Exotics Exam 4 (Birds)
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
LC - Avian biology, husbandry, and nutrition
Class aves, order psittaciformes
What is the taxonomy of birds?

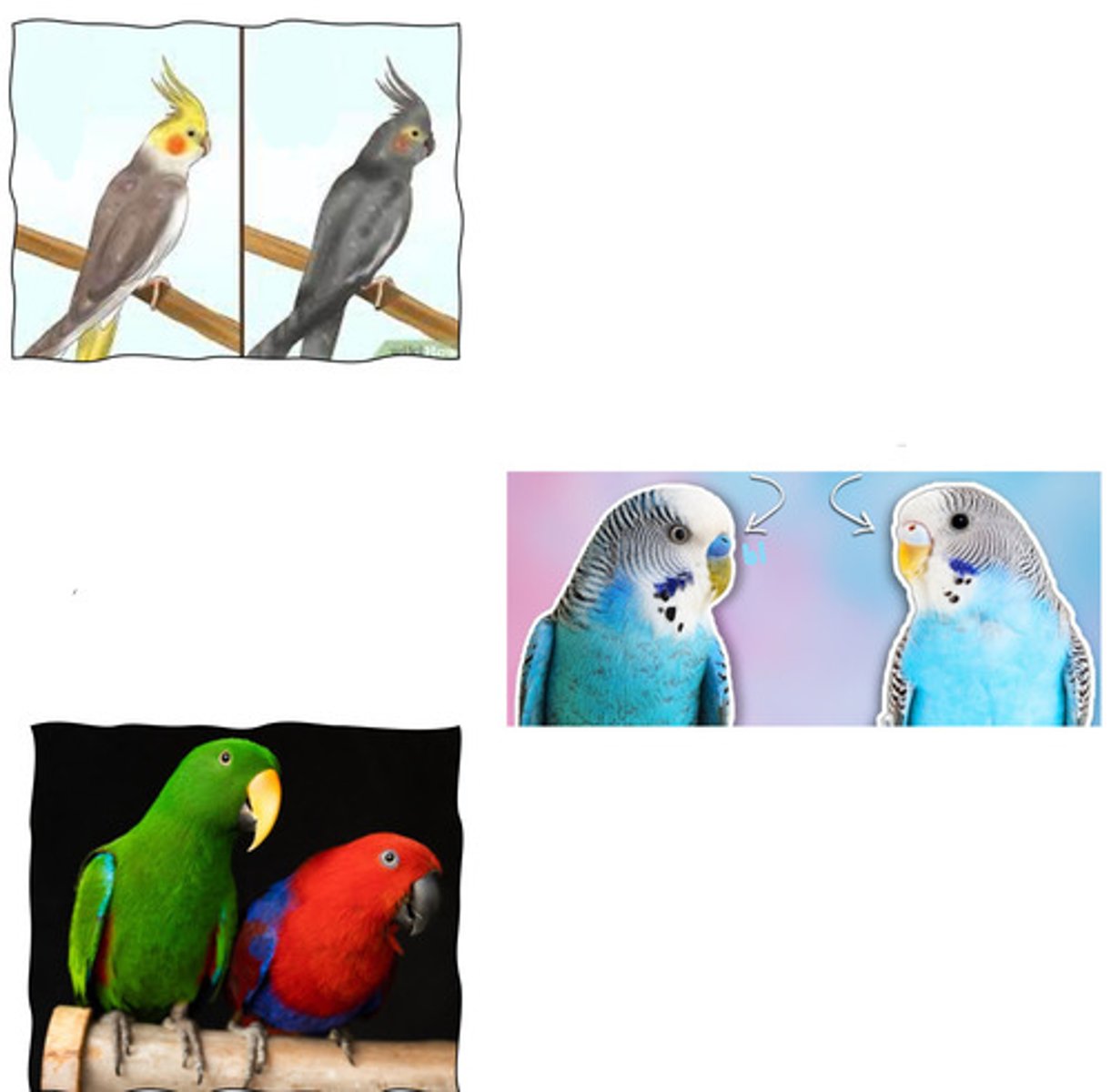
Cockatiels - males have blush on, females have bards under tail feathers
Budgerigars - blue cere in males, brown in females (determined by e2)
Eclectus parrots - males green, females red
How can you tell male vs female in these 3 species of birds?
Cockatiels?
Budgerigars?
Eclectus parrots?

History of egg laying, surgery (endoscopy), DNA testing
Some bird species don't have defining sexual characteristics. How do you sex these guys?
ZZ male, ZW female (females heterogamic, this is opposite of males!)
Bird chromosomes?
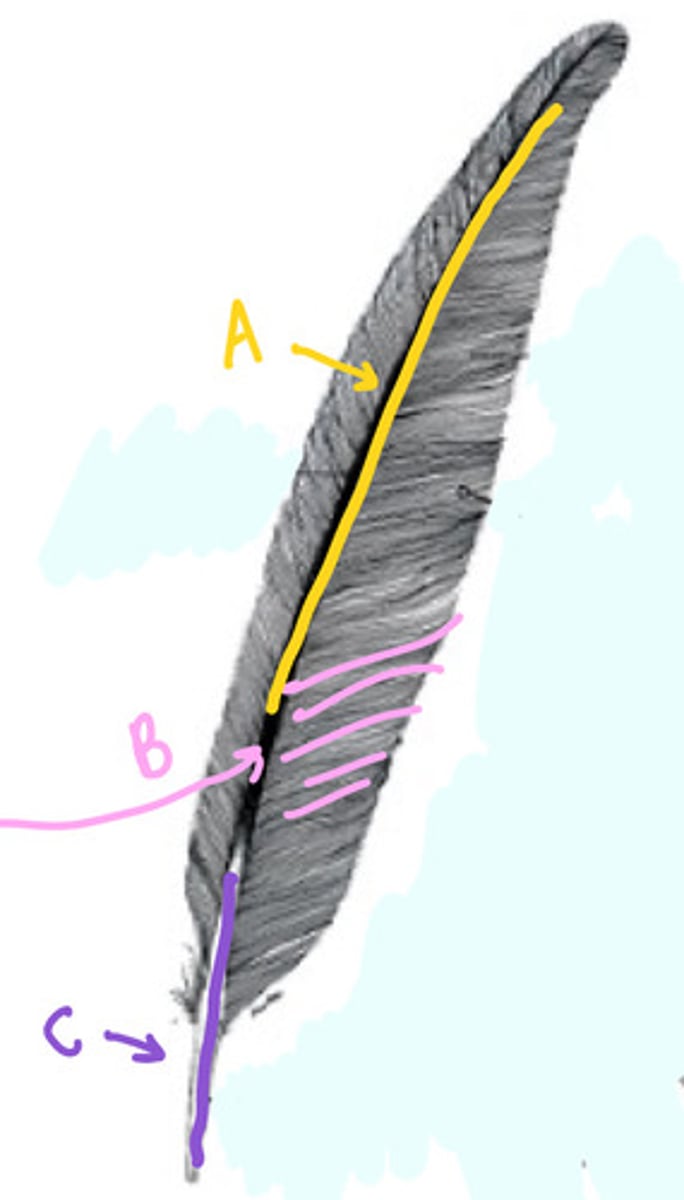
A rachis
B barbs (plus hooks)
C calamus
Name the parts of the feather
Contour - flight and coverage
Down - insulation
Powder down - flanks and produce thin keratin dust for plumage maintenance
What role do each of these feather types have?
Contour feathers?
Down feathers?
Powder down feathers?
Primary- 10; from carpometacarpus, numbered outward (in to out)
Secondary- 20; from ulnar; numbered inward (out to in)
Birds have primary and secondary wing feathers. How many do they have of each? Where do they each arise from? How are they numbered?
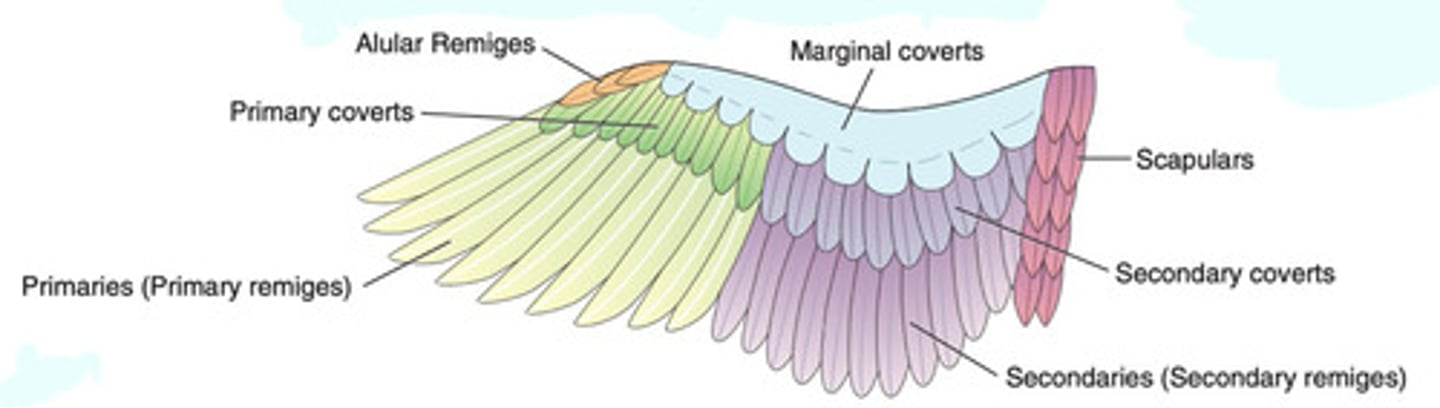
Remiges; Asymmetrical (leading edge is narrower)
Rectrices; Symmetrical
Wing feathers are (rectrices/remiges) and are (symmetrical/assymetrical) in shape
Tail feathers are (rectrices/remiges) and are (symmetrical/assymetrical) in shape
Only on primary feathers
For blood feathers (don't cut, can cause hemorrhage)
As little as possible (and symmetrically!)
Wing trimming should only be performed on what feathers?
What should you check for prior to trimming?
How much should you trim?
False, more trimmed
T/F: Smaller birds may require less feathers trimmed than bigger birds
10
7
4
How many feathers should you trim on each of these bird species:
Small budgies
Cockateals/lorakeets
Amazon parrots
Ulna and tibiotarsus; other bones pneumatized and part of air sac system
What 2 locations can you place an IO catheter in birds? Why not just anywhere?
Top rhinotheca (rhino bc looks like a horn), B gnathotheca; covered by rhamphotheca (keratin layer)
What are the top and bottom beaks of a bird called? What are both of these covered by?
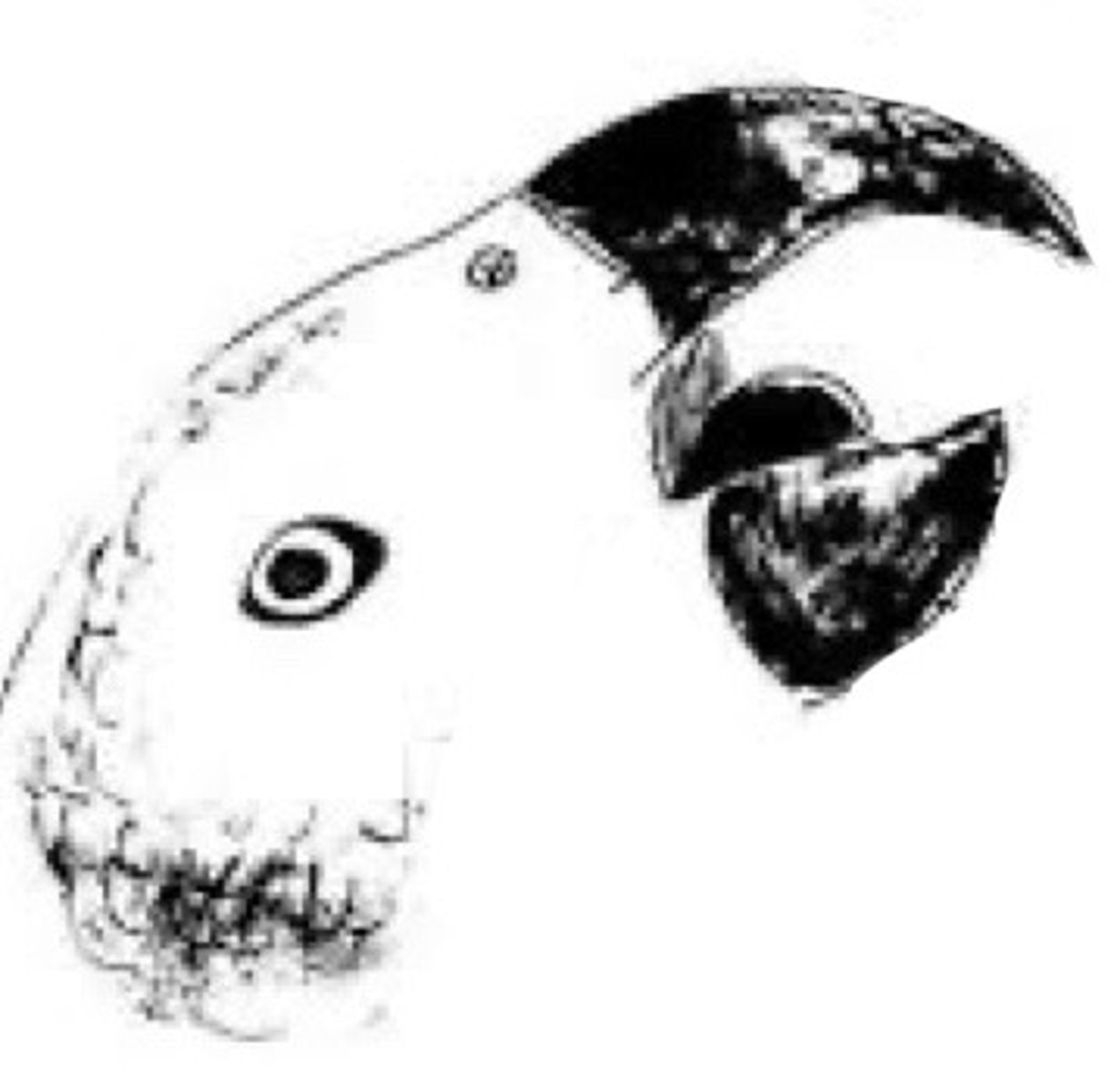
They become blunted with hypovitaminosis A
Why do we need to make sure to check birds' choanal papillae in every exam?
