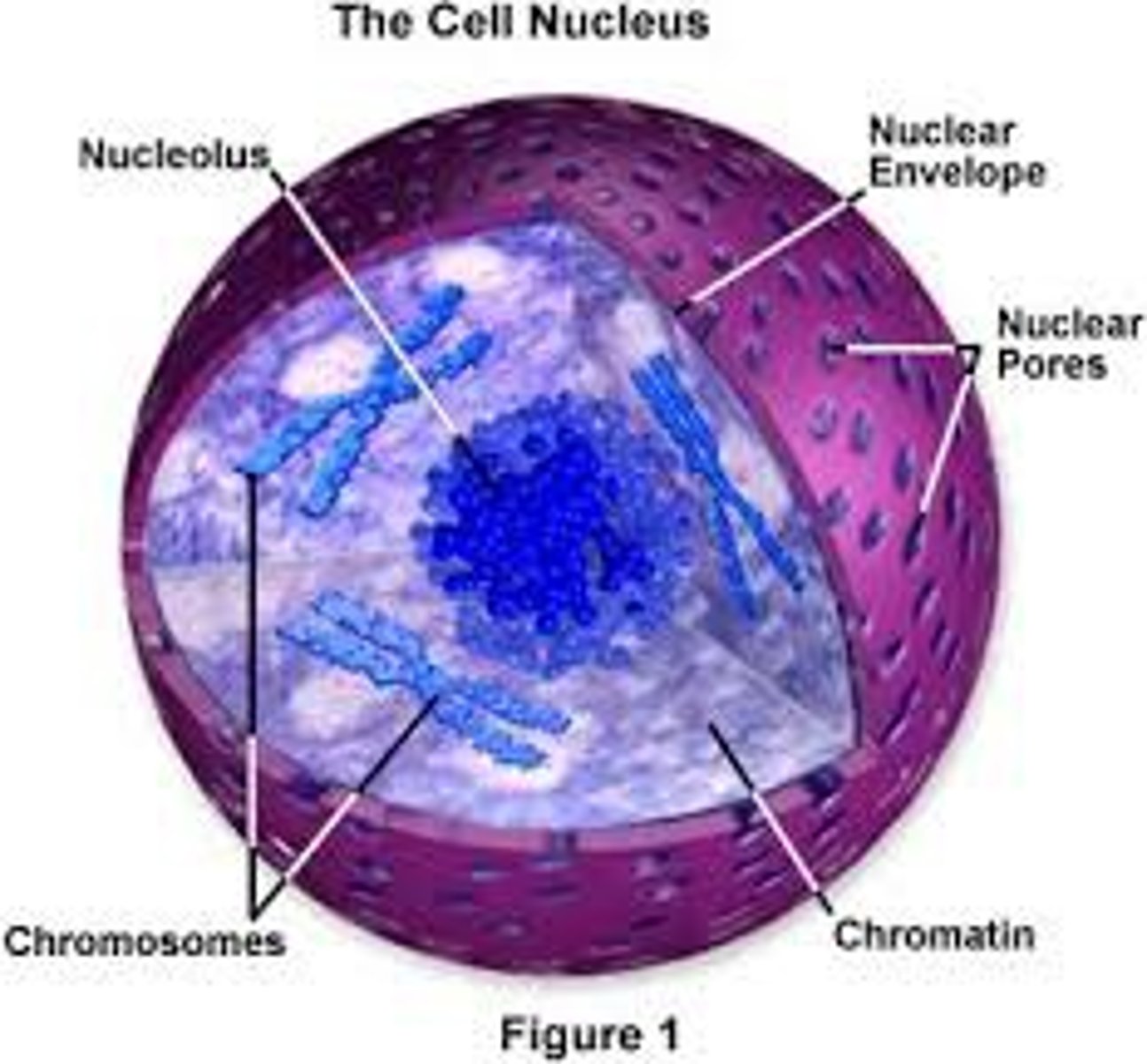
genetic material in eukaryotic cells
multiple linear chromosomes are present, may be haploid or diploid, DNA is condensed on proteins (histones)
histones
a protein that compacts and regulates DNA (in eukaryotes and archaea -not bacteria)
