EC 202- 5,6,7,8
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
producer surplus
The difference between the price producers receive for a good or service and the minimum price they are willing and able to accept
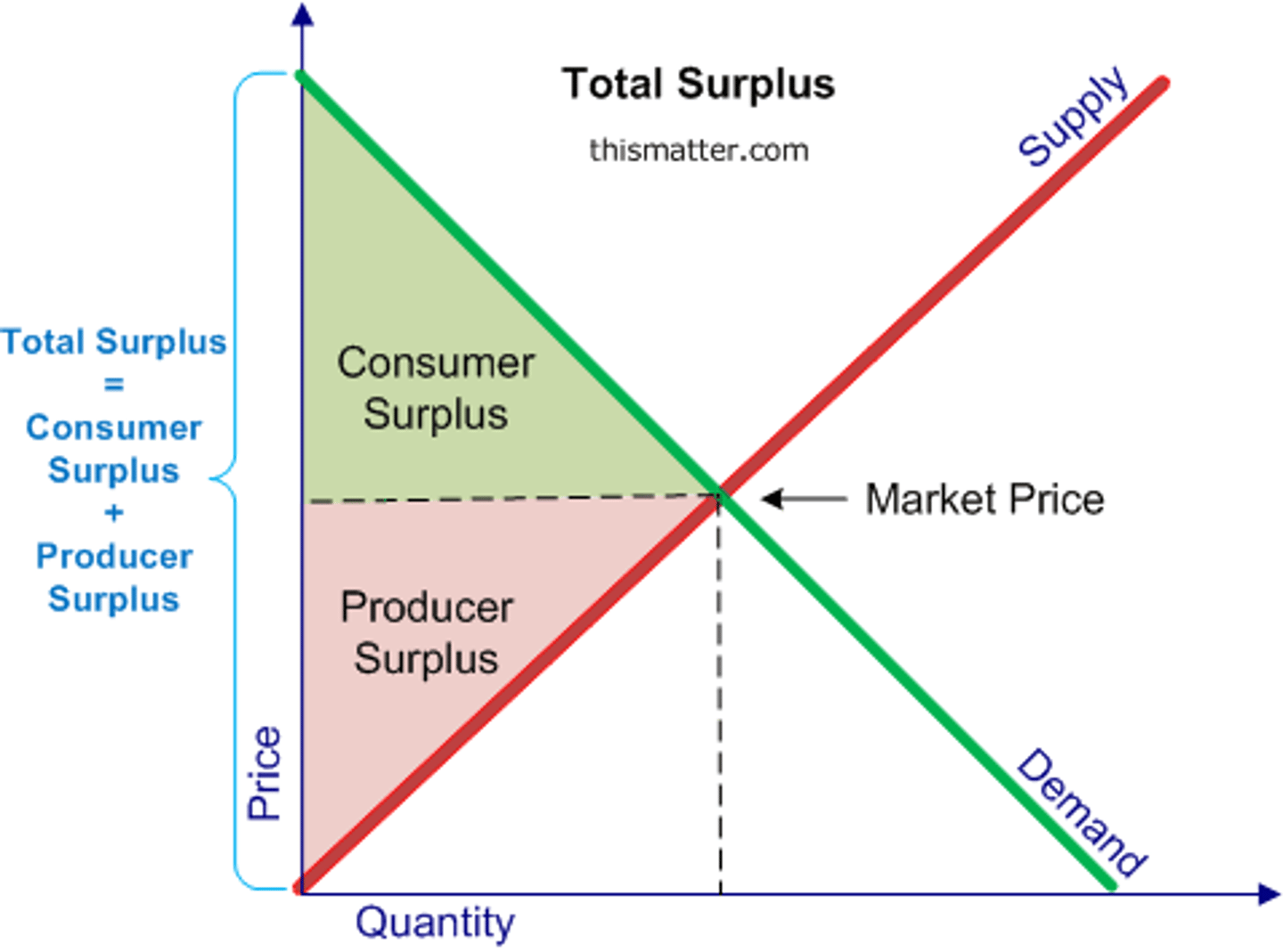
economic surplus
The sum of consumer and producer surplus; total welfare
welfare at equilibrium
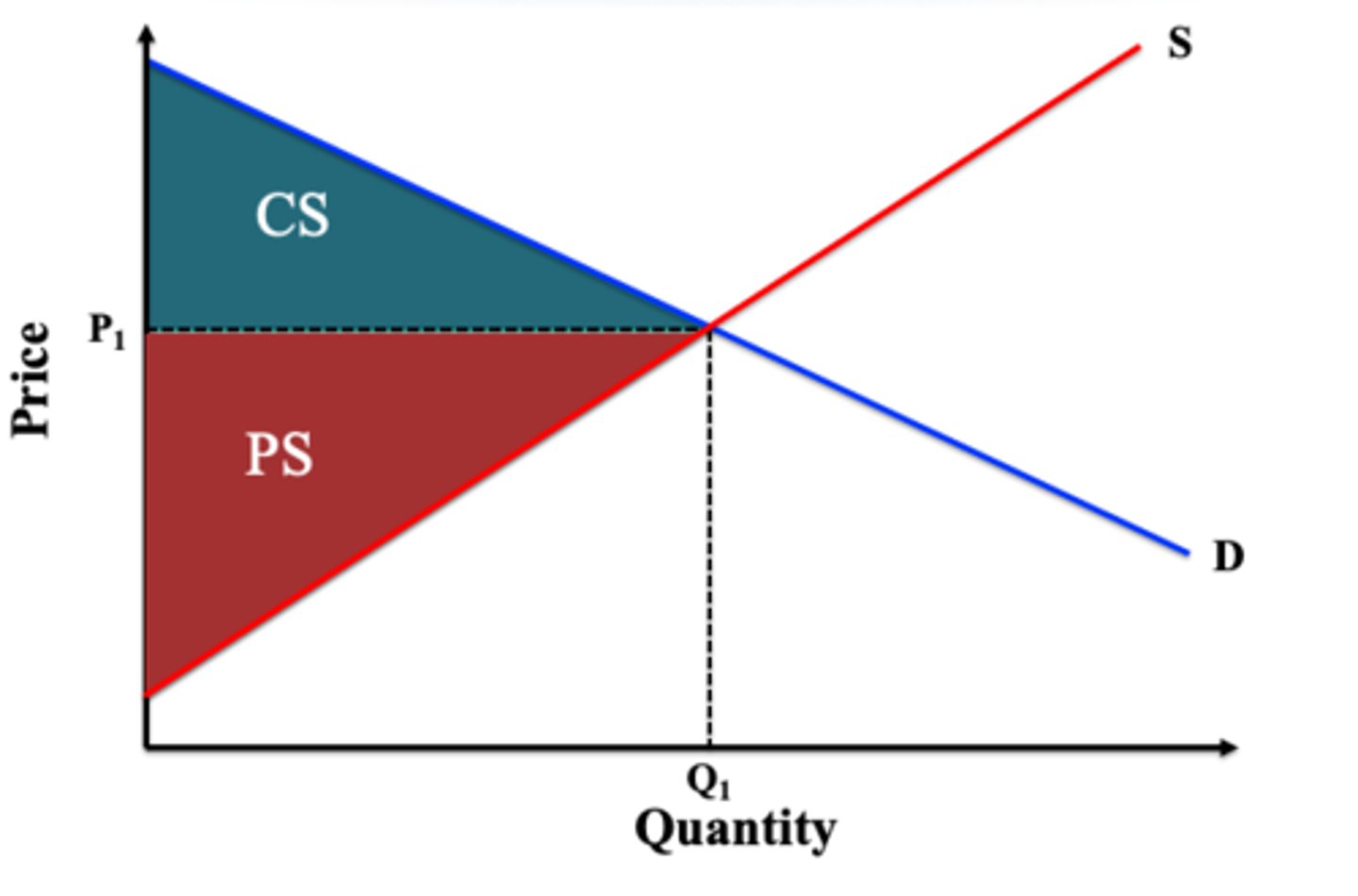
welfare at a higher price
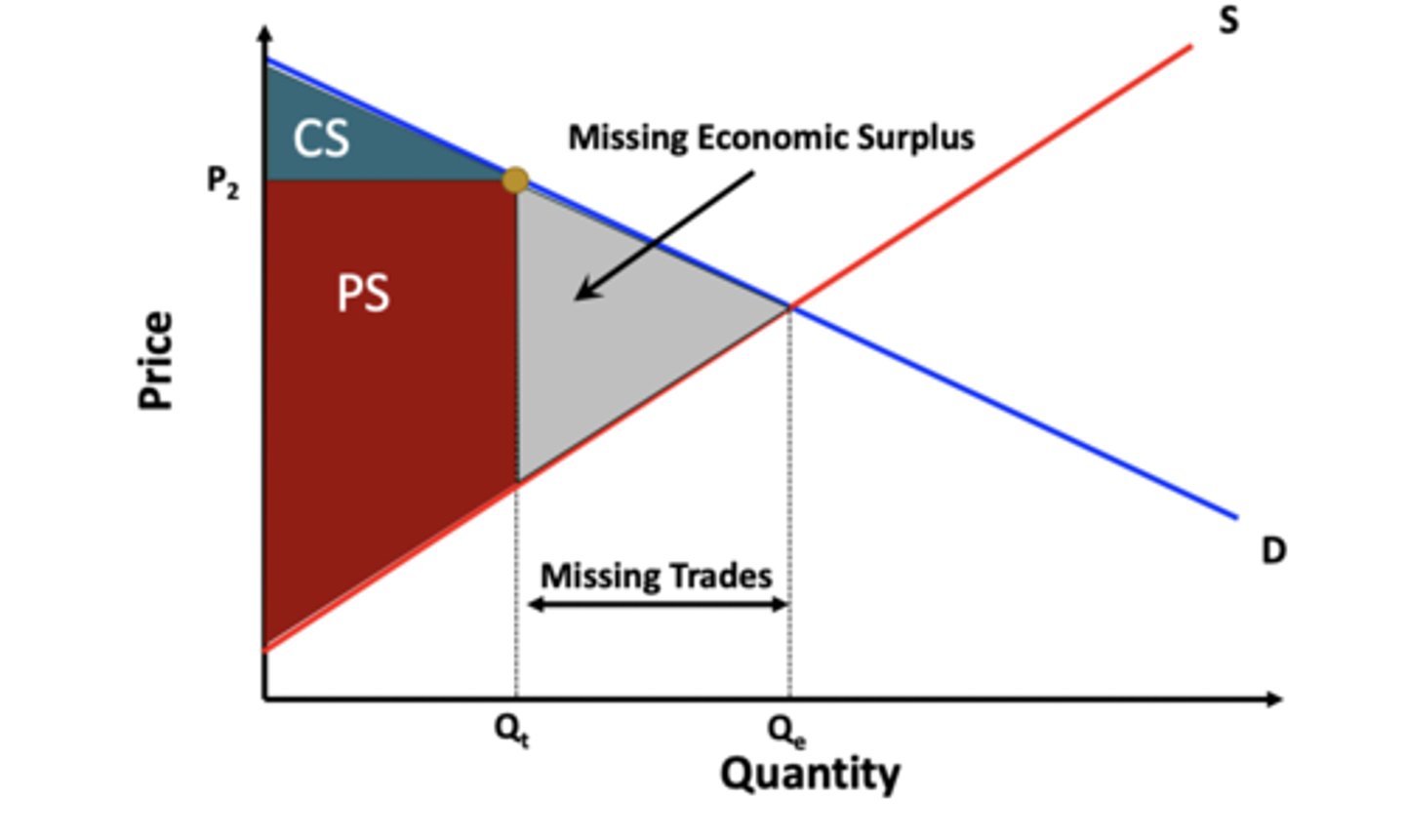
welfare at a lower price
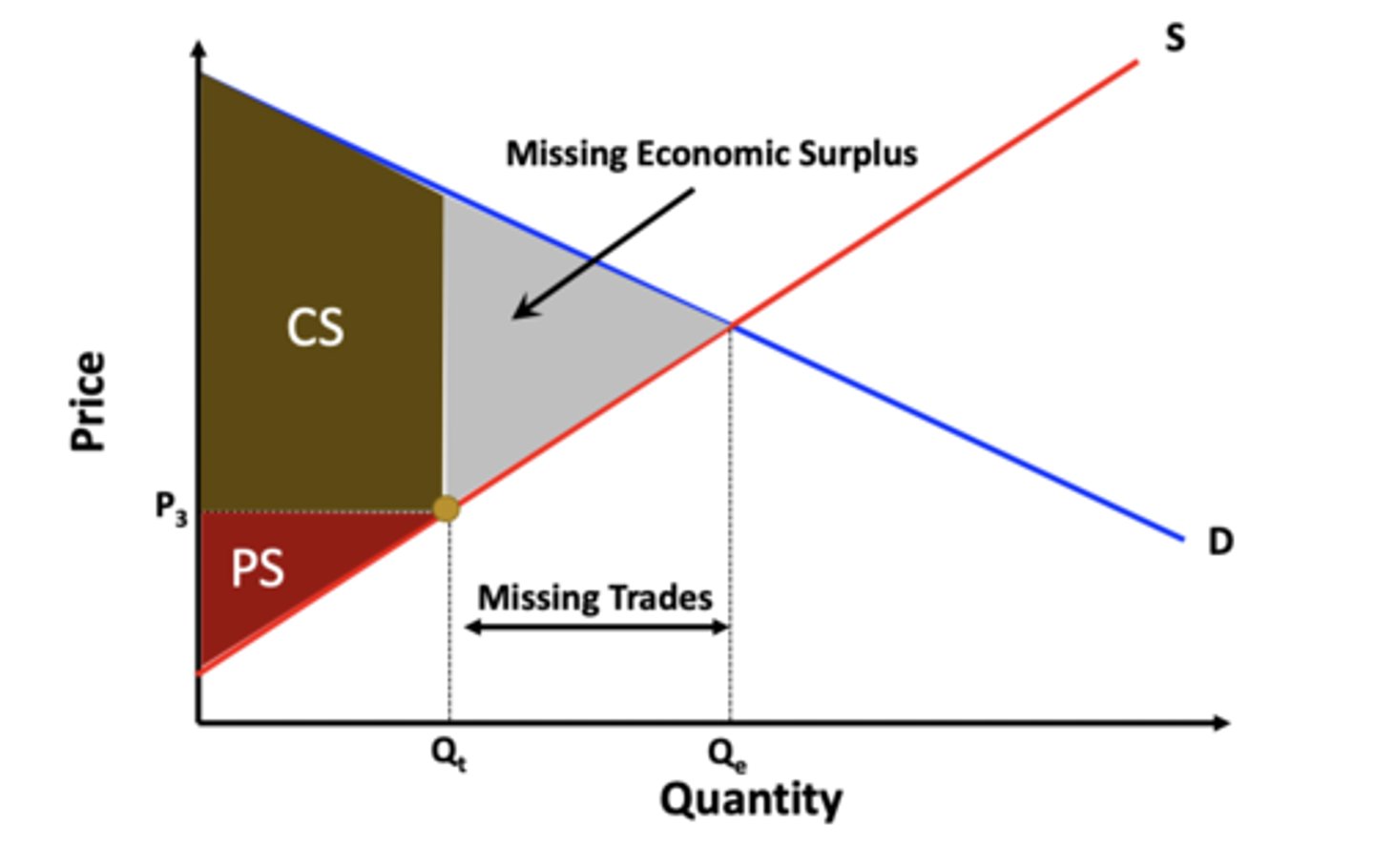
deadweight loss
The value of the economic surplus that is foregone when a market is not allowed to adjust to its competitive equilibrium
A deadweight loss _____________ as tax rates change.
changes
Suppose the equilibrium price is $50. If the actual price paid by the buyer is $60 for one item, and the minimum acceptable price to the seller is $40, then
there is a deadweight loss
Productive Efficiency
Producing output at the lowest possible average total cost of production; using the fewest resources possible to produce a good or service
Allocative Efficiency
Producing the goods and services that are most wanted by consumers in such a way that their marginal benefit equals their marginal cost
Which of the following is not correct when describing allocative efficiency?
A) It occurs where marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
