Biology Keystone 2024: Comprehensive Flashcard Set for Key Terms
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in living things.
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell. Means "little organ."
Organism
A living thing.
Eukaryote
An organism with cells that contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
Nucleus
An organelle that is the brain/control center of the cell. Contains the cell's genetic material (DNA).
Extracellular
Located outside of a cell.
Intracellular
Located inside of a cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids. Two types: smooth and rough.
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant cells that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy. Performs photosynthesis.
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell. The warehouse of the cell.
Mitochondria
An organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production. The powerhouse of the cell.
Ribosome
A non-membrane bound organelle that makes proteins.
Plasma/Cell Membrane
A selectively permeable surface that encloses the cell contents. Regulates what can enter and leave the cell.
Unicellular
A single celled organism. Ex: bacteria.
Multicellular
Made up of more than one cell. Ex: plants, animals, fungi, protists.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid. The genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring.
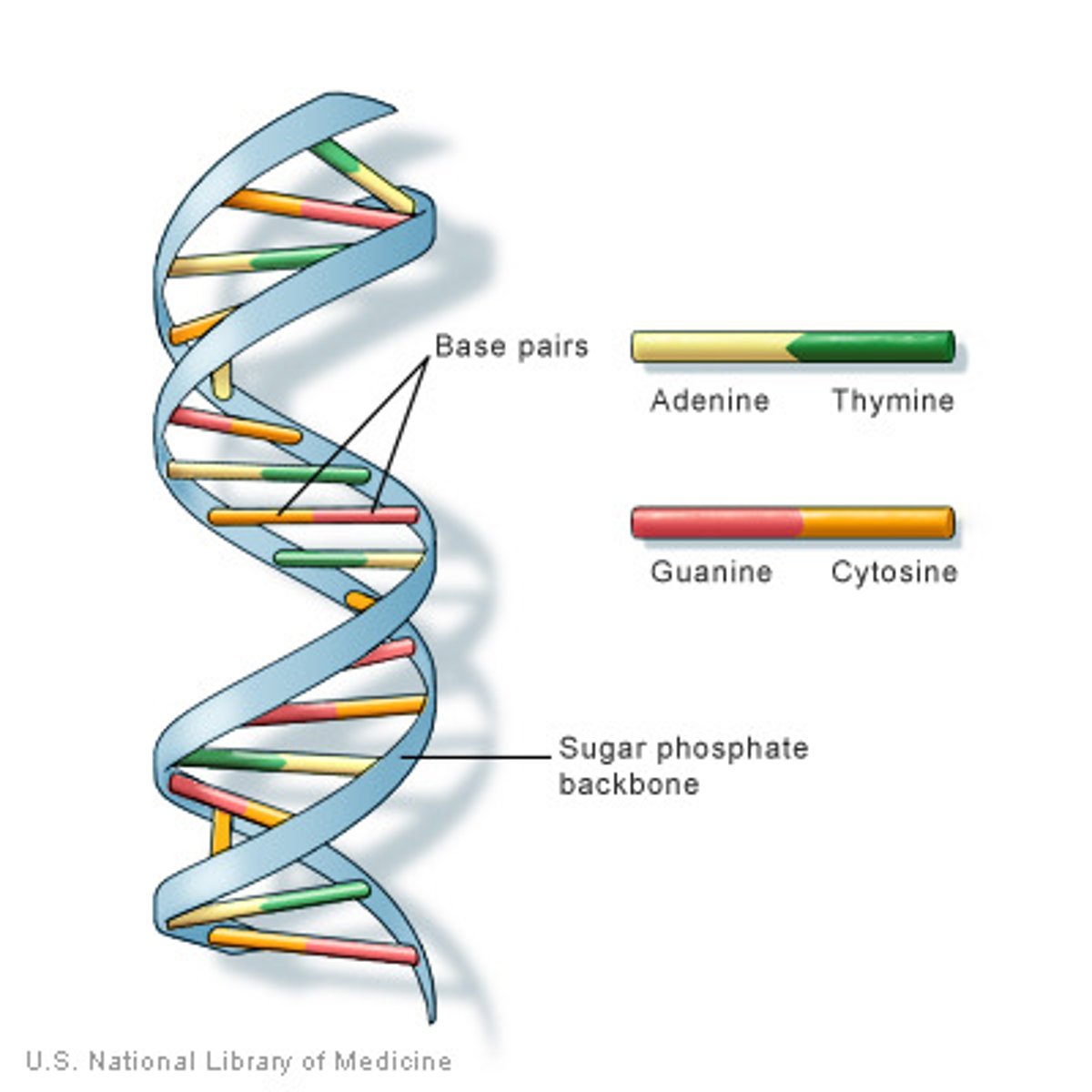
Chromosome
A structure found inside the nucleus that contains DNA organized into genes. Humans have 23 chromosomes.
Biology
The scientific study of life.
Science
An organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world.
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing.
pH
The measure of how acidic or basic a substance or solution is.
Temperature
A measure of how hot or cold something is.
Macromolecule
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules. Ex: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction.
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together.
Protein
A macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; needed by the body for growth and repair. Building Blocks: amino acids.
Carbohydrate
A macromolecule made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; major source of energy for the human body. Building Blocks: sugars.
Lipid
A macromolecule made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms; includes fats, oils, and waxes. Building Block: glycerol and fatty acids.
