Prokaryotic Microbes: Bacteria and Archaea Characteristics and Identification
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the three major categories of bacteria?
Gram-negative with a cell wall, Gram-positive with a cell wall, and those that lack a cell wall (Mycoplasma spp.).
What factors are used in the classification and identification of bacteria?
Morphology, staining, motility, atmospheric requirements, nutrition requirements, metabolic activities, ability to cause infection, and genetic composition.
What are the three basic shapes of bacteria?
Cocci (round), bacilli (rod-shaped), and vibrio or spirilla (curved and spiral-shaped).
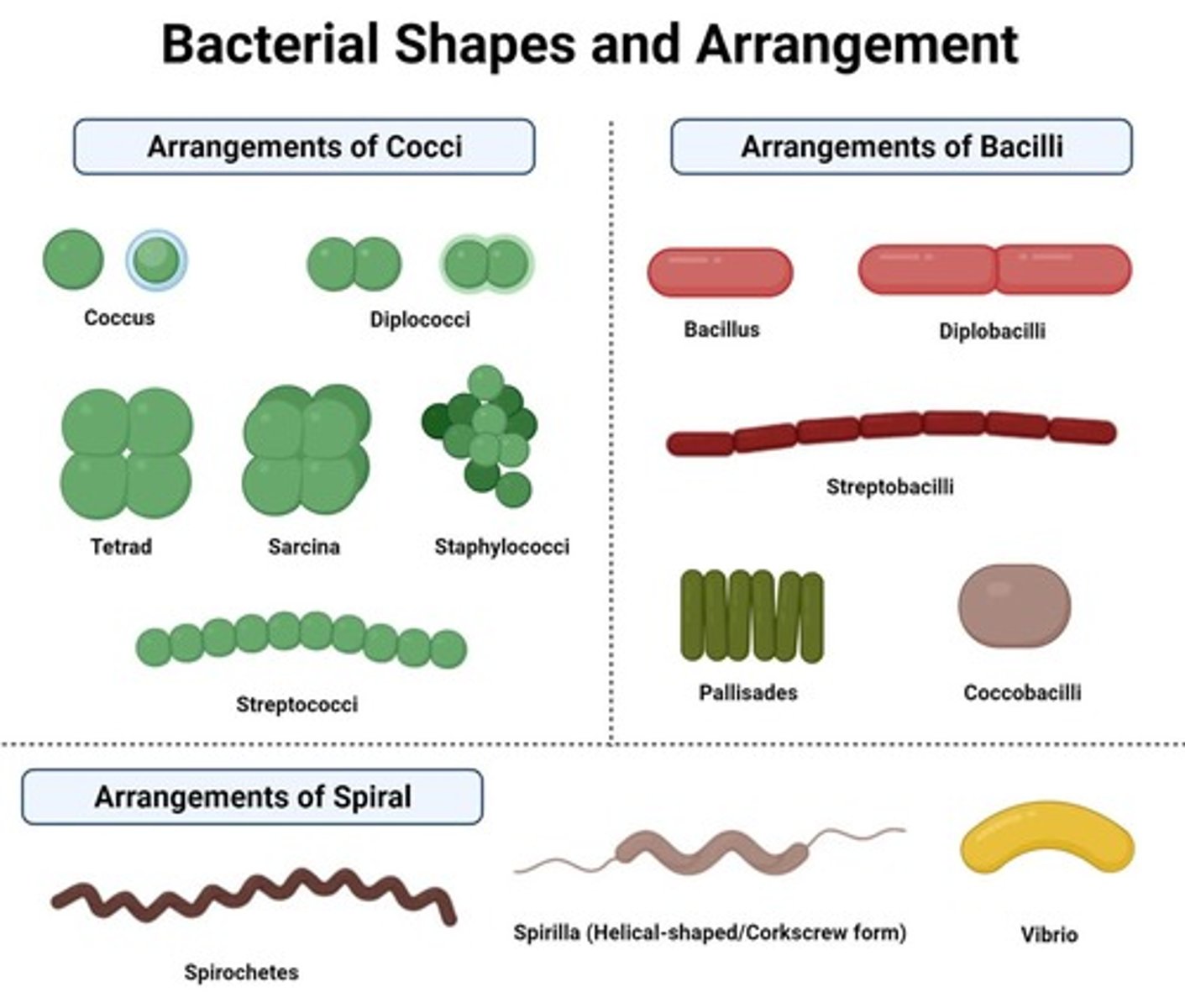
How can bacilli be arranged?