B) It occurs when the right amount of goods and services are produced
.C) It occurs when total surplus is maximized.
D) It occurs when firms produce at the lowest possible average total cost.
D) It occurs when firms produce at the lowest possible average total cost
If the market is in equilibrium, which of the following occurs?
A) Gains from trade are maximized, economic surplus is maximized, allocative efficiency is achieved, and productive efficiency is achieved.
B) Gains from trade are maximized, economic surplus is maximized, allocative efficiency is not achieved, and productive efficiency is achieved.
C) Gains from trade are maximized, economic surplus is maximized, allocative efficiency is achieved, and productive efficiency is not achieved.
D) Gains from trade are lowered, economic surplus is reduced, allocative efficiency is achieved, and productive efficiency is achieved
A) Gains from trade are maximized, economic surplus is maximized, allocative efficiency is achieved, and productive efficiency is achieved
price ceiling
a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service
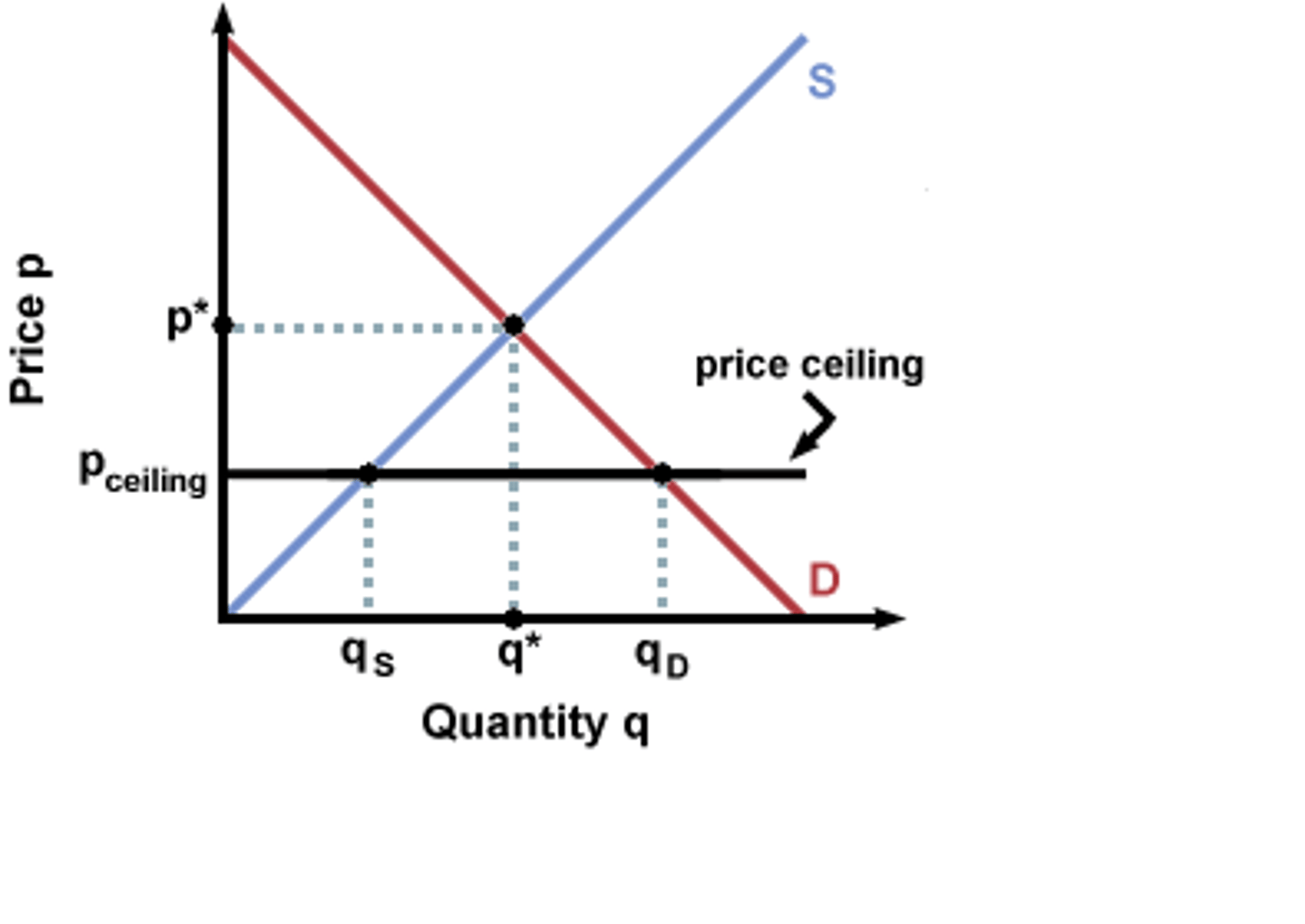
Which of the following correctly describes the social welfare impact of a price ceiling?
A) All consumers win.
B) A deadweight loss occurs.
C) All producers win.
D) Total surplus is increased.
