BIOL 2044 - GI Infections
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
biofilms
80% of infections caused by biofilms
cant study an organism in isolation - must be studied in the community they live in
found in
implants
mouth
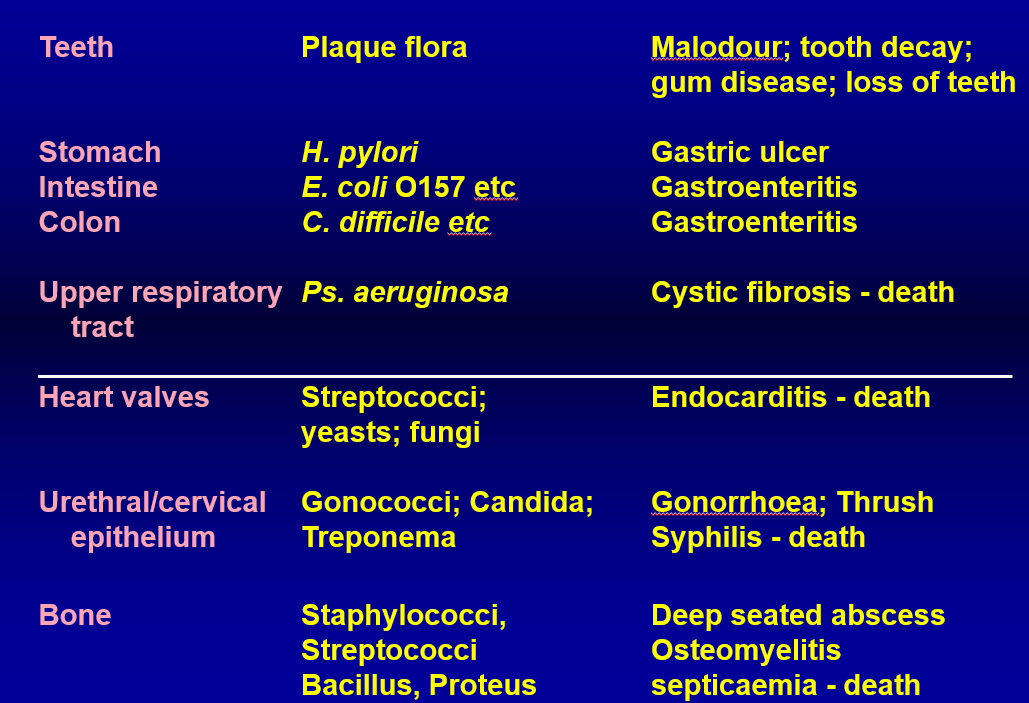
associated complications with biofilms
ASSOCIATED MEDICAL PROBLEMS
dental plaque
leads to odour, tooth decay, gum disease
stomach intestine colon infection
can cause gastroentiritis —> E. coli, C. diff, H. pylori
upper respiratory infections
can cause cystic fibrosis —> P. auruginosa
biofilms on heart valves
can cause endocarditis —> strep
urethra/cervical infections
can cause gonhhorea, cyphilis —> gonococci, candida
bone diseases
can cause deep seated abscess —> caused by staph, streptococci, bascillus
oral cavity
succeptible to
bacteria
fungi
mycoplasma
protozoa
viruses
normal, healthy bacteria
streptococci
lactobacilli
staphylococci
corynebacteria
anaerobes
dental plaque forming on the gum margin can lead to
dental caries
gingivitis
peridontitis
host interaction with microbe
equilibrium between endogenous bacteria and oral defence system
PHYSICAL BARRIER
keritanised epithelium
mucin production
salivary flow
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS
salivary enzymes
antibacterials
gingival fluid secretions
INFLAMMATORY REACTION
bacteria produce a range of molecules sensed by other bacteria which helps to recognise commensal bacteria from pathogens
acquisition of oral flora
at birth: sterile
within hours: streptococcus, S. salivarius —> acquisition of oral flora depends on time of birth, pre/post partum, caesarian, vaginal, who handles the baby
by one year old:
streptococcus
lactobactilli
neisseria
staphylococci
fusobacterium
actinomyces
when teeth first appear, initial colonisation is by streptococci, Mutans, streptococci Sanguis on the teeth and in gingiva
other streptococci adhere strongly to gums and cheeks but not the teeth
colonisation of crevaces of the teeth tend to be prevotella (an anaerobe)
a loss of microflora as teeth are lost —> 2nd childhood microflora
organisms acquired reflect the surfaces to which they can adhere (dramatic shift between enammel and dentures)
bacteria in oral cavity
10^8 bacteria a shed
>300 species from dental plaque, 5% of salivary flora
1mg of plaque contains 10^6 flora
flora of healthy gingiva is mostly fulcatative anaerobic bacteria and aerobic bacteria
>40% of oral cavity is unculturable
dental caries
due to a high sugar diet and poor hygeine
holes in teeth, malodour
plaque
formed by long filamentous structure surrounded by bacteria (bacterionema maturococci and strep sanguis) —> gives corn cob shape
strep sanguis forms lactic acid and the maturococci converts lactic acid —> butyric acid
interact with eachother
plaque forming bacteria
STREPTOCOCCUS
sacrolytic —> metabolise sucrose and other sugars
glucosyl transferases —> cleaves sucrose into either soluble glucans or insoluble mutans