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus. Building Blocks: nucleotides.
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers. Aka: building blocks.
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Adhesion
The property of water that allows water to stick to other surfaces.
Cohesion
The property of water that allows water molecules to stick to itself.
Freezing Point
The temperature at which liquid water turns into a solid when cooled.
Atom
The basic unit of matter.
Organic Molecules
Molecules that contain carbon.
Energy
Carried in the molecule ATP. Powers different biological processes.
Bioenergetics
The study of how energy flows through living organisms.
Cellular Respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen.
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate. The main energy source that cells use for most of their work.
Energy Transformation
A change from one form of energy to another.
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria.
Biochemical Conversion
The changing of organic matter into other chemical forms such as fuels.
Photon
A particle of light.
Plastid
A group of plant organelles that are used for storage of starches, lipids, or pigments.
Impermable
Materials through which water does not easily pass.
Active Transport
The movement of materials through the cell membrane, using energy. Goes against the concentration gradient.
Passive Transport
The movement of materials through the cell membrane, not using energy. Goes with the concentration gradient.
Osmosis
The movement of water across the cell membrane.
Homeostasis
The process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment.
Concentration Gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance. Flows from high to low.
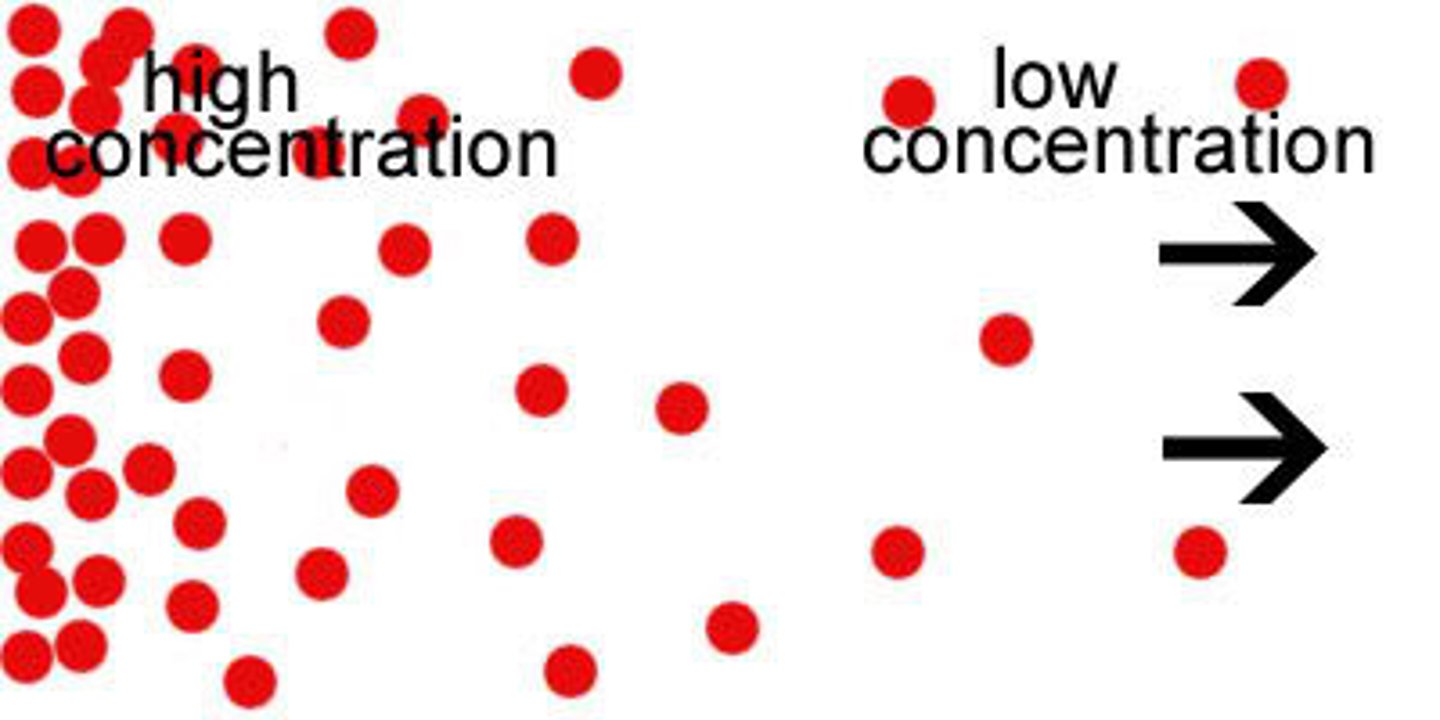
Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent.