B) A deadweight loss occurs
price floors
government imposed limits on how low a price can be charged
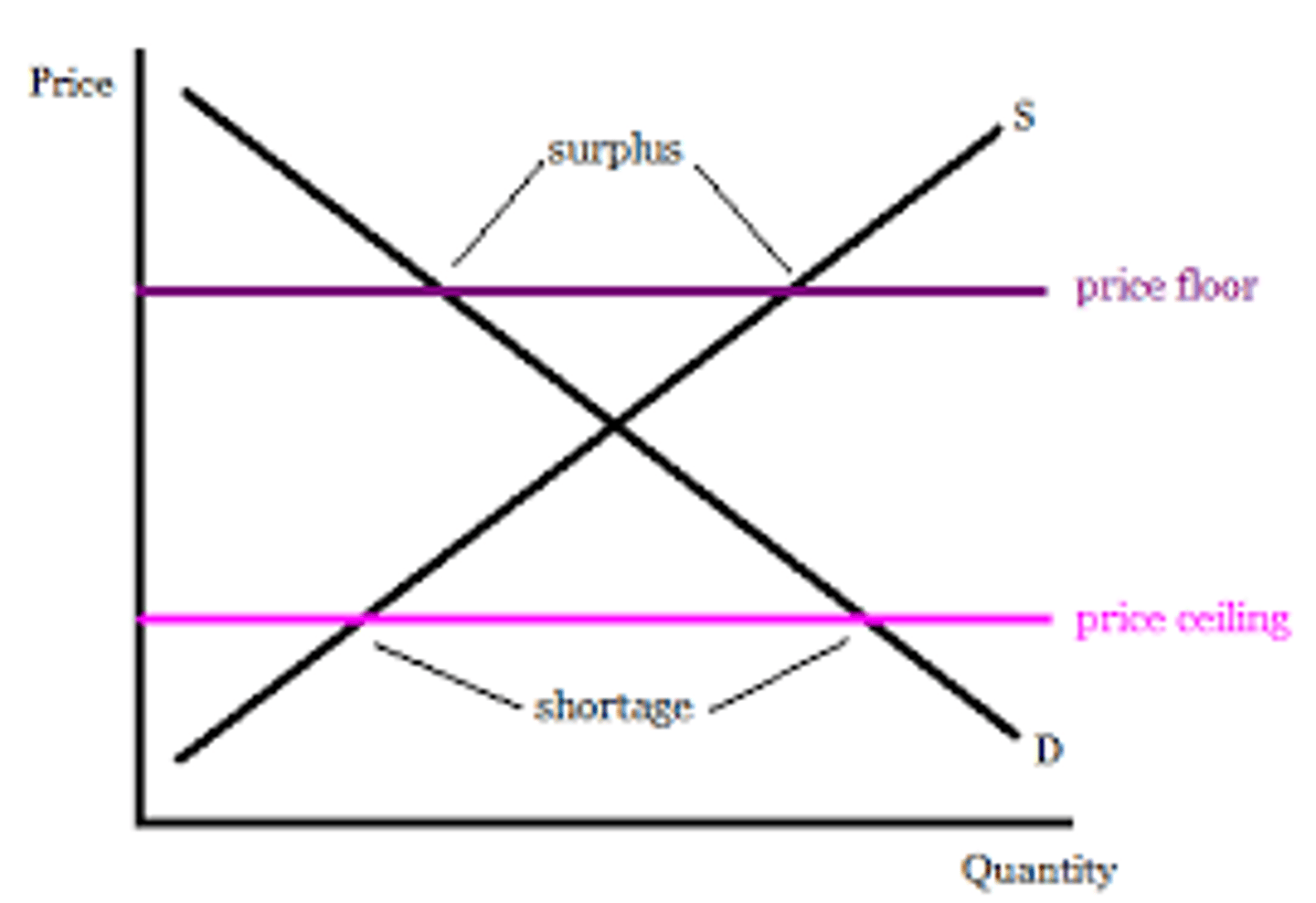
Which of the following correctly describes the social welfare impact of a price floor?
A) Total surplus is decreased.
B) All producers lose.
C) There is no deadweight loss.
D) All consumers win
A) Total surplus is decreased
a tax on demanders
shifts the demand curve to the left
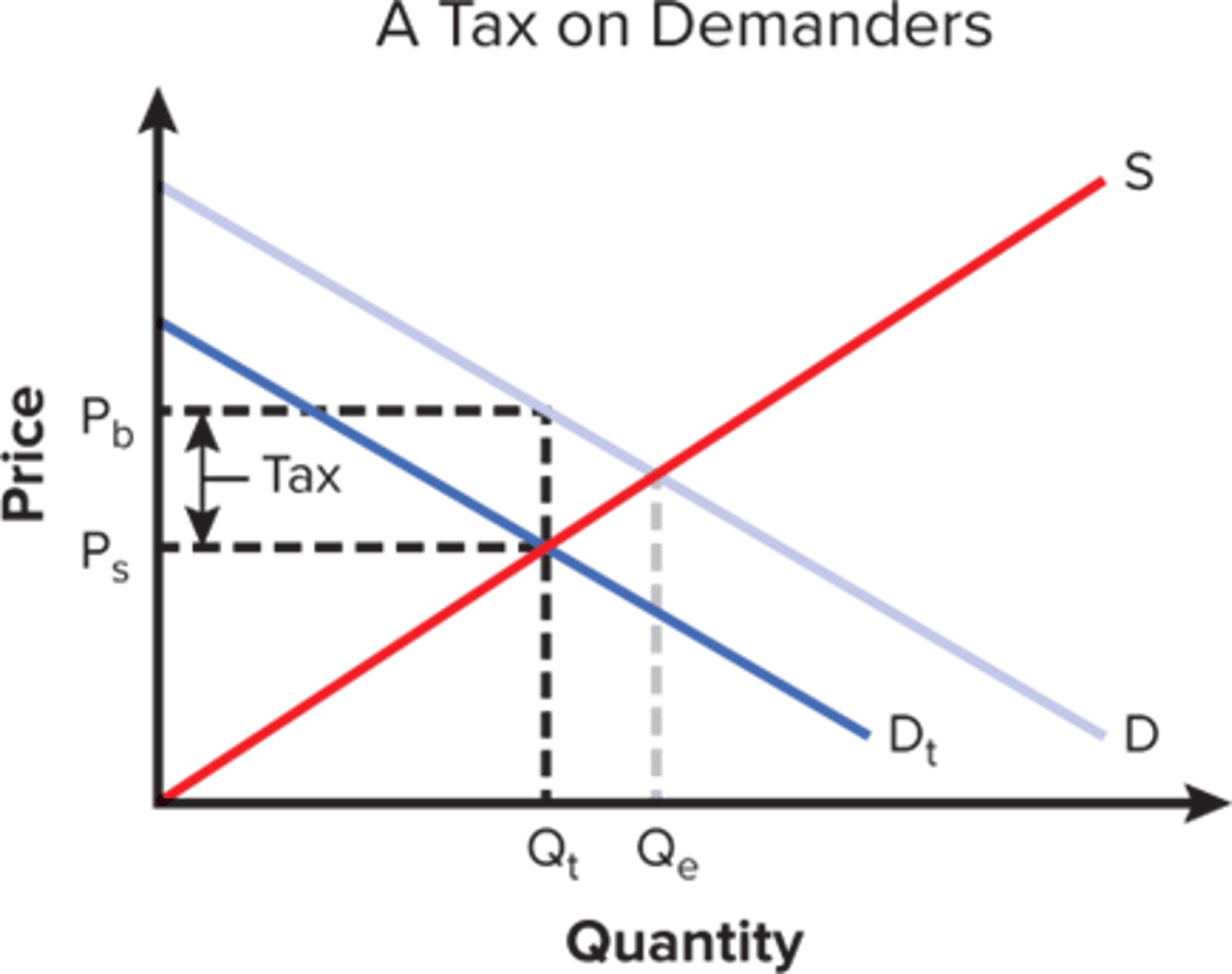
Without taxes, a market moves to _______ and _______ surplus is maximized.
equilibrium; economic
welfare types
tax revenue + consumer surplus+ producer surplus + DWL
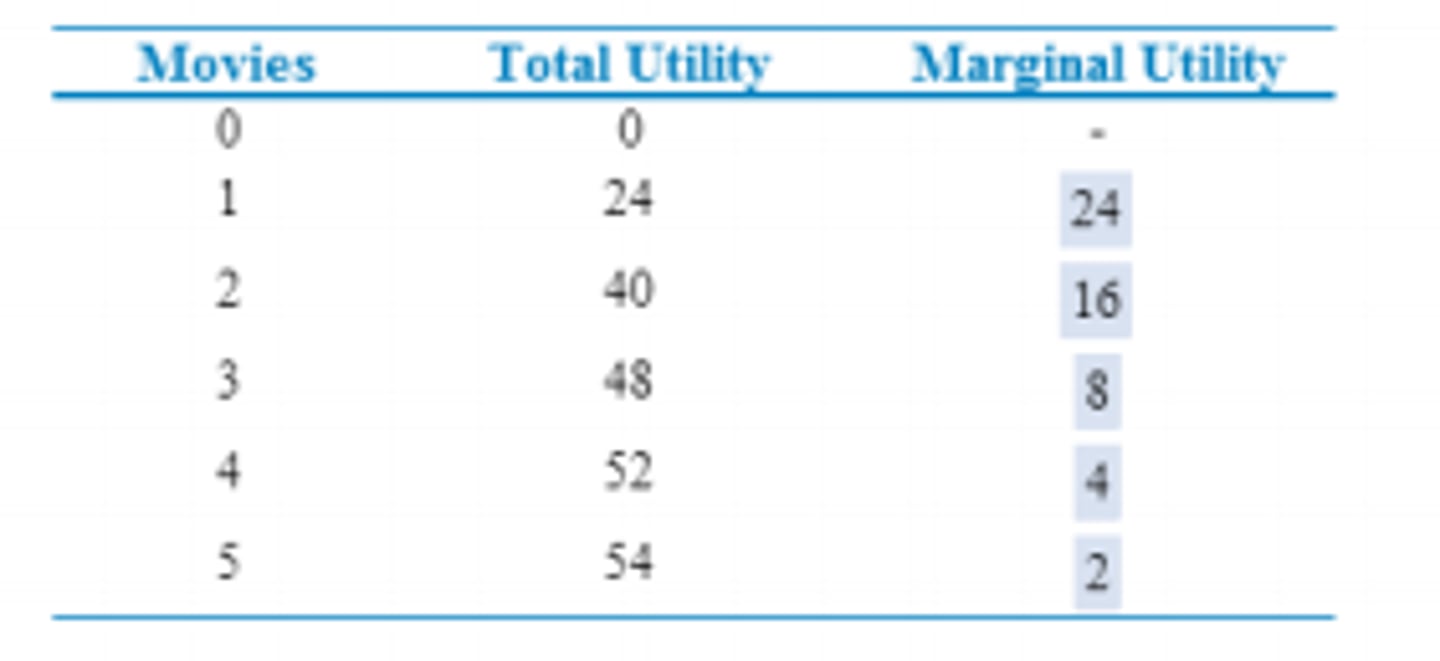
marginal utility
The additional satisfaction or happiness received from the consumption of an additional unit of a good or service; dividing the change in total utility by the change in the total number of units consumed
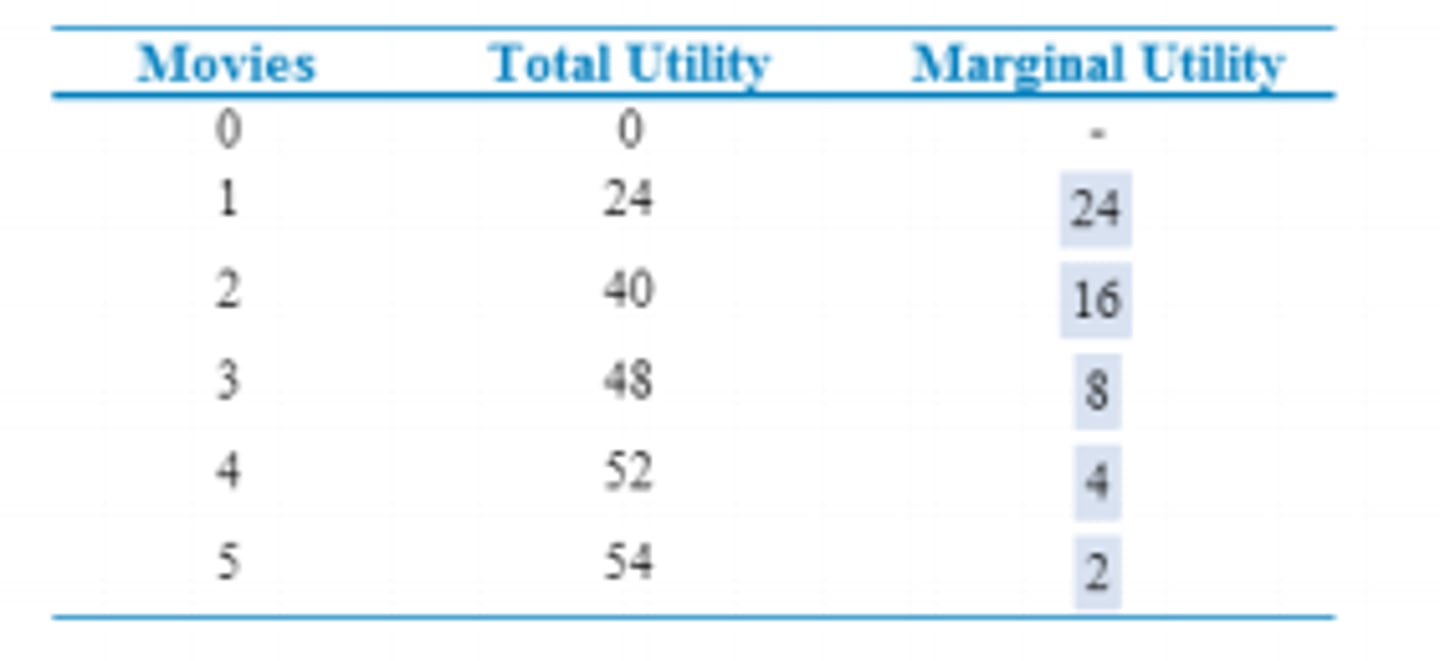
total utility
The total satisfaction or happiness received from the consumption of a good, service, or combination of goods and services; calculated by adding up the marginal utility (MU) of each unit consumed
Marginal utility is
A) negative, but never positive.