Endoplasmic reticulum
Phospholipid bilayer consisting of smooth & rough ER
smooth ER
Lipid metabolism
Detox reactions
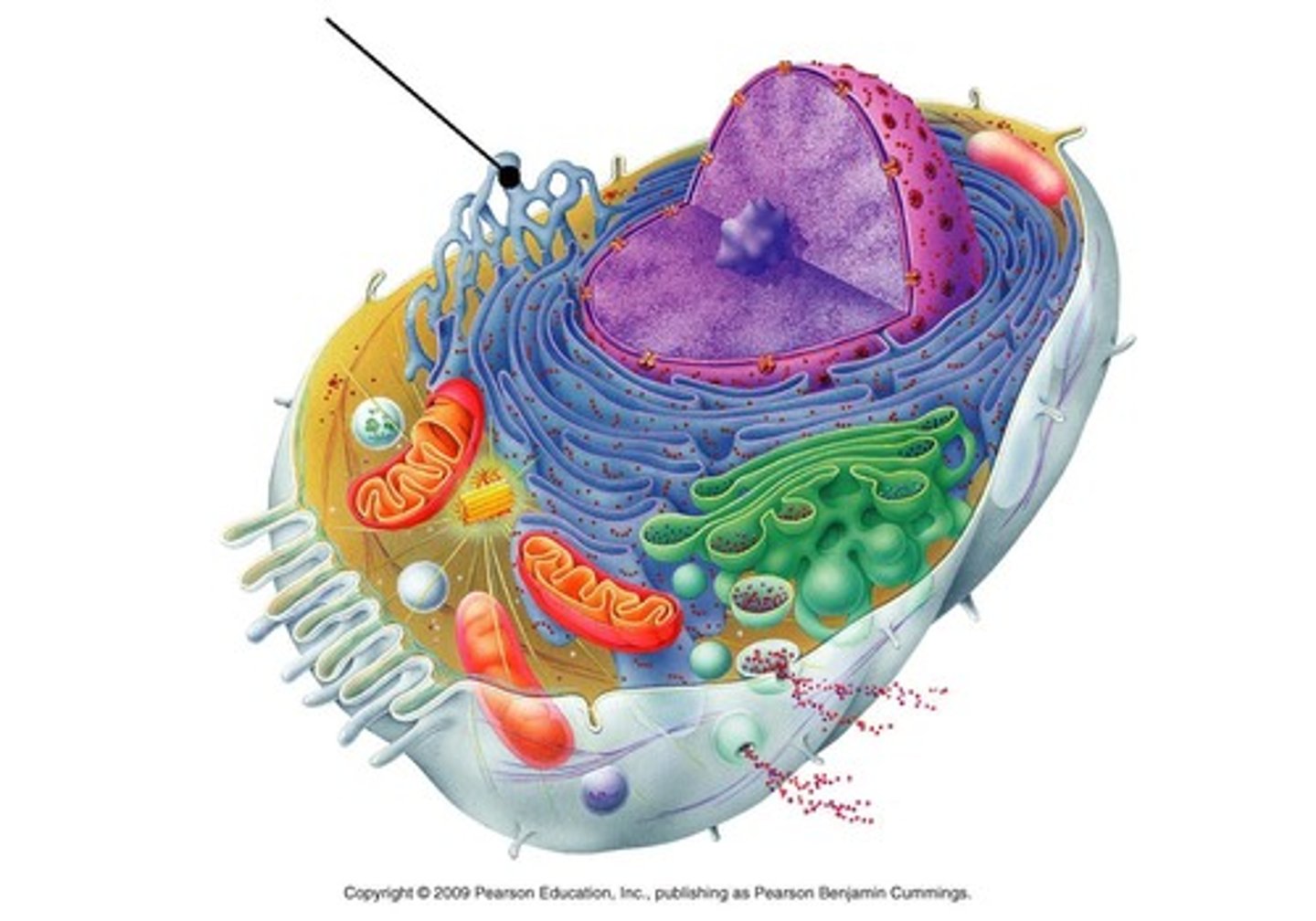
rough ER
Have ribosomes docked
Protein synthesis
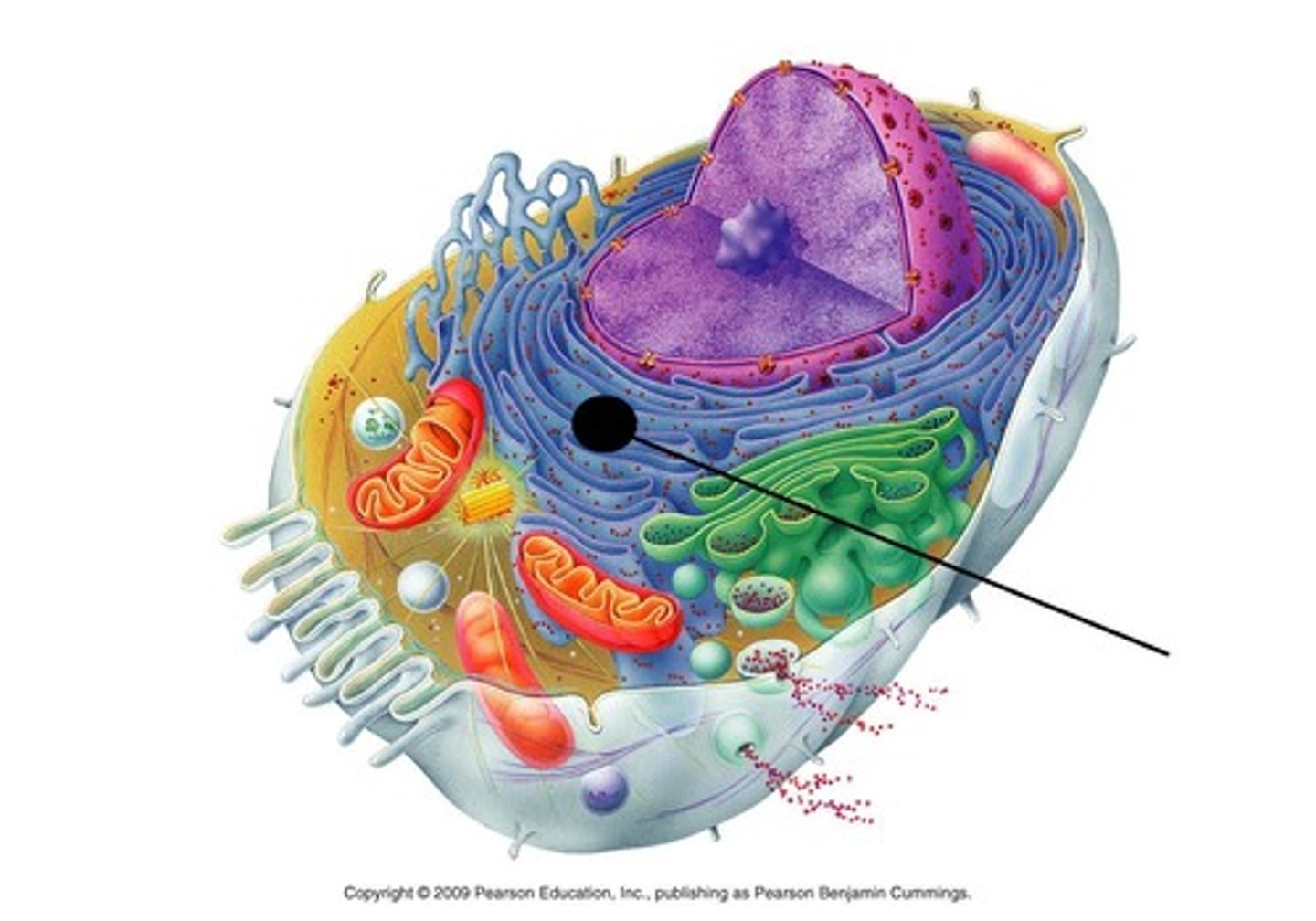
Eukaryote ribosome
Two subunits (40S & 60S) =80S
Translate mRNA into proteins
Have similar structure to prokaryotes but different shape
Antibiotic resistant (selective toxicity -70s but not 80s)
selective toxicity
refers to a drug's ability to target harmful microbes or cells without damaging the host's own cells.