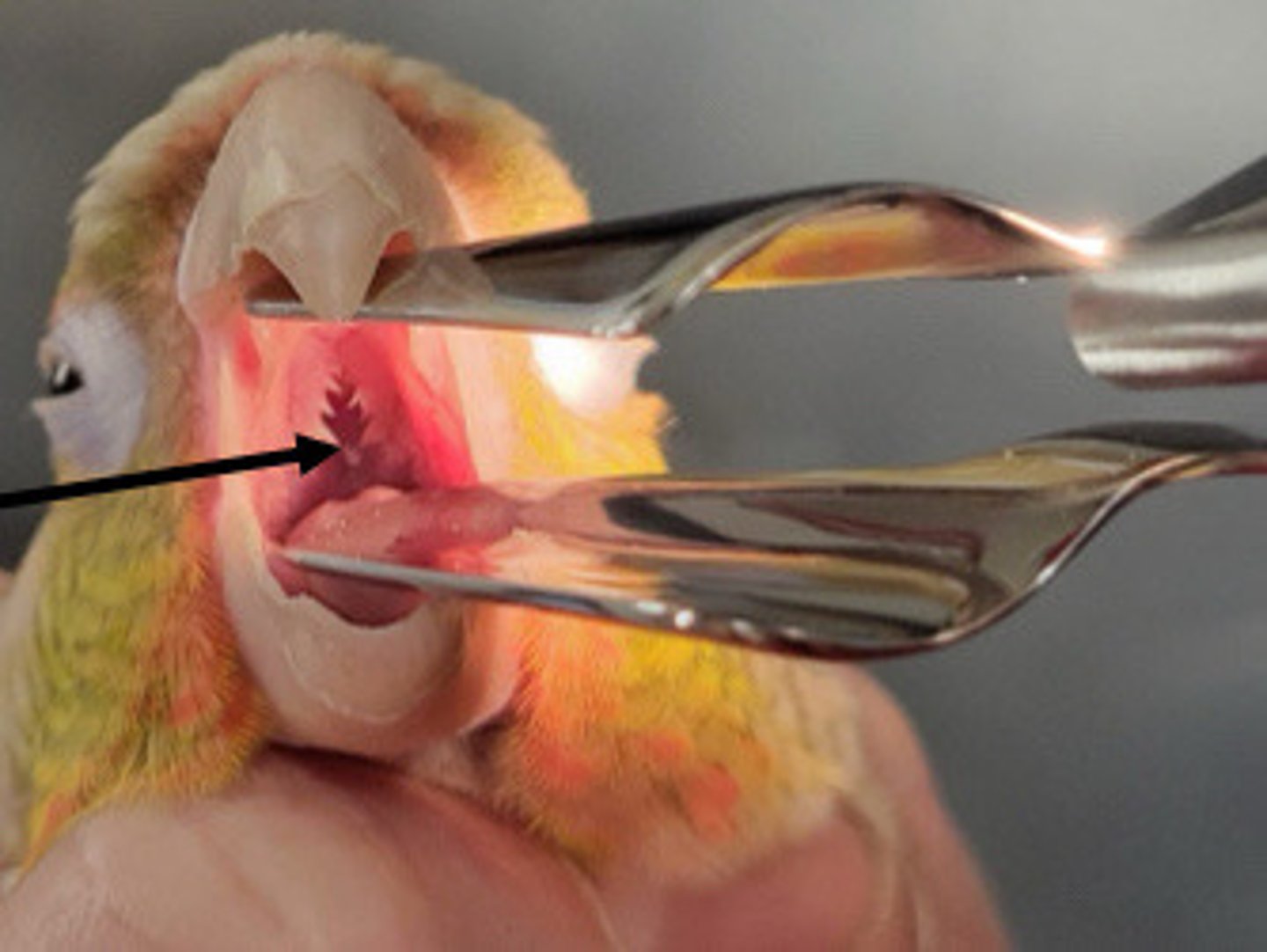
Yes glottis; no epiglottis; easy to intubate; use uncuffed ETT
Do birds have a glottis? Epiglottis? Are they easy or hard to intubate? What special ETT should be used?
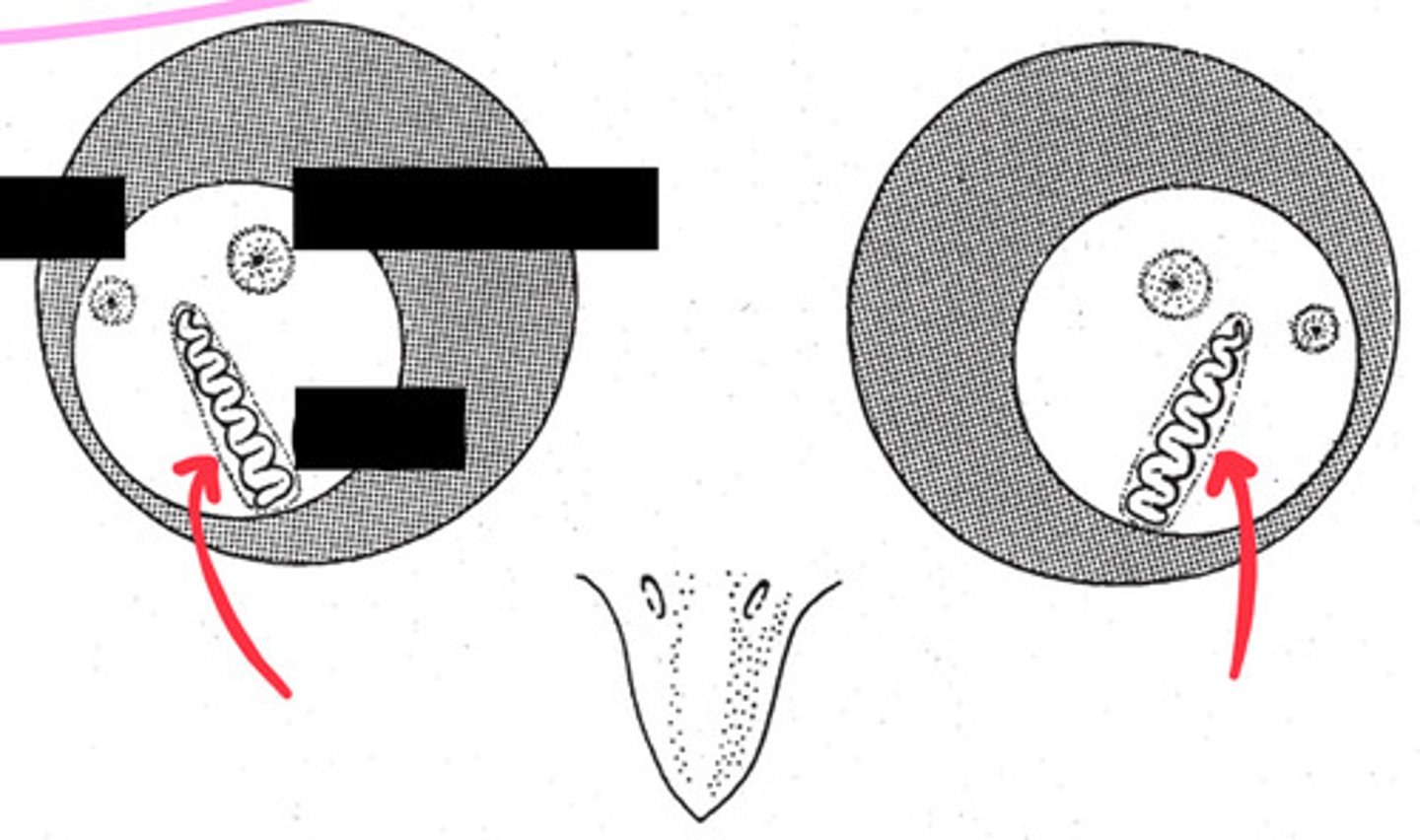
Flat shape (chickens), globose shape (most birds), tubular shape (owls)
What are the 3 most common bird ocular shapes and what bird species have them? (List in order of the pictures)

Pecten
The __________________ is a unique eye structure in birds. It is found in the fundus and provides nutrients to the retina and vitreous body. The red arrows are pointing to it in this picture.
They have a striated iris muscle
We cannot accurately do a PLR test in birds, why?
Avascular; Rigid (scleral ossicles)
Birds have (vascular/avascular) retina with a (rigid/flexible) globe
Crop; Owls nor ducks
The _____________ is a storage structure that is present in most birds. It is not present in these 2 =
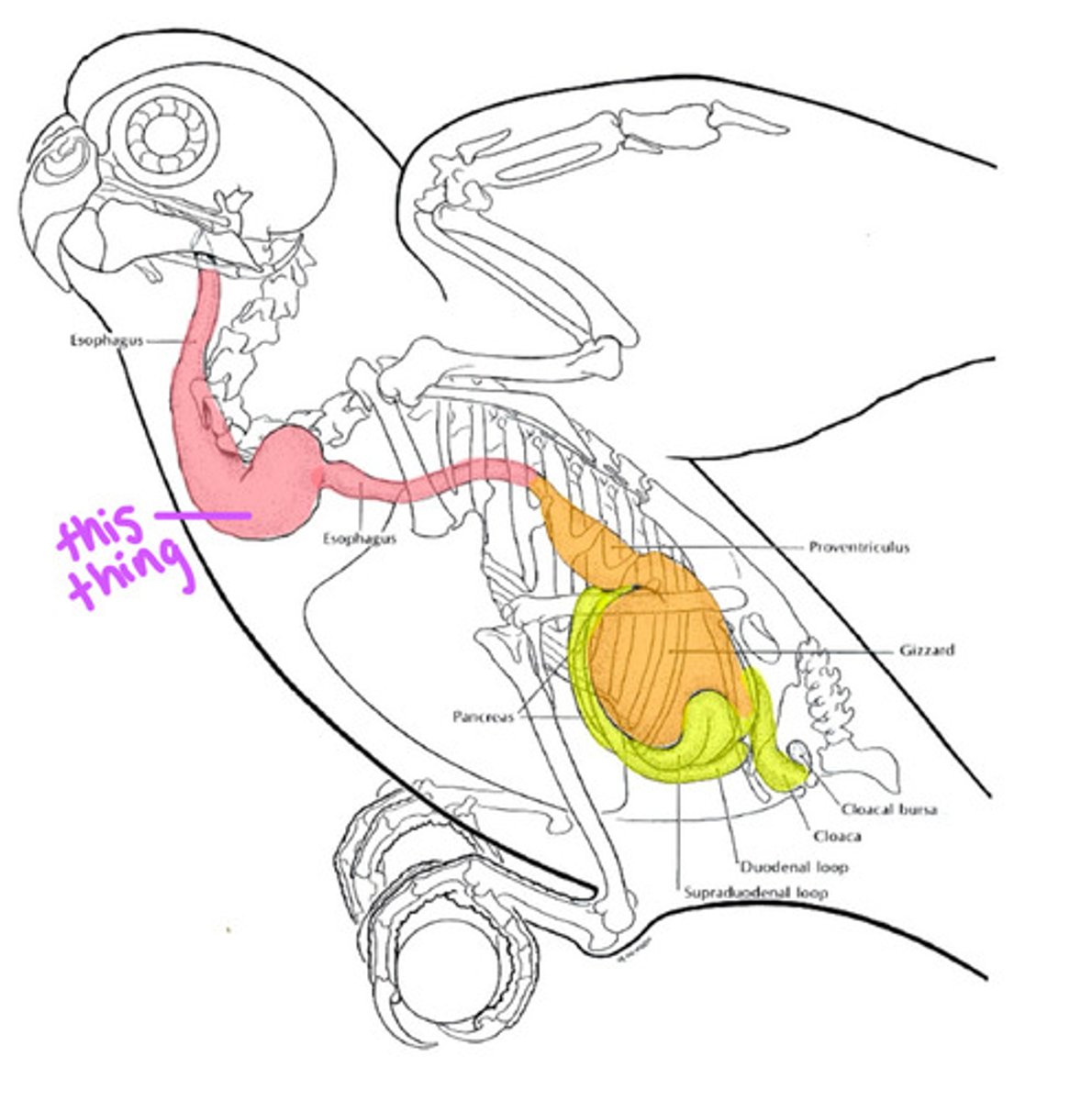
Proventriculus which is secretory (first stomach) and Ventriculus which is muscular (second stomach); they are connected by the isthmus
The avian stomach consists of two parts, name them and their role. There is also something that connects the two stomachs, what is it called?