B) positive or negative, but never zero.
C) positive, negative, or zero.
D) increasingly negative
C) positive, negative, or zero.
The demand curve is downward sloping because
marginal utility decreases as more of a product is
consumed
If total utility is decreasing, marginal utility
is negative.
Utility Maximization
The process of obtaining the greatest level of overall satisfaction or happiness from consuming goods and services, subject to consumers' preferences, incomes, and prices
The theory of consumer behavior assumes that
consumers behave rationally, maximizing their
satisfactions
Equal Marginal Principle
Consumers utility is maximized utility when they allocate their limited incomes so that the marginal utility per dollar spent on each of their final choices in a bundle is equal
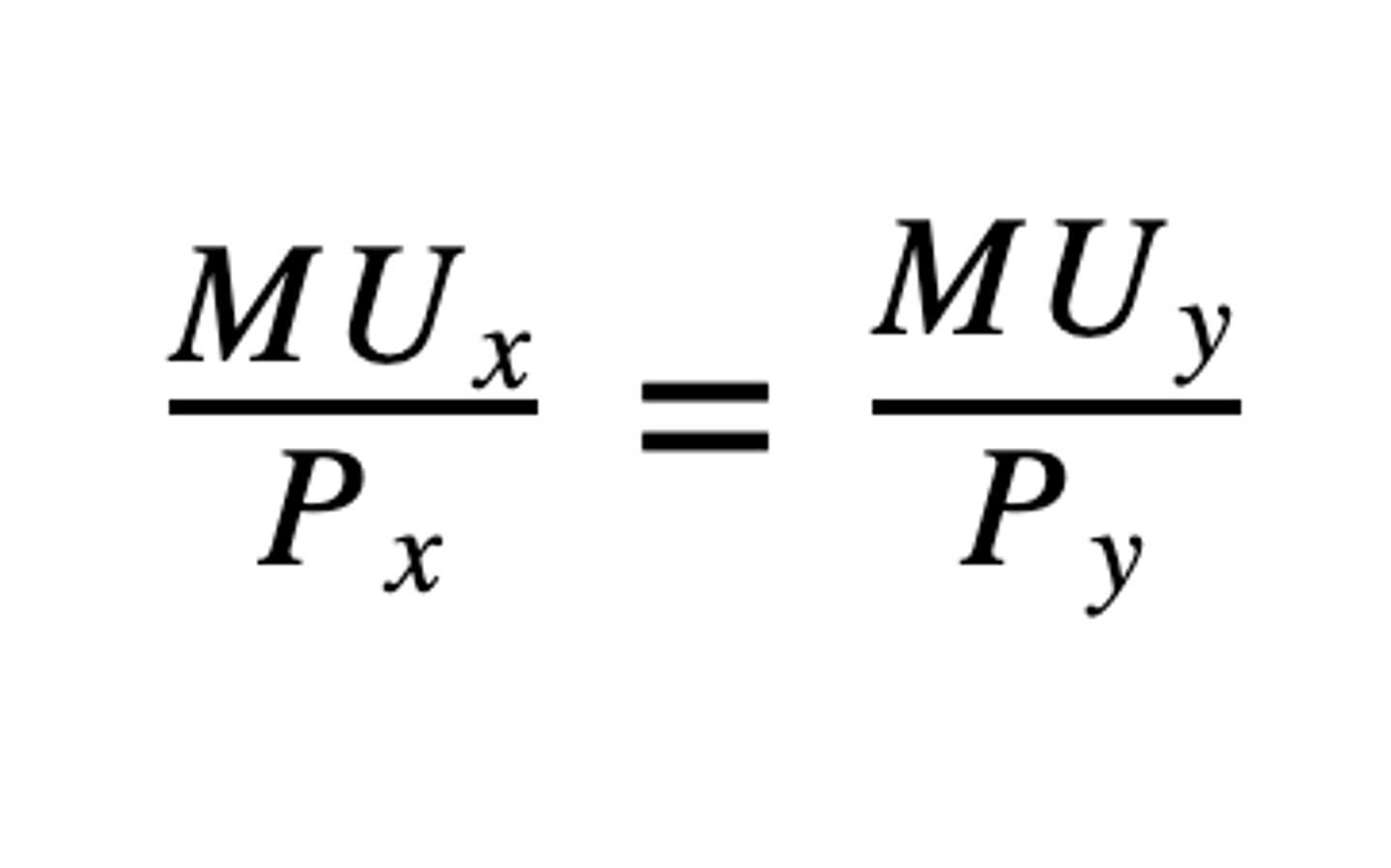
equal marginal principle formula
MU_x/P_x = MU_y/P_y:
MU_x: Marginal utility derived from good X
MU_y: Marginal utility derived from good Y
P_x: Price of good X
Budget Line
A line showing the different combinations of two products that can be purchased with a given budget and at a known set of prices

Indifference Curves
A curve that shows the combinations of two products that generate the same amount of total utility or satisfaction
Characteristics of Indifference Curves
• Indifference curves are downward-sloping.
• Indifference curves further from the origin are preferred to
those closer to the origin. (higher utility value)
• Indifference curves cannot cross.
• All combinations on the curve provide the same utility as other
combinations on the curve
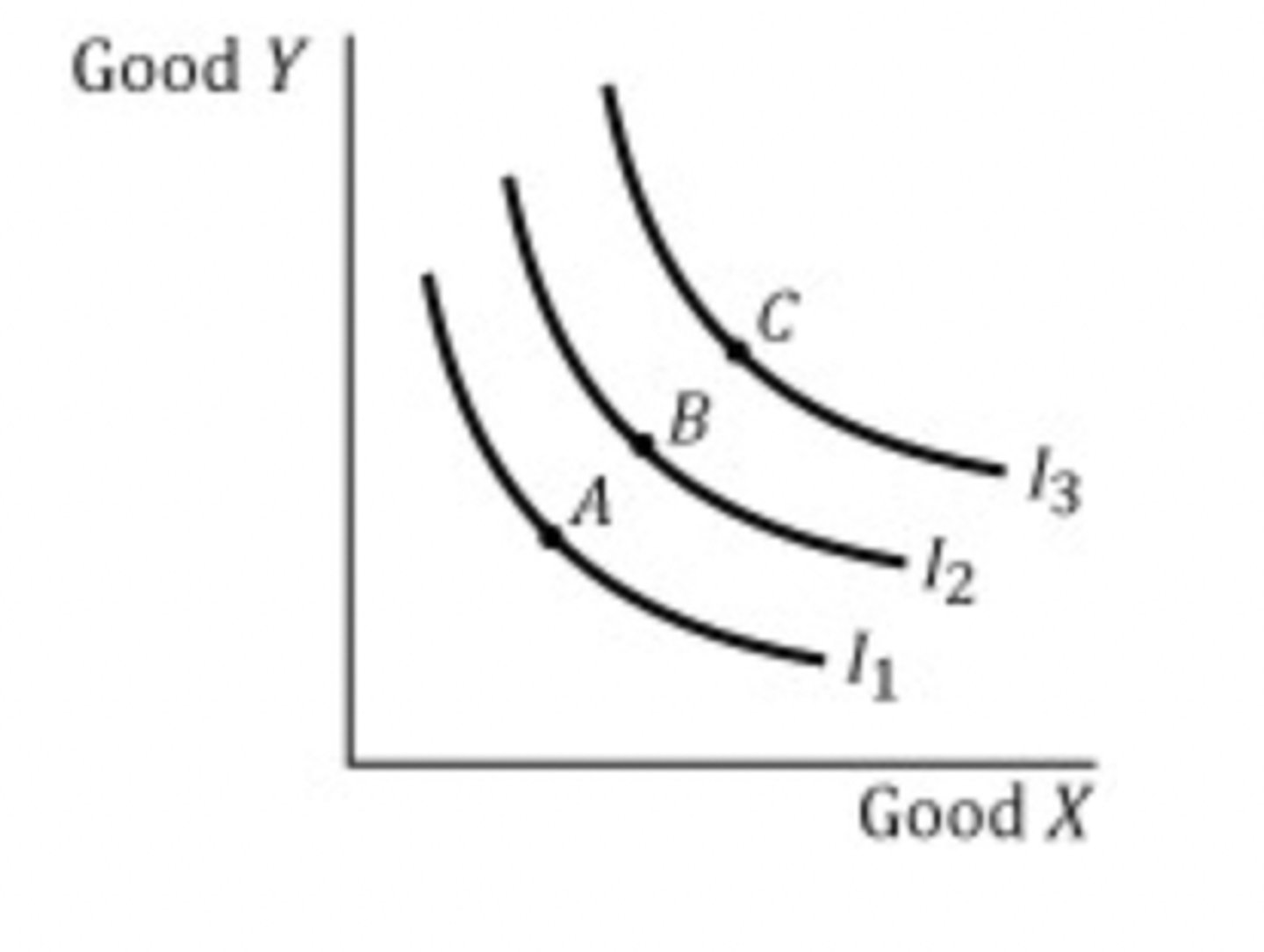
Indifference curves show the ________ of combinations of two products
total utility
Explicit Costs
Monetary payments made by individuals, firms, and
governments for the use of land, labor, capital, and
entrepreneurial ability owned by others. Also known as
accounting costs.