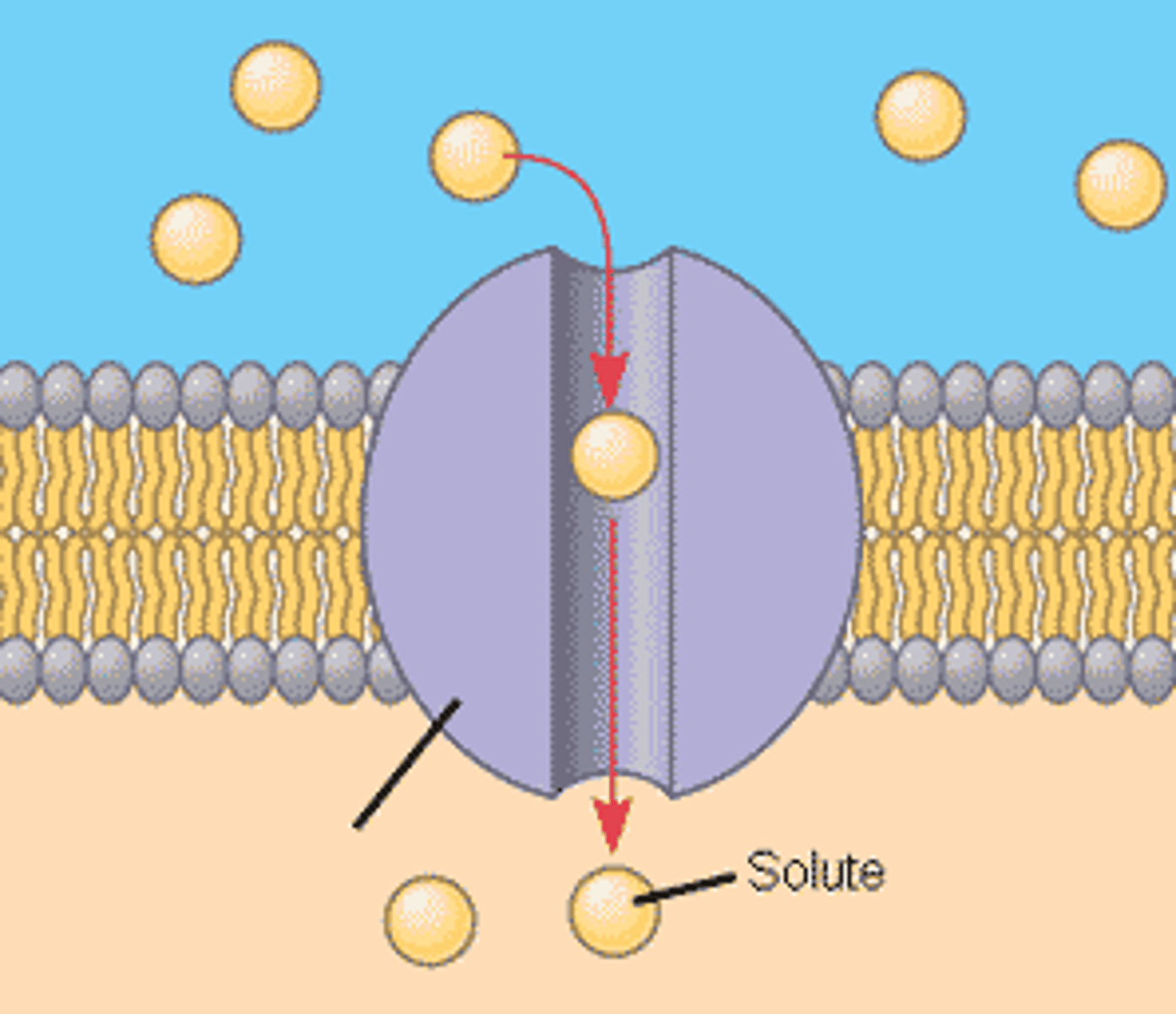
Transport Proteins
A membrane protein that helps a certain substance or to cross the membrane.
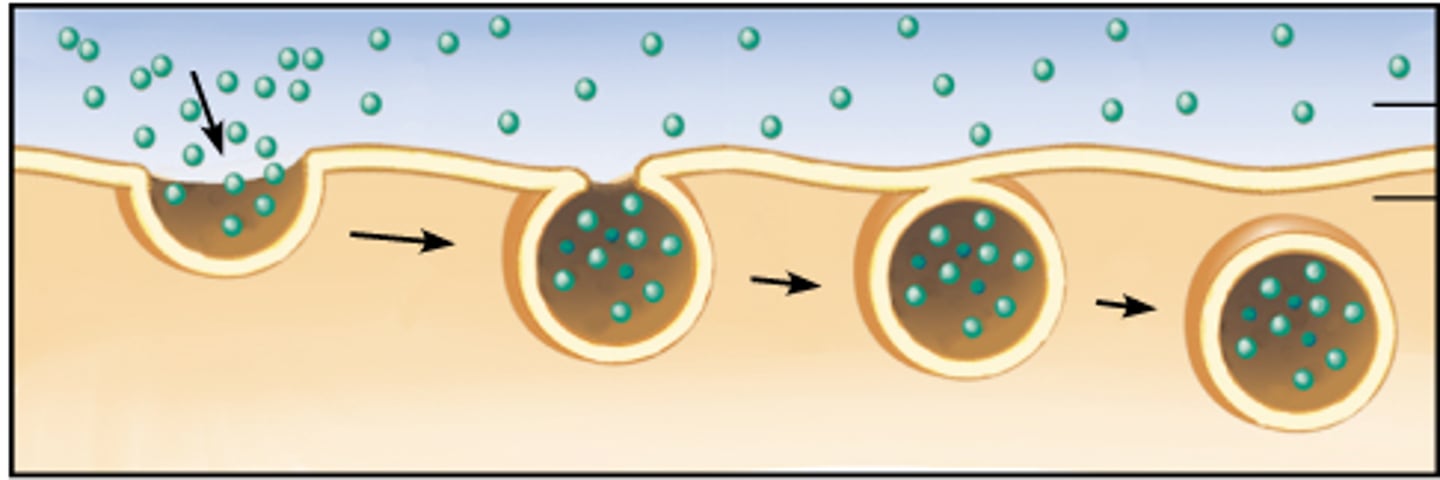
Endocytosis
A process by which a cell takes material into the cell by folding the cell membrane around the material and bringing it inside.