Meckel's diverticulum; 2
The demarcation between the small and large intestines is at the __________________________. Large intestine has _____ ceca (can be large or vestigial).
(CUP! C you pee)
Coprodeum- rectal emptying, water reabsorption
Urodeum- repro tract, ureters empty
Proctodeum- bursa of fabricus and phallus here
What are the 3 parts of the cloaca? What are their roles?
Several
Surrounded by air sac diverticuli
30% looped, 70% nonlooped
Not very
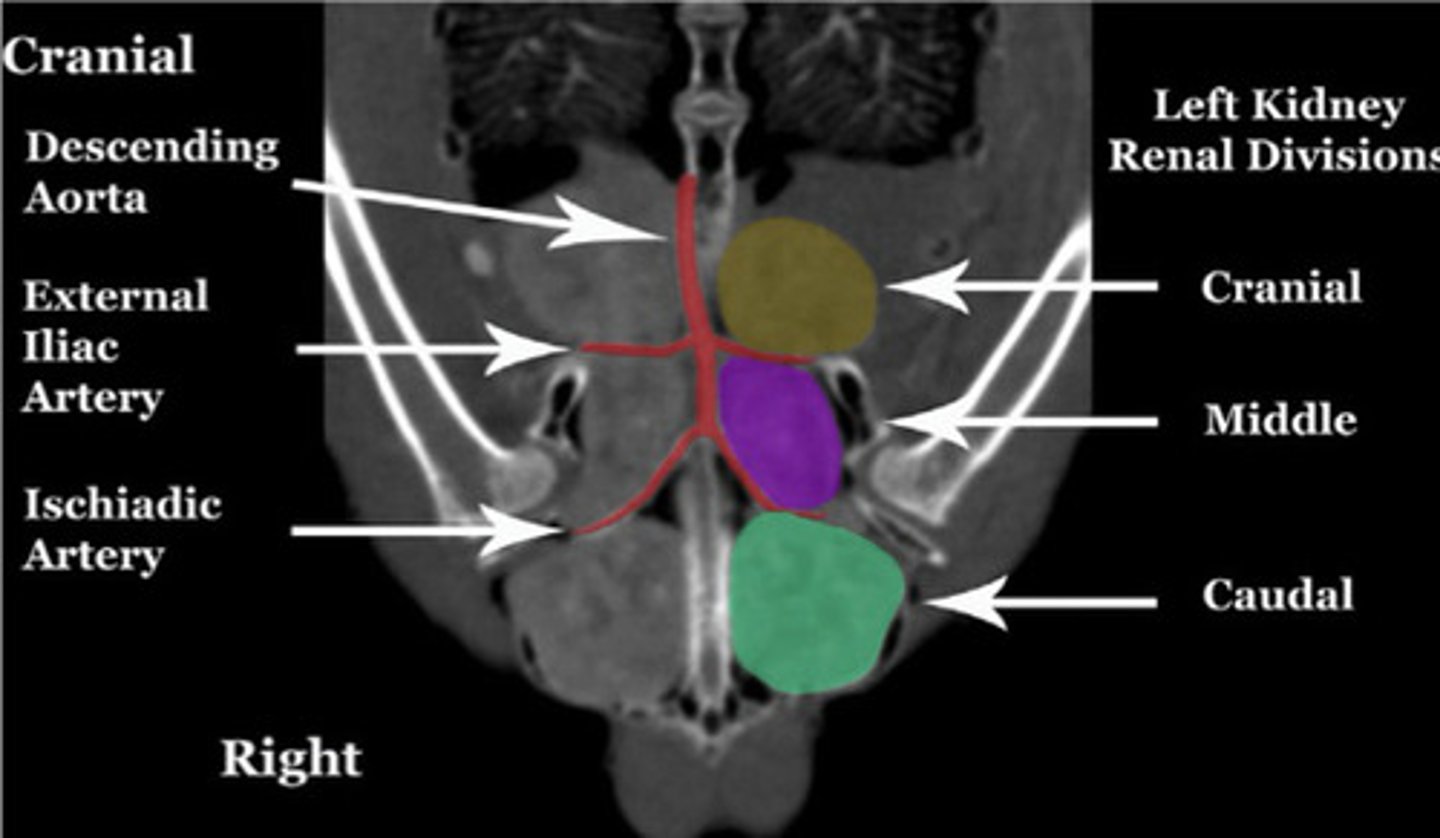
Bird kidneys are composed of (one/several) lobe(s)
Why is US'ing them difficult?
What types of nephrons do they have and what % do they make up?
Is their urine concentrated?
They excrete uric acid
Birds are uricotelic. What does this mean?
Left; Both
Girl birds have a (right/left/both) sided reproductive system
Boy birds have a (right/left/both) sided reproductive system
24hr
Eggs take about ____________ to be produced
Phallus
Male ratities (flightless birds) and ducks have a ______________ that has a lymphatic erectile mechanism
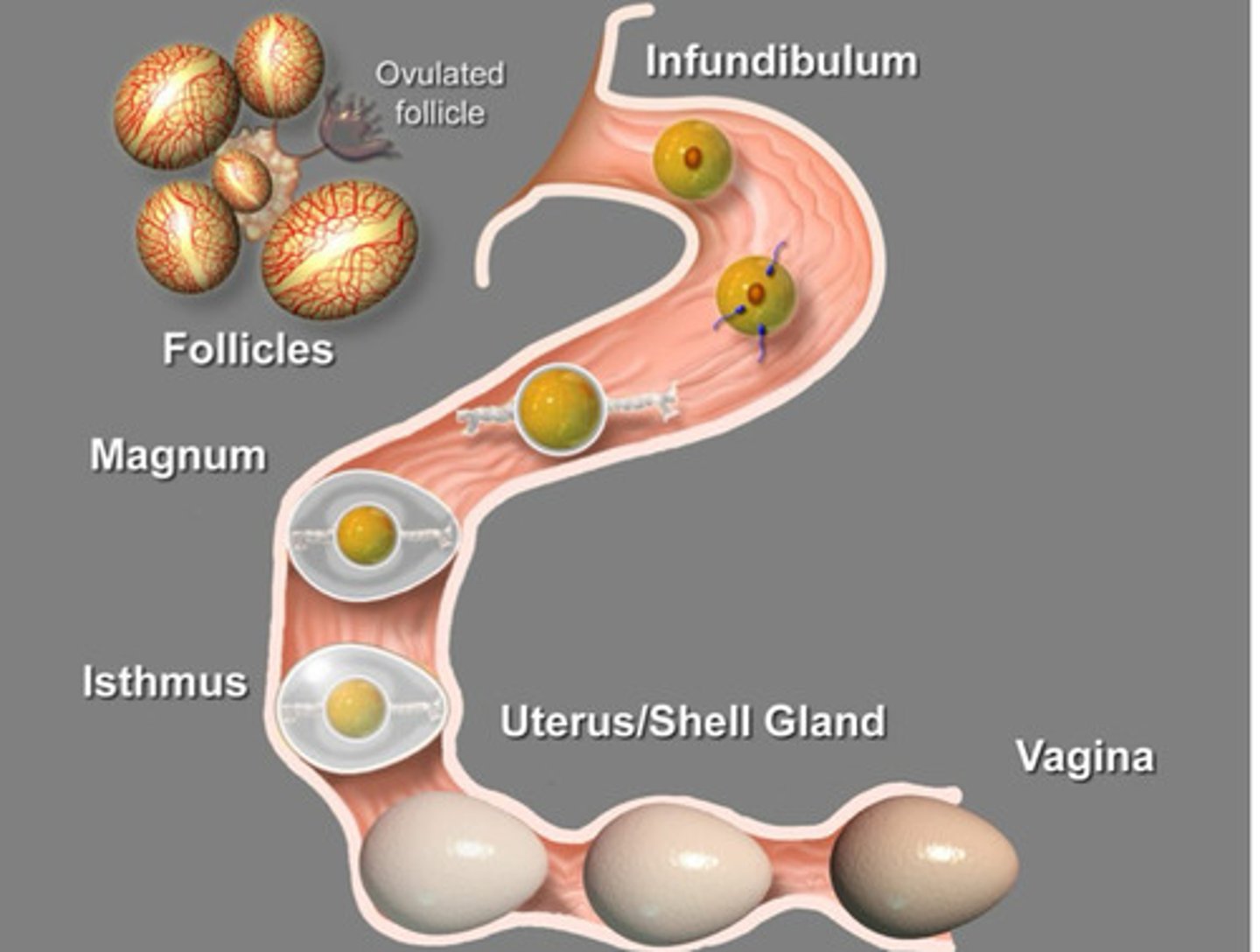
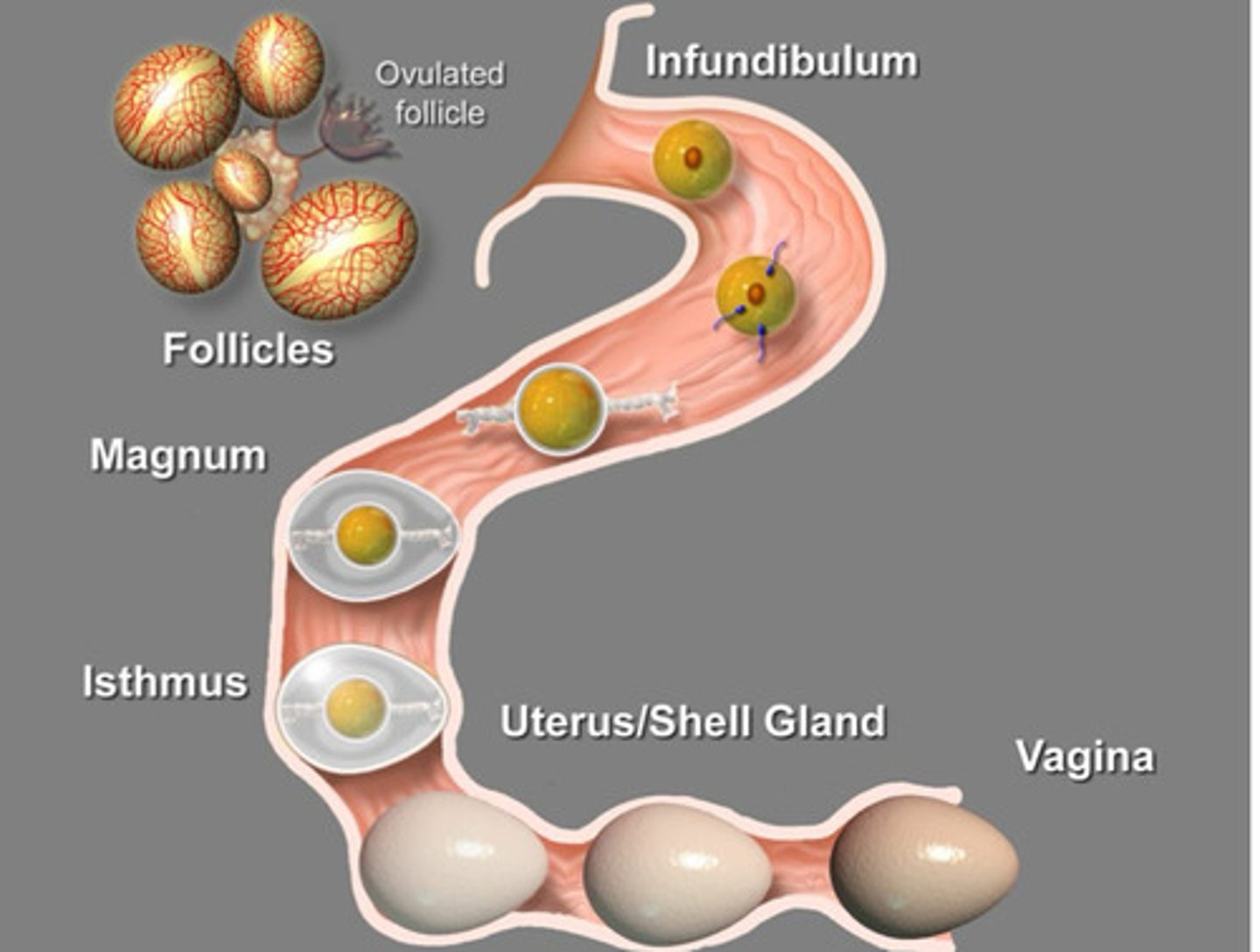
Infundibulum- site of fertilization
Magnum- albumen deposition
Isthmus- soft shell deposition
Uterus- hard shell made
Vagina- seal pores, sperm storage
The parts of the oviduct (in order) are: Infundibulum, magnum, isthmus, uterus, and vagina. What are each of their roles?
True
T/F: Testicles in birds are internal
4
Large
Right
Birds have a ______ chambered heart
Their heart is (large/small)
The ascending aorta is on the (left/right)
Because of the uni-cuspid muscular right AV valve
Why are birds predisposed to right-sided heart failure?