They can be single, paired (diplobacilli), in chains (streptobacilli), or in stacked arrangements (palisades).
What are examples of medically important Gram-positive cocci?
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp.
What is the average size of a bacillus?
1 µm wide and 3 µm long.
Name examples of medically important bacilli.
Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Haemophilus, and Bacillus spp.
What are examples of curved bacteria?
Vibrio spp., Helicobacter spp., and Campylobacter spp.
What are examples of spiral-shaped bacteria?
Borrelia spp. and Treponema spp. (e.g., syphilis).
What does the Gram stain help to differentiate?
It divides bacteria into Gram-positive (stain blue-ish purple) and Gram-negative (stain pink-ish red).
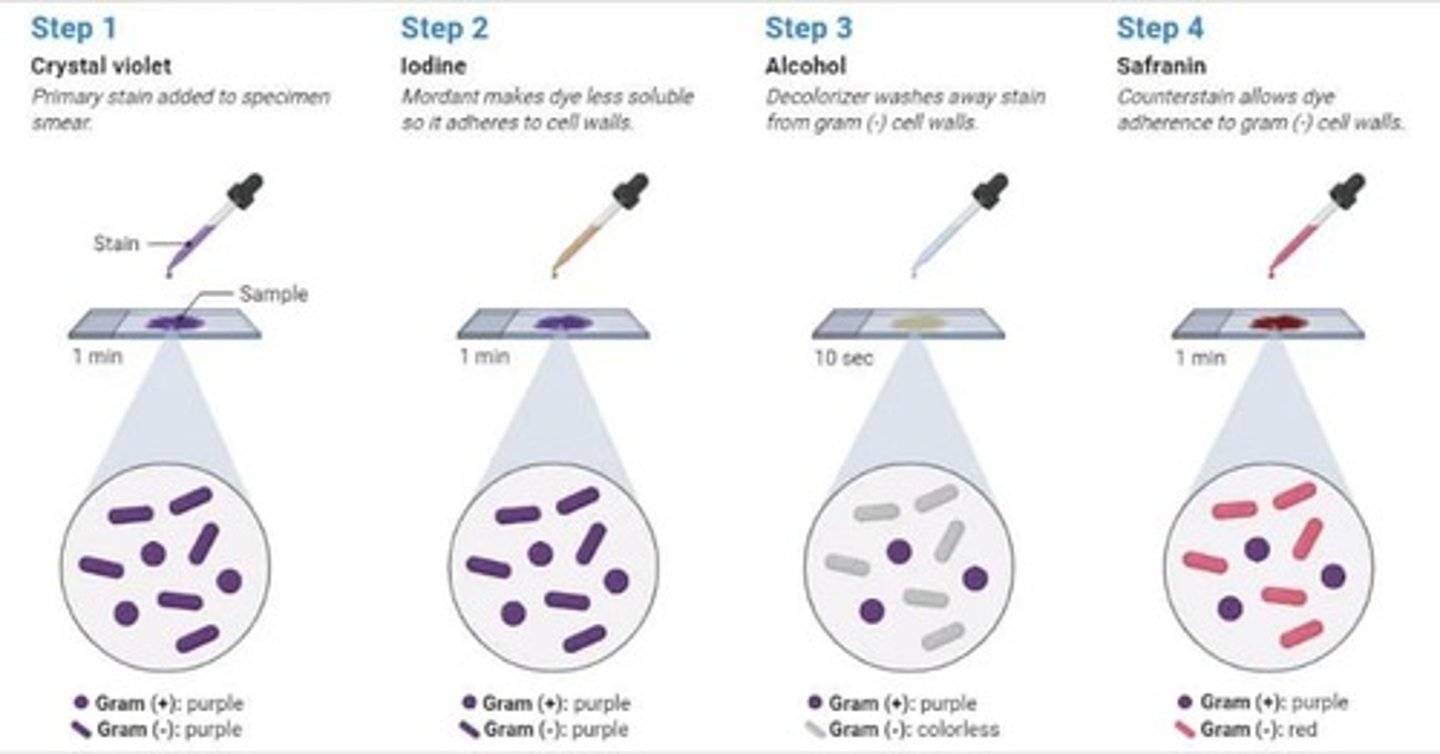
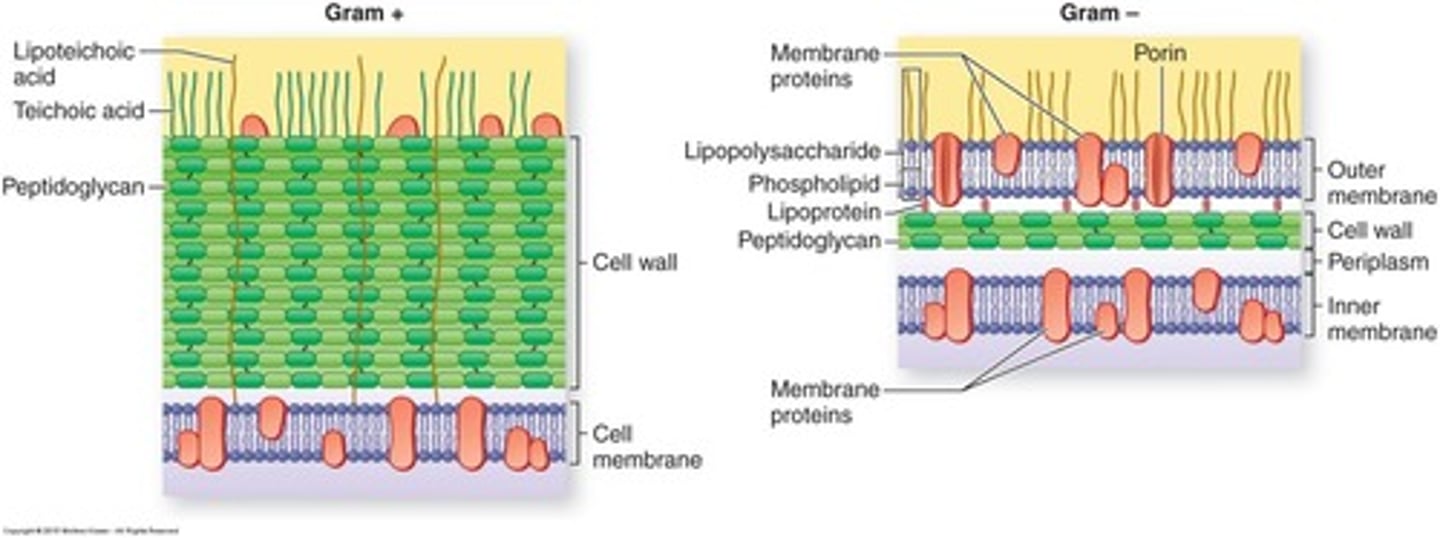
What is the reason for the different staining results in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan that retains the blue stain, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer that allows the blue stain to be washed away.