Explicit Costs
are there ever zero explicit costs?
no; opportunity cost always
Implicit Cost
The opportunity costs of using owned resources; costs
for which no monetary payment is explicitly made.
Generally, accounting profits are
greater than economic profits, because accounting profits
do not consider implicit costs
Increasing Marginal Returns
A characteristic of production whereby the marginal product of the next unit of a variable resource utilized is greater than that of the previous variable resource
Diminishing Marginal Returns
A characteristic of production whereby the marginal
product of the next unit of a variable resource utilized is less than
that of the previous variable resource
Marginal product
) usually increases then decreases and may become
negative
When total product is rising
marginal product is positive.
Average fixed cost
A) equals marginal cost when average variable cost is at its
minimum value.
B) is total variable cost divided by the number of units of
output.
C) declines and then rises in a U-shape as output expands.
D) declines continually as output expands
declines continually as output expands.
average total cost
total cost divided by the quantity of output
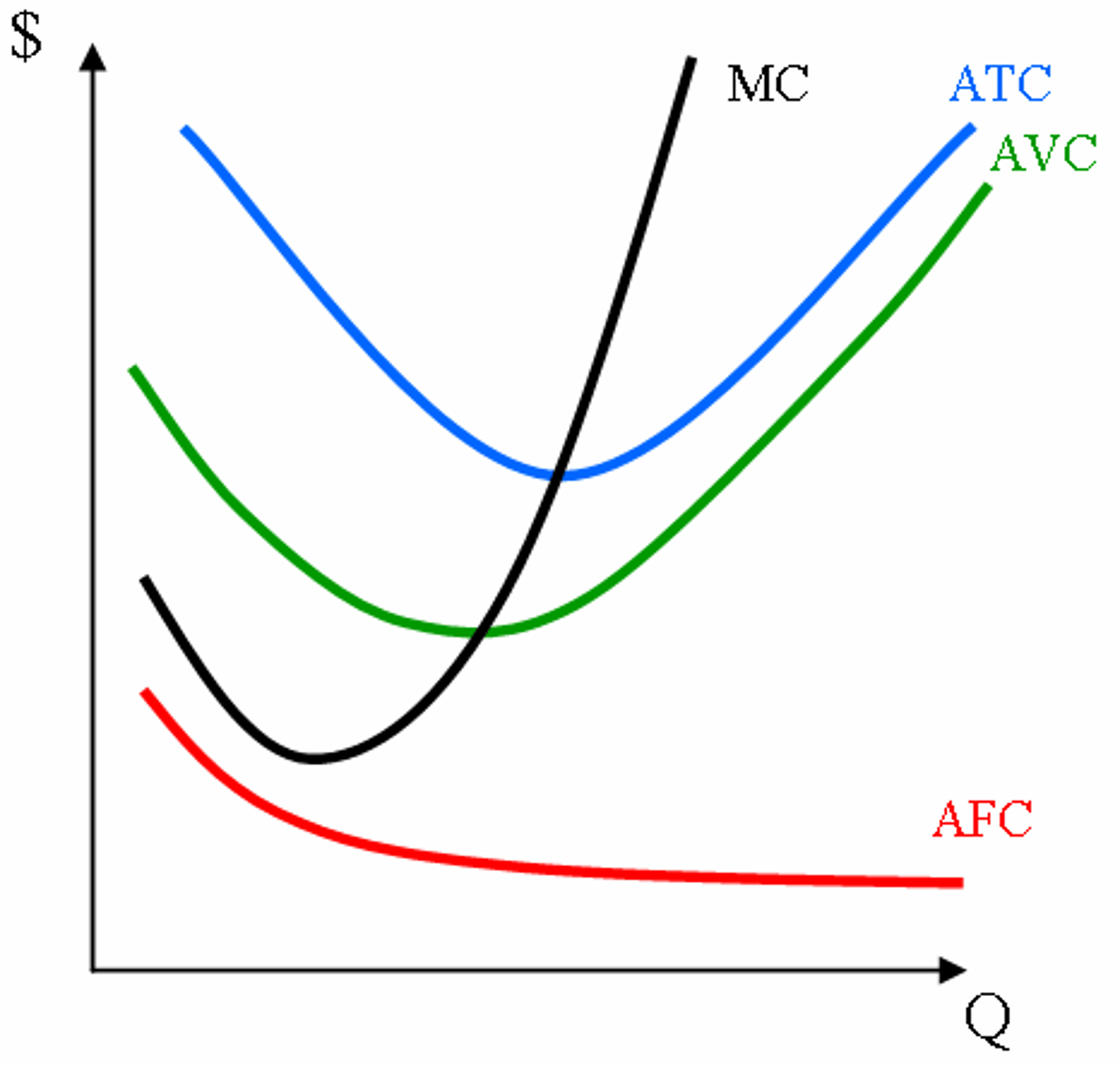
average variable cost
total variable cost divided by the quantity of output
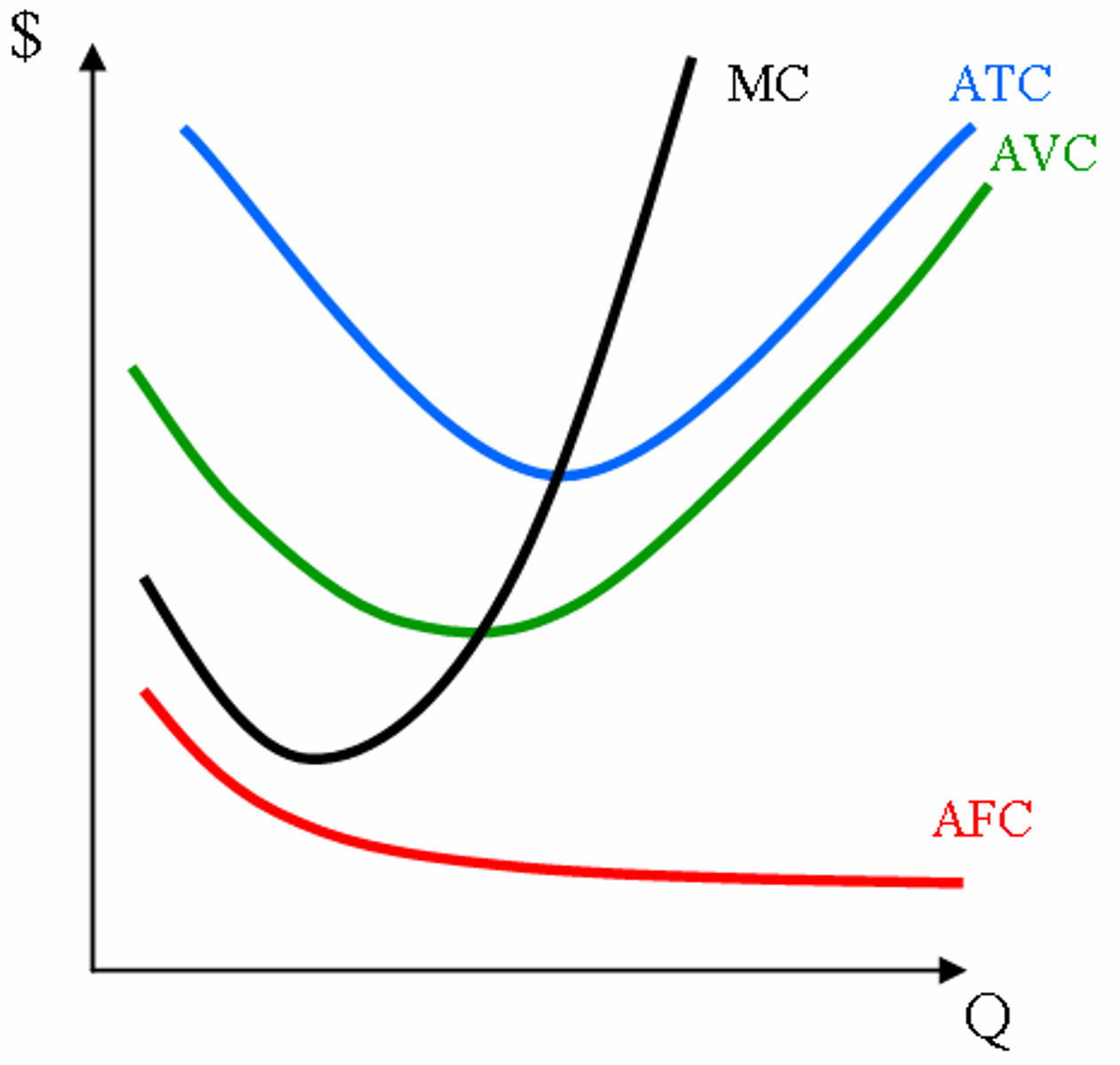
average fixed cost
total fixed cost divided by the quantity of output
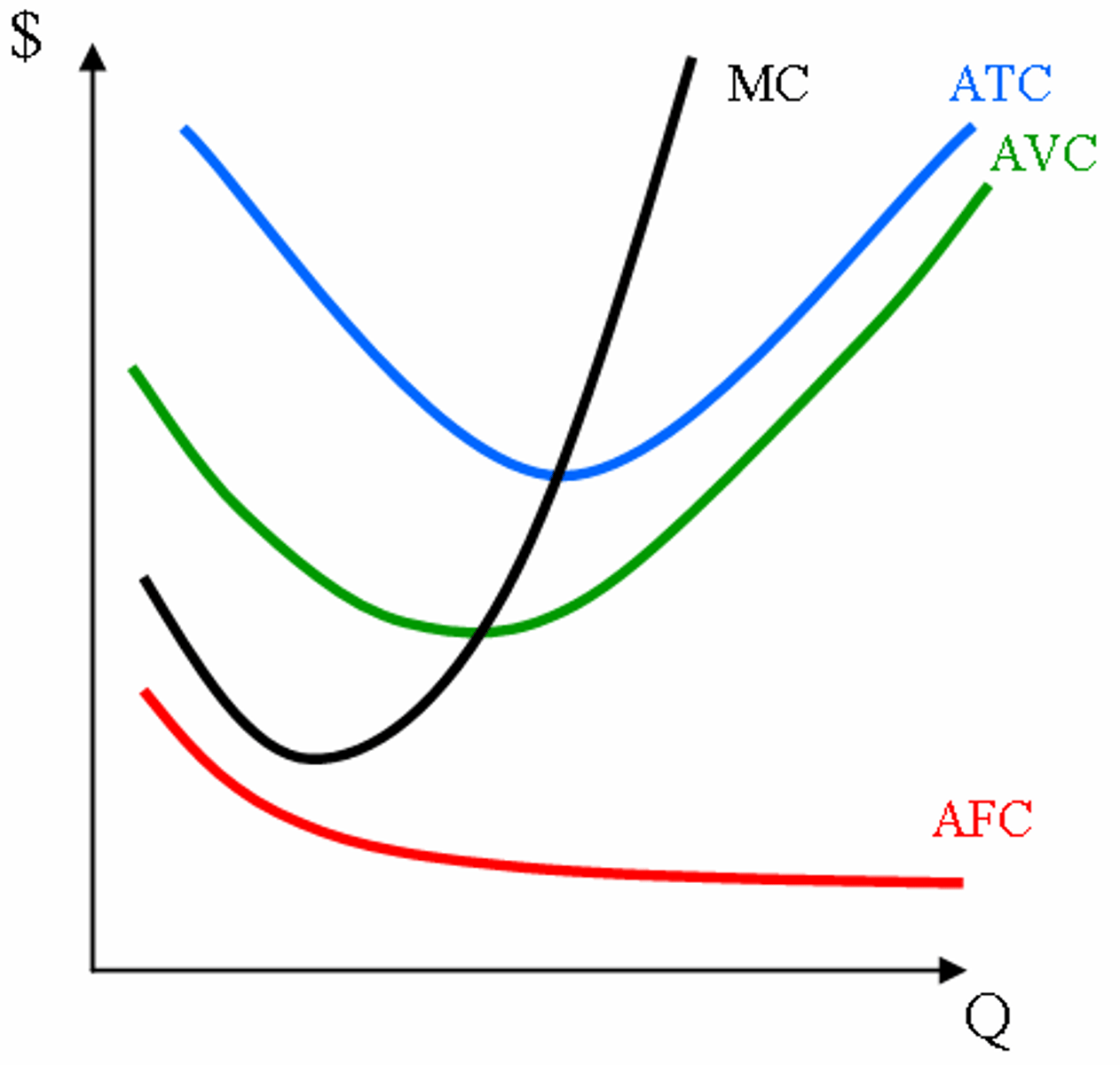
Marginal Cost
The additional cost associated with one more unit of
an activity. For production, it is the change in total cost due to the
production of one more unit of output

Situation: You currently have a 68% free throw completion
average (68/100) for the season. Your completion rate for the
next two games will impact your new average.