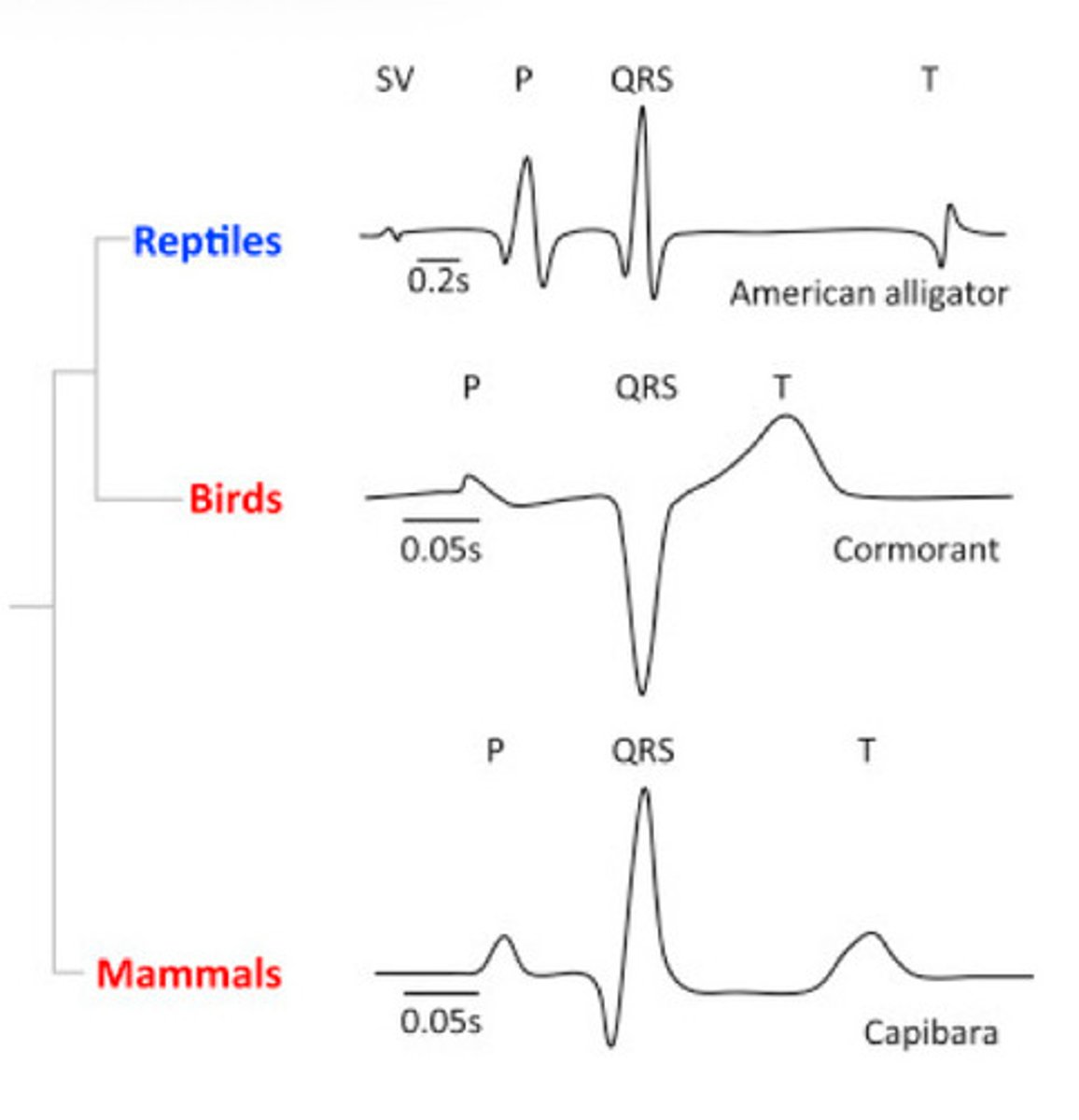
It is inversed (negative mean electrical axis)
What is special about a bird ECG?
Cardiac output (SV and HR)
Birds have a higher arteriole blood pressure. What does this come from?
The infraorbital sinus only has a dorsal opening (difficult drainage)
Upper respiratory infections in birds can be really severe because of what anatomical issue?
Sound box with vibrating membranes (they lack vocal cords)
How do birds make noise?
A. Vibration along their vocal cords
B. Sound box with vibrating membranes
C. By yappin'
D. Both A and B
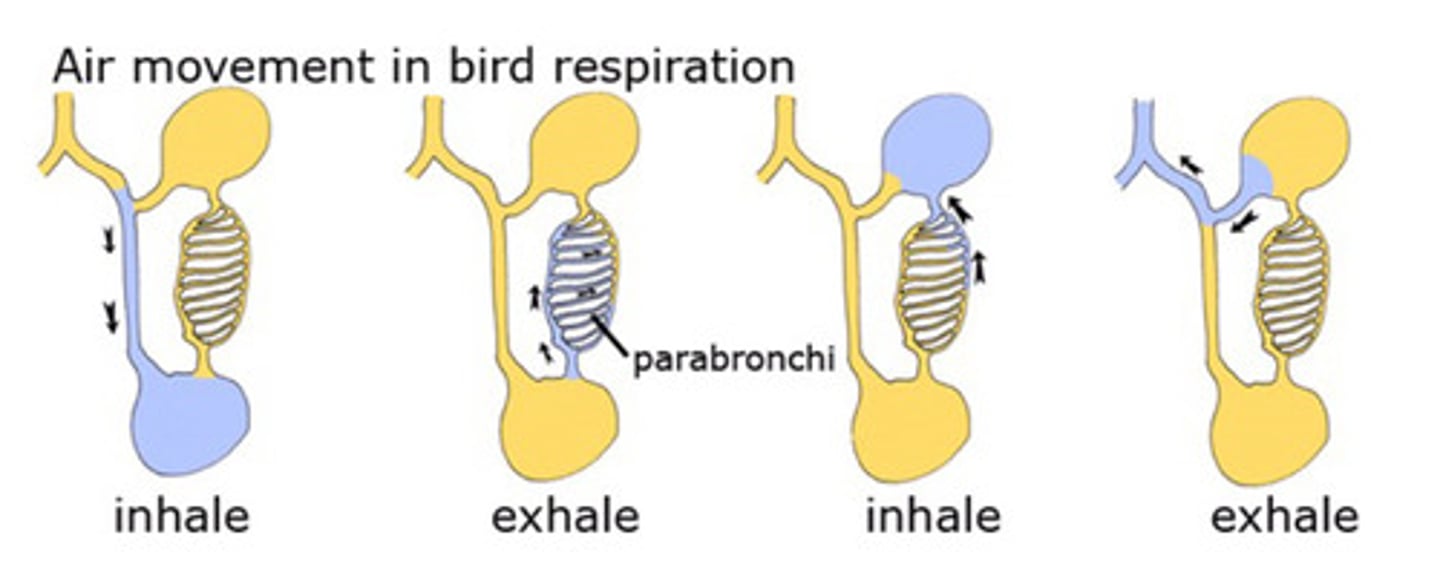
2; 2
Birds have _____ primary bronchi leading to their _____ lungs
The non-expandable lungs lead to secondary bronchi and air capillaries, these capillaries utilize counter-current gas exchange within capillaries
How do birds oxygenate?
Inspiratory: Abdominal, caudal thoracic (both paired)
Expiratory: Cranial thoracic, cervical (these 2 paired), interclavicular
Birds have 9 total air sacs. Name them (inspiratory and expiratory) =
Inspiration 1, expiration 1, inspiration 2, expiration 2
What is the respiratory cycle of birds?
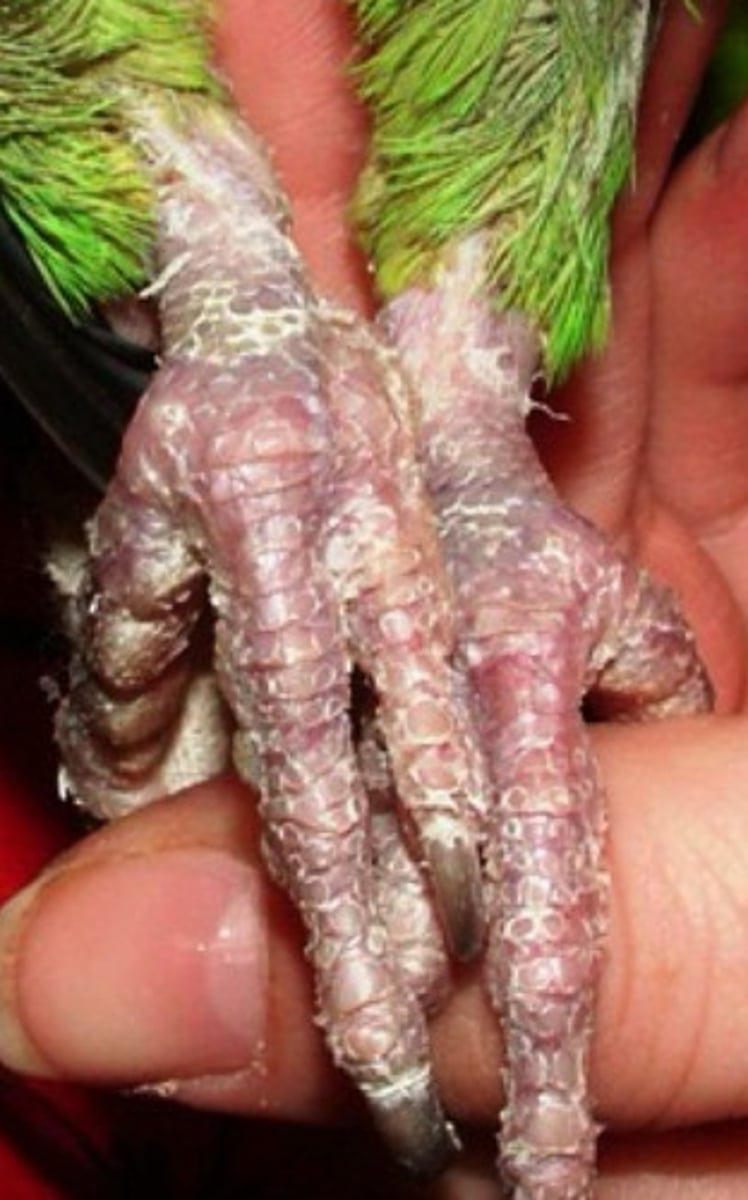
Pododermatitis
Too low of humidity in birds can predispose them to what?
Flicker frequency (birds more sensitive to it)
Avoid fluorescent lighting, halogen okay (likely need UV too)
12/12hr cycle
Light is an important part of husbandry in birds.
What do you need to be careful of?
What kind of light should you use?
How long should it be on vs off?
1.5-2.5 wing length (should be able to spread wings without touching)
Stainless steal or powder-coated (NO galvanized wire unless washed)
Natural wood (be careful of rope and cement)
What is the minimum cage size you should have for parrots?
What should your cage material be made of?
What is the ideal perch substrate?
All of the above (C would be incorrect if not washed)
Which cage material is appropriate for birds?
A. Stainless steel
B. Powder-coated
C. Washed galvanized wire
D. All of the above
Pellets 60-70%
Greens 20%
Fruit 10%
Nuts/seeds 5%
What % of each type of food should birds have in their diet?
True
T/F: Birds crave variety in their diet, change pellet type often!
Budgies and cockatiels, 25%
What two bird species are natural seed eaters? What % seeds should make up their diet?
Lorikeets
____________________ are nectivorous and eat things like pollen, nectar, flowers, soft fruits, and insects.
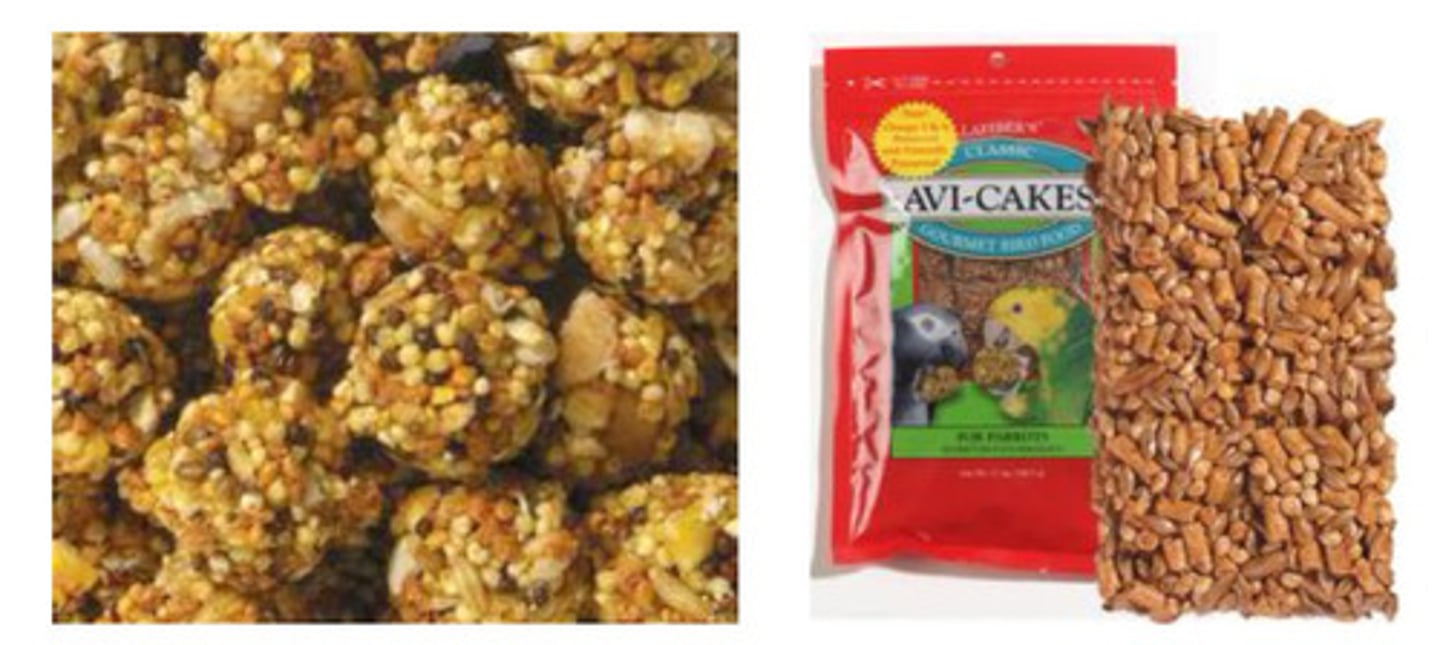
Fortified whole seeds (Nutri-berries, Lafeber AVI-cakes), foot friendly shapes are great for enrichment!