What are Gram-variable bacteria?
Bacteria that do not consistently stain purple or pink after Gram staining, such as Gardnerella vaginalis.
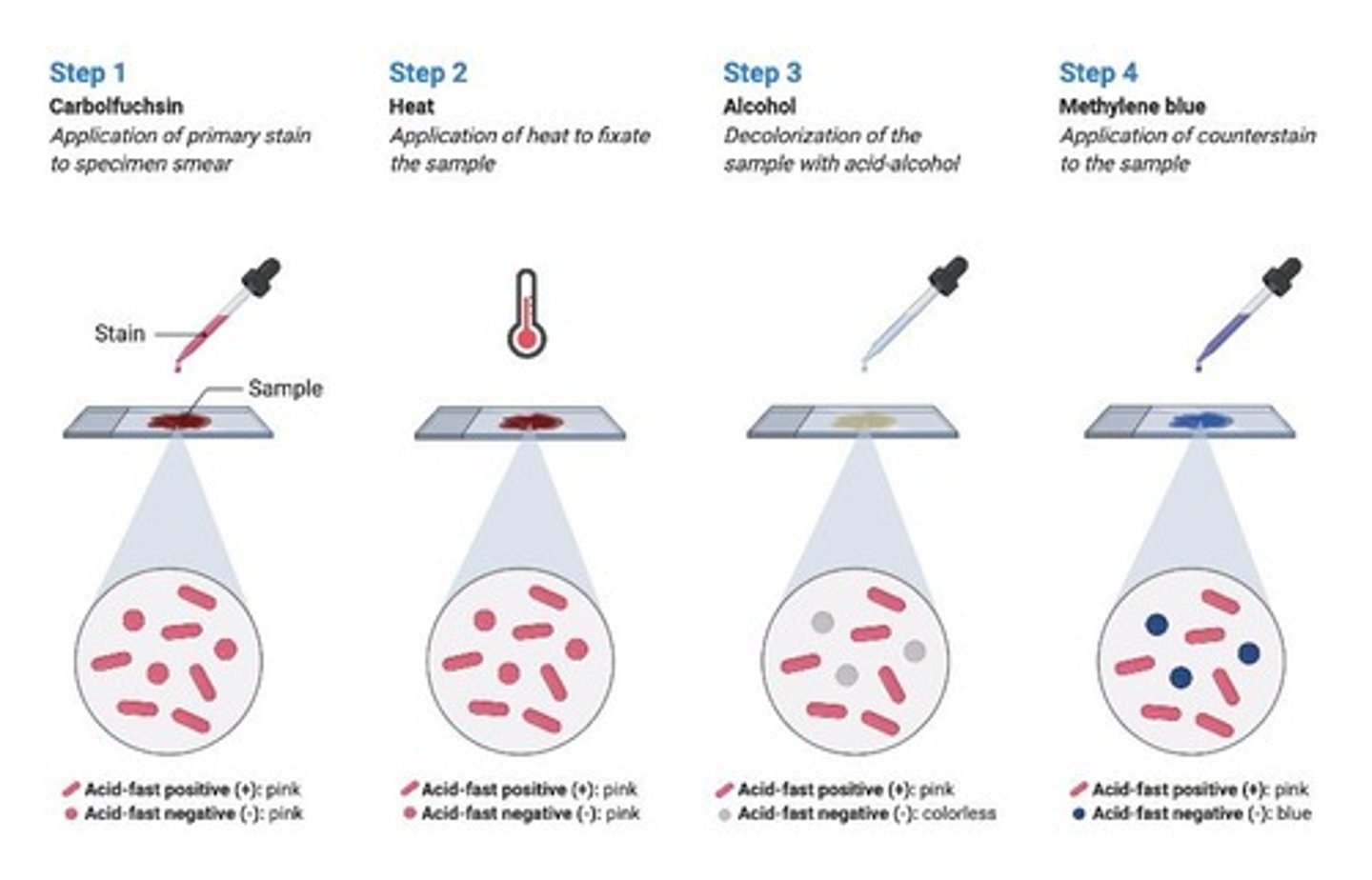
What is the significance of the acid-fast stain?
It is used to identify bacteria like Mycobacterium that do not stain well with the Gram stain due to their cell wall structure.
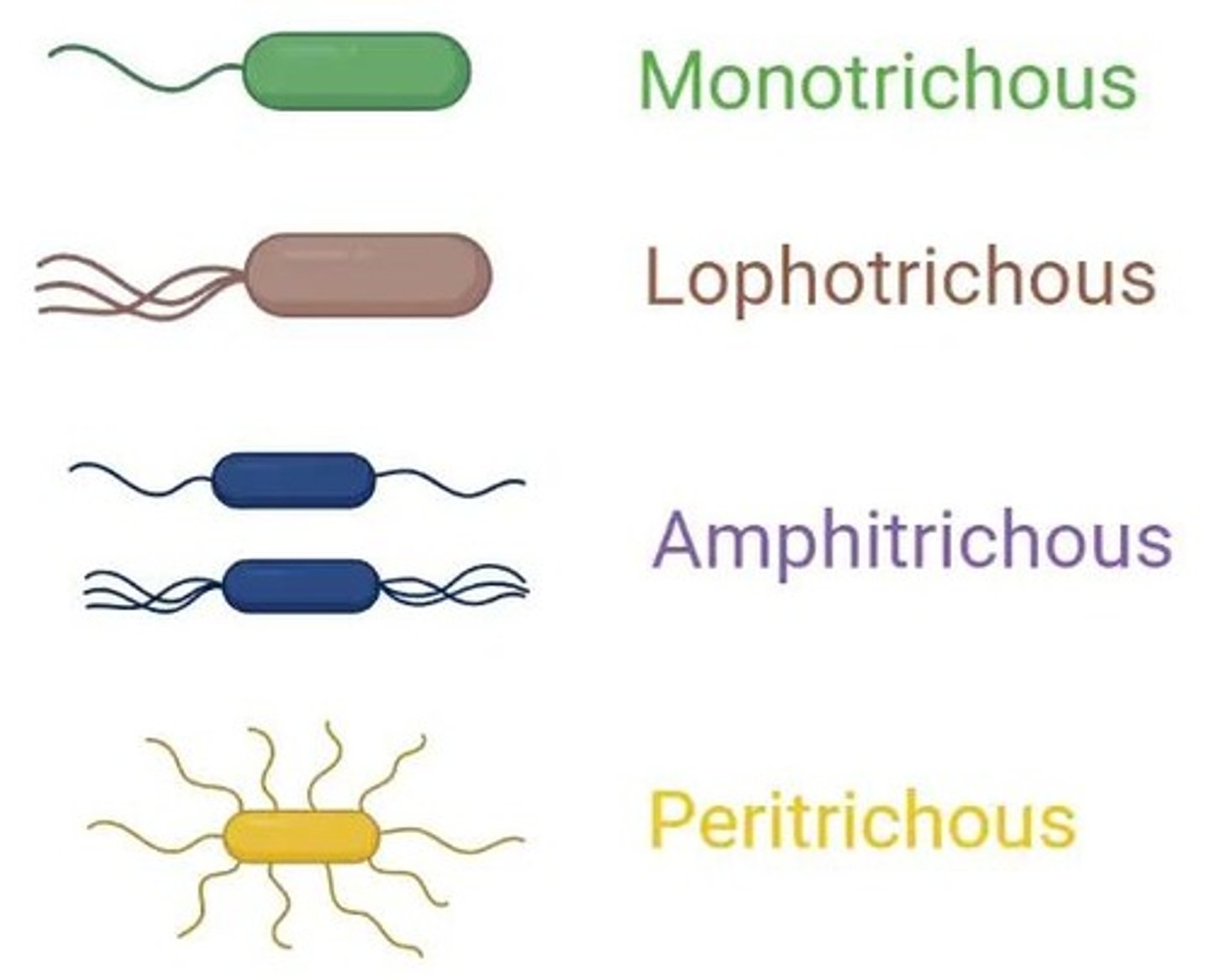
What is a characteristic of motile bacteria?
If a bacterium can swim, it is motile and typically has flagella.
What is colony morphology in bacteria?
The appearance of bacterial colonies on nutrient media, which can vary in size, color, shape, elevation, and edge appearance.
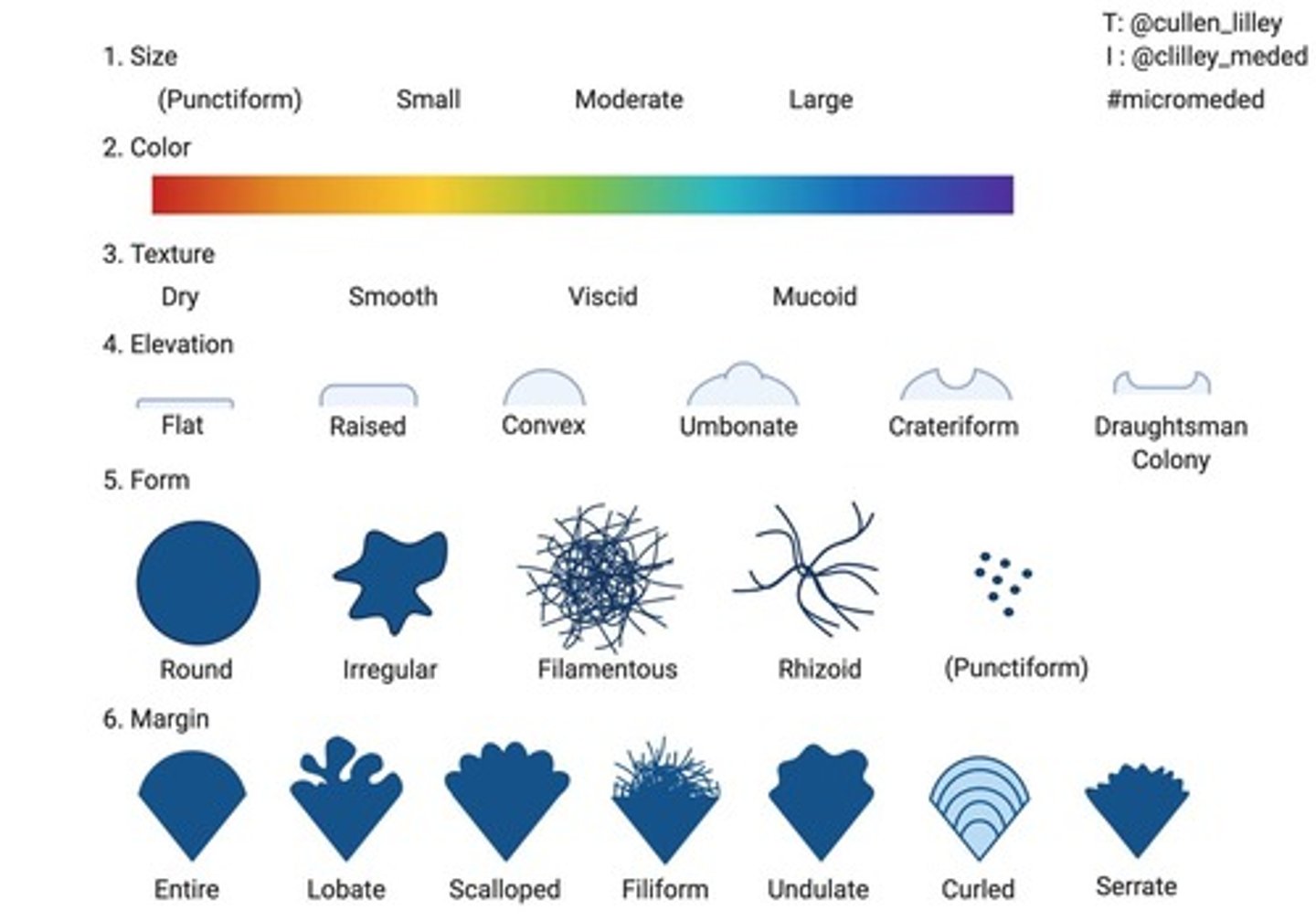
What factors can influence the appearance of bacterial colonies?
Differences in species, size, color, overall shape, elevation, and enzymatic activities.
What determines the size of colonies generated in a certain time?
The organism's generation time.
What is the generation time of E. coli under optimal conditions?
Approximately 20 minutes.