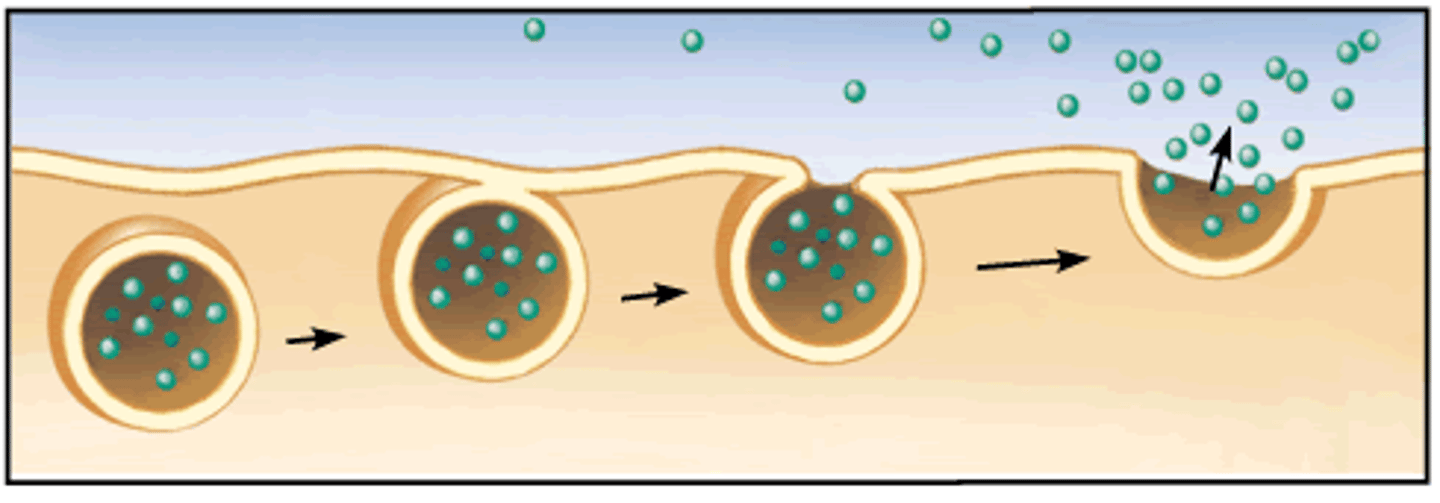
Exocytosis
A process by which the contents of a cell are released to the exterior through fusion of a vacuole with the cell membrane, and then expulsion of the material.
Facilitated Diffusion
The movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through transport proteins.
Hydrophobic
Water hating. Ex: lipids.
Hydrophilic
Water loving. Ex: polar molecules.
Simple Diffusion
The movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Isotonic
When the concentration of two solutions is the same.
Hypotonic
When comparing two solutions, it is the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes.
Hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, it is the solution with the greater concentration of solutes.
Cell Cycle
A series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide.