fructosyl tranferases —> adds a fructose to a growing fructan or makes inulin (insoluble) —> broken down into glucose
acidogenic bacteria ferment glucose into lactic acid, formic acids which lower pH
aciduric bacteria grow at low pH —> plaque adjacent to ennamel has low pH (4) which decalcifies hydroxyapatite enamel
OTHER SPECIES IN PLAQUE:
VEILLONELLA
gram -ve anaerobe
thrives in acidic environment of caries and is thought to slow development of caries
converts lactic acid of other species to less acidic products
LACTOBACILLUS
gram +ve
grows aerobic and anaerobically
found symbiotic in gut but in the mouth is a sign of development of caries
peridontal disease
can either be non destructive gingivitis or can be destructive peridontitis
non destructive gingivits
poor hygeine
inflammed and bleeding gums
destructive peridontitis
usually get as older unless very poor dental hygeine
gum and bone loss
gingivitis
FUSOSPRIOCHETES
spirochetes and fusiform bacteria live in normal flora and in mouth
in case of bleeding oral cavity bacteria can cause infection which leads to oral cavity
diseases include:
acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivits referred to as trench mouth
caused by prevotella fusobacterium, traponella borella
peridontitis
TERONEMA DENTICOLA
spiral shape bacterium
gram -ve
elevated in people with disease
motile, highly proteolytic
contributes to destruction of tissue
PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS
gram -ve anaerobic bacteria
found particularly in chronic forms
AGGREGATIBACTER ACTINOMYCETEMOMITANS (AA)
gram -ve
facultative rod
aggressive preidontitis in young patients
produces leukotoxins which kills PMNs and monocytes, cytoskeletal distending toxin, immunosuppression factors that inhibit blastogenesis
antibody production and active supressor cells
anaerobic metabolism: protein degradation and ammonia (provokes immune response and contributes to tissue destruction)
measuring species interaction
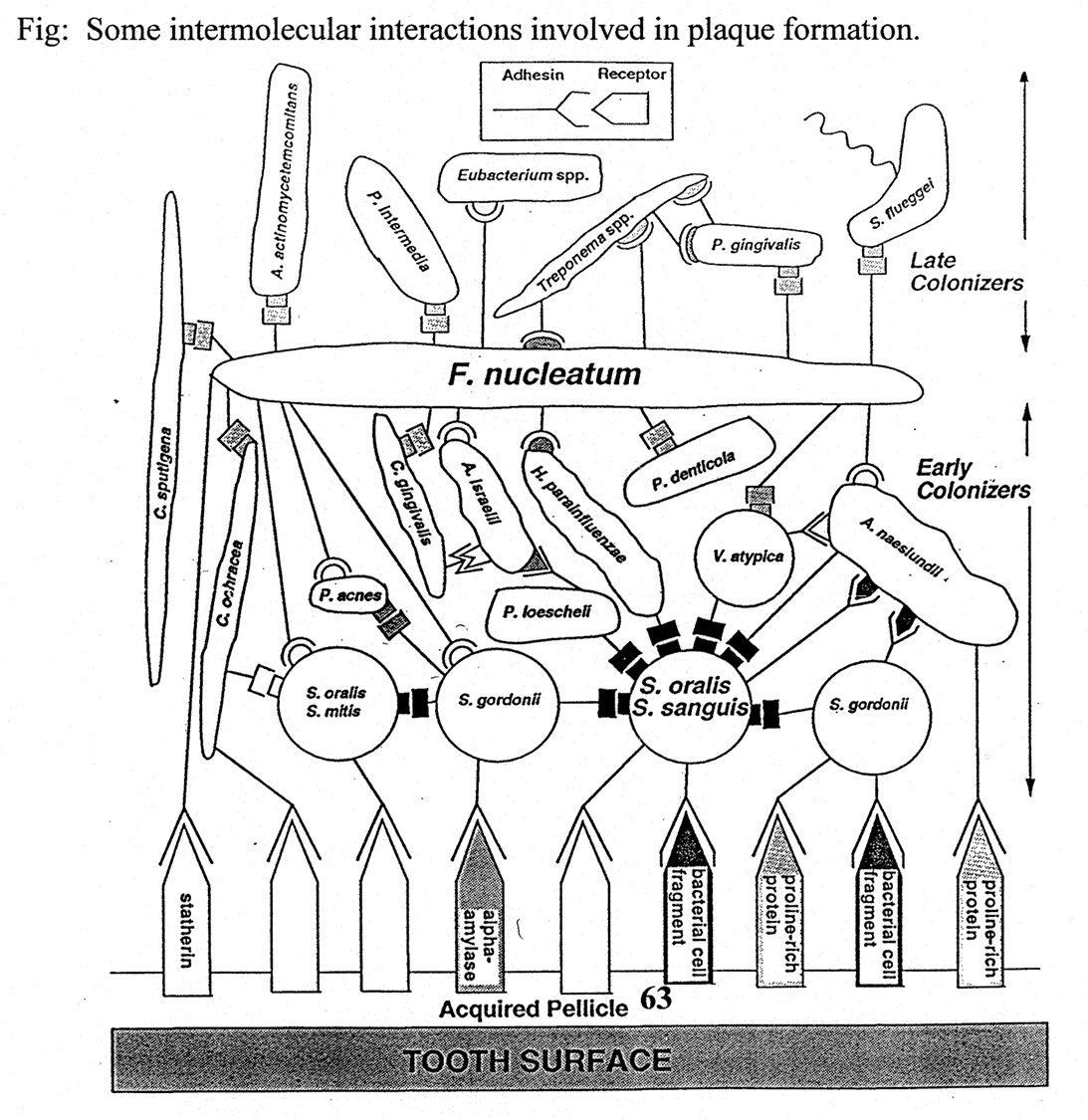
can culture bacteria together and see if they form coaggregates
primary species - bind to salivary proteins (the acquired pellicle)
the secondary bacteria bind to pioneer species (vionella) but cant bind acquired pellicle
tertiary colonisers cant bind to acquired pellicle or pioneer species
cell cell communication
cell cell signalling molecules used for quorum sensing
intra species communication —> gram negative bacteria produce small peptides which help promote stimulating peptodes which help promote single species biofilm formation
inter species: 4,5 dihydroxy 2,3 pentadione also called autoinducer 2
stimulate plaque formation and virulence determination
anti pathogen strategy
can control but not eliminate biofilm
attempts to kill coloniser species such as fusobacterium
human microbiome project attemot to sequence genome of the microbiome rather than culturing
microbial colonisation