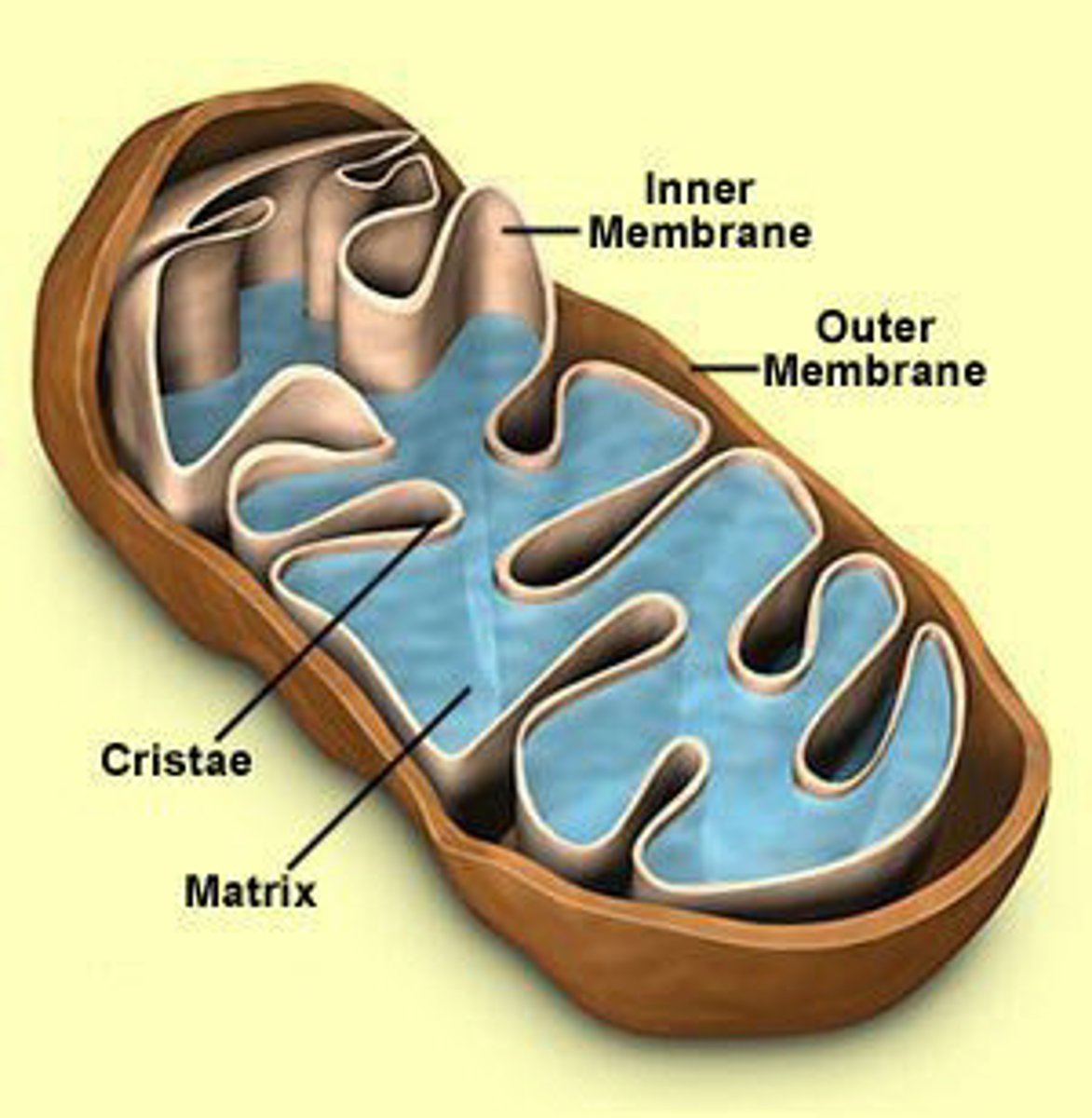
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, Site of respiration, double lipid bilayer
-Look, behave, and reproduce like bacteria (autonomously)
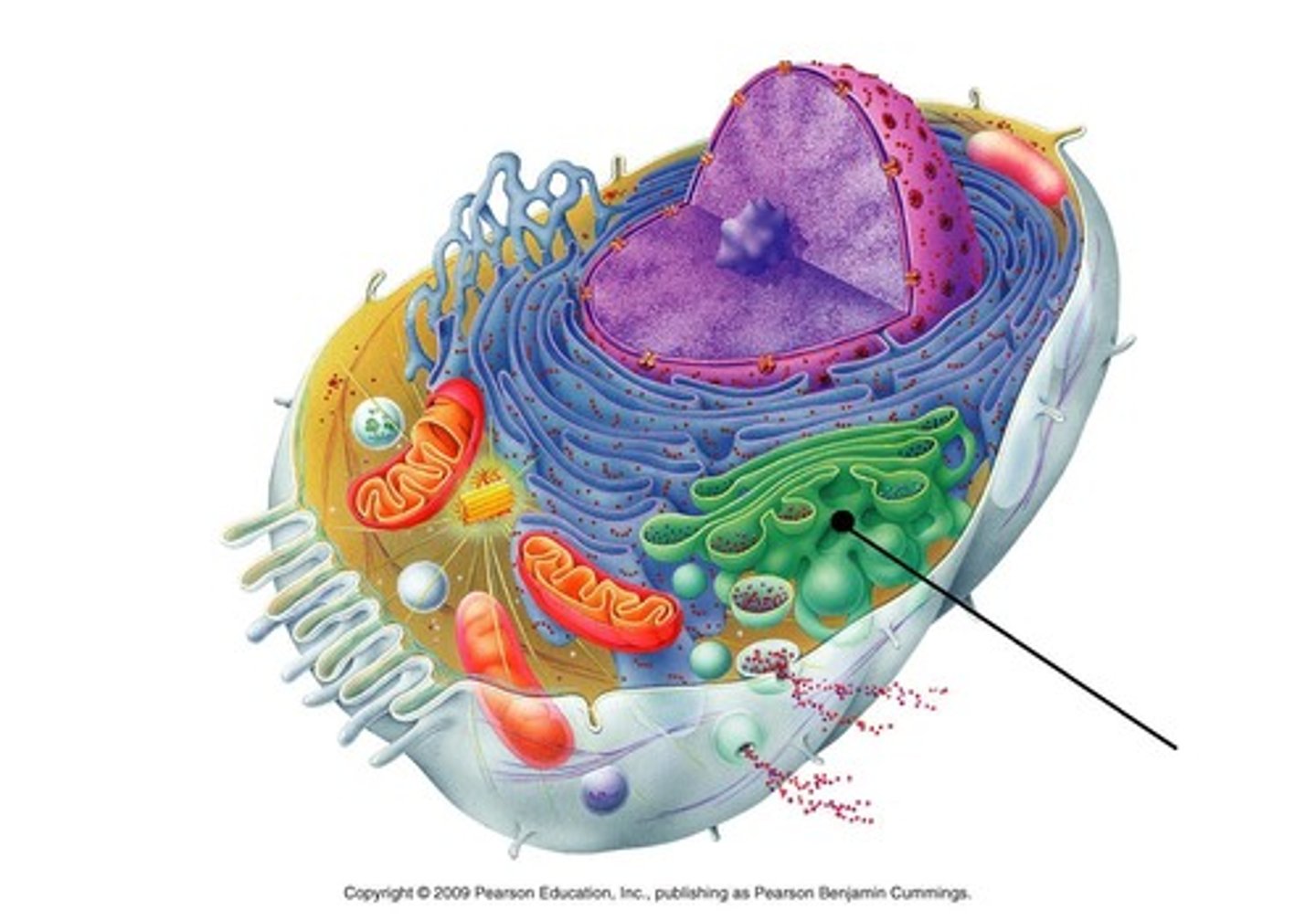
Golgi body
-"Stack of pancakes"
-Protein trafficking centers; Import, processing, export
