Biology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/80
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
What is Taxonomy?
Study of classification
2
New cards
Who created the first classification system?
Aristotle
3
New cards
Grasses/Herbs
Soft stem (Short)
4
New cards
Shrubs
Several woody stems (Medium height)
5
New cards
Trees
One woody stem (Large/tall)
6
New cards
How do you group animals?
By where they dwelled (water, land, Air)
7
New cards
Who is the father of Taxonomy?
Carolus Linneaus
8
New cards
genus
Capital and underlined/Italicized
9
New cards
Species
Small letter and underlined/Italicized
10
New cards
When can you mate?
In the same genus
11
New cards
Sapien
Wisdom
12
New cards
Folium
Leaves
13
New cards
Alba
White
14
New cards
Felis
Cat
15
New cards
Felis SP
all cats
16
New cards
Homo
alike
17
New cards
Domains in order
1. Animal
2. Plant
3. Prostia
4. Fungus
5. Monera
18
New cards
Kingdoms in order
1. Phylum
2. class
3. order
4. family
5. genus
6. species
19
New cards
Sub class
1. Phylum
2. Class
3. order
20
New cards
Super order
4. Family
5. Genus
6. Species
21
New cards
Subclass/Suborder
Breaks things down
22
New cards
Sub
Below
23
New cards
Super
Above
24
New cards
Who made the 3rd kingdom?
Ernst Haeckel
25
New cards
Monera
has to be a prokaryote
26
New cards
what does EU mean?
True
27
New cards
Protozoa
Green and moves
28
New cards
Fungus
Doesn’t move
29
New cards
where is Phylum used?
Used in plants
30
New cards
What is a phylogenetic tree?
It shows evolutionary history
31
New cards
What is derived traits?
Traits not previously seen
32
New cards
what are segments?
They allow you to move
33
New cards
what is cladistics?
traces evolutionary history of a group by using shared traits
34
New cards
What is cladogram?
depicts evolutionary history
35
New cards
what is an amphibian?
has 2 lives
36
New cards
Tracing phylogeny
Embryos
37
New cards
what is a fossil record?
common characteristics
38
New cards
what is Morphological data?
outer structure
39
New cards
homology
similar structure
40
New cards
analogy
Common environment
41
New cards
Behavioral
care of young
42
New cards
molecular
DNA/Proteins (cytochromes)
43
New cards
Molecular clock
Percentage difference between organisms
44
New cards
Morphology
Outer structures
45
New cards
homologous organs
