chapter 3
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what is NIC
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware component required for a computer to connect to a network, allowing it to send and receive data.
T or F: NIC is only wired
FALSE!
what is Network Hardware
selection of essential components that enable the connectivity and communication of devices within computer networks.
what is function of CPU
executes instructions
consists of ALU, CU, registers (all cats roar)
What is the role of the ALU?
Performs arithmetic and logical operations.
What is the function of the control unit?
Manages execution of instructions.
Coordinates between hardware and memory.
What is a register in the CPU?
Small, fast storage locations.
Temporarily hold data and instructions.
Describe the fetch-decode-execute cycle.
Fetch: Retrieve instruction from memory.
Decode: Interpret the instruction.
Execute: Perform the instruction.
What is cache memory?
Located within the CPU.
Stores frequently accessed instructions and data.
Improves CPU performance by reducing access time.
What is the relationship between cache size and performance?
Larger cache size = better performance.
What are cores in a CPU?
Independent processing units within the CPU.
More cores allow multitasking and parallel processing.
What are the limitations of adding more cores?
Increased communication overhead between cores.
Diminishing returns for some applications.
How does clock speed affect CPU performance?
Higher clock speed = faster execution of instructions.
Overclocking can increase performance but risks overheating and instability.
What is RAM?
Volatile memory used for temporary data storage.
Faster than secondary storage.
What is ROM?
Non-volatile memory used for permanent storage.
Stores firmware and boot instructions.
HDD compared to SSD
slower
prone to damage
cheaper
high power consumption
SSD compared to HDD
faster
durable
expensive
low power consumption
A component in the CPU sends signals to manage the fetch-decode-execute cycle. State the name of this component
control unit
characteristics of IP address
Unique identifier
Can be static or dynamic
Network allocated IP addresses
what is Dynamic IP address
The address changes when a computer connects to a network
it may change everytime the computer connects to the network or once every few times
it can be used to uniquely identify a device (on a network)
Describe how the sensor and the microprocessor are used to automatically refill the water bowl
Sensor continually send digitised data into microprocessor
microprocessor compares data to stored value(s)
if value is outside the range/matches microprocessor sends signal to release water to refill the water bowl
..bowl is filled by SET AMOUNT / bowl filled for CERTAIN TIME
Actuator used to release water
Whole process repeats until turned off / stopped
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a type of integrated circuit on a single chip.
True or False?
The terms CPU and microprocessor can be used interchangeably.
TRUE
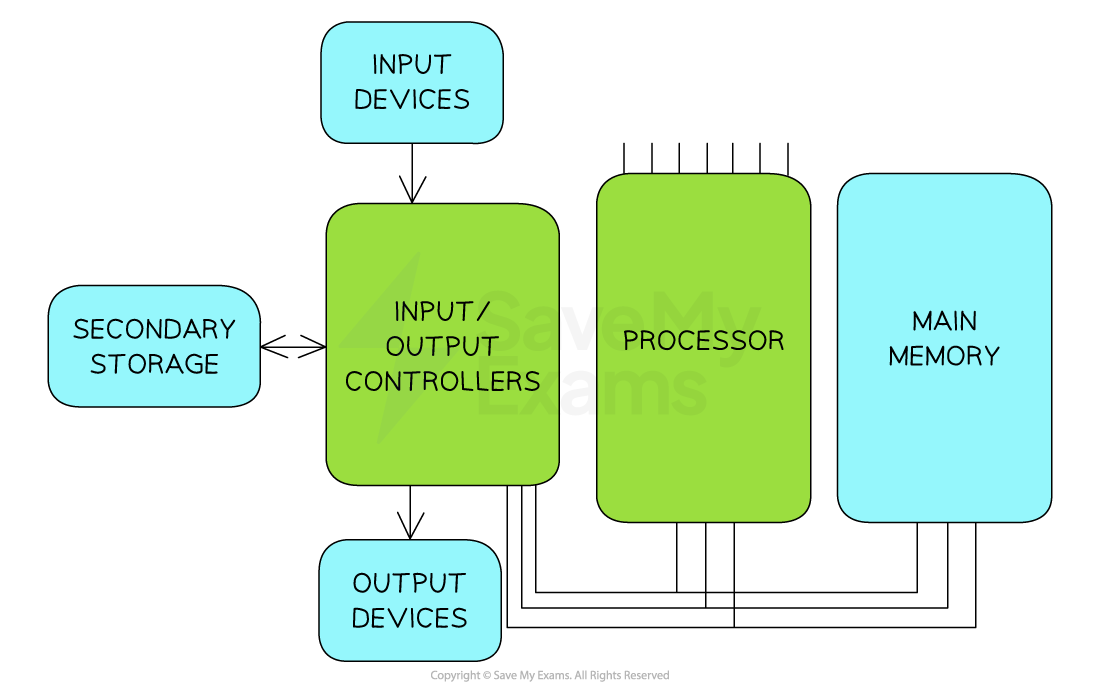
what is Von Neumann Architecture?
a design of the CPU proposed by John Von Neumann in the 1940s, which most general-purpose computers are built upon.
what is role of system clock
generates timing signals on the control bus to synchronize the operations of the CPU and other components.
main role of Processor in CPU
contains ALU and is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
What is the function of the Control Unit (CU) in the CPU?
controls the operation of the memory, processor, and input/output devices by directing the flow of data and instructions within the CPU
function of buses
Carry data through components.
Buses (apple undergo dancing bothways cats bounce daily)
Address bus – unidirectional CPU to memory only
Data Bus – bi-directional CPU to memory and back to CPU
Control Bus – bi-directional Control Unit to other computer components
Immediate Access Store
Stores the instructions that are to be processed, which are fetched by the CPU