helicobacter pyori: can get inti stomach and penetrate mucous lining —> protected from immune system and decreases competition with other cells
produces urease which neutralises acid
causes stomach ulcer and can also cause cancer
produces vaculating cytotoxin A which kills cells in lining of teh stomach and allow bacteria better access to nutrients
kills the cells that they invade and creates holes in the stomach lining —> forms ulcers
TLPA ad TlpD genes are acid sensors and causes bacteria to swim away from acid (mucin layer has a gradiet pH)
urease bacteria convert H2O and (NH2)2CO —> HCO3- + NH4+
NH4+ helps to neutralise acid and facilitate survival
intestinal flora
contain lots of microbial cells
100x as many microbial genes as host
colon bacteria = 60% of dry mass of feaces
bacteria in colon form biofilm like layers and high cell density which promotes quorum sensing
many bacteria are anaerobic but aerobes in calcum close to anus
early gut microflora
colonise with large no of E. coli and streptococcus
within days create environment favourable for bfidobacterium, bacteriocides, clostridium, rhuminococcus
breast fed babies become dominated by bfidobacterium which is beneficial to development of babies
mature gut species
bacterodietes —> 1/3 of all bacteria
clostridium, fusobacterium
rheuminococcus
bfidobacterim —> beneficial all throughout life
people have tried to generalise communities to 3 types
T1: high bacteroides
T2: prevotella common and low bacteroides
T3: high levels fo rheuminococcus
commesnal coexistance
organisms use fermented unused energy substrates
microboime health dysbiosis relationship
different axes can lead to different conditions
continual effect on gut/immune system between pathogens and commensal bacteria
3 main innumosensory cells:
m cells
dendritic cells
surface enterocytes
PRRs include:
toll like receptors
nucleoside binding oligomerisation domains/caspase recruitment domain isoforms
cytoplasmic proteins which recognise endogenous proteins/stress response from community
leads to activation of NFKb signalling molecules if we enter dysbiosis
PSA: polysaccharide
key olecule
capsular polysaccharide which resembles hairs on a kiwi fruit
2 of 8 polysaccharides have zwitterionic structure essential for modulating the immune system
PSA restores CD4 t cell levels
mutant bacteria lacking PSA doesnt restore t cells and generates inflammatory response
inbalance of TH1 cells which moves to TH2 cells
leads to inbalance between B and T cells
production of IL4 and IFN gamma which causes imbalance, PSA helps restore this
IL17 potent inflammatory cytokine associated with autimmunity
adding B fragilis bacterai you can dampen the immune response 8
gut flora repress pathogens
gut floar can prevent harmful effects from competitive exclusion
overgrowth of C. diff can cause pseudoembranous colitis but can be prevented by exclusion of bacteria
can be done by fecal transplant