• Game 1: You complete 8/10 free throws for an 80% completion
rate. Will your seasonal average increase, decrease, or stay the
same?
Answer: Increase. Your game rate was 80% which is higher than
your season average.
- New season average: (68 + 8)/(100 + 10) = 69.1%
LRATC Curve
A curve showing the lowest average total cost possible
for any given level of output when all inputs of production are
variable
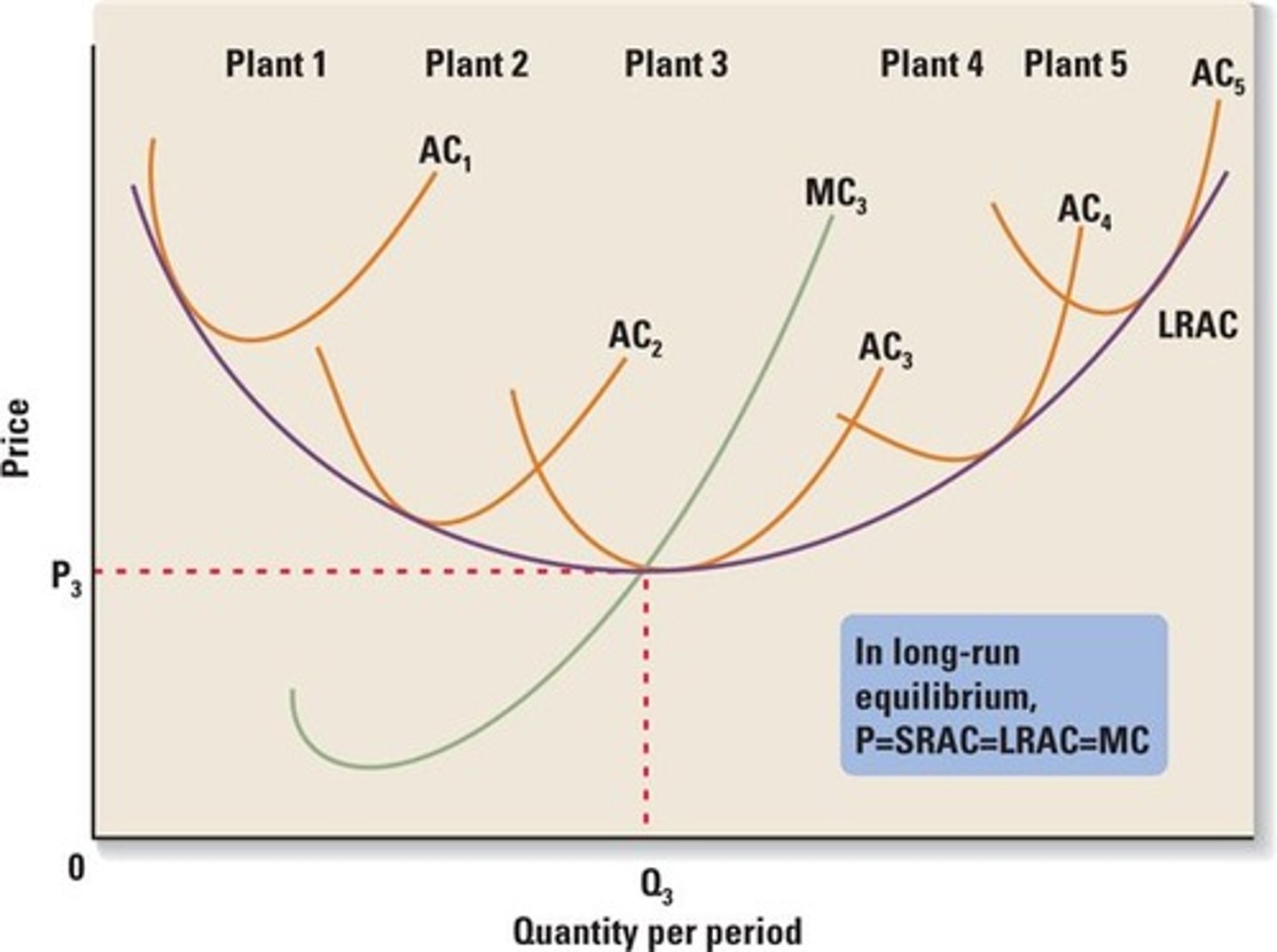
Which of the following statements describes a difference
between the short run and the long run?
A) The law of diminishing returns is an issue in the long run
but not in the short run.
B) All resources are fixed in the short run, and all resources
are variable in the long run.
C) Some resources are fixed in the short run, and all
resources are variable in the long run.
D) Variable costs are more important for decision making in
the short run than in the long run
All resources are fixed in the short run, and all resources are variable in the long run.
Economies of Scale
A condition in which the long-run average total cost of
production decreases as production increases
Constant Returns to Scale
A condition in which the long-run average total cost of
production remains constant as production increases
Diseconomies of Scale
A condition in which the long-run average total cost of
production increases as production increases
LRATC Curve (scale)
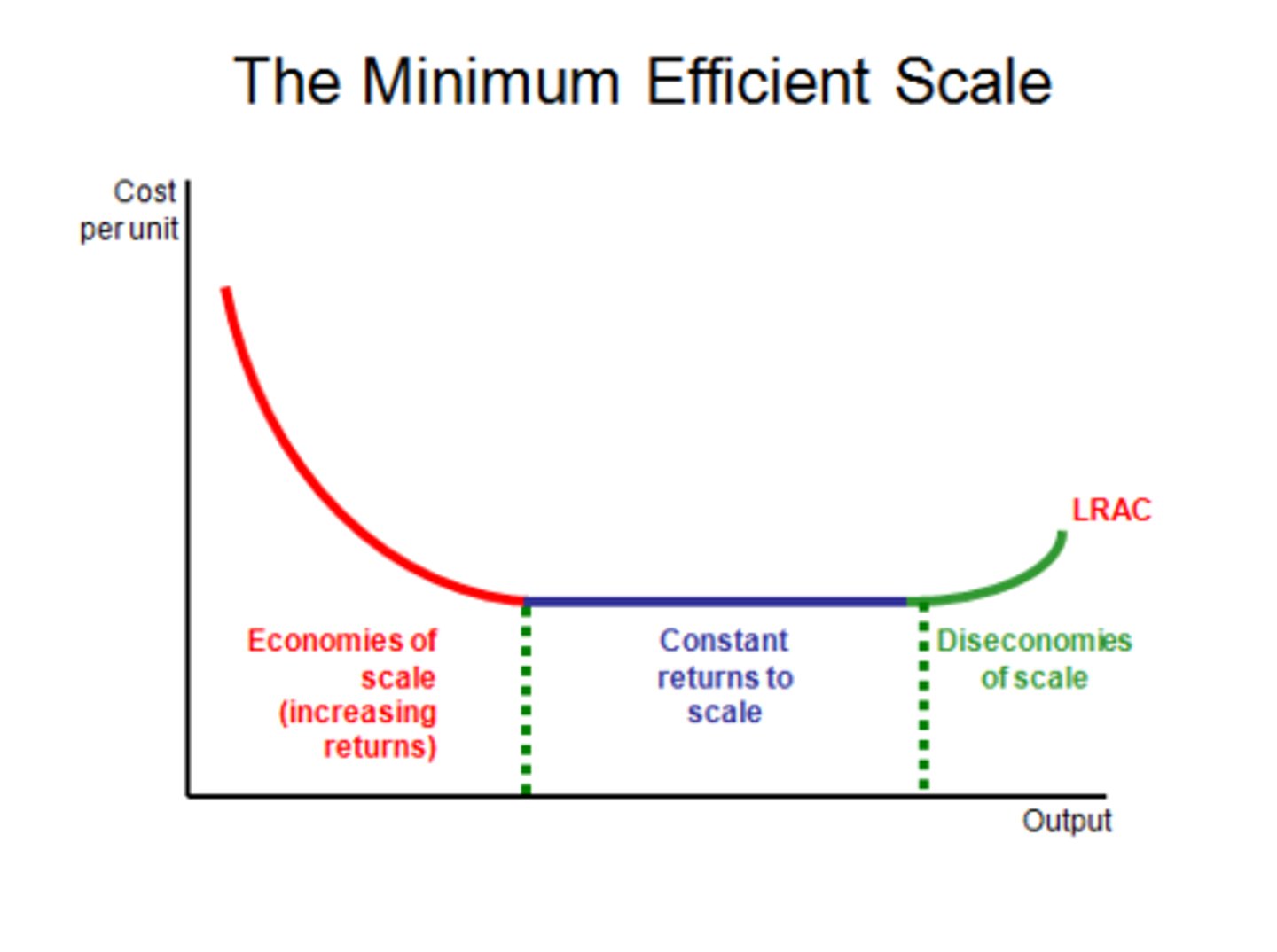
One reason a firm may experience economies of scale is
the firm experienced specialization in labor and management
A firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale if
costs increase as output expands.
