Explanantions and types of conformity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is social influence?
looks at human behaviour as influenced by other people and the social context in which this occurs.
What are examples of social influence?
conformity, obedience and minority influence.
What is conformity?
a type of social influence involving a change in belief or behaviour in order to be in line with a group.
it is also known as majority influence (or group pressure)
What are the two explanations of conformity?
The dual process model explains conformity
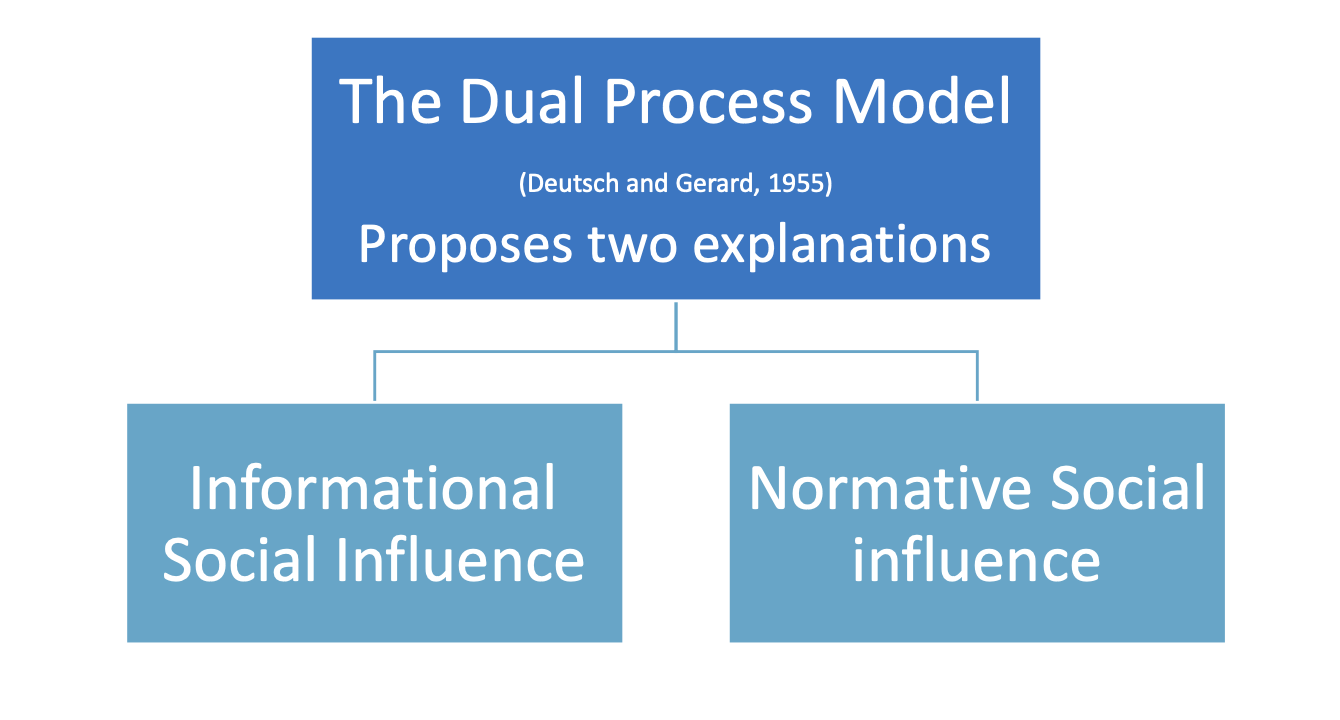
What is informational social influence (ISI)?
when an individual is unsure about something, they may seek the opinions of others: especially if they believe they are in a better position to form an opinion
more likely to happen in an unfamiliar situation or an ambiguous situation so we look to others for guidance
if conformity due top ISI, it is likely that the individual will believe the opinions they adopt, they will be converted to that way of thinking
(conforming to be right)
What is normative social influence (NSI)?
the desire to be liked
the motivation is to be accepted by others and to be liked and respected by them and not rejected
this does not mean the individual will agree with the group and any conformity will be dependent on the groups presence
(conforming to be liked)
What are the three types of conformity?
Compliance, identification and internalisation
What is compliance?
An individual goes along with group to gain approval, this leads to a change in their public behaviour but not their private beliefs so results in a short term change.
(normative SI)
What is identification?
Has elements of both compliance and internalisation as the individual accepts the attitudes and behaviours they are adopting as true but the purpose of doing so is to be accepted as a members of the group
(Informational and normative SI)
What is internalisation?
An individual changes their public behaviour and their private beliefs. They have actually accepted the group’s point of view or beliefs. This type of conformity therefore results in a long-term change.
(informational SI)
What is the level of processing of the types of conformities?

Evaluation of explanations of conformity: Evidence to support NSI
Research supports the concept of NSI, suggesting people shape their behaviour out of a desire to fit in with their reference group (free will / environmental determinism)
Asch found that participants said they conformed because they felt self-conscious and were afraid of disapproval.
Evaluation of explanations of conformity: Evidence to support ISI
Research supports the concept of ISI as exposure to other people’s beliefs and opinions can shape many aspects of social behaviour (nurture)
Jenness (1932) asked 101 Psychology students to individually estimate the number of white beans in a jar. They were then split into groups of 3, asked to discuss and give a group estimate. Finally they were asked for an individual estimate again. It was concluded that because of the ambiguous nature of the task, participants were likely to change their estimate due to ISI.
Evaluation of explanations of conformity: negative
It is difficult to distinguish between compliance and internalisation as it is difficult to know when each is actually taking place.
NSI and ISI can operate together
NSI may not be detected as easily.
Evaluation of explanations of conformity: issue/ debate
Conformity is a nomothetic concept (general law that applies to everyone)
However, the theory does not account for individual differences. For example, nAffiliators are individuals who are more concerned with being liked by others and have a strong need for social connection. These type of people are more likely to conform