Mitosis
Part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides.
DNA Replication
The process of making a copy of DNA.
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases.
Centriole
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only.
Asexual Reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
Sexual Reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents.
Prophase
First stage of mitosis. Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms.

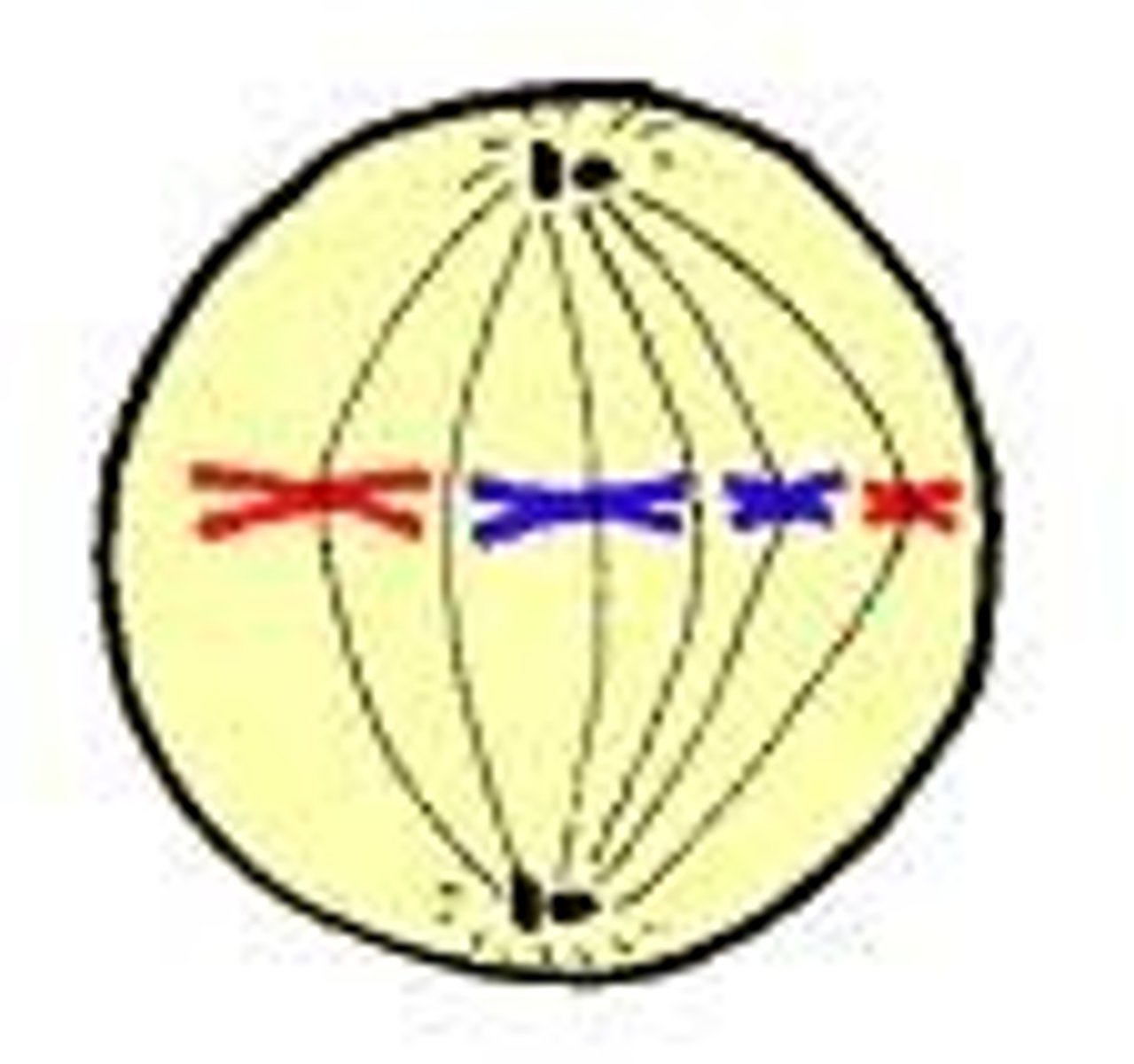
Metaphase
Second stage of mitosis. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
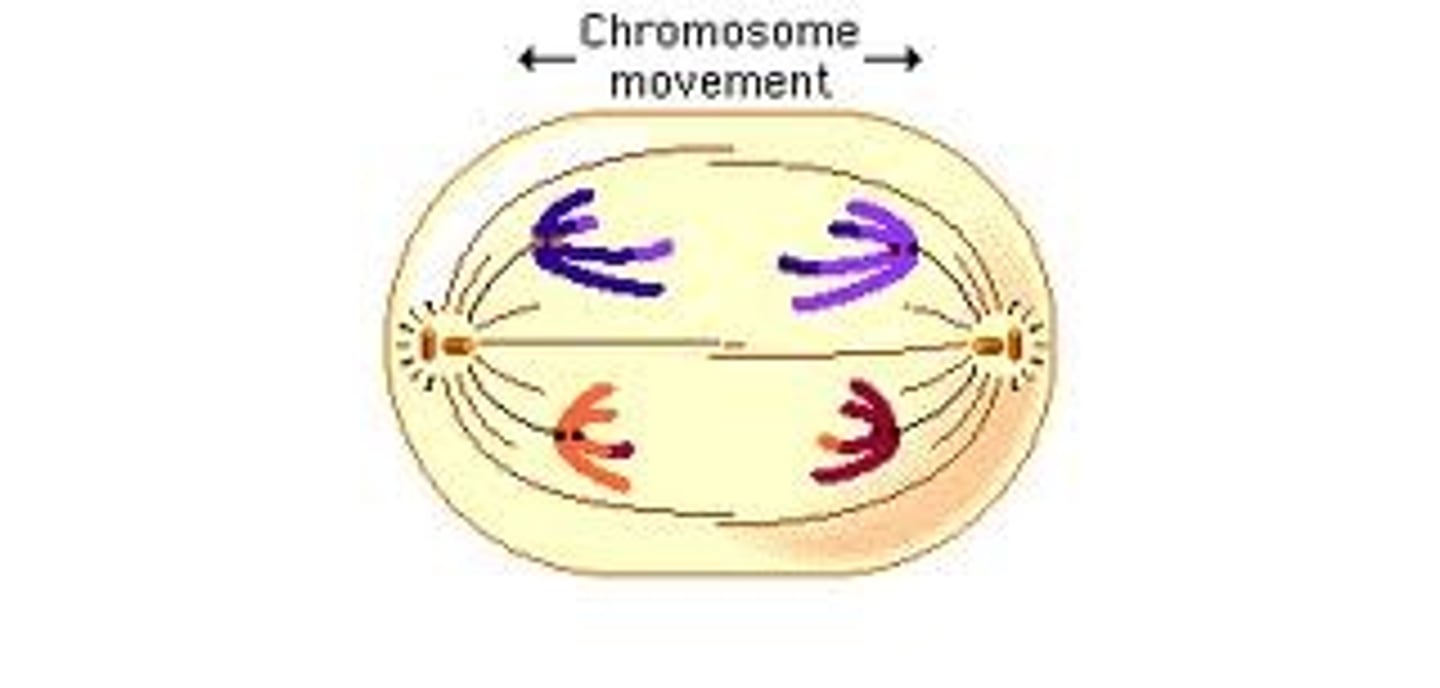
Anaphase
Third stage of mitosis. The chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase
Fourth stage of mitosis. The cell begins to form a cleavage furrow (animal) or cell plate (plant) and divides.