Similar structures and different structure
46
New cards
Analogous organs
legs, wings, flippers, similar
47
New cards
Vestigial organs
Things you have at one time
examples- Goosebumps, abdominal, muscles, gland, membrane, wisdom teeth.
examples- Goosebumps, abdominal, muscles, gland, membrane, wisdom teeth.
48
New cards
hallifias
salt water
49
New cards
thermo acid hallifias
heat
50
New cards
Whats another name blue-green alge
Cyanobacteria
51
New cards
Antibiotics work
Diplococcus pneumonia
52
New cards
turns into rheumatic fever
streptococcus
53
New cards
blood poising
staphylococcus
54
New cards
How is bacteria sorted?
By shape and arrangement
55
New cards
Bacillus
e coli
56
New cards
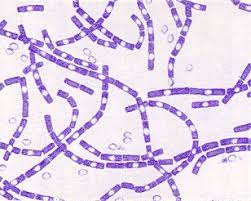
Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax
57
New cards
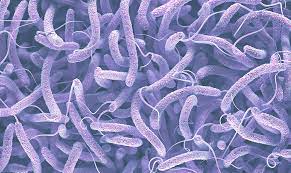
vibrio cholerae
Cholerae
58
New cards
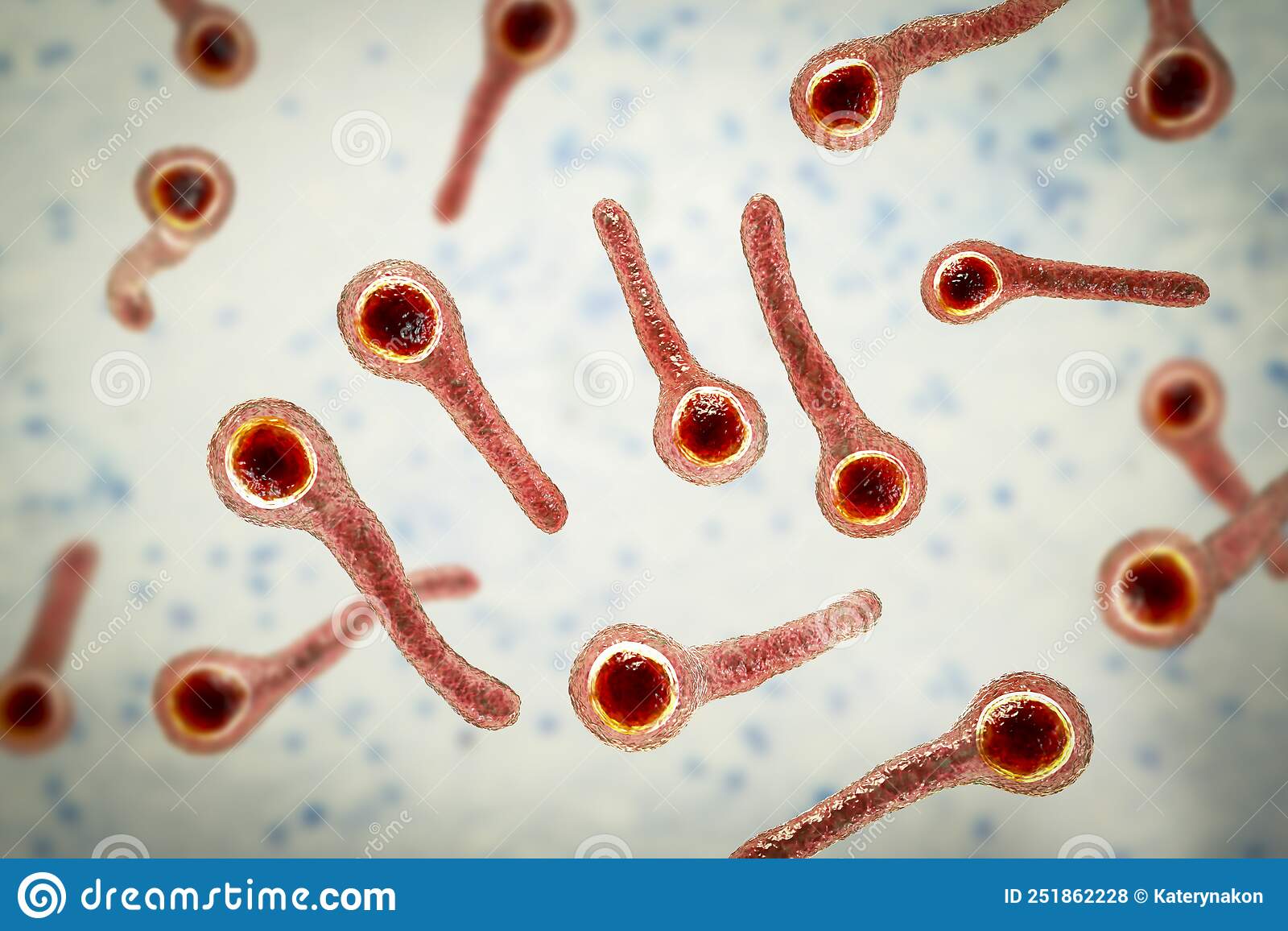
Clostridium tetani
Tentanus
59
New cards
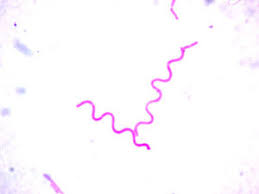
Spirillum/spirilla
60
New cards
characteristics of a prokaryote
1. Unicellular
2. Phospholipid ( helps protect)
3. Prokaryotic ( No nucleus/organelle)
4. Ribosome (Makes protein)
5. Cell wall (Not cellulose) peptide
61
New cards
Methanogens
Swamps, marshes, guts of animal
62
New cards
Halophiles
Salt water conditions
63
New cards
Thermoacidophiles
Hot springs, Geysers
64
New cards
Marshgas
Made of methine
65
New cards
Halo
salt
66
New cards
How do you kill bacteria?
Gargle salt water
67
New cards
Thermo
Hot temps
68
New cards
Acid
Ph levels
69
New cards
characteristics of an Eukarya Domain
1. Unicellular/colonial/multicellular
2. Nucleus/organelles
3. Wide variety of body forms
70
New cards
Protista characteristics
1. Mostly unicellular
2. Eukaryote
3. no specialized tissue
71
New cards
what are two main things in protista?
1. Alge
2. Protozoa
72
New cards
Alge
All blue-green, Grouped by color
73
New cards
Green
Bobox
74
New cards
Brown
Sorgaseus
75
New cards
Red
Alge to make up seaweed
76
New cards
fire
Gives off poison
77
New cards
Protozoa
First animal
grouped by movement
grouped by movement
78
New cards
Amoeba
Pseudopods (false feet)
79
New cards
Paramecia
Cillia ( Many tiny hairs)
80
New cards
Euglena
Flagella (A few long hairs)
81
New cards
Sporozoa
No movement (Usually cause disease)