What are good seed choices?

Carotenoids and vitamin A
Goitrogens (interferes with iodine uptake)
What do orange and red veggies produce for birds?
What about brassicacae (kale, broccoli, collard greens, bokchoy)?
Avocado - persin - pericardial effusion
Onion - alkaloids - local irritation and anemia
Chocolate - theobromine - cardiotoxic and neurotoxic
Alcohol - alcohol - hepatoxic, neurotoxic
Meat - bacteria/iron - systemic disease, hemochromatosis
Name 5 foods that are toxic to birds, what is in them that makes it toxic, and what clinical pathology you see with it?
LC - Intro to companion bird medicine
Non-stick fume toxicity (polytetrafluroethylene, PTFE), tracheal disease (seed FB), humidity (aspergillosis)
3 reasons you could see a bird in acute respiratory distress?
Complete rings; Hard for seeds to pass through can get FB
Structure of bird tracheal rings? Why is this important to know?
Heavy metal (lead/zinc) toxicity, bornavirus, trauma
If you have a bird come in with neurologic signs, what are your 3 main differentials?
If they're made of lead/zinc can be toxic
Why is it important to ask about toys?
They hide clinical signs (prey species), they have high compensatory mechanisms, have a higher metabolism so they decompensate faster
What are the reasons why birds may decompensate faster and arrive with acute-on-chronic presentations?
Observe in cage first and have equipment ready to go
What do you need to do before a hands-on physical examination?
Excessive sternal motion, open beak breathing, extended neck, head/tail bob, wings extended from body to
Signs of dyspnea in birds?
Feces, urates (the white stuff), urine
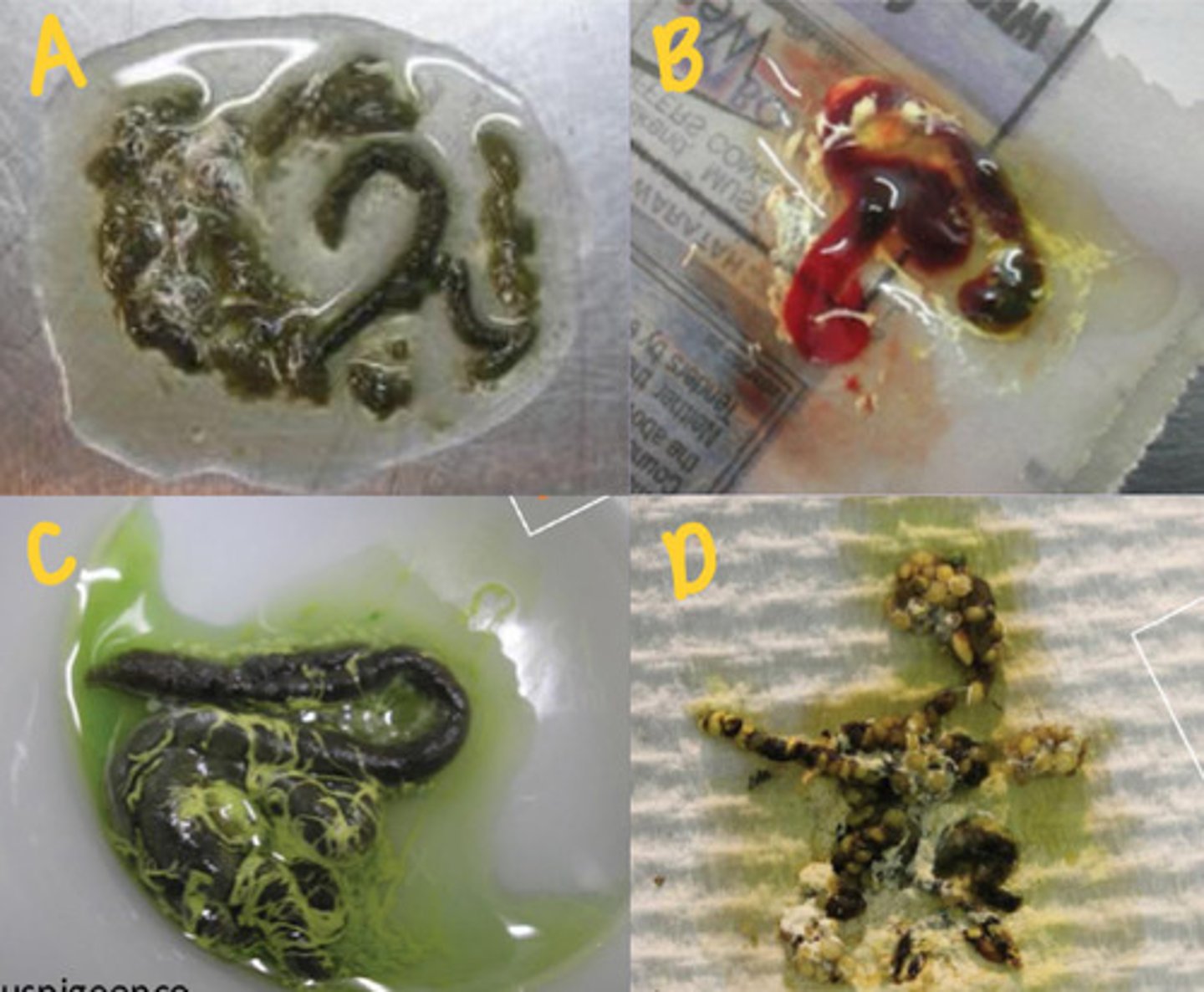
What are the 3 components of bird droppings?
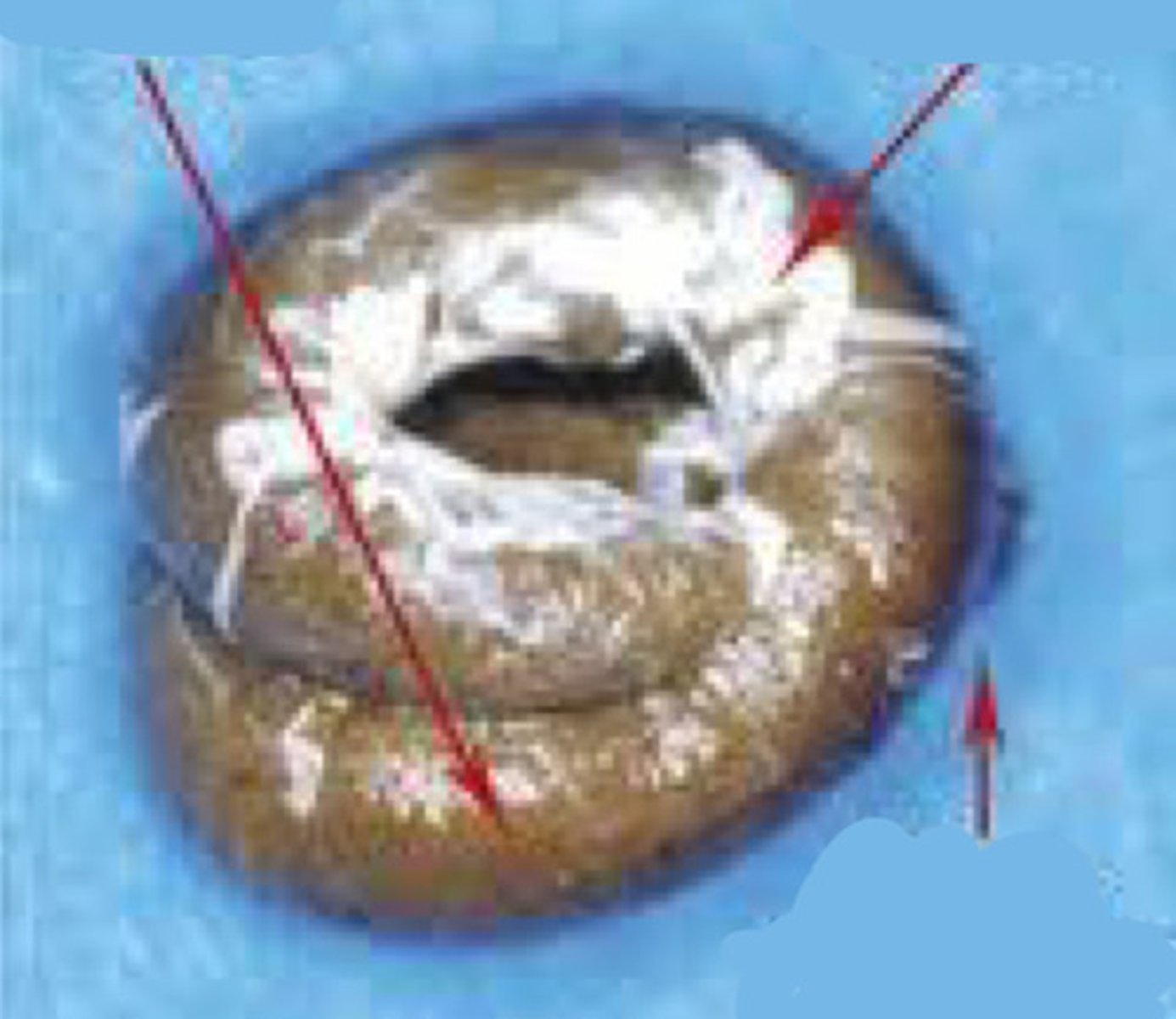
A polyuria
B frank blood
C biliverdinuria
D undigested food
What do these droppings (A-D) tell you about what is going on with the bird?

Urates from reptilian-type nephrons, Urine from mammalian-type nephrons
Where are urates produced? Where is urine produced?
Put in oxygen cage and wait, make sure they're warm, warn owners of the risk of doing a PE prior
What should you do with a bird that is weak, unaware of the environment, and in respiratory distress? Can you do a physical exam?
Parrots - beaks
Raptors - talons
Fowl - not much, but can bite and slap with wings
What are the primary weapons for parrots, raptors, vs fowl?
Towels for parrots, leather gloves and towel for raptors
What equipment is recommended for handling parrots and raptors?
Extend the neck!! (If leave any S shape, can bite!!), form ring with index finger and thumb
What is the primary failure when holding parrots that may lead to bites? How should you restrain them?
Turn off lights
What is something you can do to help catch a bird for a physical exam?
Dehydration
What does ropey saliva indicate in birds?
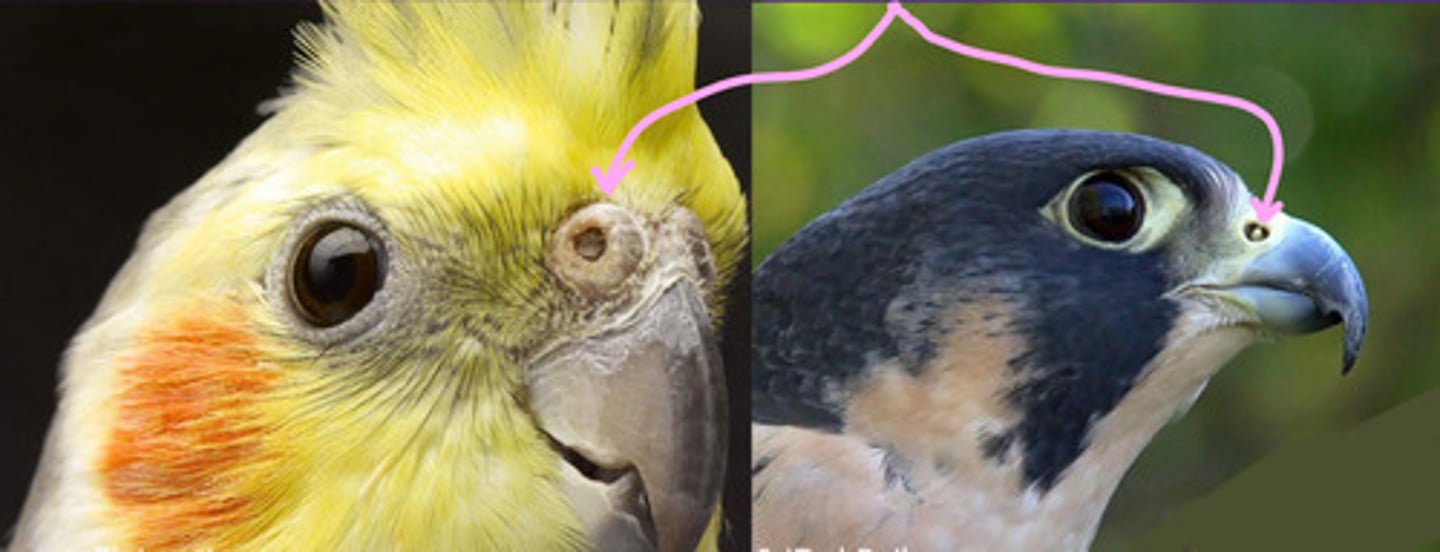
Nasal operculum, yes
What is this in these birds' noses? Is this normal?