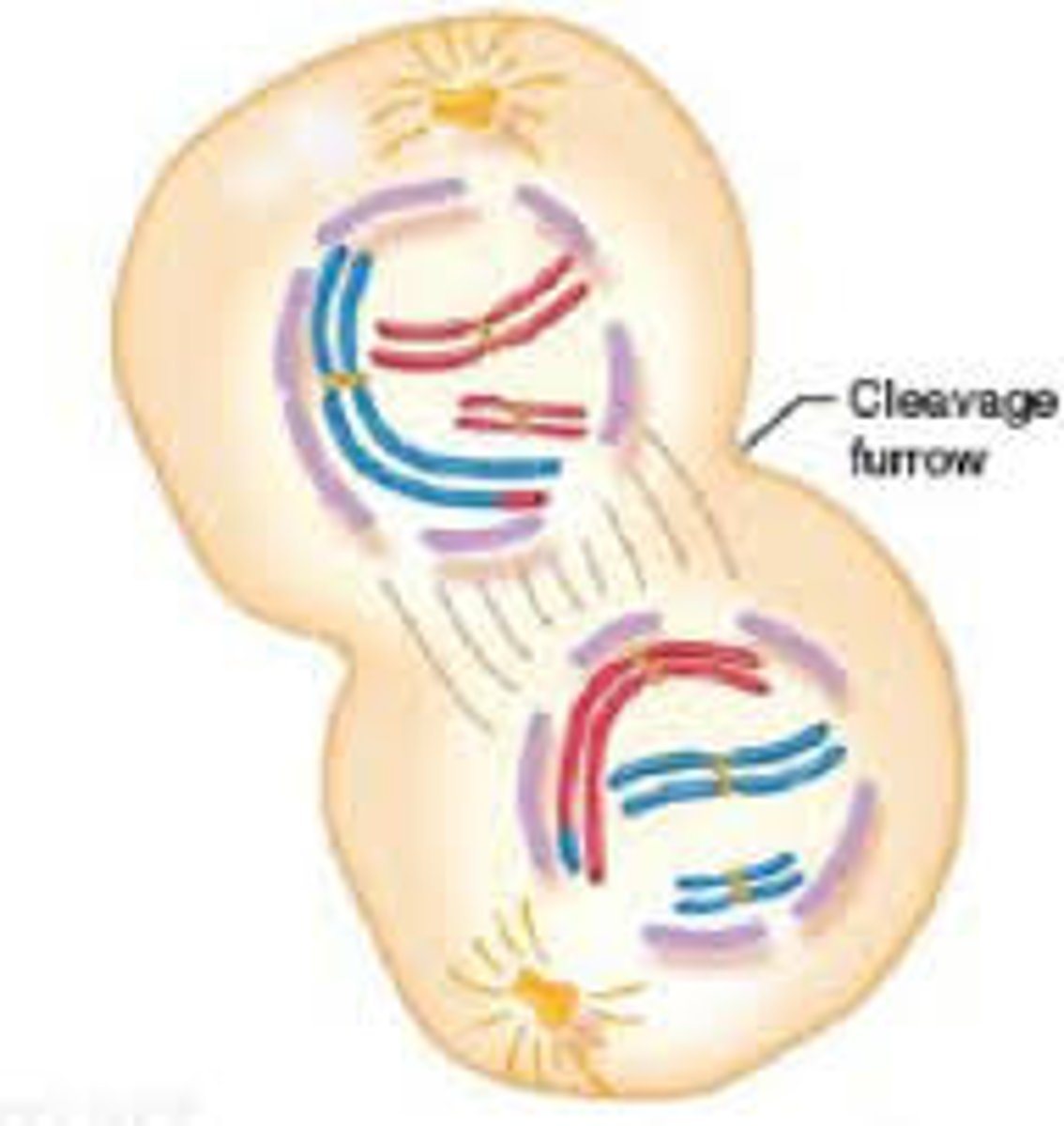
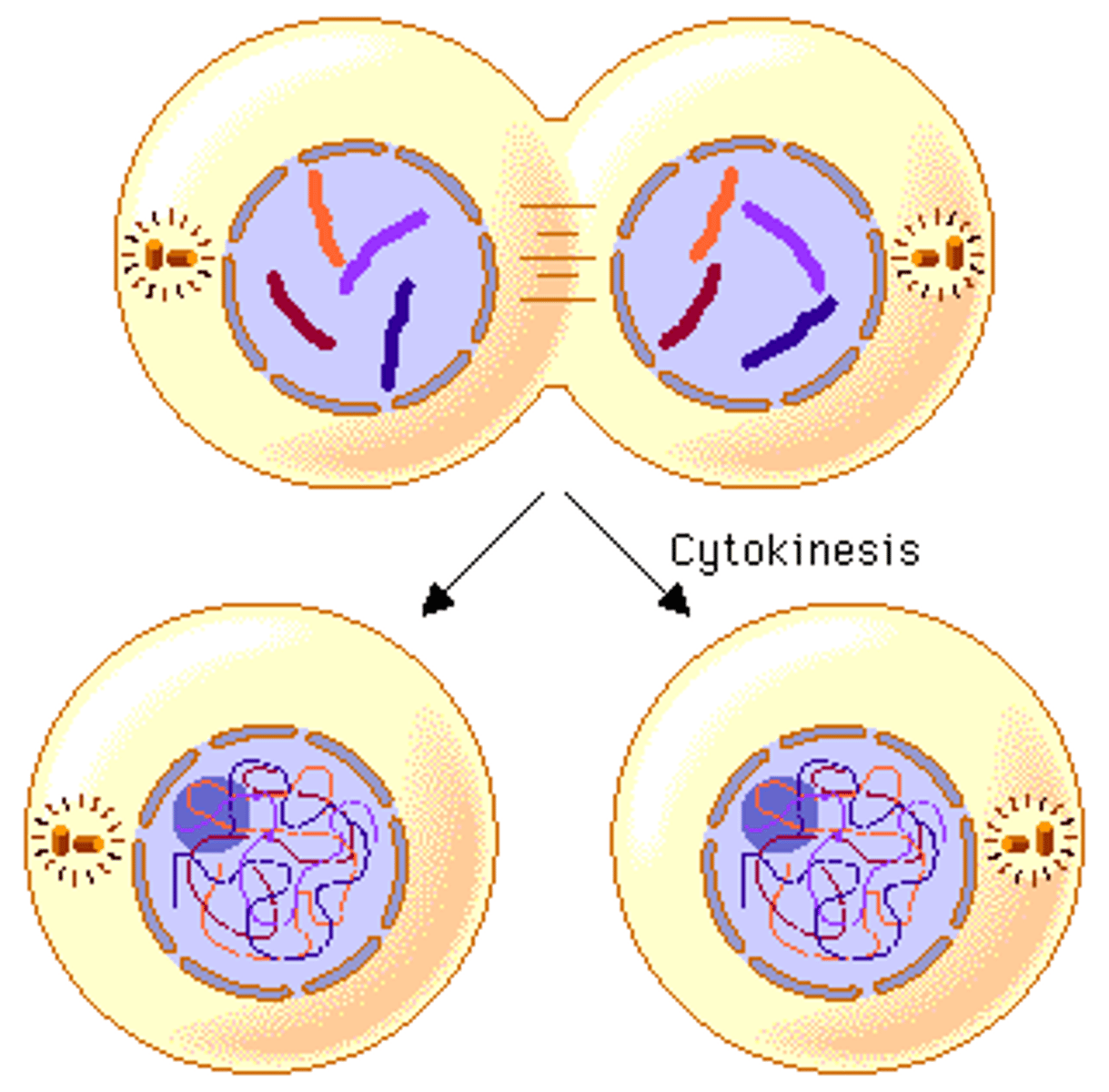
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division. Results