-Composed of a lipid bilayer (vesicles bud off)
cytoskeleton of eukaryotes
made of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, allowing the cell to maintain its shape, move, divide, and organize its internal components efficiently (polymerized into chains)
-Actin (red) used for muscle contraction; cause motion inside of cell contract and change shape
-microtubules (green) can grow, push, pull
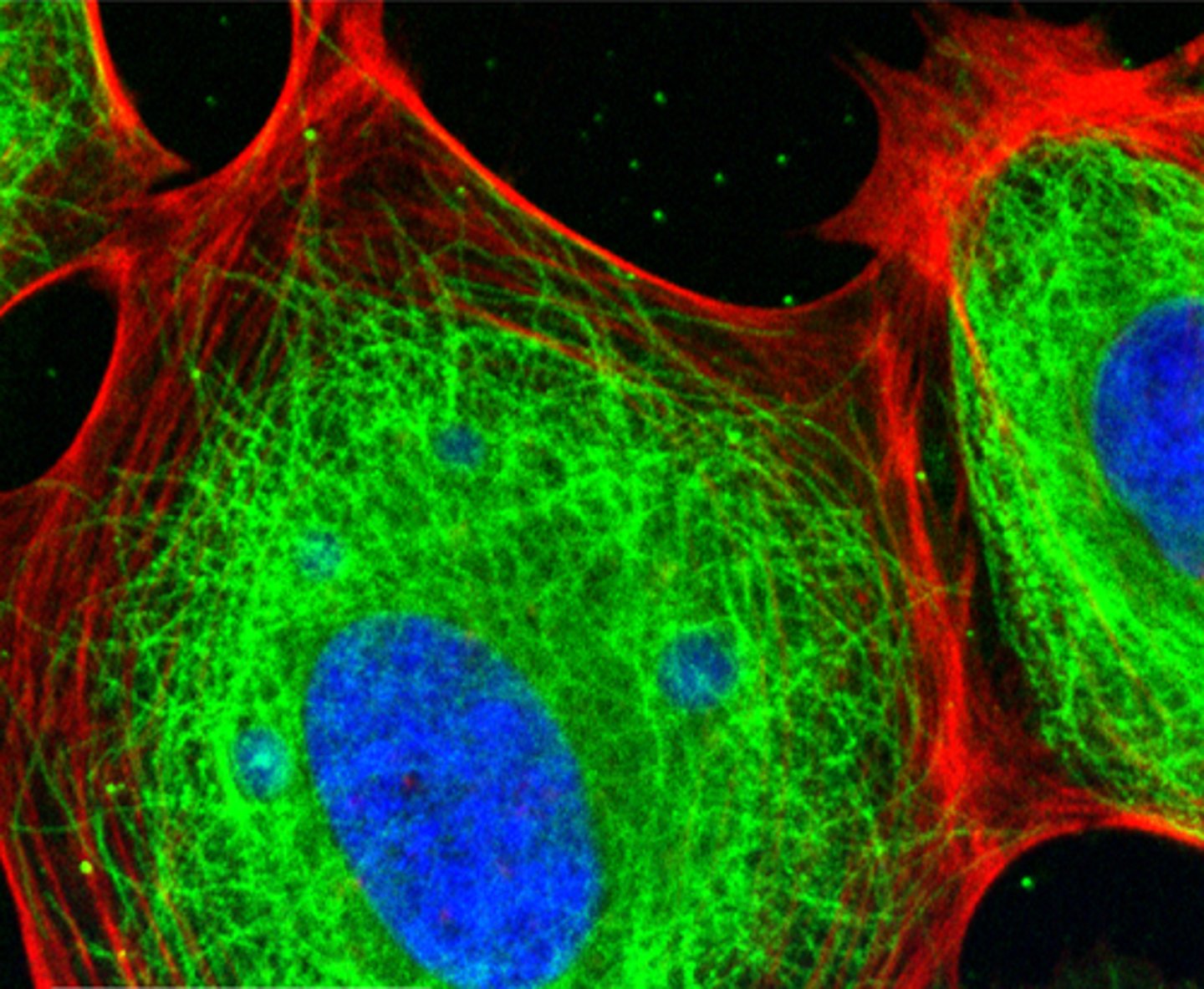
Vacuoles
storage sites for water food, enzymes and waste, lipid enclosed space, vary in size/func
Central vacuoles
provide turgor pressure