Chemistry - 1 Atomic Structure - 1.4 Fractional Distillation and Paper Chromatography
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Miscible
Describes two liquids that are soluble in each other
Why is it difficult to get a pure substance with simple distillation?
Some vapour may be given off before the substance reaches boiling point - the boiling points are too close together.
Fractional distillation
Used to separate liquids with similar boiling points using a fractionating column
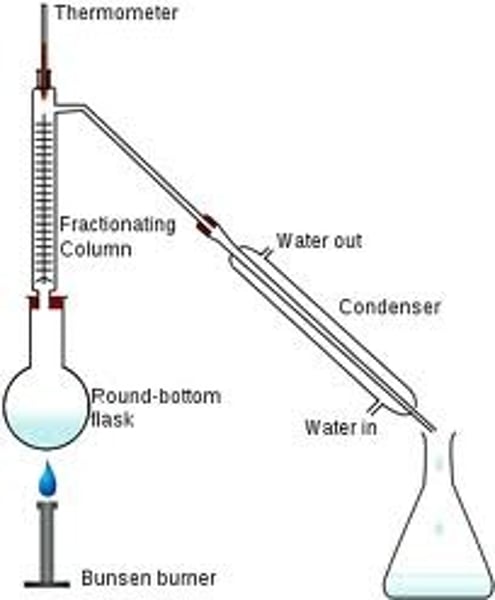
Fractionating column
a glass tube filled with beads
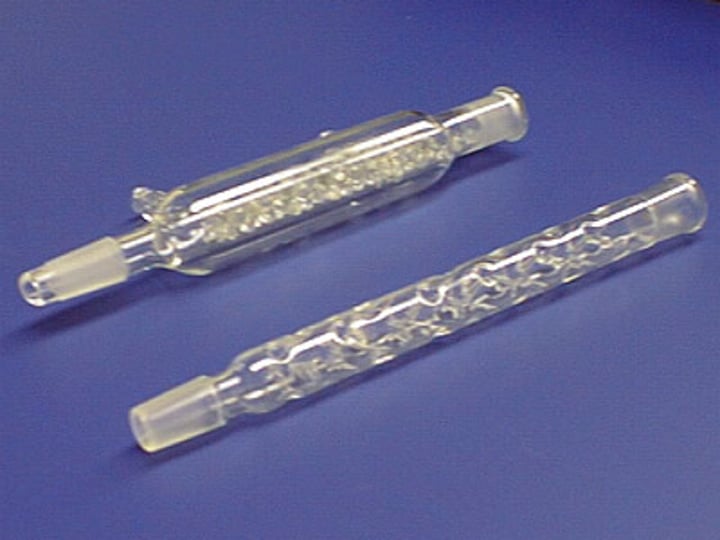

How does a fractionating column work? [3]
- Vapours must pass over the beads to reach the condenser
- The substance with the higher boiling point is more likely to condense lower down, where the temperature is lower
- The substance with the higher boiling point will continue to rise through the tube and reach the condenser
The use of fractional distillation [2]
- Use of ethanol as a biofuel
- In oil refineries, to separate crude oil
Chromatography
A technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material (solubility)
Paper chromatography [4]
- Draw a pencil line on some absorbent chromatography paper to indicate the starting point
- Use a capillary tube to dab small amounts of solution on the line
- Suspend the paper in a small amount of water (up to the line)
- See which solution travels the furthest