TOPIC 2 - Resistance and Ohm's law (basic knowledge)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Definition of resistance
Resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for charge to flow through a wire or component.
Measuring resistance
- Resistance has the symbol R
- The unit for resistance is Ohm's
- It has the unit symbol _

Recall the definition of current
Current is the rate of flow of charge.
Resistance is the...
opposition to the flow of current.
If a component has a high resistance...
it is harder for electrons to get through that component.
Therefore, if the resistance of a component is relatively high...
the current running through it (and anything in series with it) will be relatively low.
Recall the definition of voltage
Voltage is the amount of energy per coulomb of charge.
When each coulomb of charge passes through a component that has relatively high resistance, it transfers...
MORE energy to the component.
Therefore, if the RESISTANCE of a component is high...
- The energy transferred to it will be high
- The voltage across the component will be high
For any given component in a series or parallel circuit: As resistance goes up...
current goes down
- Current is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to resistance
For any given component in a series or parallel circuit: As resistance goes up...
voltage goes up
- Voltage is PROPORTIONAL to resistance
Describe the components that obey Ohm's law
- The temperature of some components DOES NOT increase when current increases.
- For these components, the resistance is FIXED (CONSTANT) for any value of voltage and current.
- They obey Ohm's law.
Explain why resistance increases when current increases
- Conductors consist of fixed positive ions and a sea of delocalized electrons.
- When the conductor is in a circuit, the electrons flow from the - end to the + end of the battery.
- If the conductor gets hotter as current increases, the fixed ions vibrate more.
- There are more collisions between the flowing electrons and ions.
- Therefore, the electrons find it harder to flow, and RESISTANCE INCREASES.
Resistors in series
The total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances.
(R = R1 + R2 + R3)
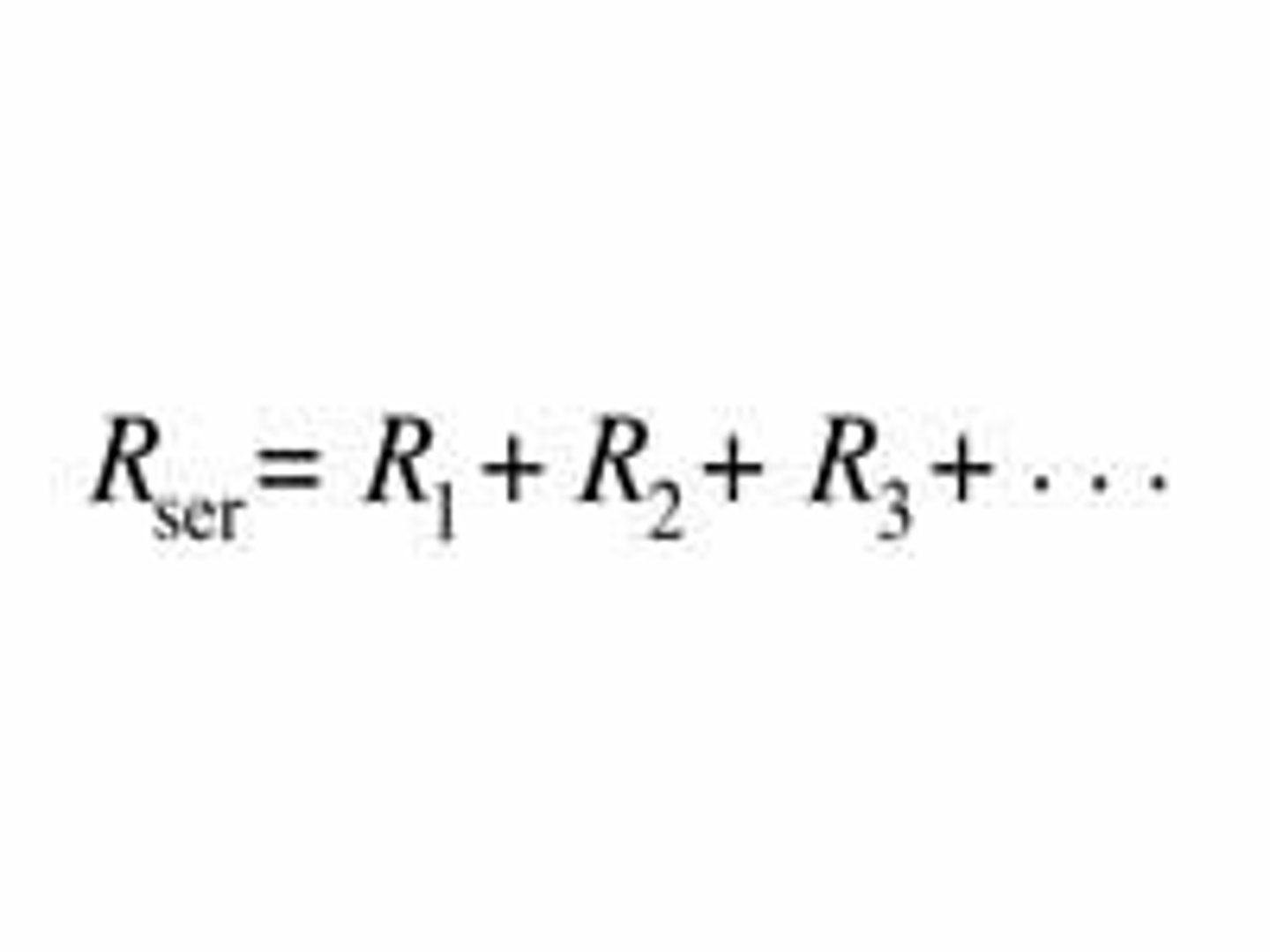
Resistors in parallel
The total resistance is less than that of the smallest resistor.
- The more resistors you add in parallel, the smaller the total resistance becomes.
- This is because you are adding more branches for the charge to flow through.
Fixed resistors
Fixed resistors have a resistance that remains constant.
Variable resistors
- Variable resistors can change the resistance by changing the length of wire that makes up the circuit:
- A longer wire = more resistance