Perfect Competition Characteristics:
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Standardized/homogeneous product
- Price takers / No price control
- Easy entry and exit
- Perfect information on the market
Marginal Revenue
The change in a firm's total revenue that results from a one-unit change in output produced and sold
Average Revenue
Revenue per unit sold, equal to total revenue divided
by the quantity of output produced and sold
How Does a Perfectly Competitive Firm Respond to Changes in Market Prices?
raises cost and revenues; MR line shifts up
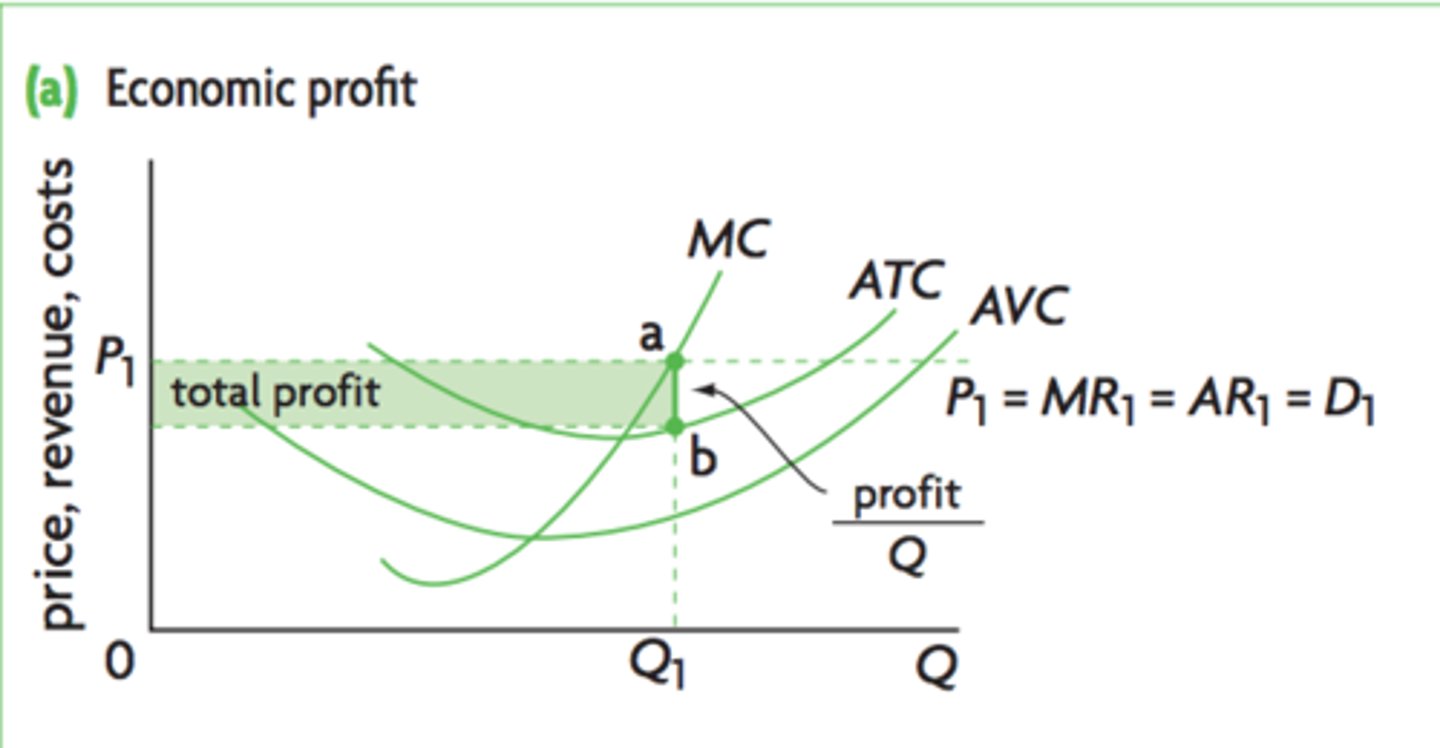
Determining Short-Run Economic Profits for a Perfectly Competitive Firm
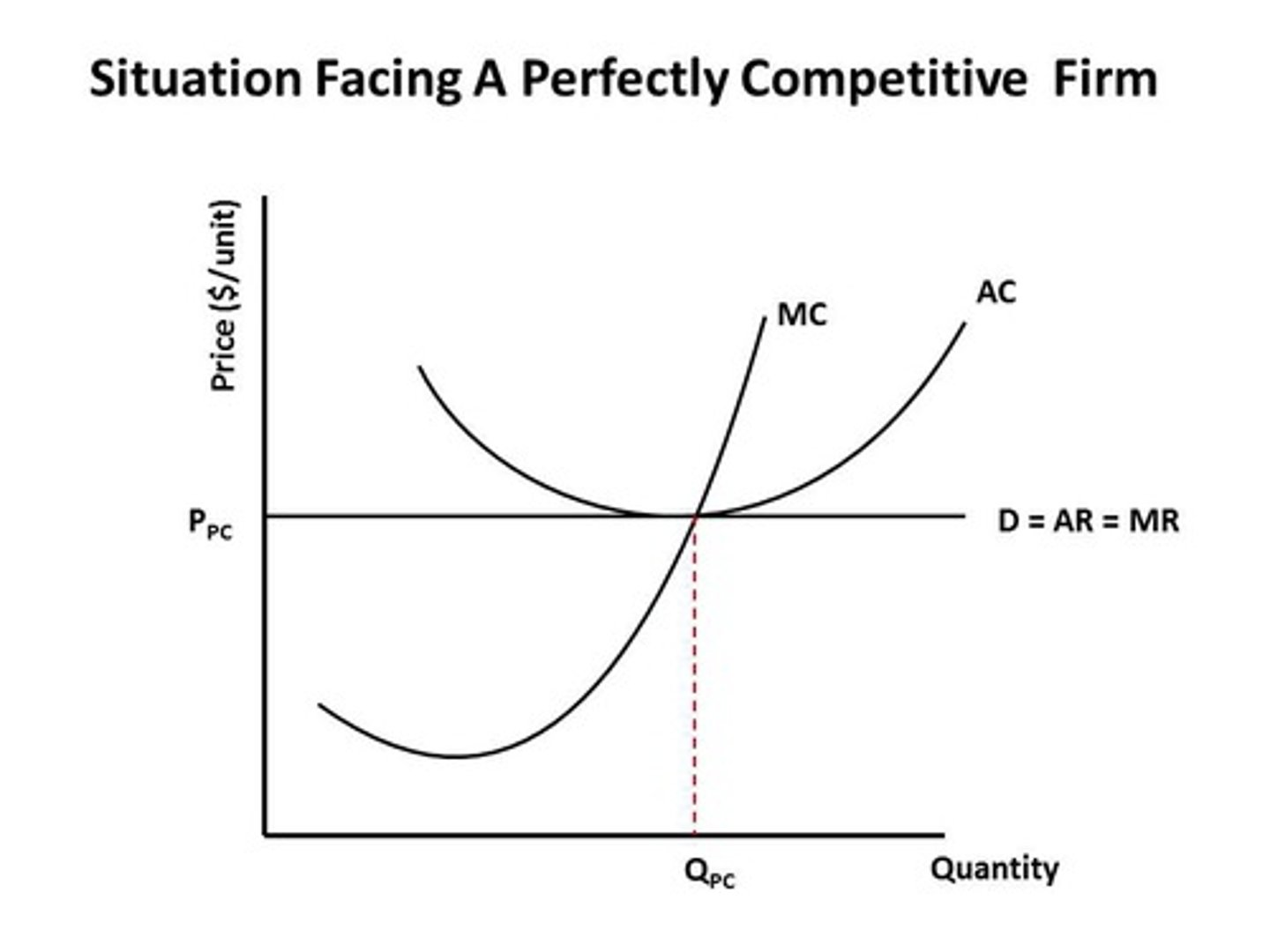
Determining Normal Profits for a Perfectly Competitive Firm
In a perfectly competitive industry, firms seek to maximize
total profit
Determining When a Perfectly Competitive Firm Will Shut Down or Operate at a Loss in the Short Run
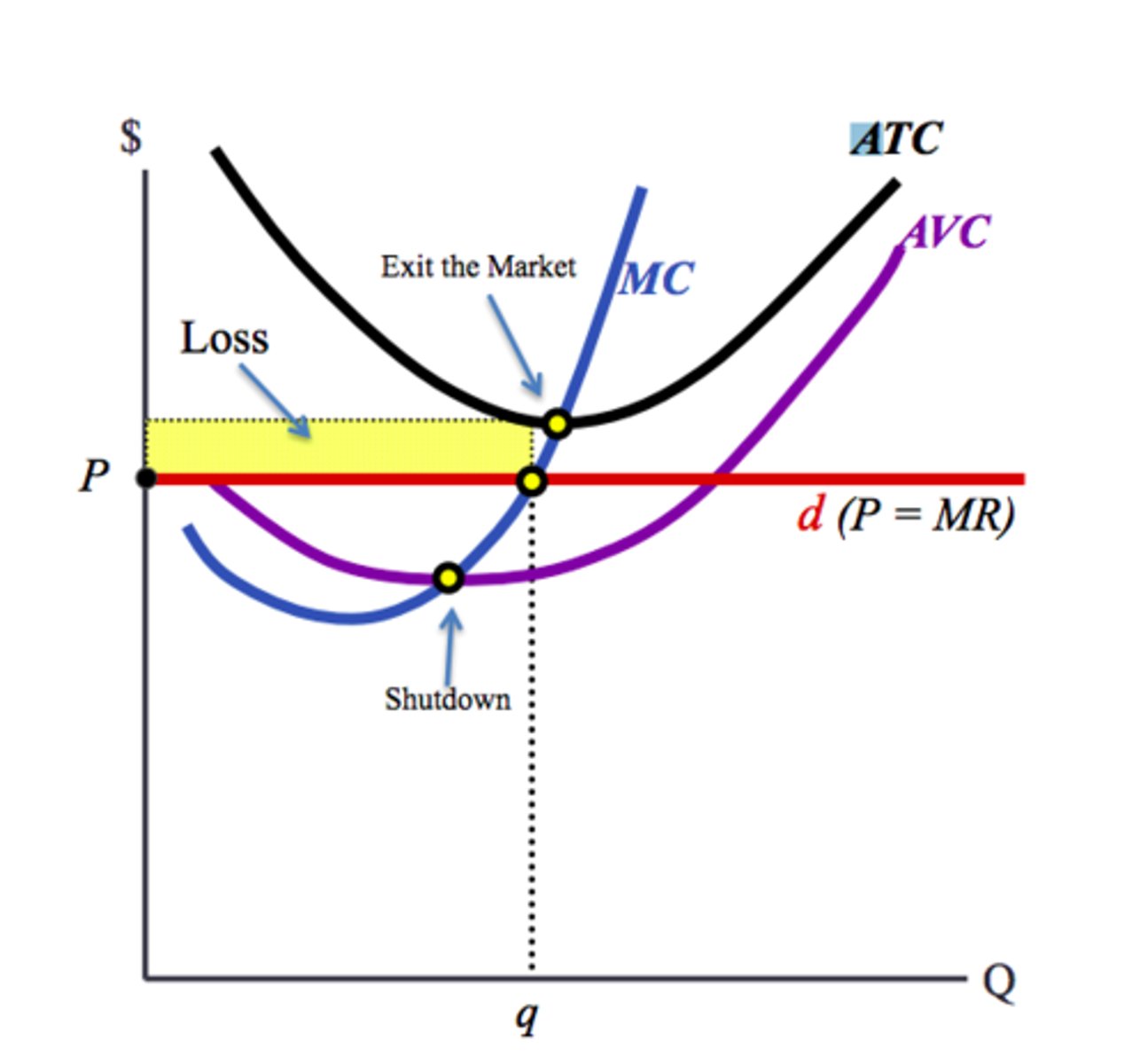
Shutdown Point
Numerically, this point occurs when
marginal revenue equals marginal cost at the minimum average
variable cost. Graphically, this point occurs where the price, or
marginal revenue curve, intersects the marginal cost curve at the
minimum point of the average variable cost curve (AVC)
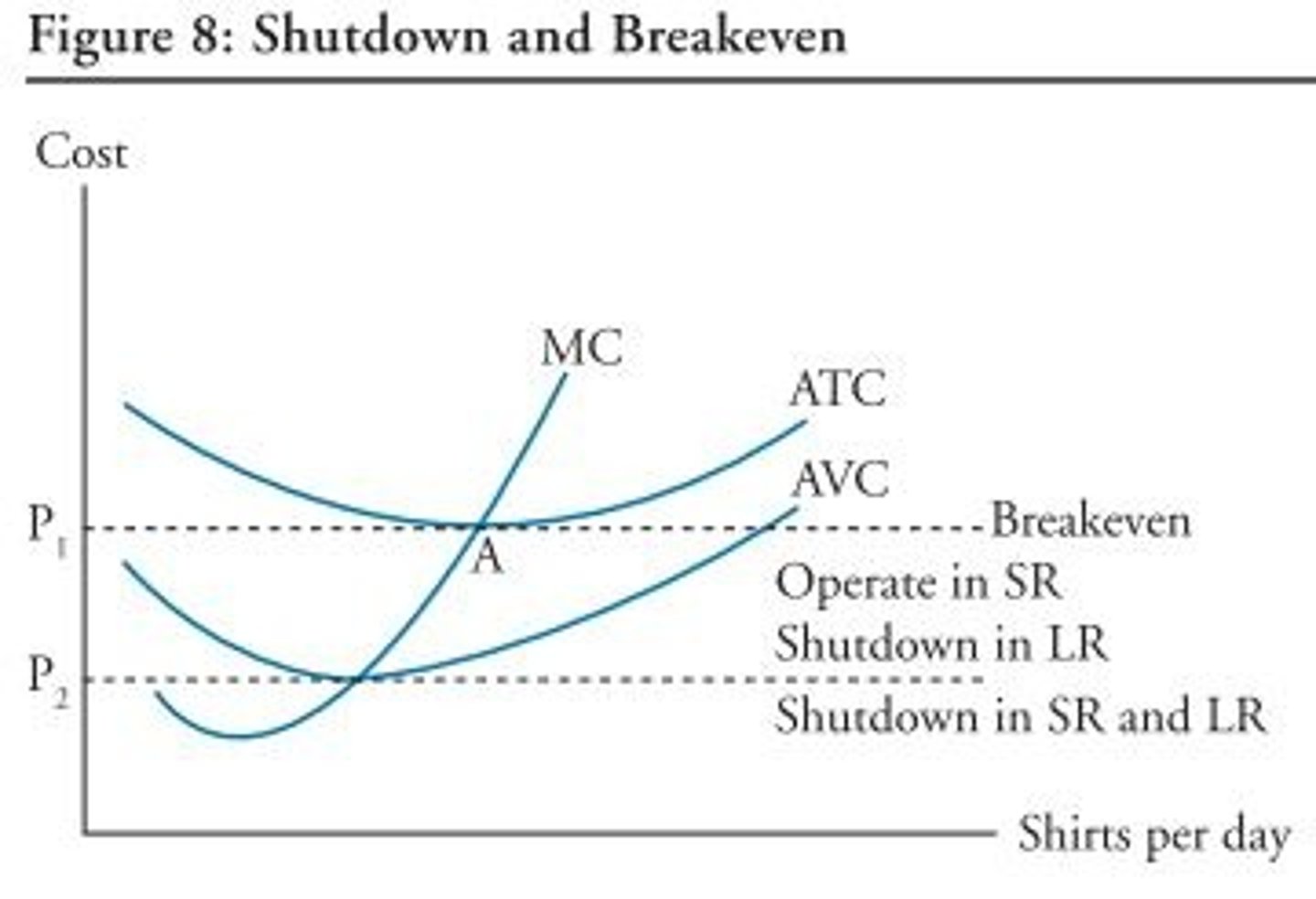
In the short run, if ATC is greater than price at the output level
where MC = MR then
A) new firms may be incentivized to enter the industry.
B) the firm may be able to minimize losses.
C) the firm will shut down.
D) the firm will realize an economic profit
B) the firm may be able to minimize losses.
Assume the Unico Corporation is producing 40 units of output
and selling the output in a perfectly competitive market for $5 per
unit. Its total fixed costs are $110, and its average variable cost is
$4 for each of the 40 units of output. Unico
A) earns a profit of $40.
B) maximizes its profits.
C) earns a loss of $70.
D) should shut down
earns a loss of $70.