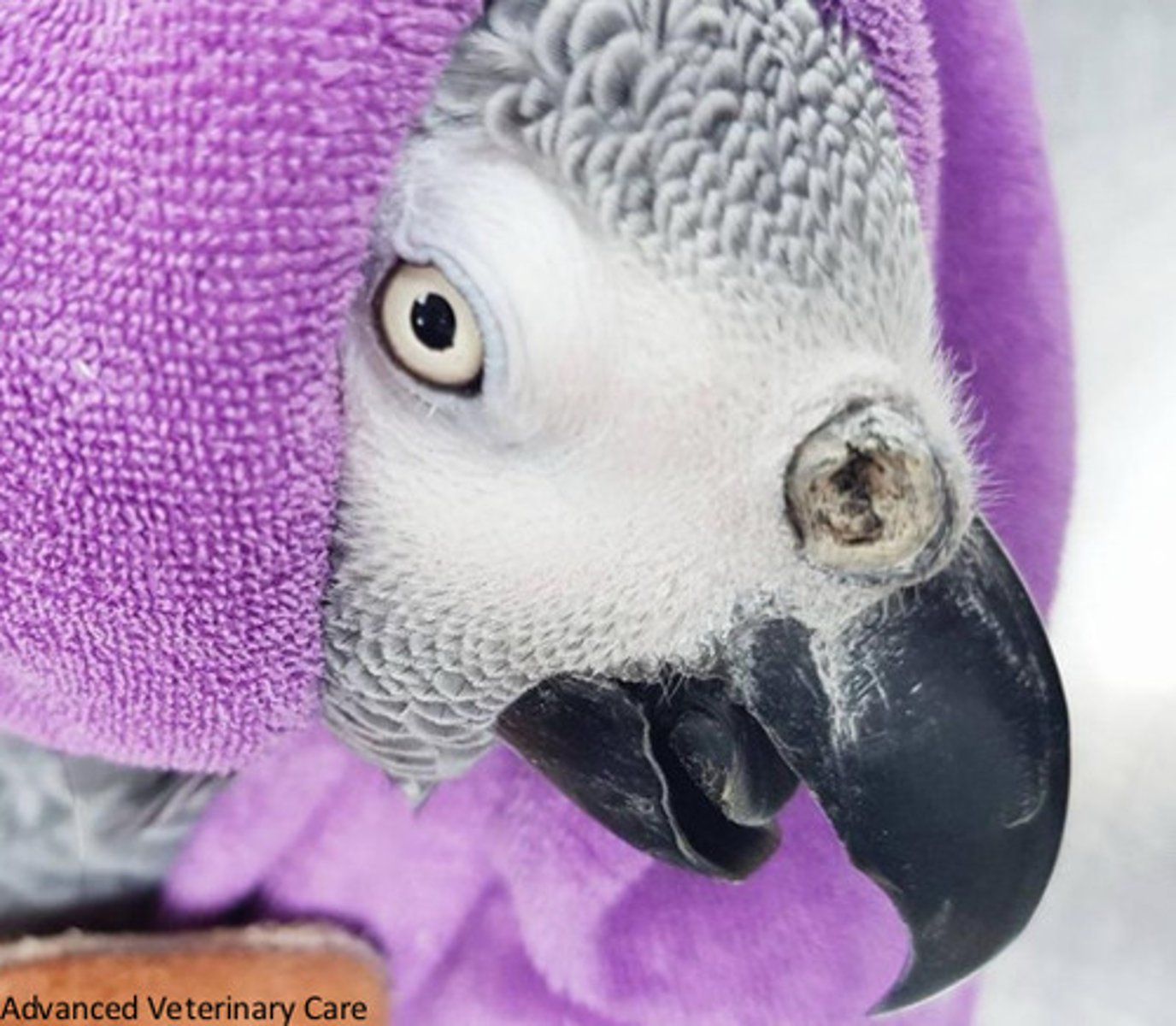
Hypovitaminosis A and aspergillosis
This bird has rhinoliths in his nose. What diseases are these indicative of?

Below and above keel and in axillary region for heart and air sacs (picured), on back for lungs
(Don't want to hear anything for air sacs and lungs)
Where should we auscultate for heats, lungs, and air sacs on a bird?

Palpate the keel bone (in chickens will still be able to palpate a little even if obese, obese parrots won't feel it at all)
How can we assess BCS in birds?
Concave in most; Some convexity in poultry and waterfowl is normal
How is the coelom shaped in most birds? How about in poultry and waterfowl?
Cardiovascular status; Should fill up instantaneously, if see it fill at all then it is delayed (indicating hypovolemia, heart disease, or atherosclerosis)
What does the ulnar vein reill time indicate? When is it considered normal and abnormal?
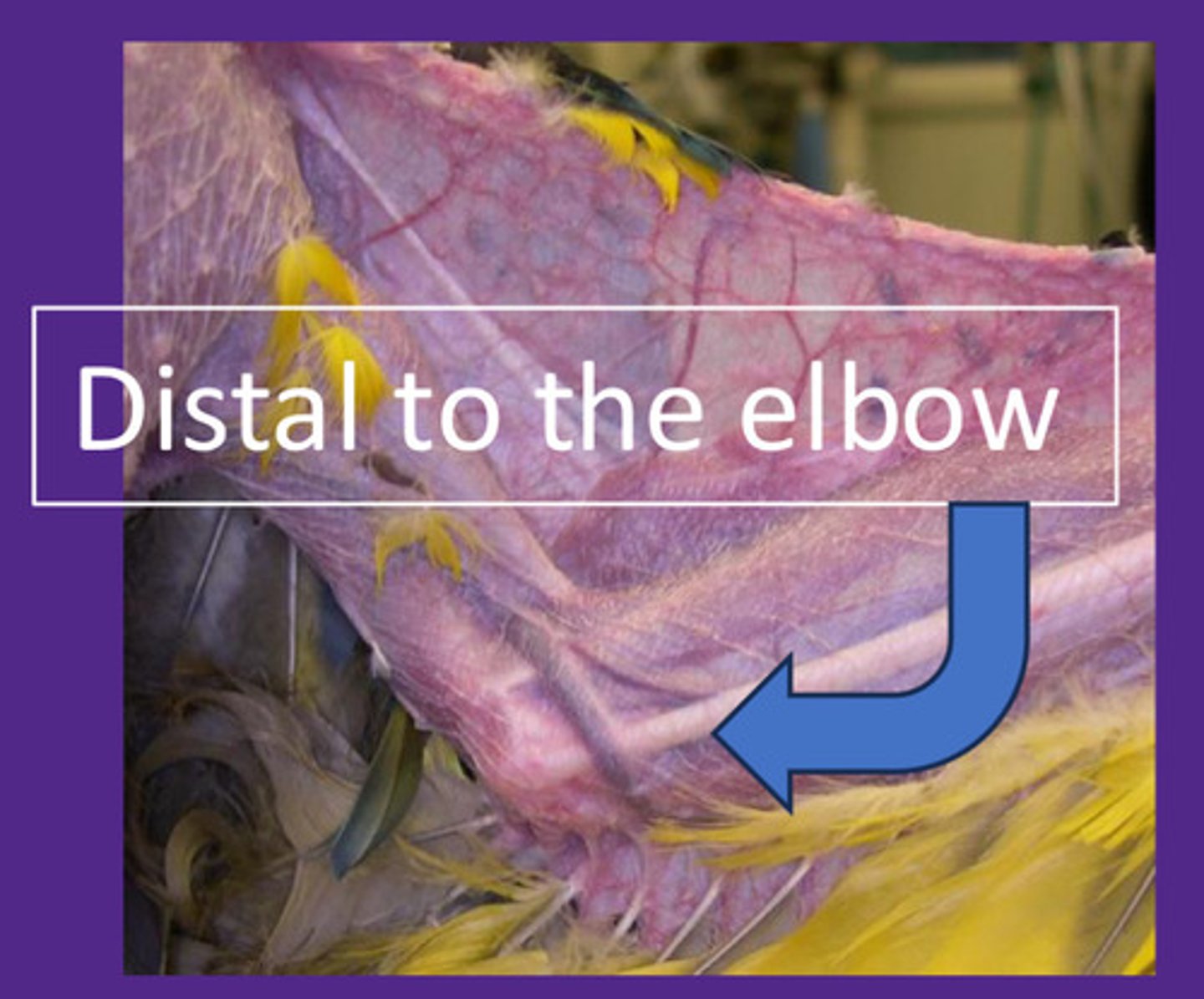
For papillomas, mucosal color, hydration/CRT, and especially important in amazon parrots for psittacine herpesvirus
Why is it important to do a cloacal examination?

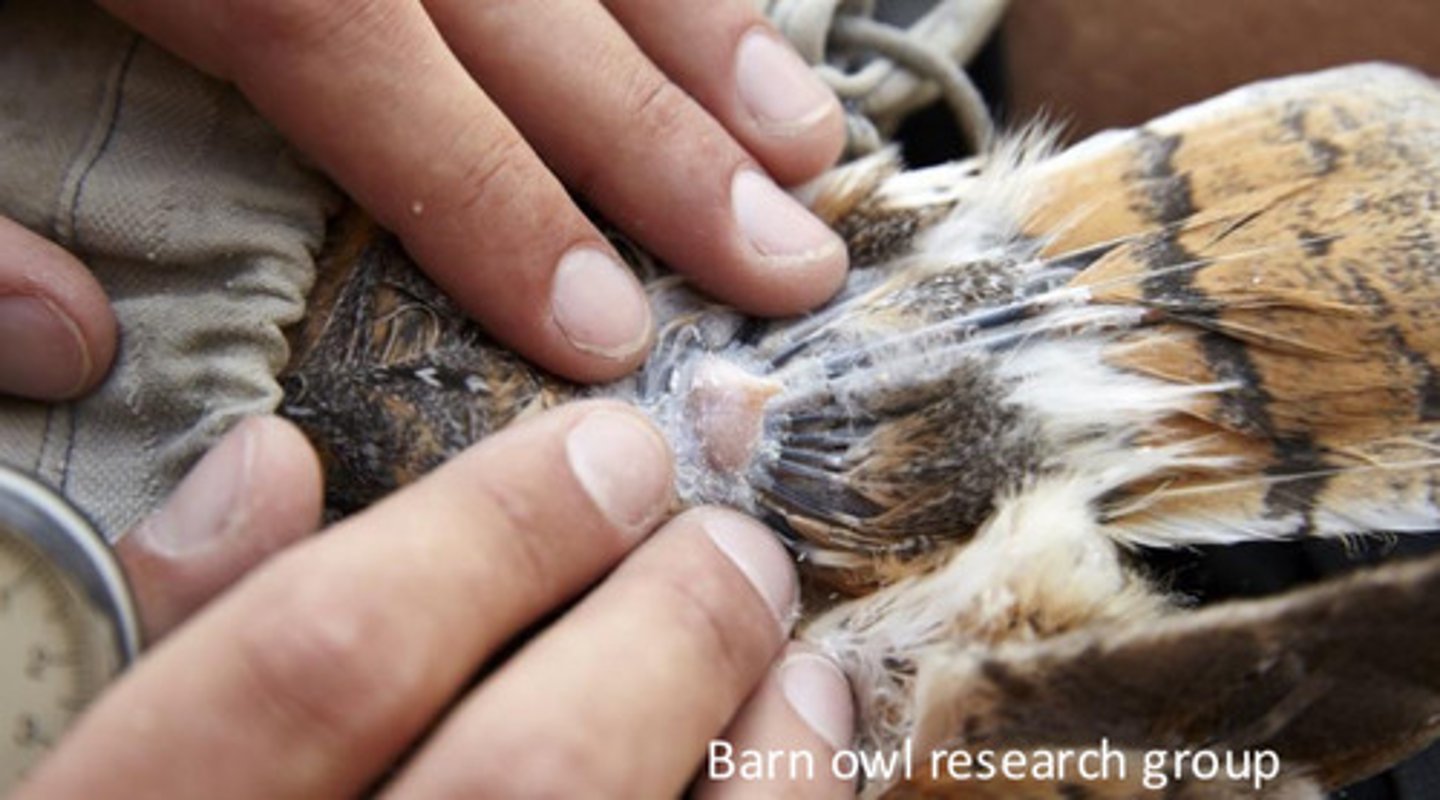
Uropygial gland; used for grooming; amazon, hyacinth macaws do not have
What is the gland at the base of the tail? What is it for, and what species do not have one?