in two daughter cells.
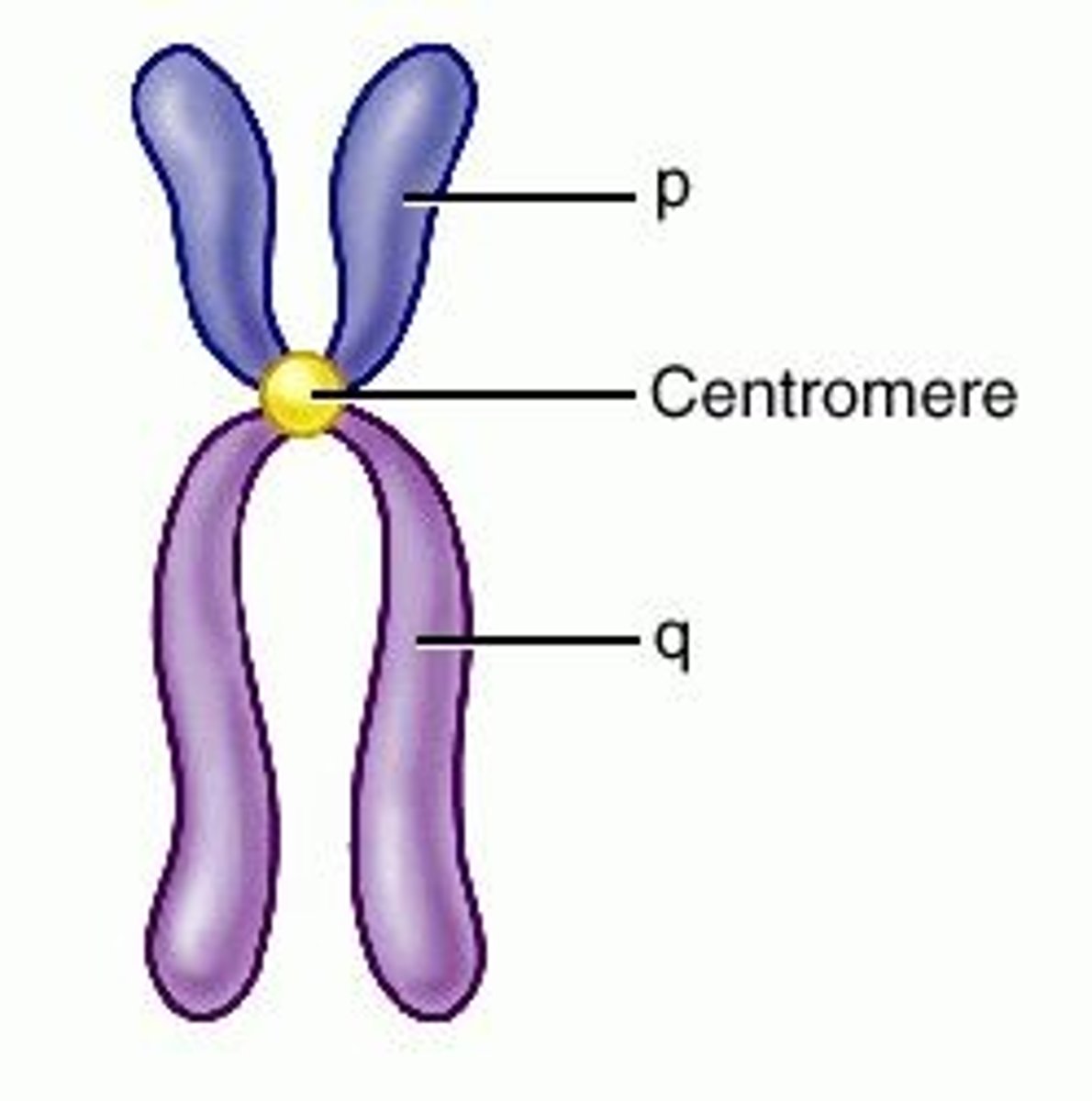
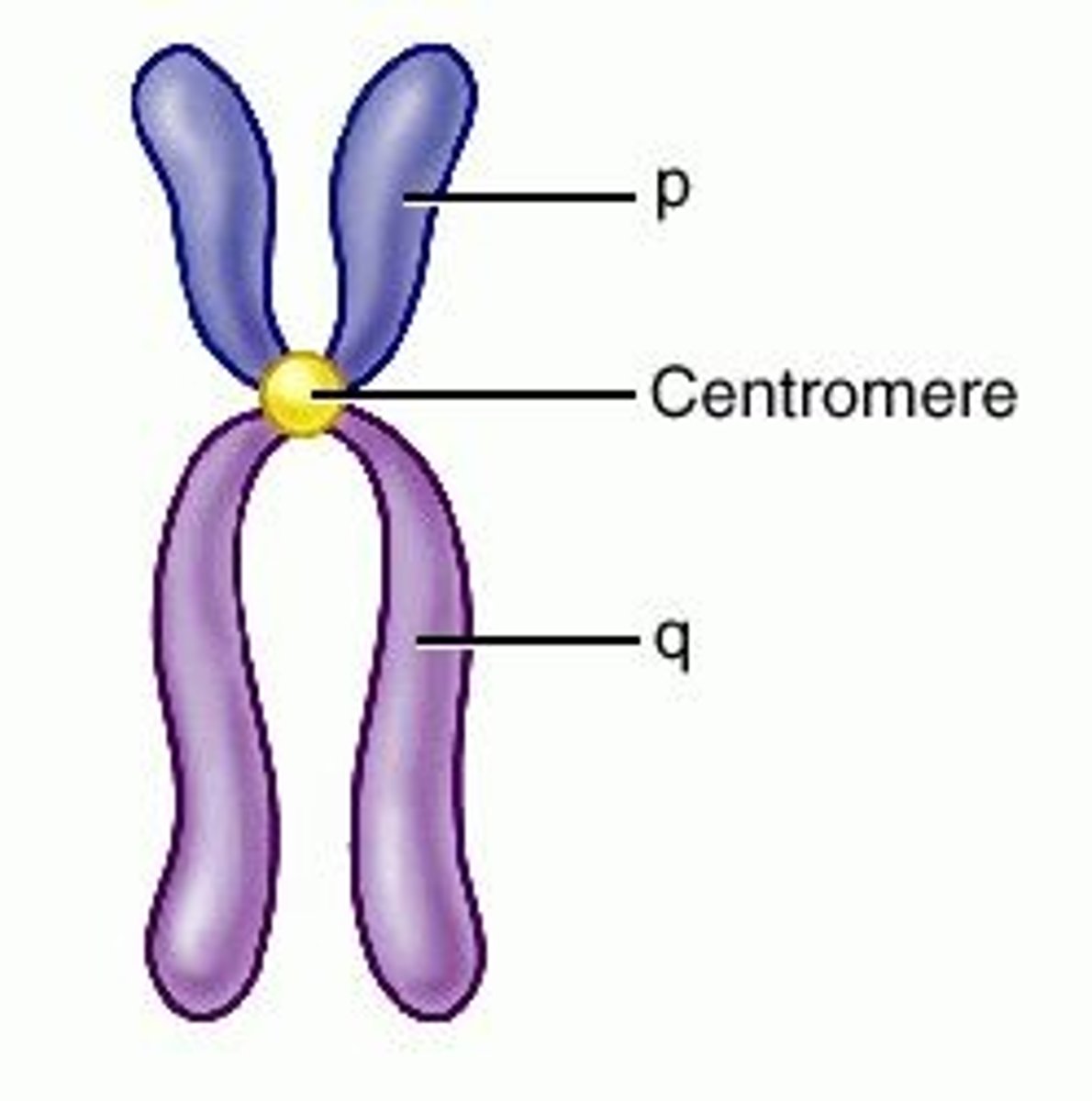
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached.
Microtubules
Thick hollow tubes that make up the cilia, flagella, and spindle fibers.