Determining the Shape of a Perfectly Competitive
Firm's Short-Run Supply Curve
connect dots at these points where they intersect with marginal revenue lines
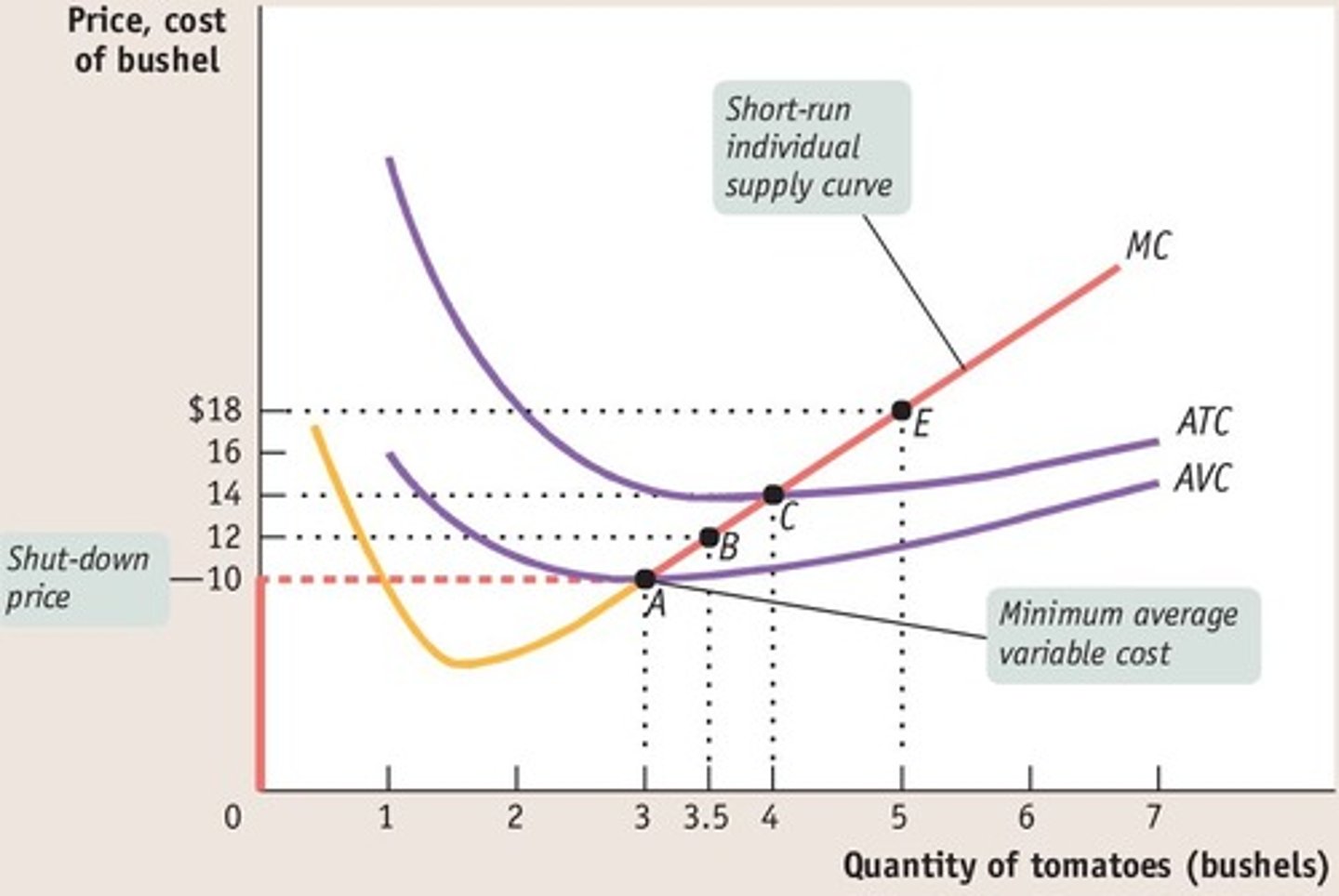
A perfectly competitive firm's short-run supply curve is at its
lowest point when MC equals the minimum point of
A) the average fixed cost curve.
B) the marginal revenue curve.
C) the average total cost curve.
D) the average variable cost curve
D) the average variable cost curve
in the long run, if ATC equals price at the output level where MC =
MR then
A) new firms may be incentivized to enter the industry.
B) the firm will shut down.
C) the firm will earn a normal profit.
D) the firm may be able to minimize losses
D) the firm may be able to minimize losses
In the long run, perfectly competitive firms achieve
A) allocative and productive efficiency.
B) allocative efficiency, but not productive efficiency.
C) productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency.
D) neither allocative nor productive efficiency
A) allocative and productive efficiency.
Which of the following statements describes what perfectly
competitive firms experience in the long run?
A) Price equals ATC.
B) Price equals the minimum point on AVC.
C) Price equals the minimum point on ATC.
D) Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
C) Price equals the minimum point on ATC.
Constant-Cost Industry
An industry in which the firms' cost structures do not
vary with changes in production
Which of the following statements describes a perfectly
competitive market under conditions of constant cost?
A) The market supply curve becomes perfectly elastic in the
long run.
B) The market rarely experiences changes in the price and
quantity sold in the short run.
C) If 50 units can be produced for $150, then 150 units can
be produced for $350 and 200 units for $450.
D) The market rarely experiences changes in supply in
response to changes in demand.
A) The market supply curve becomes perfectly elastic in the
long run.