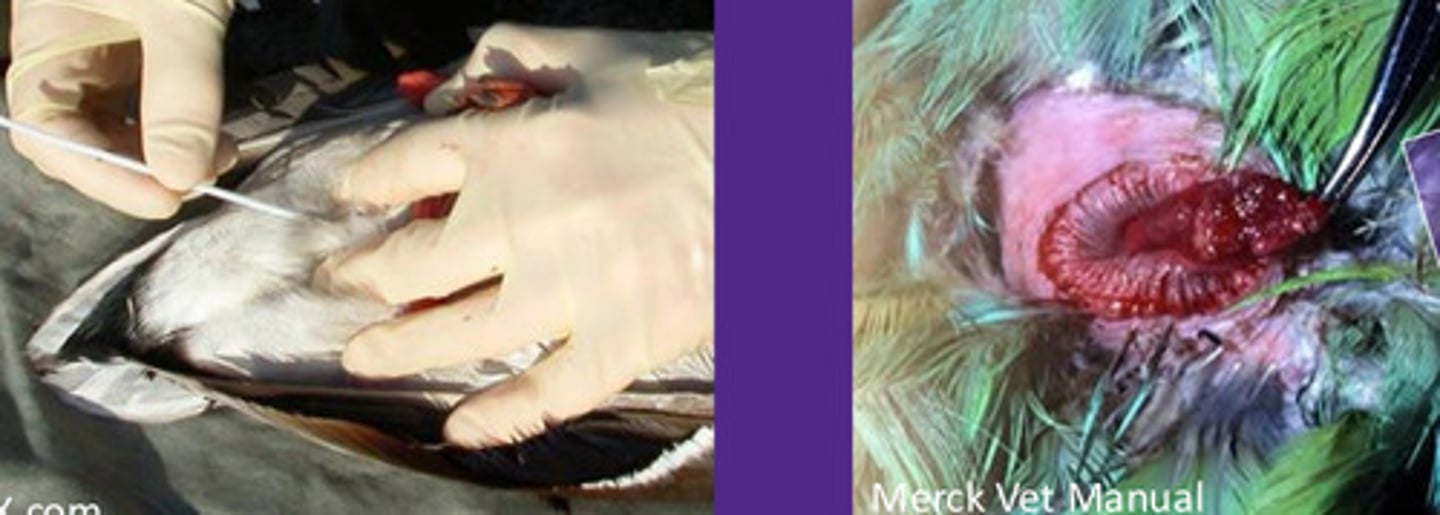
Conjunctival, choanal, and cloacal swab; Used for testing of chlamydia, bornavirus, and other agents for PCR
How do you do a CCC swab (in what order), and what do you use it for?

In critical patients; auscultate heart/lungs, assess ulnar vein, coelomic palpation, BCS, hydration, weight (no more than 30s)
When should you do an abbreviated physical exam, and what does it involve?
LC - Avian non-infectious diseases
Lead based paint (<1978), toys, linoleum, shotgun pellets, fishing weights, etc
Lead is toxic to birds. What are some at home things that could contain lead?
Newly galvanized wire and metal containers, pennies, fencing clips, kennel bolts, bird toy snaps, fertilizers, etc
Zinc is toxic to birds. What are some at home things that could contain lead?
Goes to RBCs, then replaces calcium in bones, skeletal muscle (causing weakness), smooth muscle (causing GI stasis), and nerves (causing neurologic signs)
Pathophysiology of birds ingesting/inhaling lead?
Goes to RBCs, then accumulates in kidney, liver, and pancreas causing corrosive effects (pancreatitis, hemorrhagic gastroenteritis, liver/kidney failure, neuro signs due to oxidative stress)
Pathophysiology of birds ingesting zinc?
Lead- liver, muscles, nerves (and bone)
Zinc- liver, kidney, pancreas
What organs does lead affect? What about zinc?
History, blood/tissue levels (won't show true value as it accumulates in organs), +/- radiographs (may not see if not a physical metal object)
How can you diagnose lead/zinc toxicity?
Chelation* (Ca-EDTA, succinate, penicillamine)
Endscopy/surgery if see it (surgery not reccomended because of adhesions and coelomitis)
Cathartics (to lubricate and help inc movement, be careful not to dehydrate)
How do we treat lead/zinc toxicity?
PTEF (polytetrafluoroethylene) overheated non-stick pans
Sudden death usually (can see dyspnea, wheezing, incoordination)
Targets lungs; pulmonary edema, necrosis, hemorrhage
Oxygen, supportive care, +/- furosemide and AB (usually die tho)
Teflon toxicity
What causes it?
Signs?
What tissue does it target/necropsy lesions?
Tx?
Cotinine
Dermatitis (can see respiratory signs too)
Remove source, decontaminate, supportive care
Nicotine/second hand smoke is toxic to birds because of what metabolite?
Most common clinical sign?
How do you treat it?
Lories and lorikeets* (and mynahs, starlings, toucans) because they have adapted to love iron diets in the wild (so they absorb more)
Listlessness, poor feathers, dyspnea (due to organomegaly and ascites)
Hx, BW, rads to see hepatomegaly, biopsy*
Reduce vitamin C, tannin tea, chelation (deferiprone), phlebotomy weekly
Iron storage disease (Hemochromatosis)
What species are predisposed and why?
Clinical signs?
Dx?
Tx?
Teflon - Lungs
*Which of the following options pairs the correct affected organ with its toxin?
A. Zinc - Bone
B. Lead - Integument
C. Nicotine - Pancreas
D. Teflon - Lungs
Collect from right jugular vein, ulnar vein, medical metatarsal vein
What are the sites of blood collection?
Budgerigars
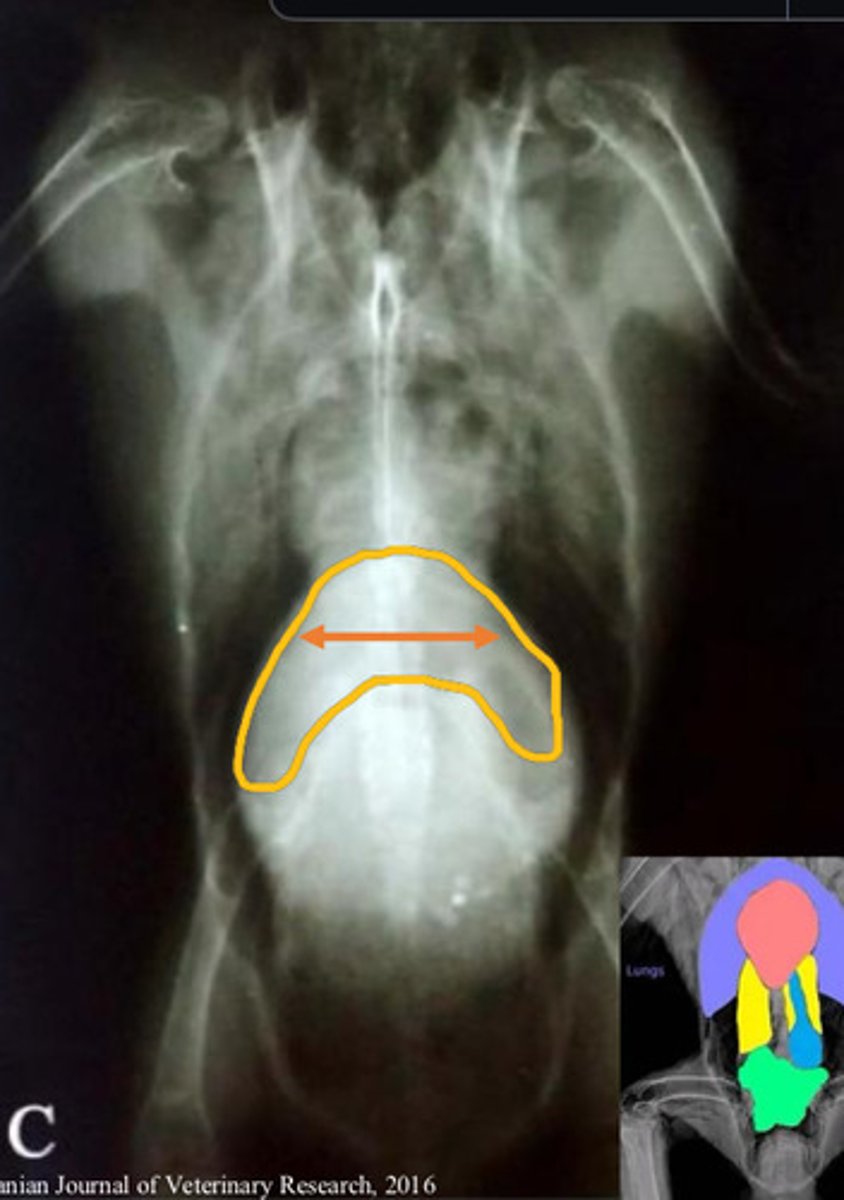
Paresis/paralysis/coelomic distention because femoral/obturator/sciatic nerves get compressed as they pass through the kidneys
Rads, histopath post morteum*
None (radiation?)
What species is commonly diagnosed with renal carcinoma?
What are the clinical signs, and why are these presented?
Dx?
Tx?
Exposure to high iron diets -> accumulates in liver -> hepatomegaly and ascites
Pathophysiology of iron storage disease?
Stop in egg laying, malformed eggs, straining/frank blood in droppings
Inflamm leukogram, hypercalcemia, imaging
Reproductive disease (egg bound/dystocia, salpingitis, and metritis)
Signs?
Dx/BW abnormalities?

Addition of tea
*What dietary reccomendations are made for a bird with hemochromatosis?
A. Addition of citric fruits
B. Addition of whole prey
C. Addition of tea
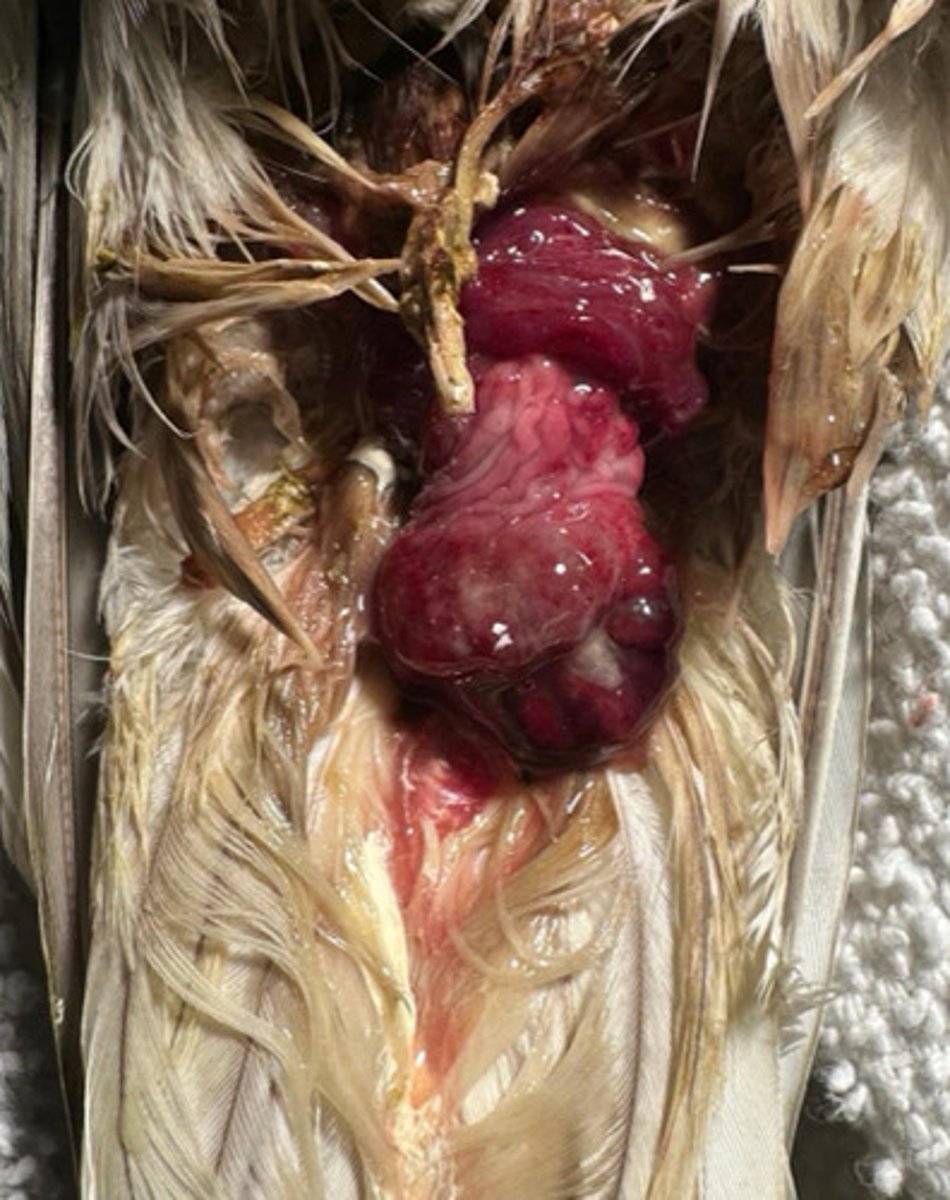
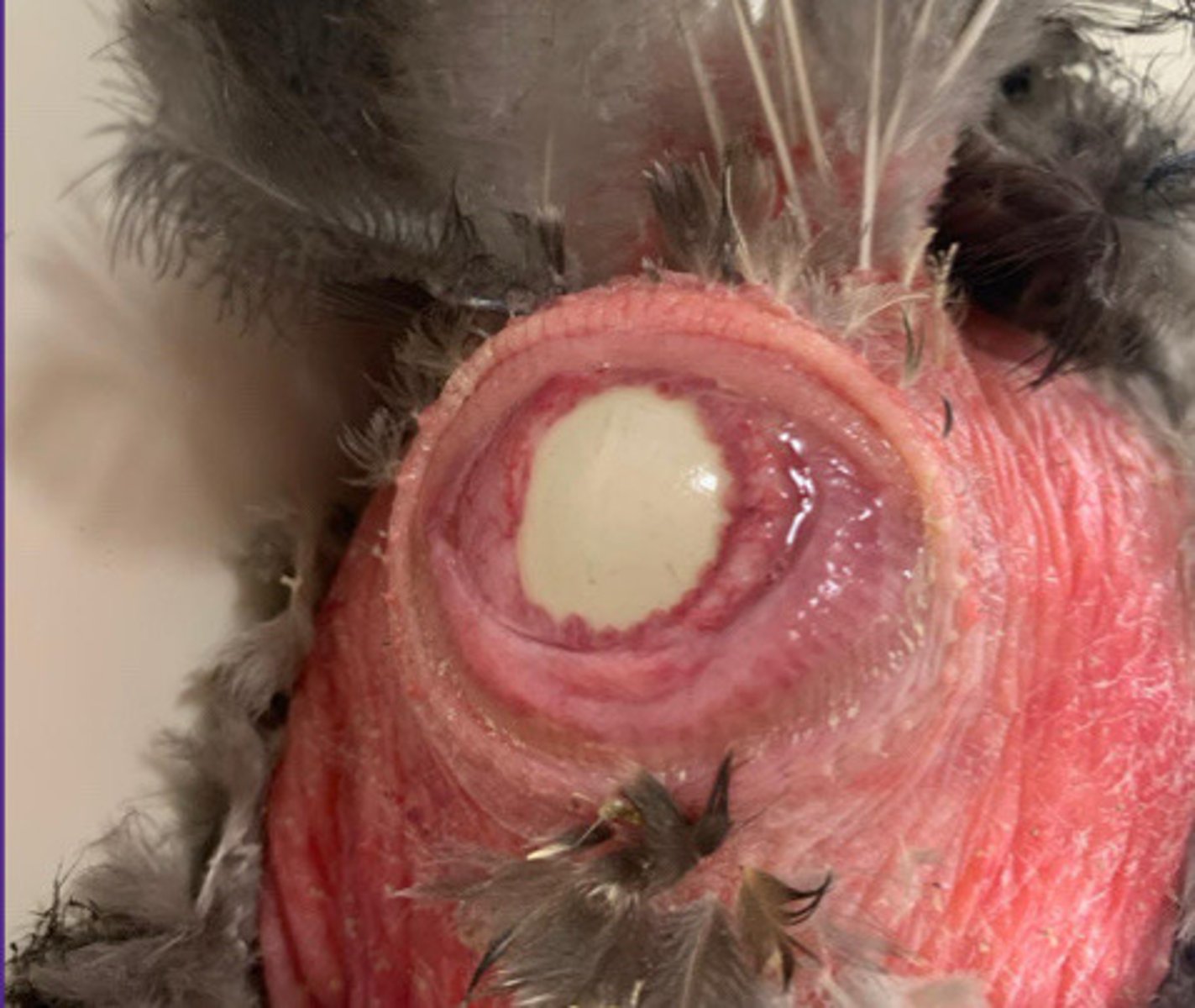
Suction out egg contents with needle though cloaca (ONLY if visible), collapse and remove eggshell; May lead to salpingitis (inflamm of fallopian tubes) and coelomitis
How do you treat a bird that is egg-bound?