How can bacteria be classified based on their oxygen requirements?
Bacteria can be classified as obligate aerobes, microaerophilic aerobes, facultative anaerobes, aerotolerant anaerobes, and obligate anaerobes.
What is the defining characteristic of obligate aerobes?
They must have oxygen to survive.
What distinguishes microaerophilic aerobes from obligate aerobes?
Microaerophilic aerobes prefer a small amount of oxygen.
What do facultative anaerobes prefer regarding oxygen?
They can grow in the presence of oxygen but prefer to grow without it.
What is the characteristic of obligate anaerobes?
They cannot grow in the presence of oxygen.
What nutritional elements do all bacteria require?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus, and nitrogen.
What are fastidious bacteria?
Bacteria with demanding nutritional requirements.
What types of waste products do bacteria produce as they grow?
Bacteria produce various waste products, including enzymes and gases.
How can pathogenic bacteria be identified?
By injecting the organism into mice or cell cultures and observing for signs of infection.
What are some examples of common pathogenic bacteria?
Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, Vibrio cholerae, and Treponema pallidum.
What is the purpose of molecular diagnostic procedures in bacteria?
To analyze a microbe's DNA or RNA for identification.
What are mycoplasmas?
The smallest cellular microbes that lack a cell wall and can assume many shapes.
What is a unique feature of mycoplasmas regarding antibiotics?
They are resistant to drugs like penicillin that target cell walls.
What distinguishes photosynthetic bacteria from non-photosynthetic bacteria?
Photosynthetic bacteria can use light as an energy source, with some producing oxygen and others not.
What are cyanobacteria known for?
They produce oxygen through a process called oxygenic photosynthesis.
What is a characteristic of archaea?
They are prokaryotic organisms that are genetically more similar to eukaryotes than to bacteria.
What environments do archaea thrive in?
Extreme environments such as acidic, hot, or salty conditions.
What is a significant difference between archaeal and bacterial cell walls?
Archaeal cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan, while bacterial cell walls do.
Do archaeal organisms have known human pathogens?
No known archaeal human pathogens of significance exist, but they are part of the human microbiome.
What is the significance of 16S ribosomal genes in bacteria?
They can be compared to identify and classify bacterial isolates.
What is the hemolysis test used for?
To determine how a microbe breaks down blood, indicating its enzymatic activity.
What are the three types of hemolysis observed in the hemolysis test?
Gamma (no response), Alpha (slight discoloration), and Beta (full discoloration).
What is the role of additional staining in bacterial identification?
It helps to visualize specific characteristics of bacteria on media.
What is the appearance of mycoplasma colonies on agar medium?
They produce tiny 'fried egg' colonies.
What are some methods for identifying bacteria?
Morphologies, staining results, motility, oxygen requirements, nutrient requirements, and biochemical/metabolic activities.