Atomic Theory
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Greek Model
Idea of atom. Democritus - atomos - indivisible
Alchemy
Practiced in Europe, Africa, Asia
beliefs: transmutation of cheaper metals to gold
John Dalton’s Atomic Theory (Billiard Balls Theory)
Theory stated that elements consisted of tiny, indivisible particles called “Atoms”
Elements are pure substances w particular mass, size, and chem behaviour
atoms of diff elements have diff properties
compounds consist of atoms of different elements combined together
in chem reactions, atoms are combined separated or rearranged
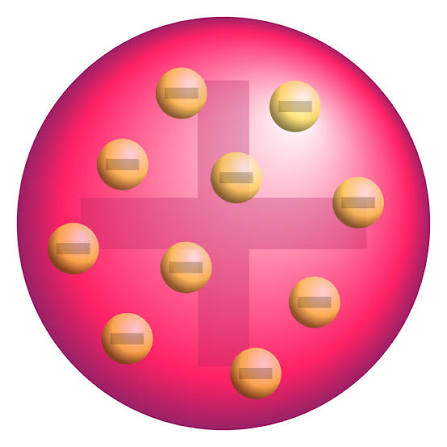
J.J Thomson’s Theory (Plum Pudding Model)
Theory stated that an the dough (the atom) is positive while the plums (the electrons) are scattered throughout the atom.
Rutherford
Discovered the nucleus by firing positively charged particles at a very thin sample of gold foil, disproving Thomson’s theory
Chadwick
Discovered the neutron by bombarding beryllium with alpha particles. Carbon atoms were formed, neutrons emitted
Bohr
Discovered that electrons move around the nucleus. And each orbit (energy lvl) represents a different amount of energy 4 electrons in the orbit
2 in first orbit
8 in 2nd (Hence octet rule)
orbits closer to nucleus are lower in energy
Electrons can move from one orbit to another by absorbing or emitting energy, giving rise to specific spectra