What are risks of doing this?
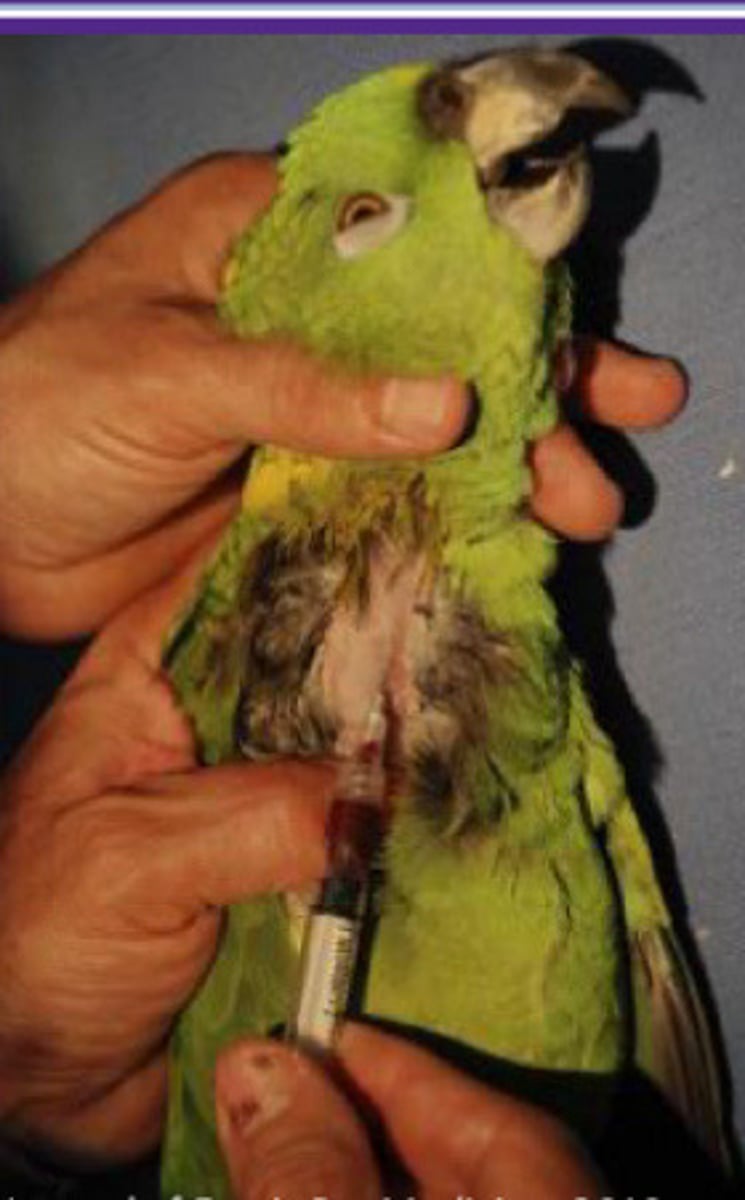
IM injection into pectoral muscles parallel to keel
Where give IM injections?
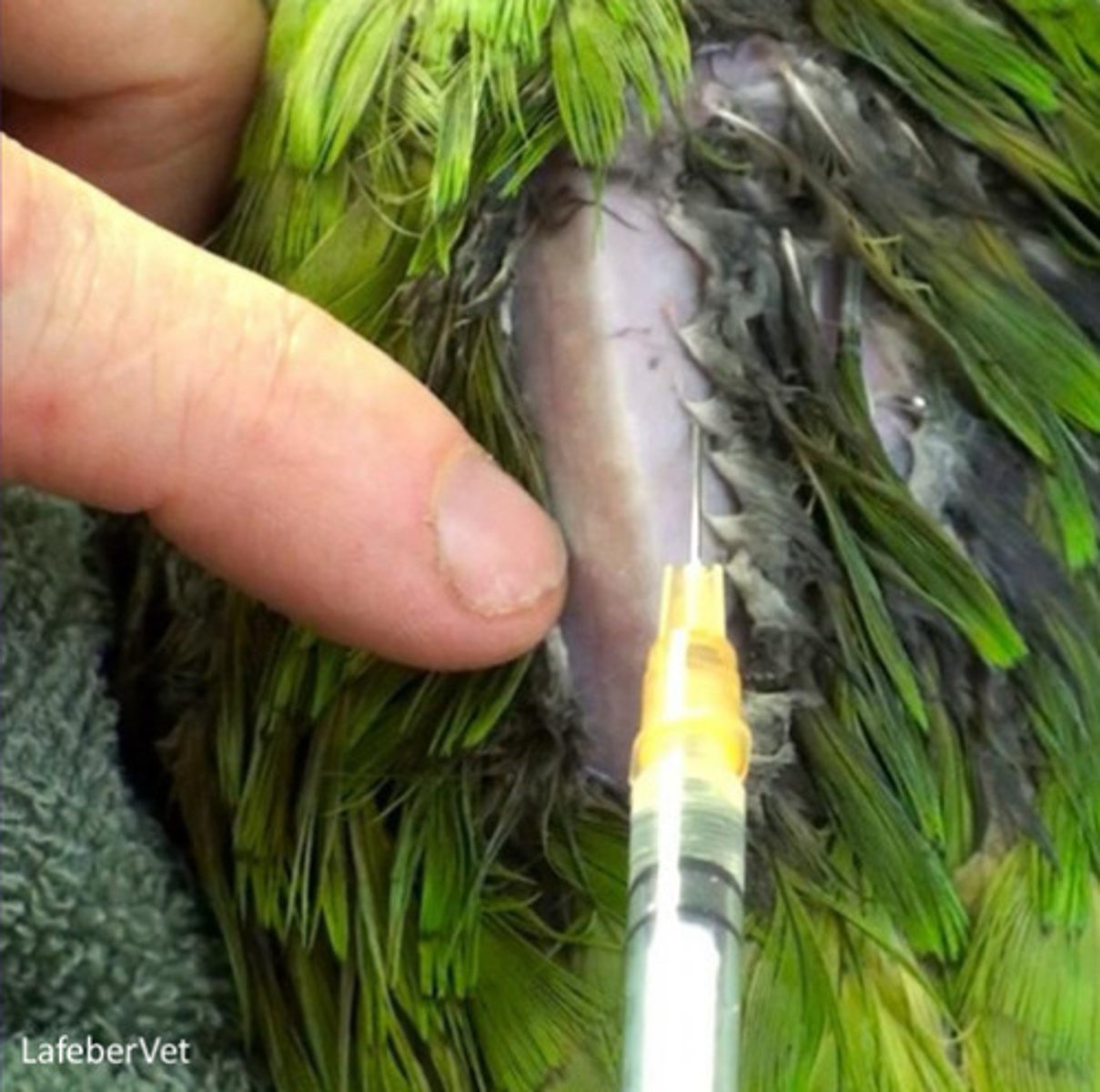
Psittacines
Excessive straining: masturbatory behavior, sexual overwork, increased intracelomic pressure, dz
What species are afected by cloacal prolapse? What are the causes?
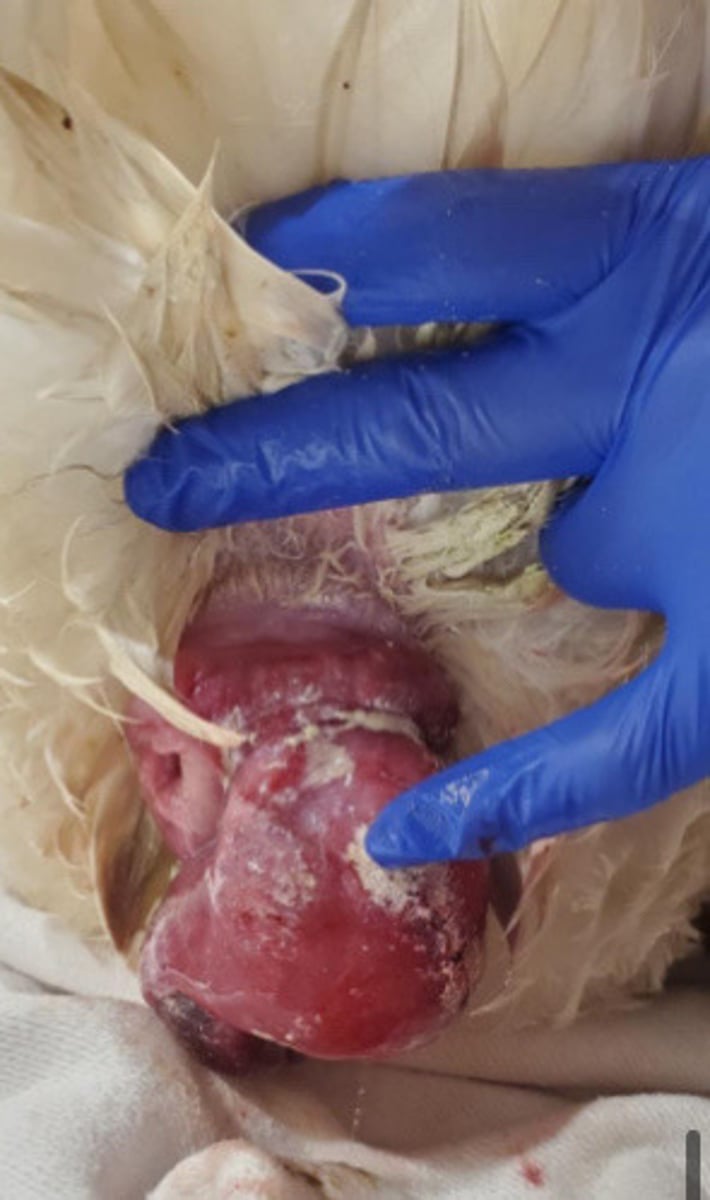
Complicated = euthanasia likely or intracoelomic surgery
Uncomplicated = temporal ventoplasty (AVOID sphincter muscle, NO purse string suture, leave space open)
How do you treat cloacal prolapse (complicated vs uncomplicated)?